Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3zi5; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.2 Å)
- Summary
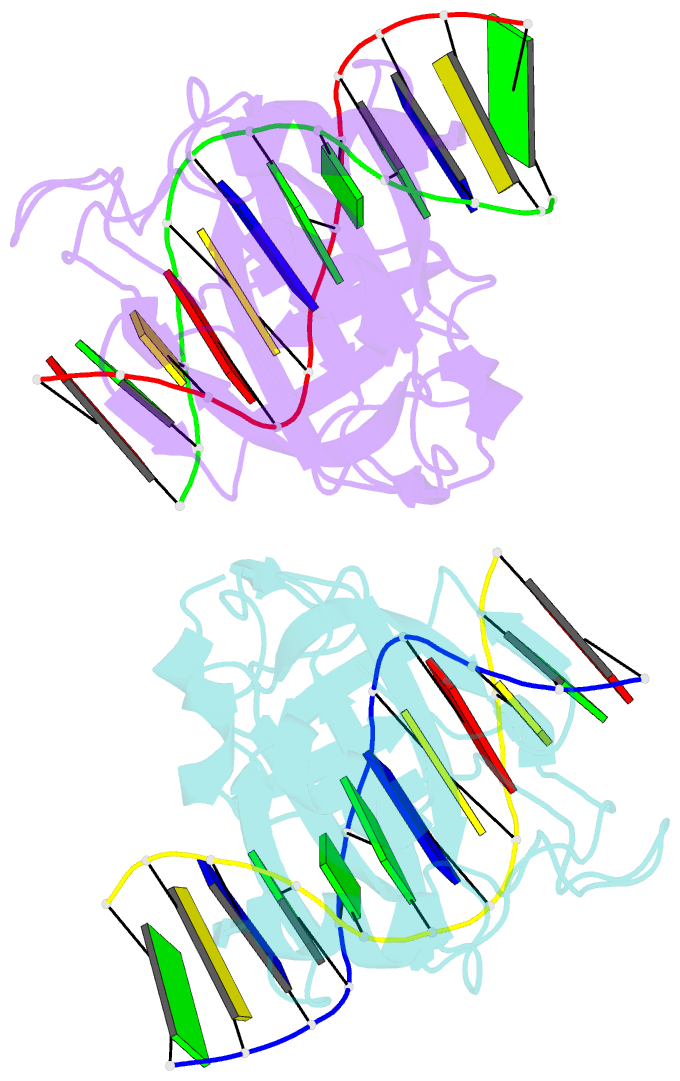
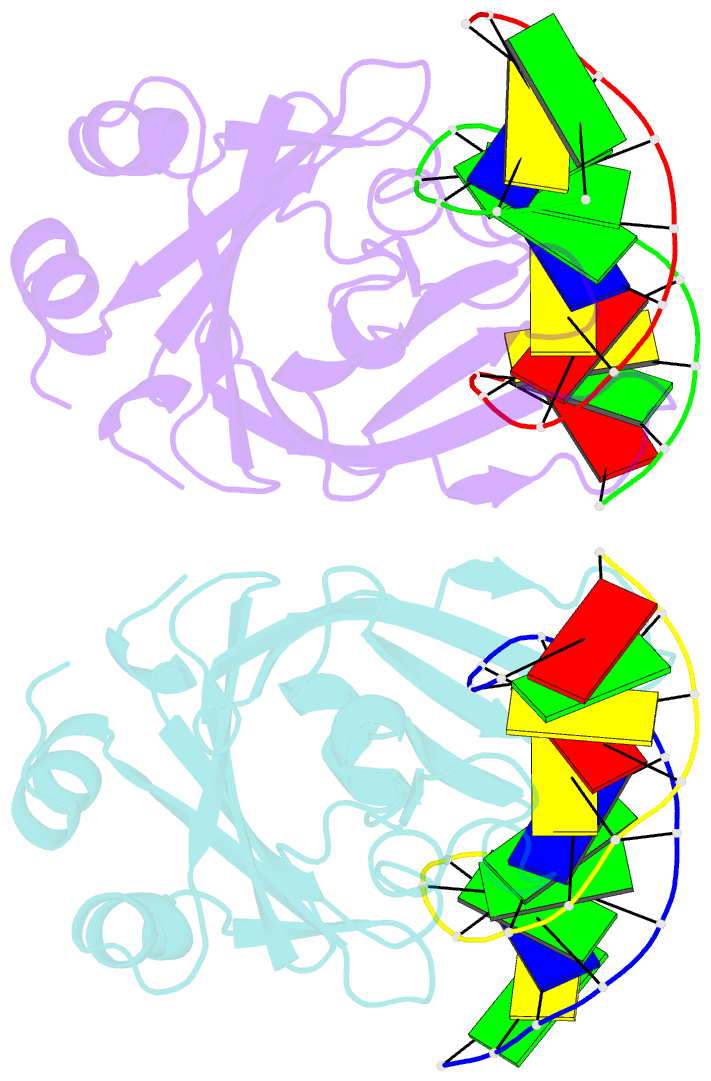
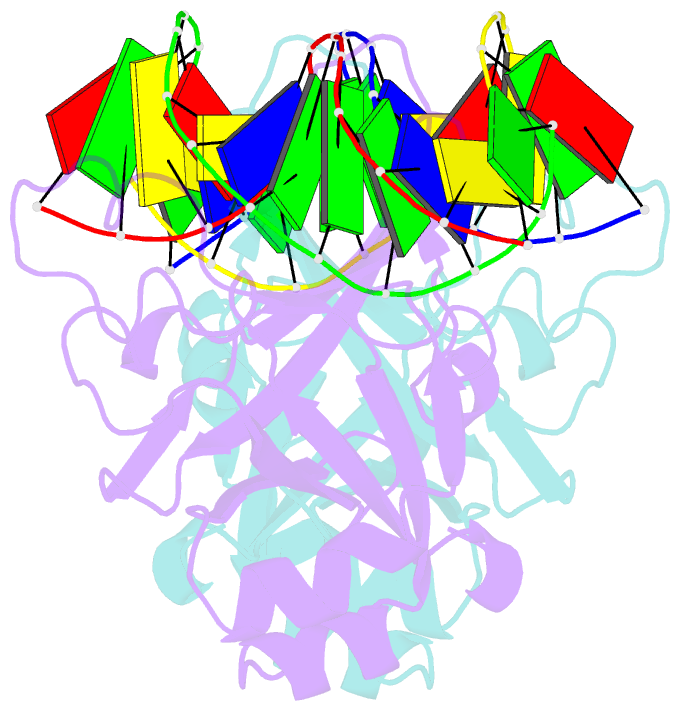
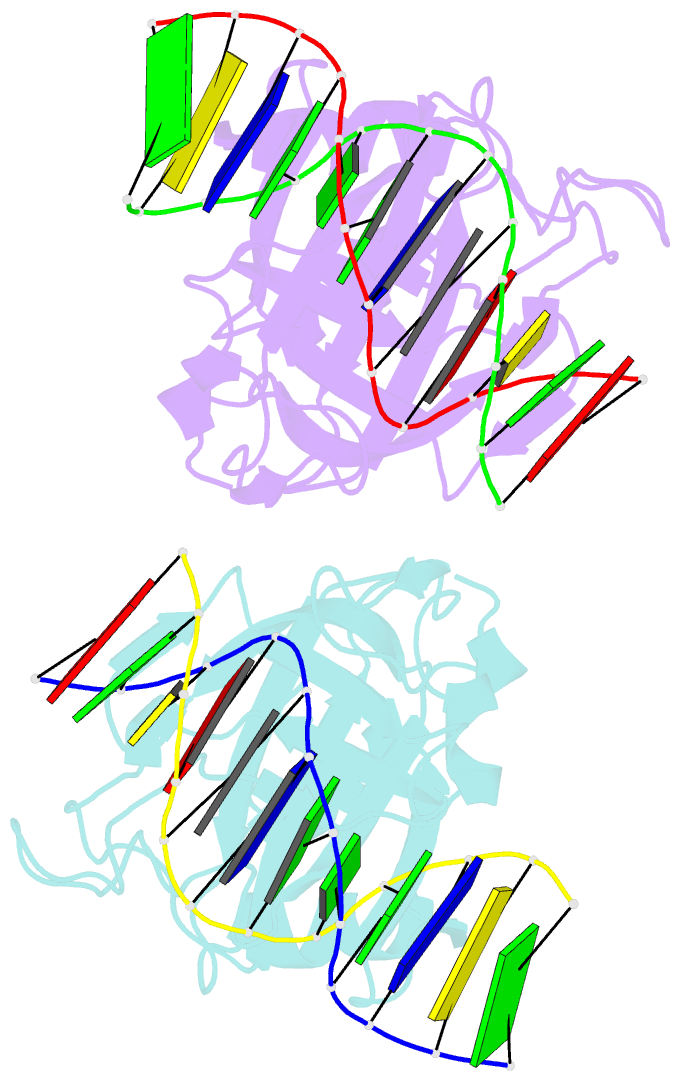
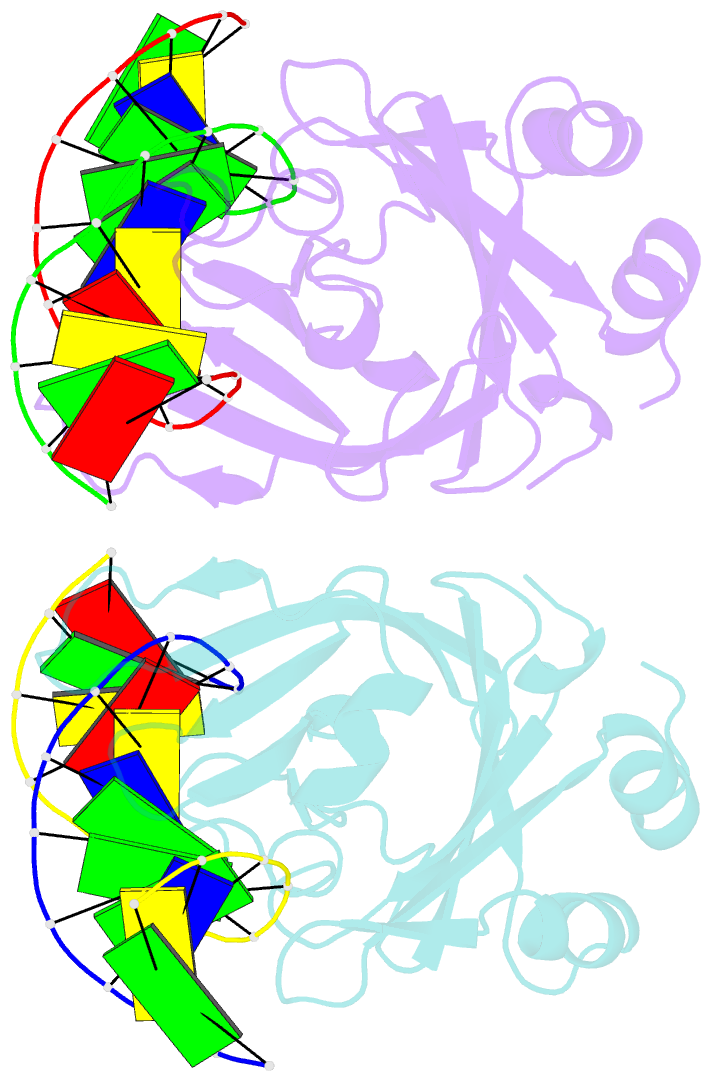
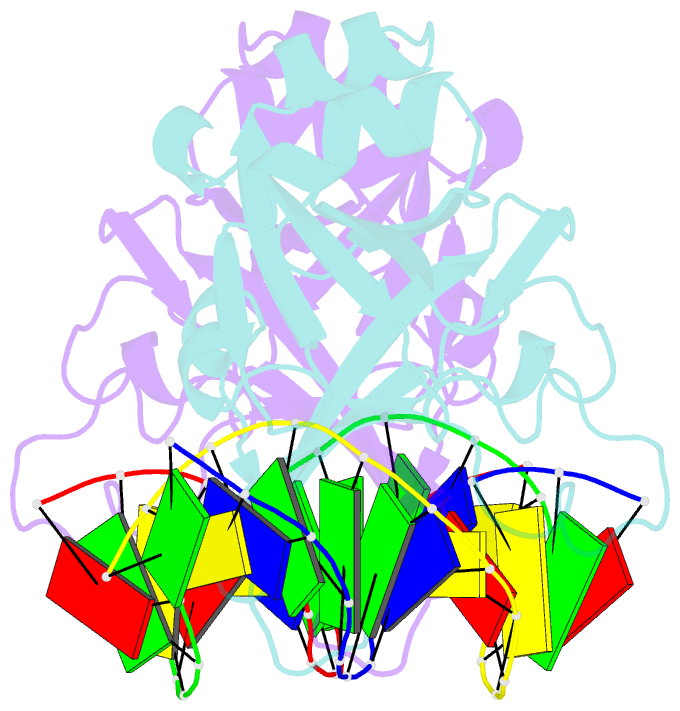
- Crystal structure of restriction endonuclease bfii c-terminal recognition domain in complex with cognate DNA
- Reference
- Golovenko D, Grazulis S, Manakova E, Sasnauskas G, Siksnys V, Zakrys L, Zaremba M (2014): "Structural Insight Into the Specificity