Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3tq6; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.45 Å)
- Summary
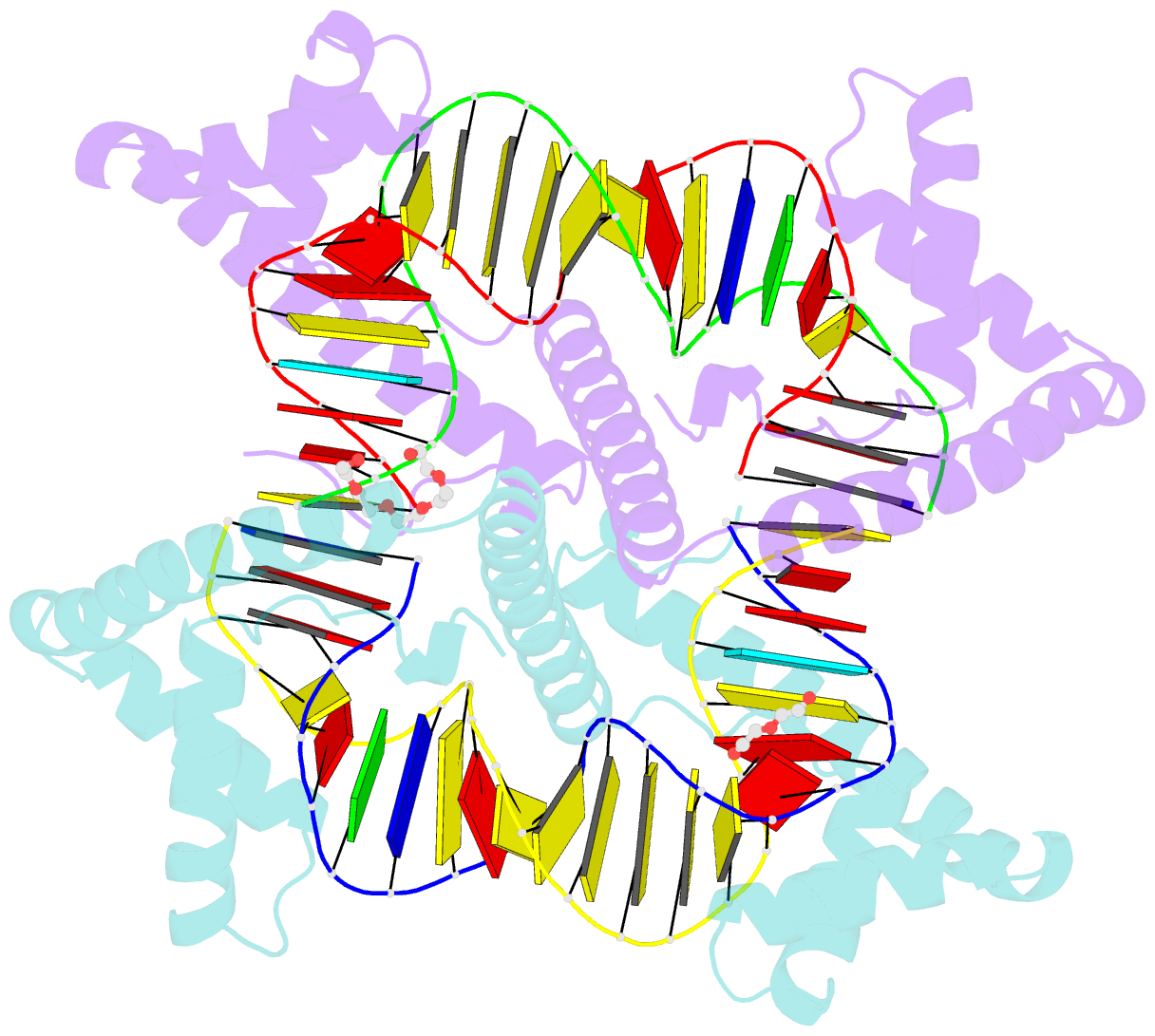
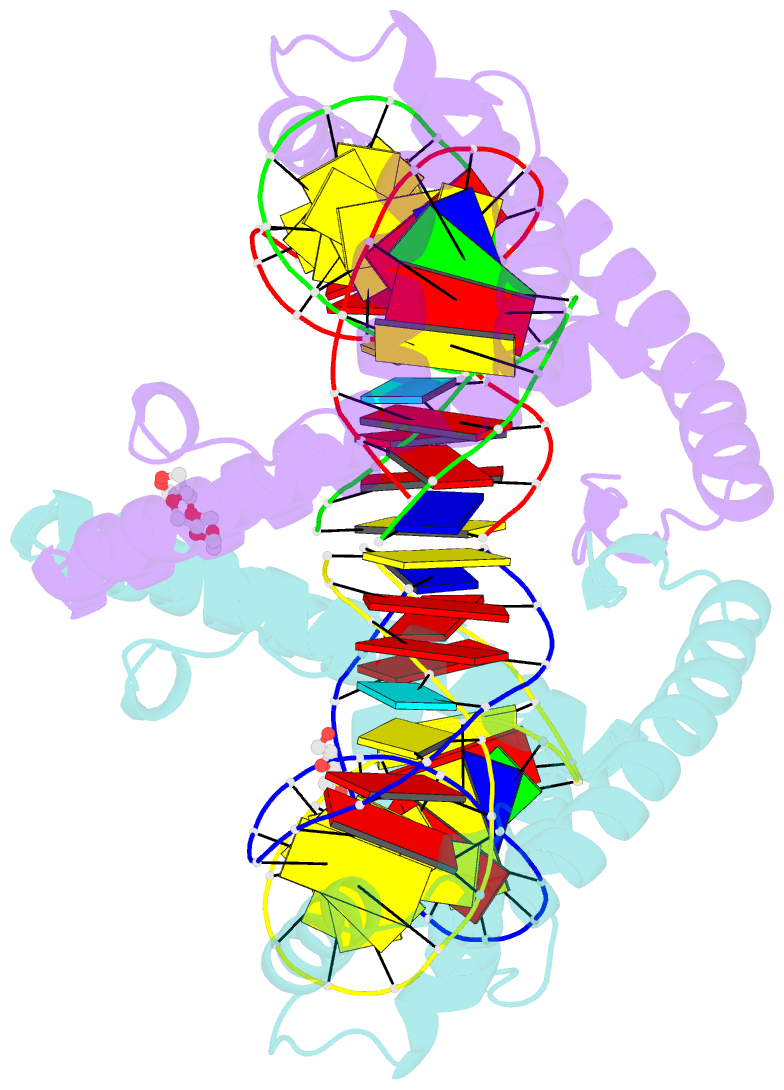
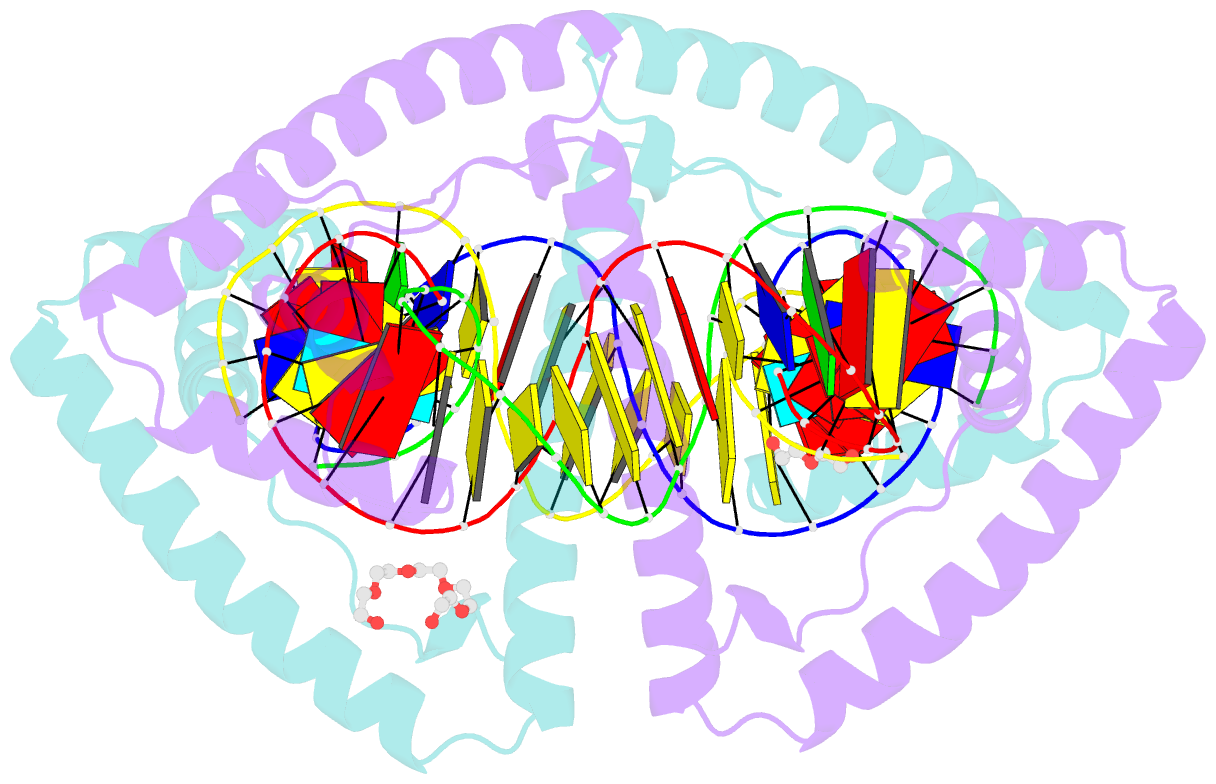
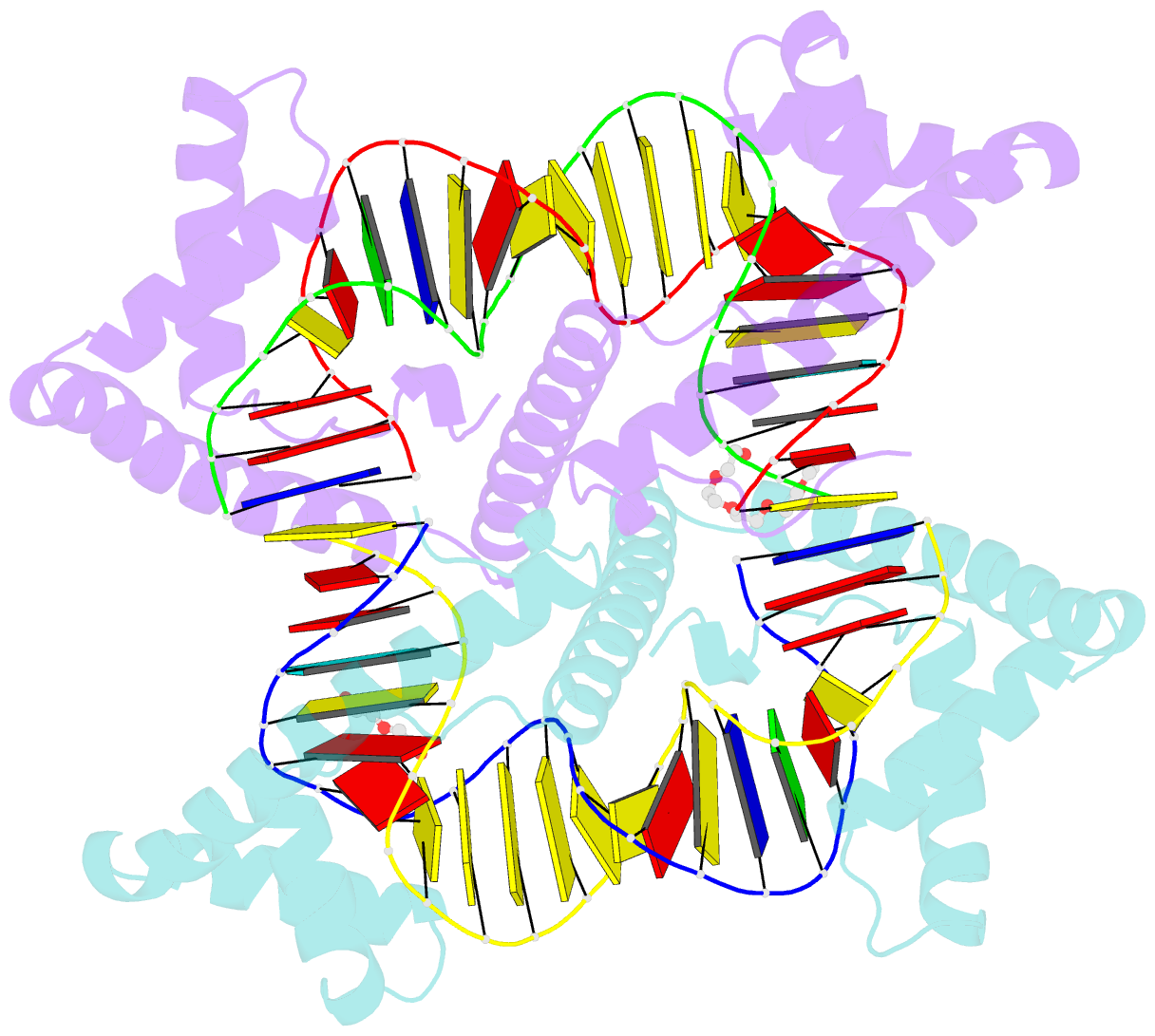
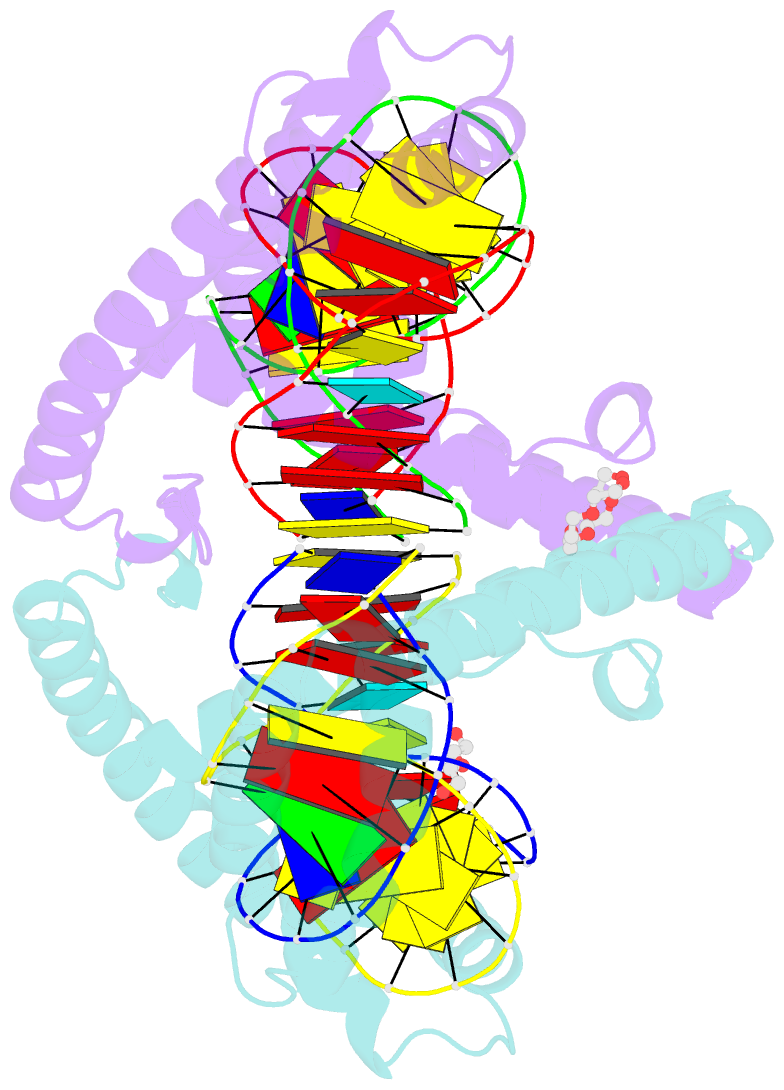
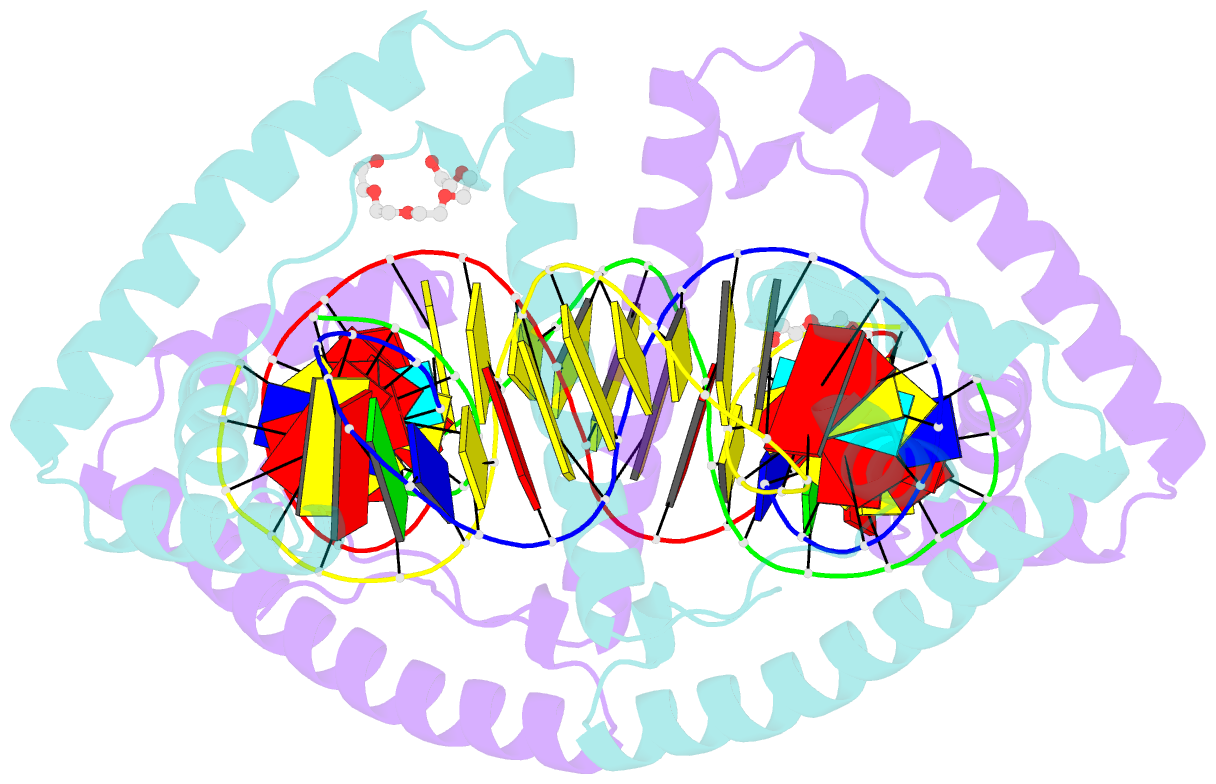
