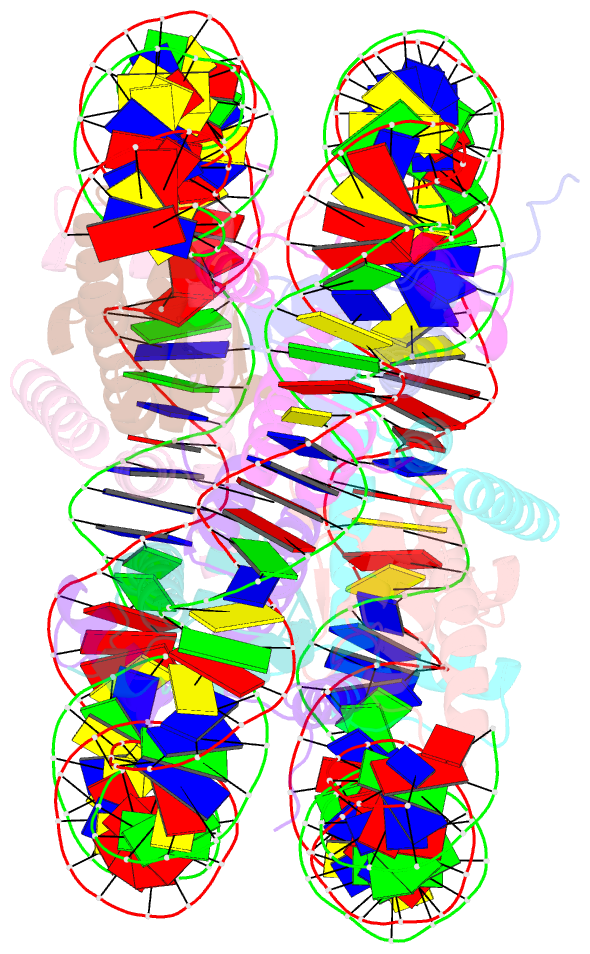
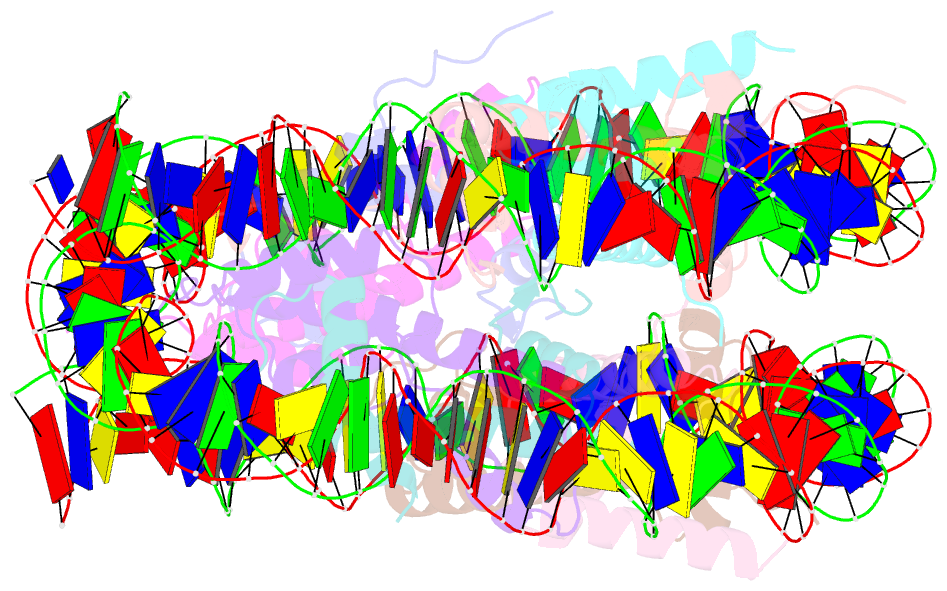
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3x1v; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- structural protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.921 Å)
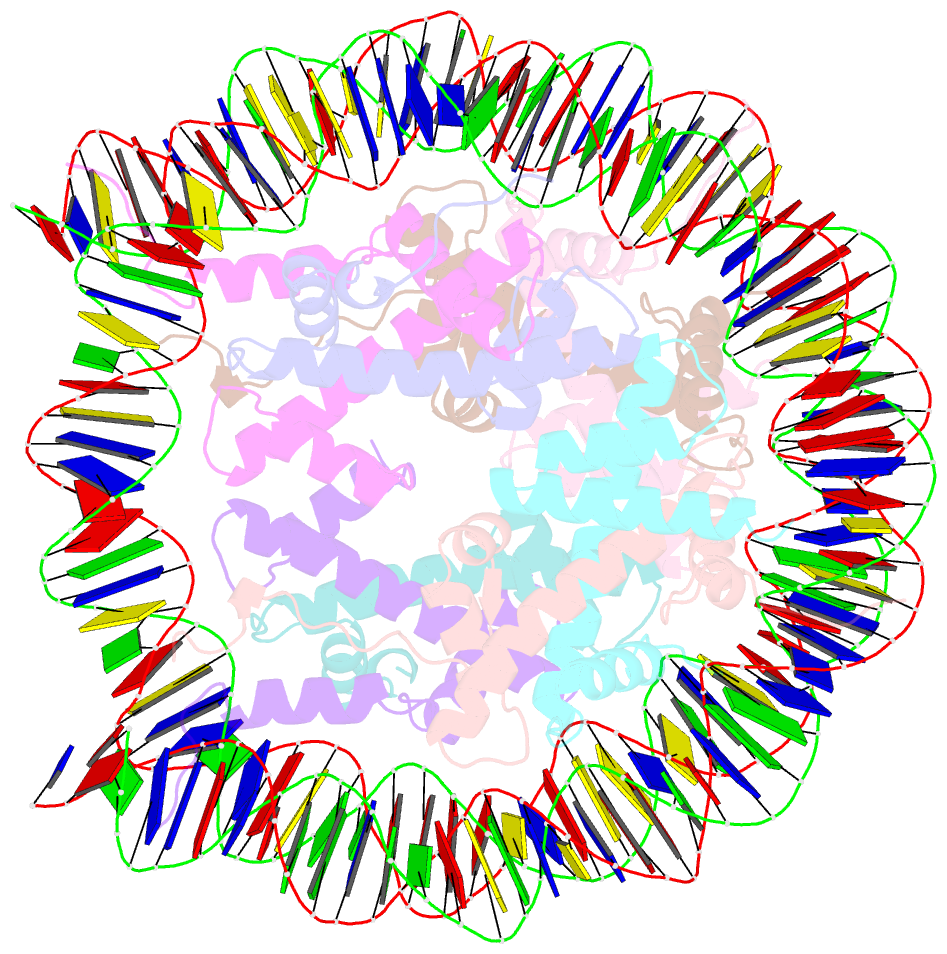
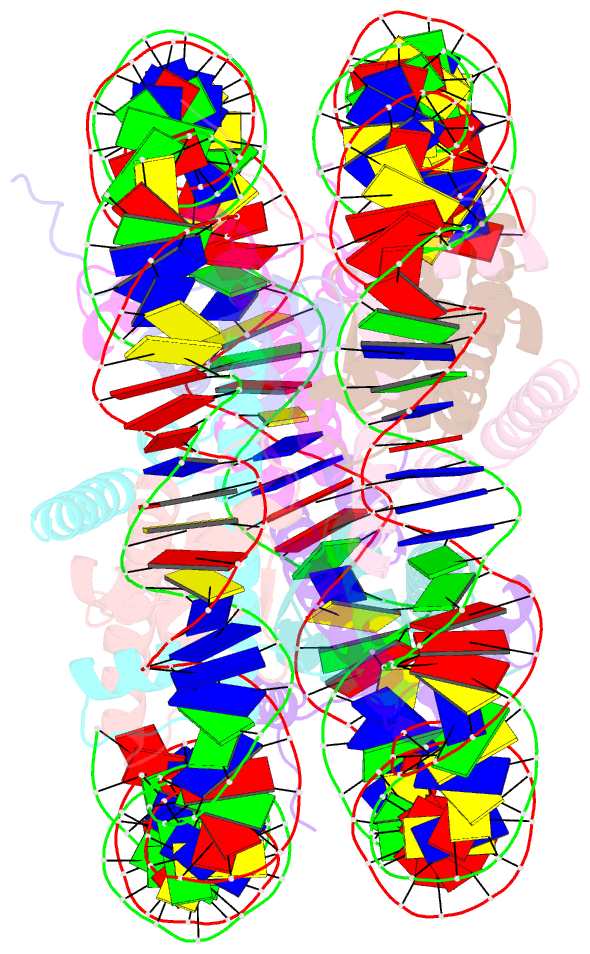
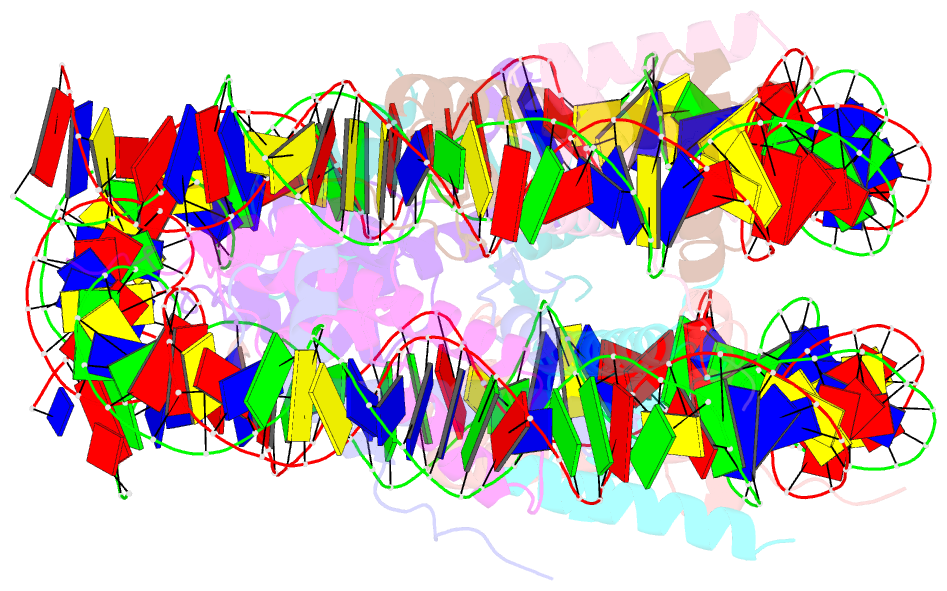
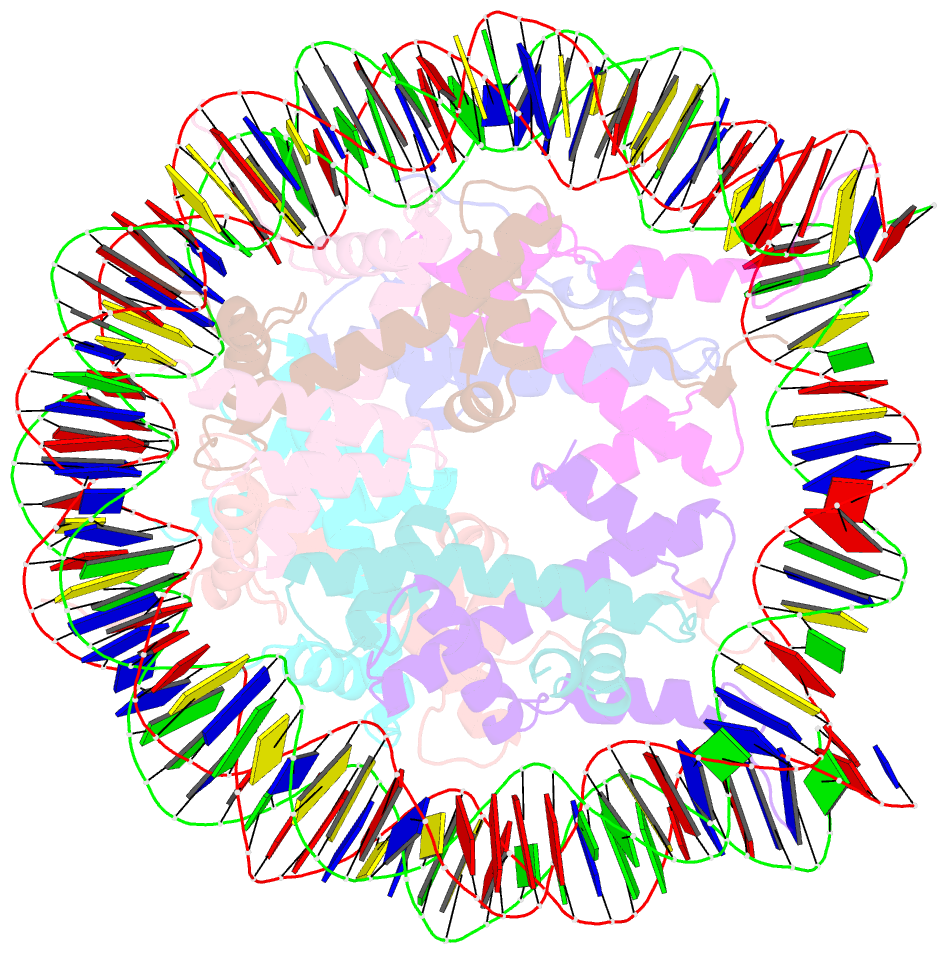
- Summary
- Crystal structure of nucleosome core particle in the presence of histone variant involved in reprogramming
- Reference
- Padavattan S, Shinagawa T, Hasegawa K, Kumasaka T, Ishii S, Kumarevel T (2015): "Structural and functional analyses of nucleosome complexes with mouse histone variants TH2a and TH2b, involved in reprogramming." Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun., 464, 929-935. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.070.
- Abstract
- Histone variants TH2a and TH2b are highly expressed in testes, oocytes and zygotes. Our recent analysis suggested that these histone variants enhance the induced generation of pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) when co-expressed along with four transcription factors, Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc (OSKM), and are associated with an open chromatin structure [1]. In the present study, we report the crystal structures of nucleosomes (NCPs) with the mouse histone variants, TH2a and TH2b. The structures revealed two significant changes, as compared to the canonical counterparts: fewer histone-DNA contacts and changes in dimer-dimer interactions between TH2a-TH2a' (L1-loop). In vivo studies with domain swapping and point mutants of the variants revealed that the residues in the histone tails and the TH2a-L1 loop are important for reprogramming. Taken together, our work indicates that the NCP variants with structural modifications and flexible tails are most likely important for enhanced reprogramming of functions.