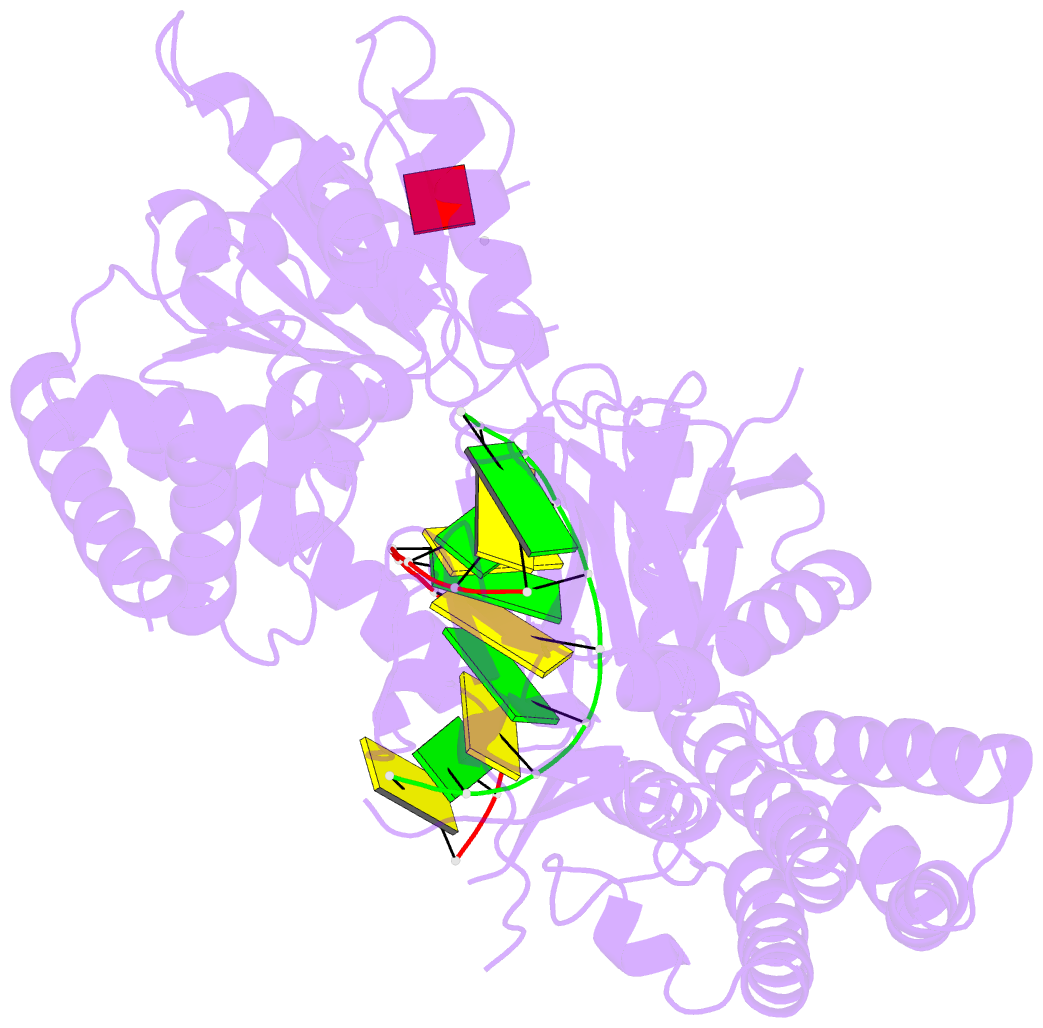
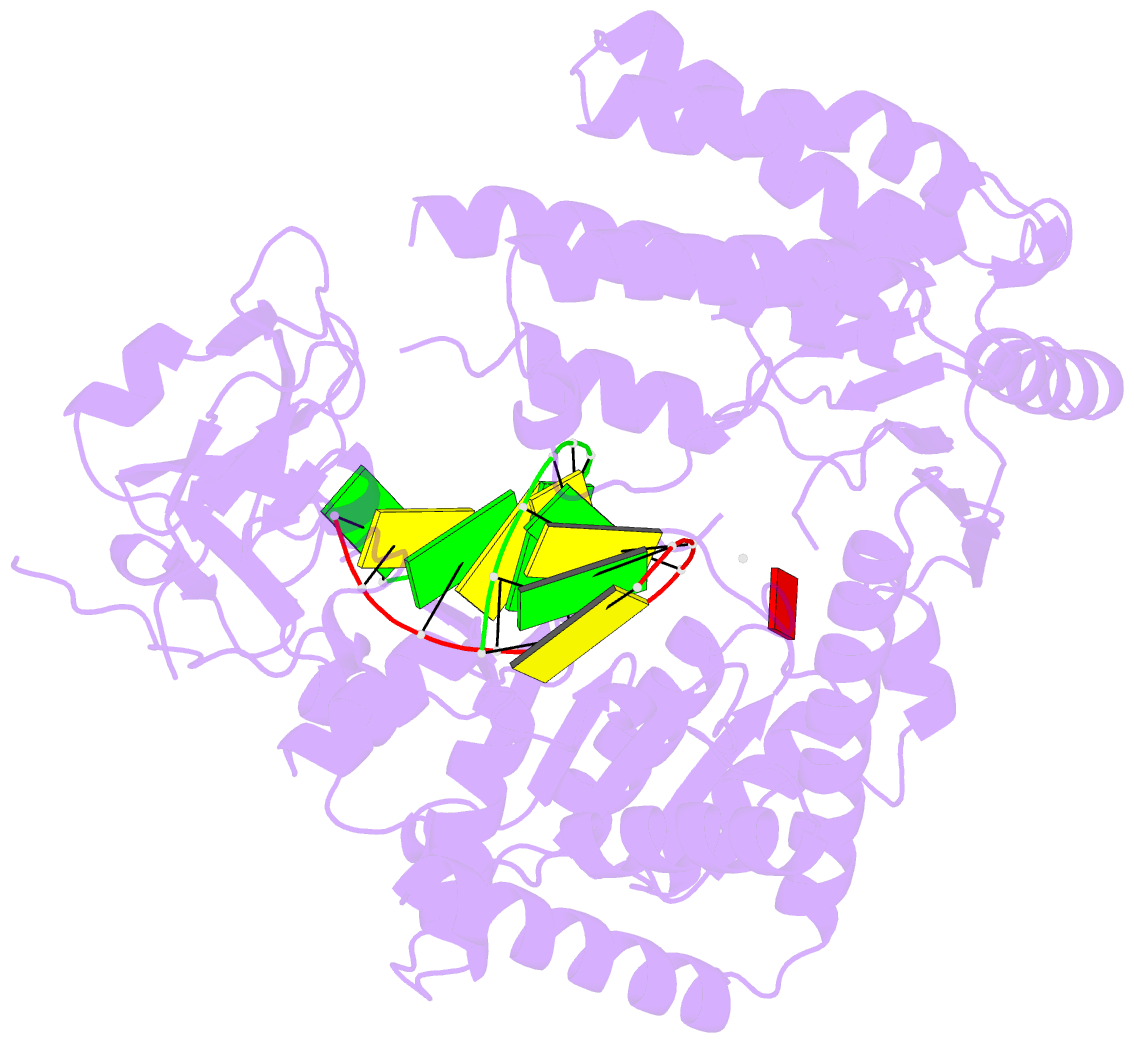
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3zd7; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
- Snapshot 3 of rig-i scanning on RNA duplex
- Reference
- Kohlway A, Luo D, Rawling DC, Ding SC, Pyle AM (2013): "Defining the Functional Determinants for RNA Surveillance by Rig-I." Embo Rep., 14, 772. doi: 10.1038/EMBOR.2013.108.
- Abstract
- Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) is an intracellular RNA sensor that activates the innate immune machinery in response to infection by RNA viruses. Here, we report the crystal structure of distinct conformations of a RIG-I:dsRNA complex, which shows that HEL2i-mediated scanning allows RIG-I to sense the length of RNA targets. To understand the implications of HEL2i scanning for catalytic activity and signalling by RIG-I, we examined its ATPase activity when stimulated by duplex RNAs of varying lengths and 5' composition. We identified a minimal RNA duplex that binds one RIG-I molecule, stimulates robust ATPase activity, and elicits a RIG-I-mediated interferon response in cells. Our results reveal that the minimal functional unit of the RIG-I:RNA complex is a monomer that binds at the terminus of a duplex RNA substrate. This behaviour is markedly different from the RIG-I paralog melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5), which forms cooperative filaments.