Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3vd1; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- antitumor protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.95 Å)
- Summary
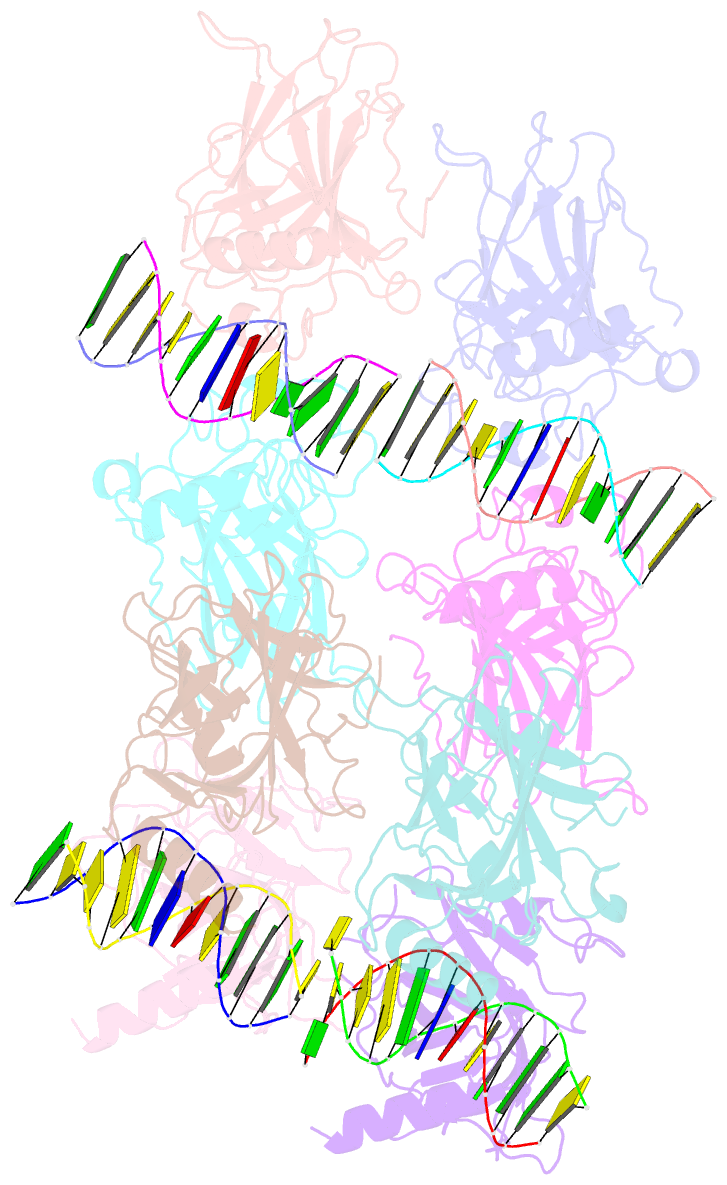
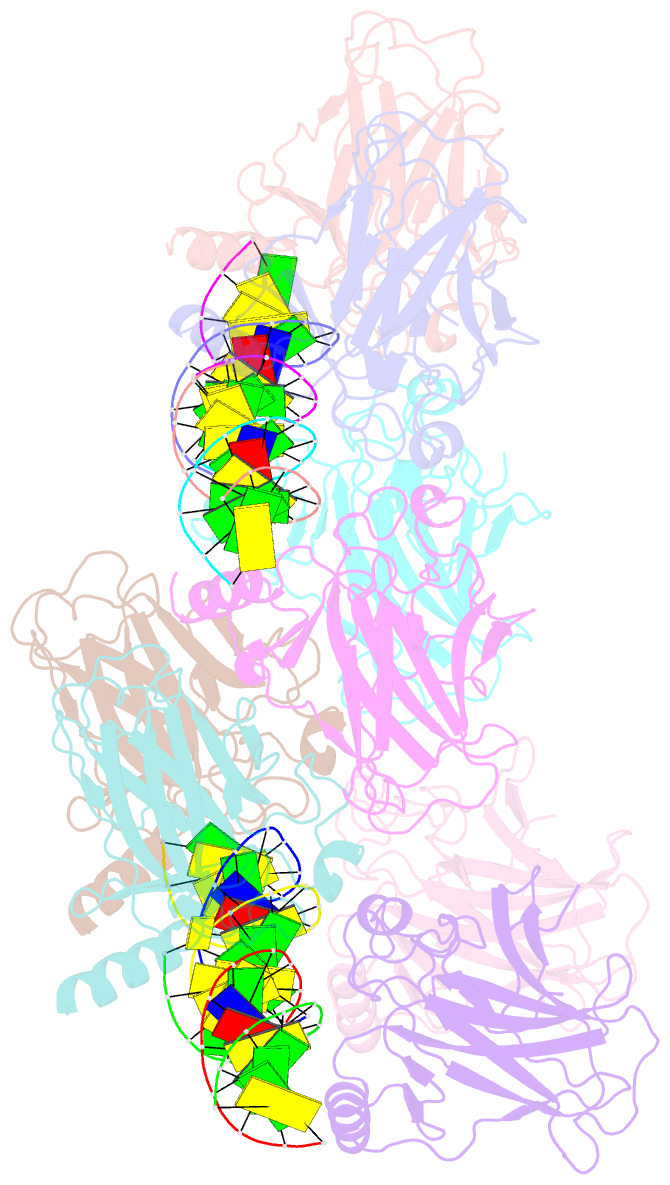
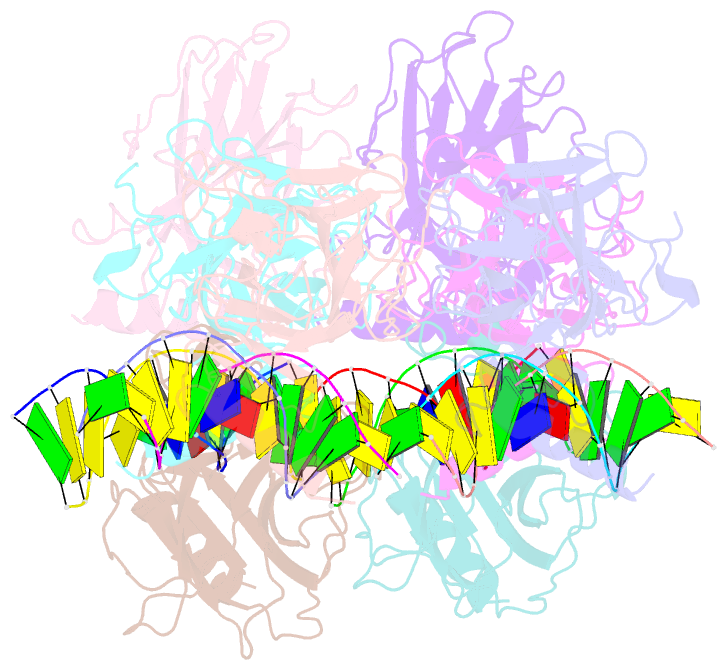
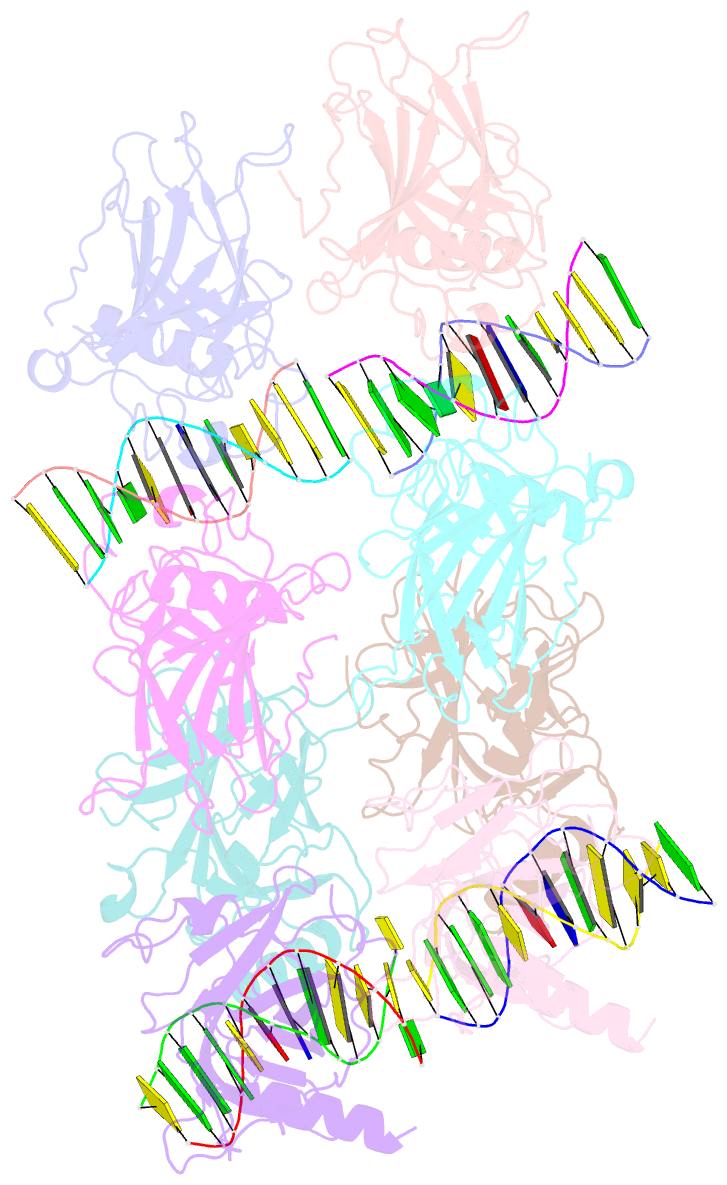
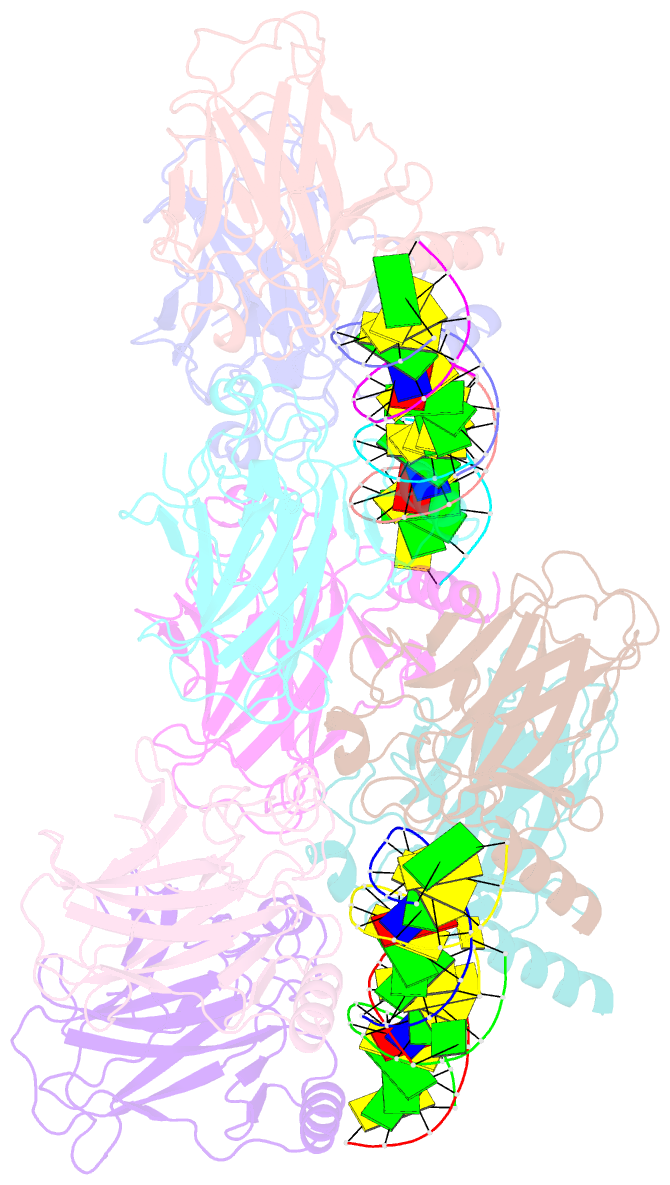
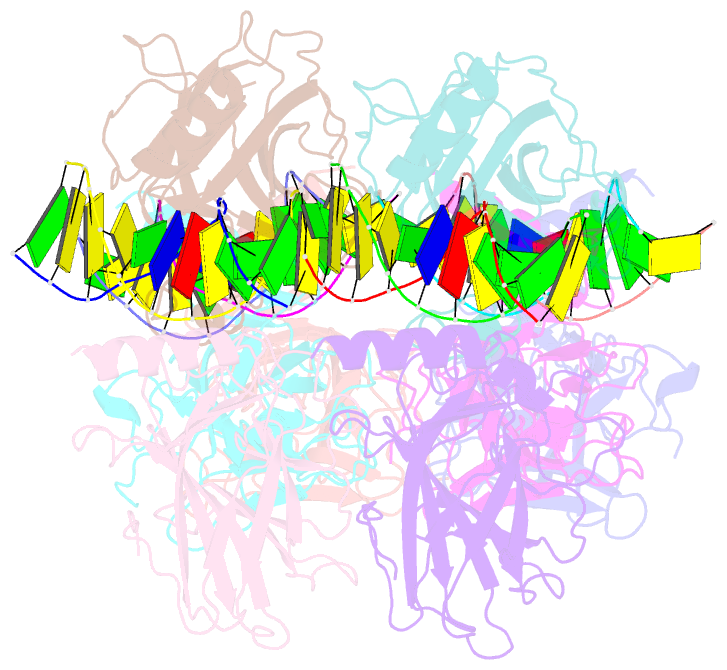
- Structure of p73 DNA binding domain tetramer modulates p73 transactivation
- Reference
- Ethayathulla AS, Tse PW, Monti P, Nguyen S, Inga A, Fronza G, Viadiu H (2012): "Structure of p73 DNA-binding domain tetramer modulates p73 transactivation." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 109, 6066-6071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115463109.
- Abstract
- The transcription factor p73 triggers developmental pathways and overlaps stress-induced p53 transcriptional pathways. How p53-family response elements determine and regulate transcriptional specificity remains an unsolved problem. In this work, we have determined the first crystal structures of p73 DNA-binding domain tetramer bound to response elements with spacers of different length. The structure and function of the adaptable tetramer are determined by the distance between two half-sites. The structures with zero and one base-pair spacers show compact p73 DNA-binding domain tetramers with large tetramerization interfaces; a two base-pair spacer results in DNA unwinding and a smaller tetramerization interface, whereas a four base-pair spacer hinders tetramerization. Functionally, p73 is more sensitive to spacer length than p53, with one base-pair spacer reducing 90% of transactivation activity and longer spacers reducing transactivation to basal levels. Our results establish the quaternary structure of the p73 DNA-binding domain required as a scaffold to promote transactivation.