Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3w3s; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ligase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.095 Å)
- Summary
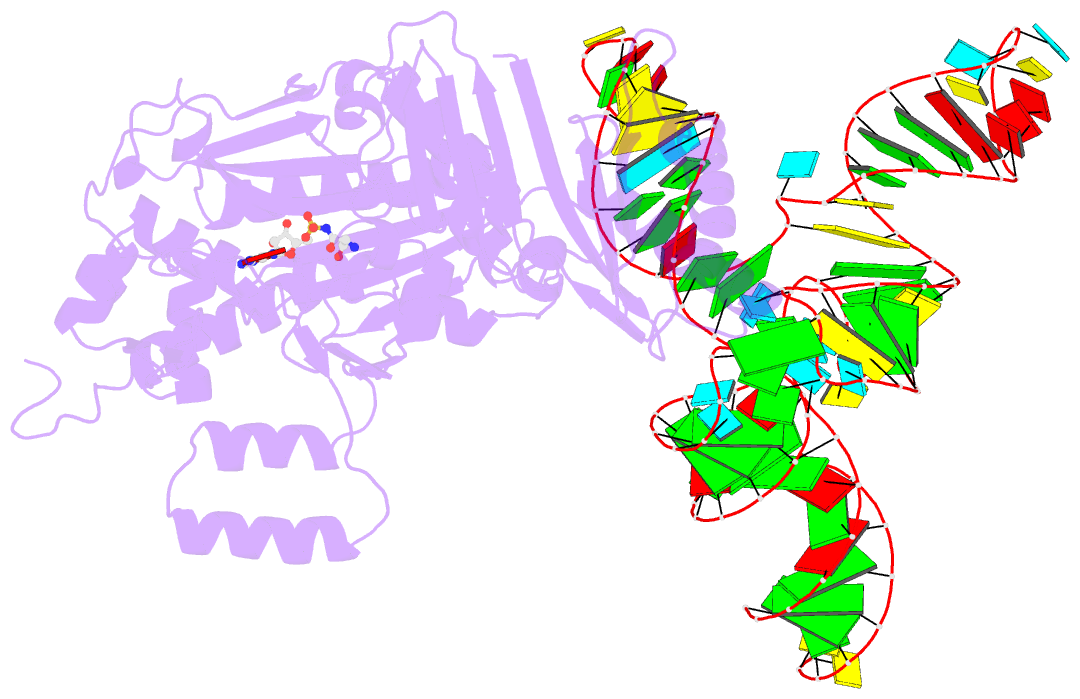
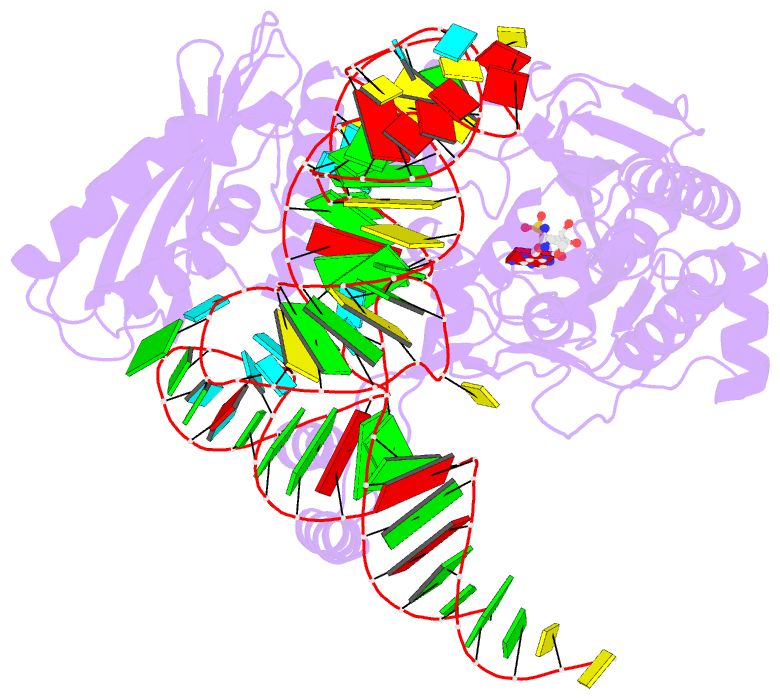
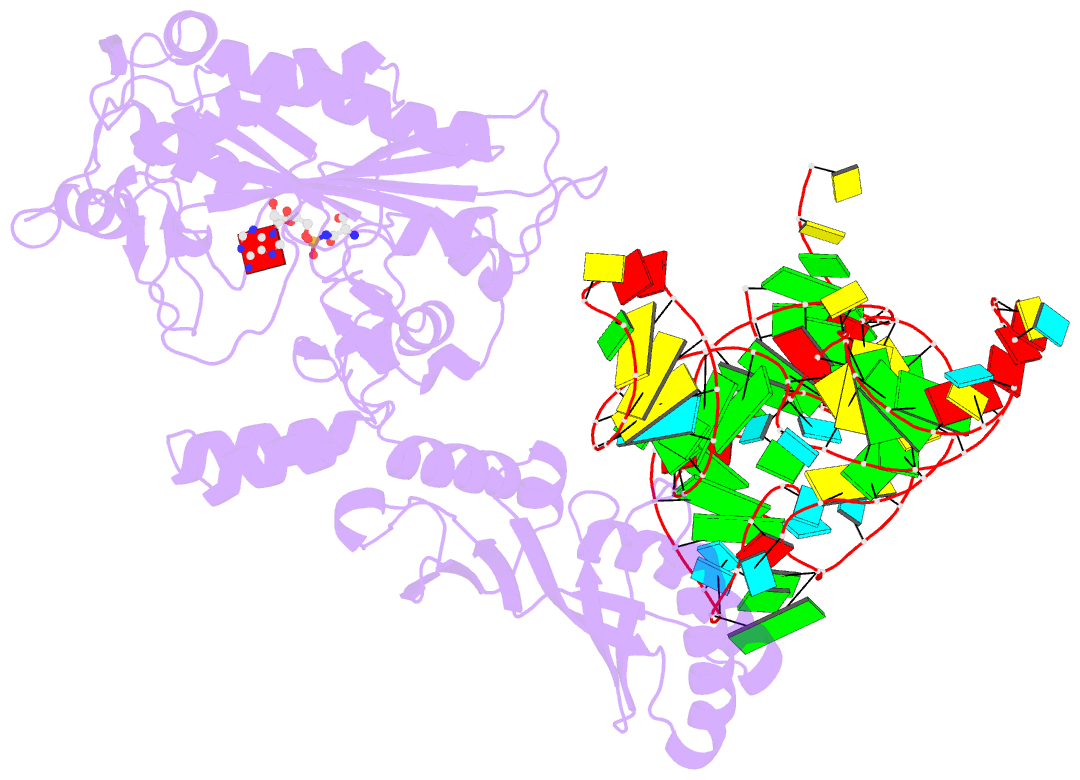
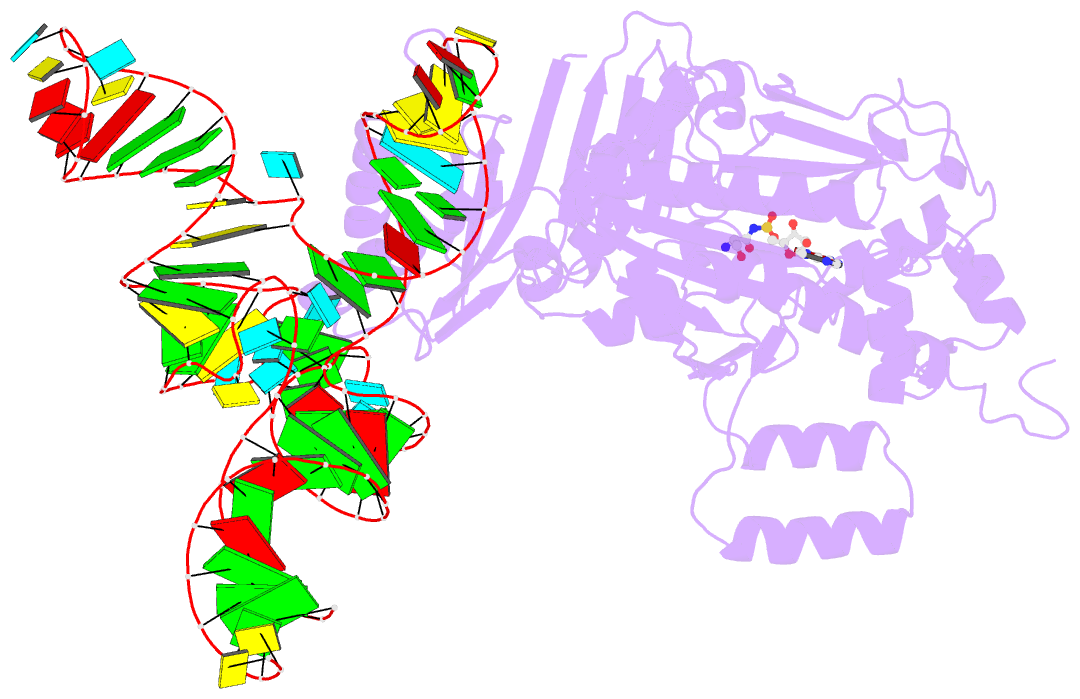
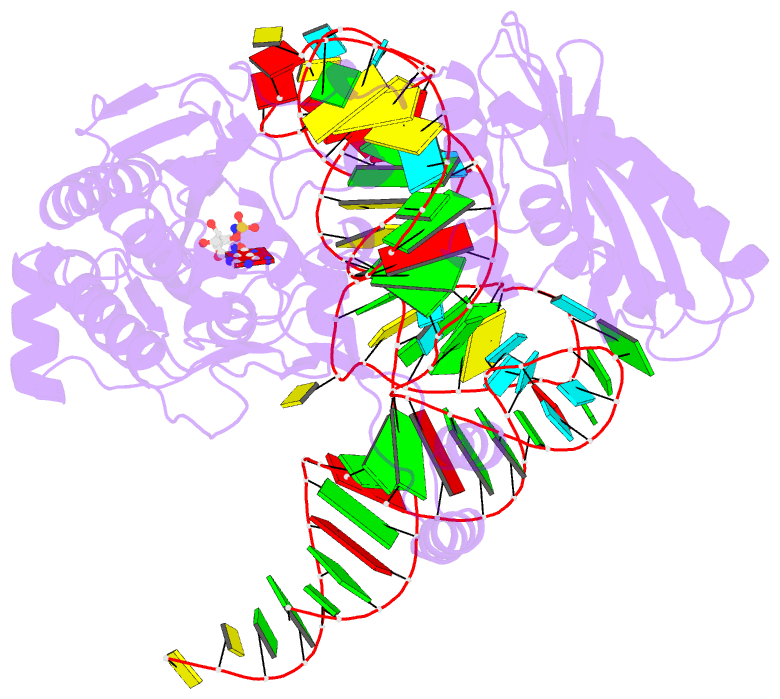
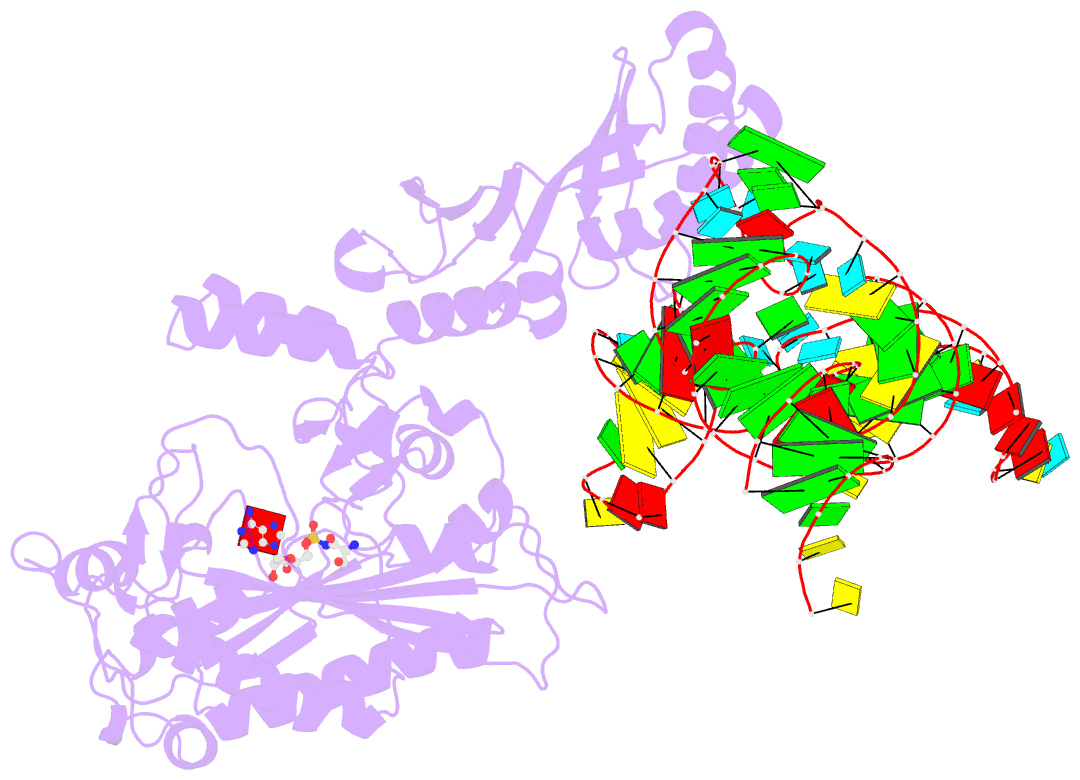
- Crystal structure of a. aeolicus trnasec in complex with m. kandleri serrs
- Reference