of the B3 DNA-Binding Domains Provided by the Co-Crystal Structure of the C-Terminal Fragment of Bfii Restriction Enzyme." Nucleic Acids Res., 42, 4113. doi: 10.1093/NAR/GKT1368.
- Abstract
- The B3 DNA-binding domains (DBDs) of plant transcription factors (TF) and DBDs of EcoRII and BfiI restriction endonucleases (EcoRII-N and BfiI-C) share a common structural fold, classified as the DNA-binding pseudobarrel. The B3 DBDs in the plant TFs recognize a diverse set of target sequences. The only available co-crystal structure of the B3-like DBD is that of EcoRII-N (recognition sequence 5'-CCTGG-3'). In order to understand the structural and molecular mechanisms of specificity of B3 DBDs, we have solved the crystal structure of BfiI-C (recognition sequence 5'-ACTGGG-3') complexed with 12-bp cognate oligoduplex. Structural comparison of BfiI-C-DNA and EcoRII-N-DNA complexes reveals a conserved DNA-binding mode and a conserved pattern of interactions with the phosphodiester backbone. The determinants of the target specificity are located in the loops that emanate from the conserved structural core. The BfiI-C-DNA structure presented here expands a range of templates for modeling of the DNA-bound complexes of the B3 family of plant TFs.