- Crystal structure of human mitochondrial transcription factor a, tfam or mttfa, bound to the light strand promoter lsp
- Reference
- Rubio-Cosials A, Sidow JF, Jimenez-Menendez N, Fernandez-Millan P, Montoya J, Jacobs HT, Coll M, Bernado P, Sola M (2011): "Human mitochondrial transcription factor A induces a U-turn structure in the light strand promoter." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 18, 1281-1289. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2160.
- Abstract
- Human mitochondrial transcription factor A, TFAM, is essential for mitochondrial DNA packaging and maintenance and also has a crucial role in transcription. Crystallographic analysis of TFAM in complex with an oligonucleotide containing the mitochondrial light strand promoter (LSP) revealed two high-mobility group (HMG) protein domains that, through different DNA recognition properties, intercalate residues at two inverted DNA motifs. This induced an overall DNA bend of ~180°, stabilized by the interdomain linker. This U-turn allows the TFAM C-terminal tail, which recruits the transcription machinery, to approach the initiation site, despite contacting a distant DNA sequence. We also ascertained that structured protein regions contacting DNA in the crystal were highly flexible in solution in the absence of DNA. Our data suggest that TFAM bends LSP to create an optimal DNA arrangement for transcriptional initiation while facilitating DNA compaction elsewhere in the genome.