- Itoh Y, Sekine S, Suetsugu S, Yokoyama S (2013): "Tertiary structure of bacterial selenocysteine tRNA." Nucleic Acids Res., 41, 6729-6738. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt321.
- Abstract
- Selenocysteine (Sec) is translationally incorporated into proteins in response to the UGA codon. The tRNA specific to Sec (tRNA(Sec)) is first ligated with serine by seryl-tRNA synthetase (SerRS). In the present study, we determined the 3.1 Å crystal structure of the tRNA(Sec) from the bacterium Aquifex aeolicus, in complex with the heterologous SerRS from the archaeon Methanopyrus kandleri. The bacterial tRNA(Sec) assumes the L-shaped structure, from which the long extra arm protrudes. Although the D-arm conformation and the extra-arm orientation are similar to those of eukaryal/archaeal tRNA(Sec)s, A. aeolicus tRNA(Sec) has unique base triples, G14:C21:U8 and C15:G20a:G48, which occupy the positions corresponding to the U8:A14 and R15:Y48 tertiary base pairs of canonical tRNAs. Methanopyrus kandleri SerRS exhibited serine ligation activity toward A. aeolicus tRNA(Sec) in vitro. The SerRS N-terminal domain interacts with the extra-arm stem and the outer corner of tRNA(Sec). Similar interactions exist in the reported tRNA(Ser) and SerRS complex structure from the bacterium Thermus thermophilus. Although the catalytic C-terminal domain of M. kandleri SerRS lacks interactions with A. aeolicus tRNA(Sec) in the present complex structure, the conformational flexibility of SerRS is likely to allow the CCA terminal region of tRNA(Sec) to enter the SerRS catalytic site.