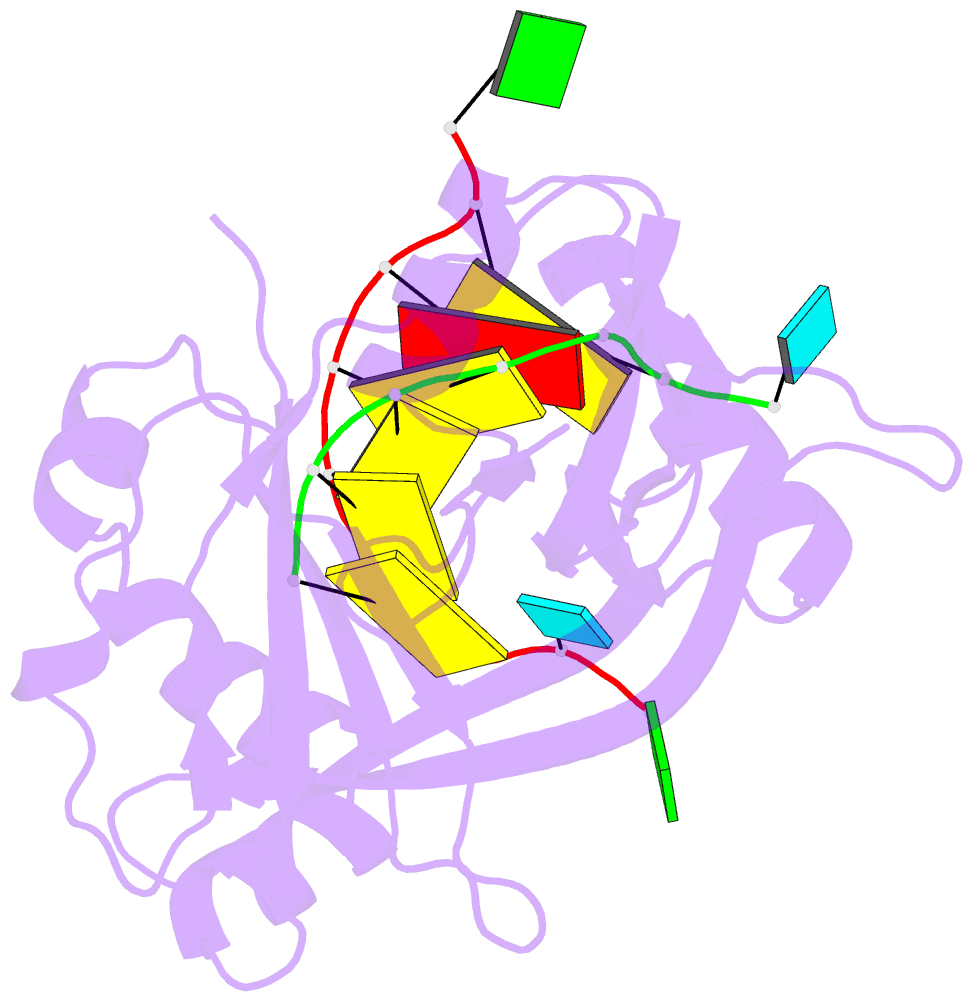
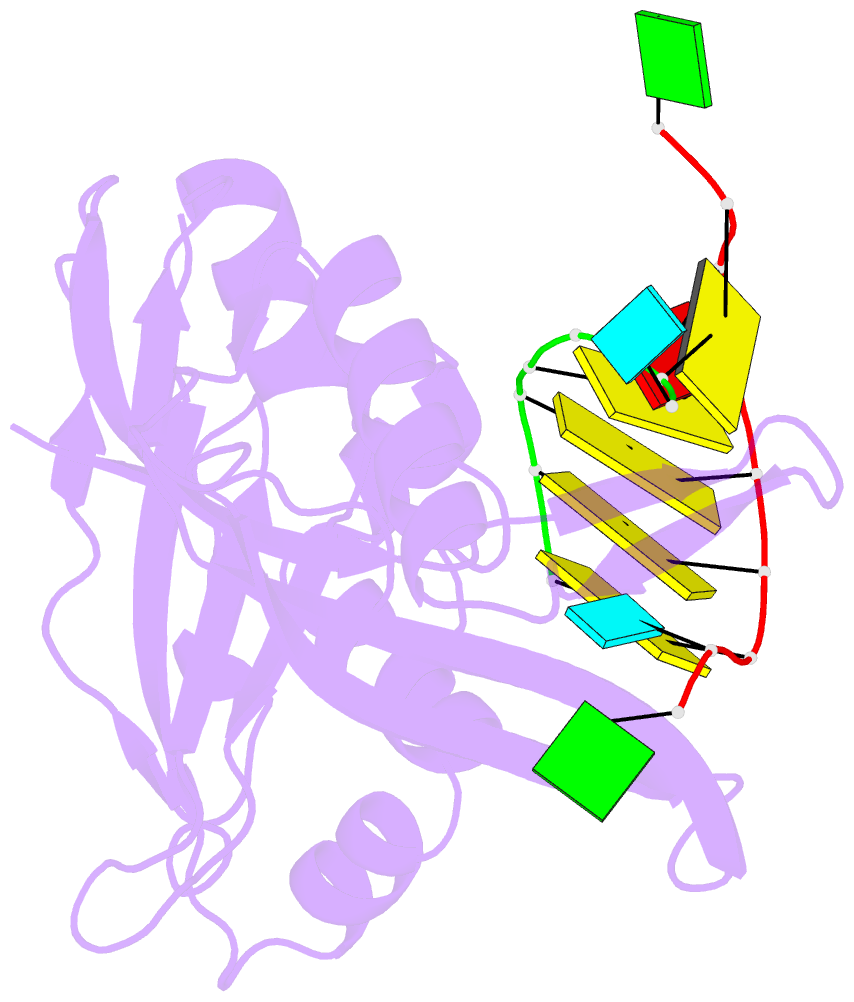
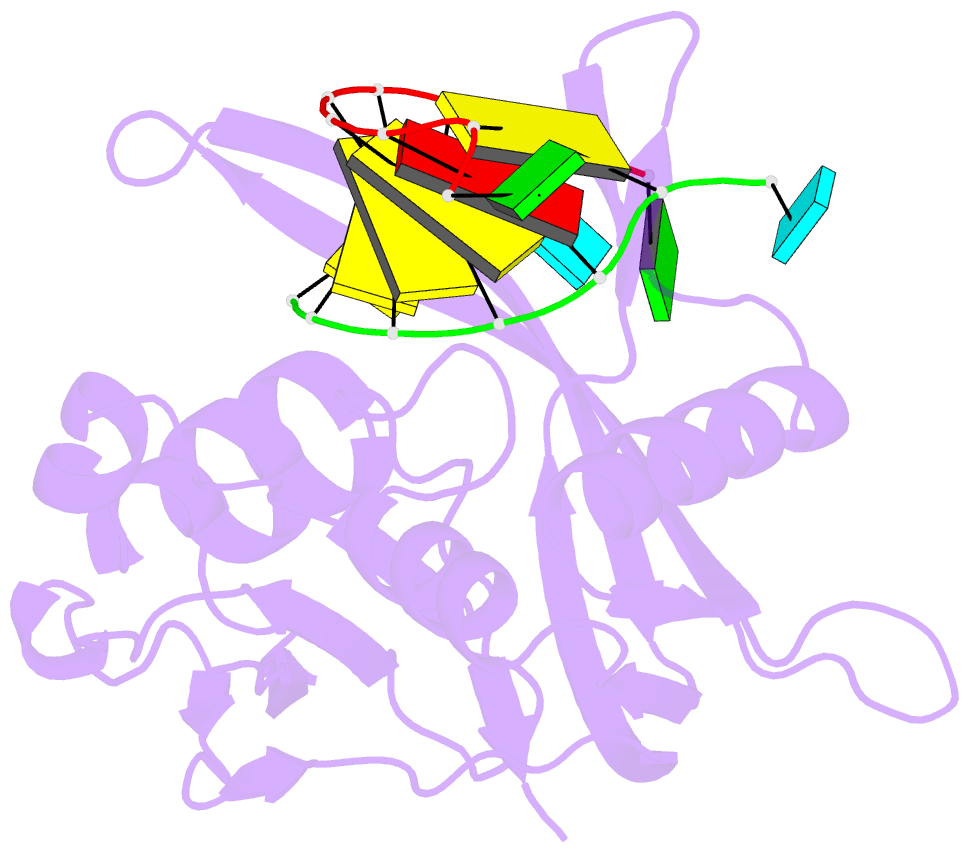
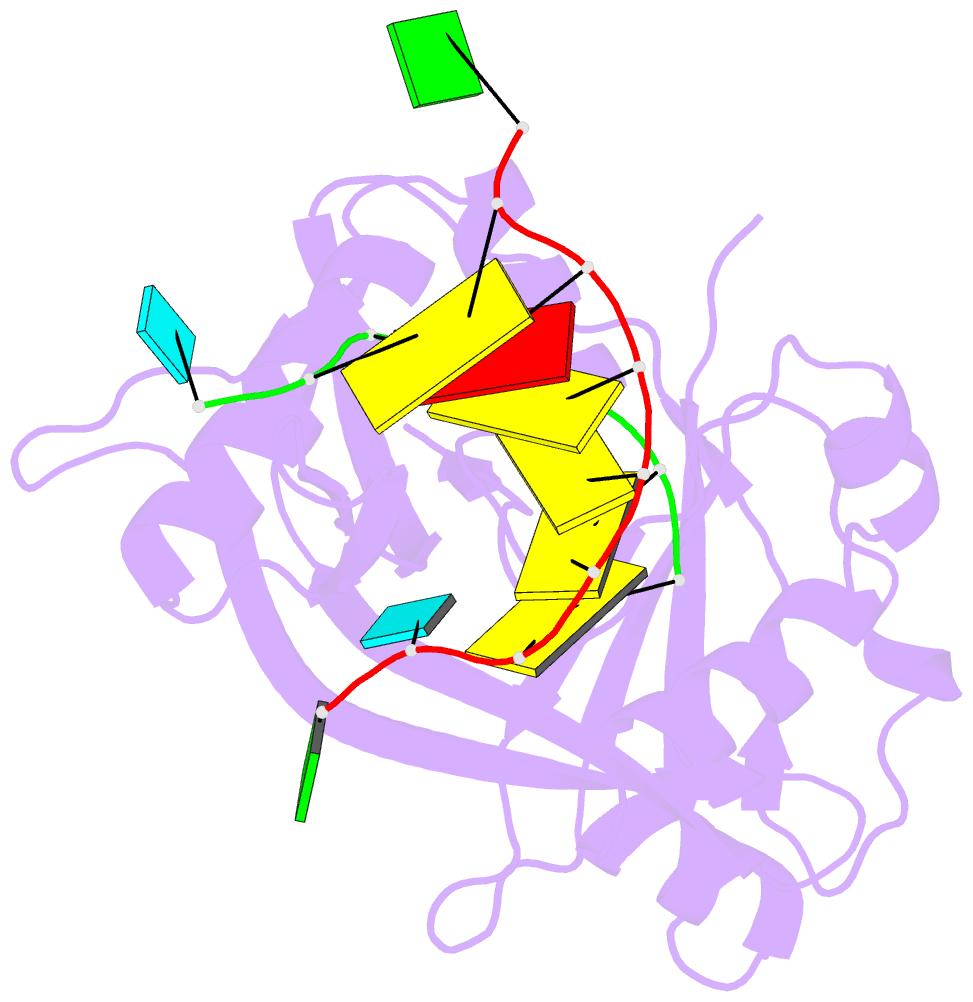
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3qrp; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.352 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of thermus thermophilus cse3 bound to an RNA representing a product mimic complex
- Reference
- Gesner EM, Schellenberg MJ, Garside EL, George MM, Macmillan AM (2011): "Recognition and maturation of effector RNAs in a CRISPR interference pathway." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 18, 688-692. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2042.
- Abstract
- In bacteria and archaea, small RNAs derived from clustered, regularly interspaced, short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) loci are involved in an adaptable and heritable gene-silencing pathway. Resistance to phage infection is conferred by the incorporation of short invading DNA sequences into the genome as CRISPR spacer elements separated by short repeat sequences. Processing of long primary transcripts (pre-crRNAs) containing these repeats by an RNA endonuclease generates the mature effector RNAs that interfere with phage gene expression. Here we describe structural and functional analyses of the Thermus thermophilus CRISPR Cse3 endonuclease. High-resolution X-ray structures of Cse3 bound to repeat RNAs model both the pre- and post-cleavage complexes associated with processing the pre-crRNA. These structures establish the molecular basis of a specific CRISPR RNA recognition and suggest the mechanism for generation of effector RNAs responsible for gene silencing.