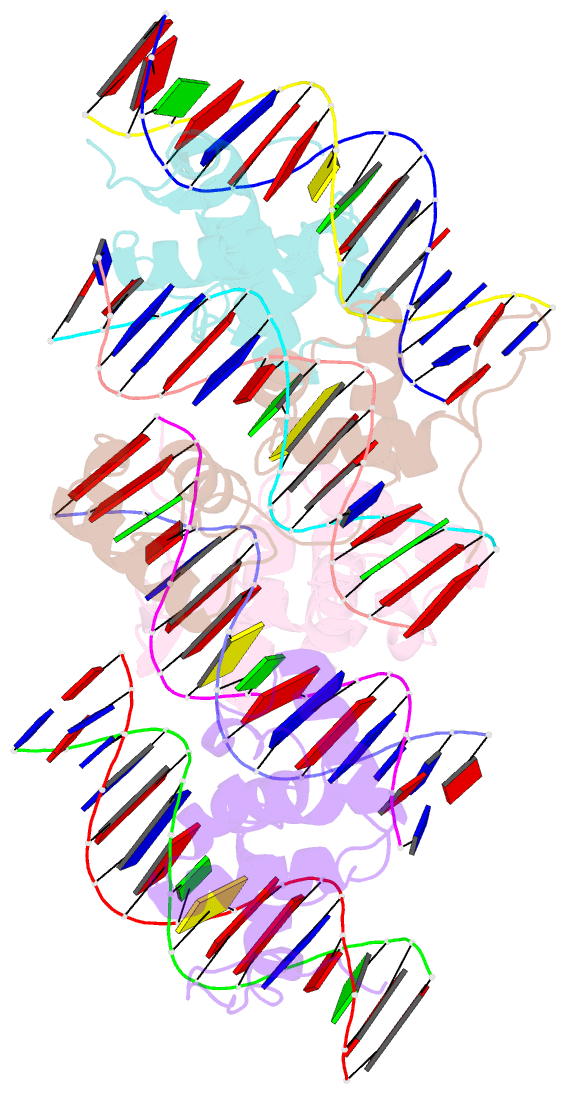
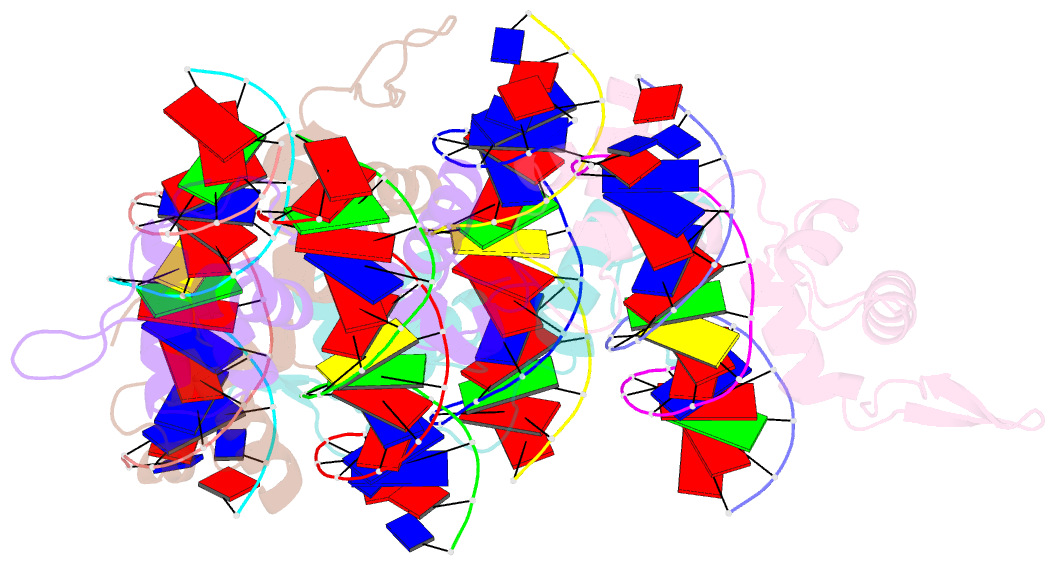
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3zqc; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.9 Å)
- Summary
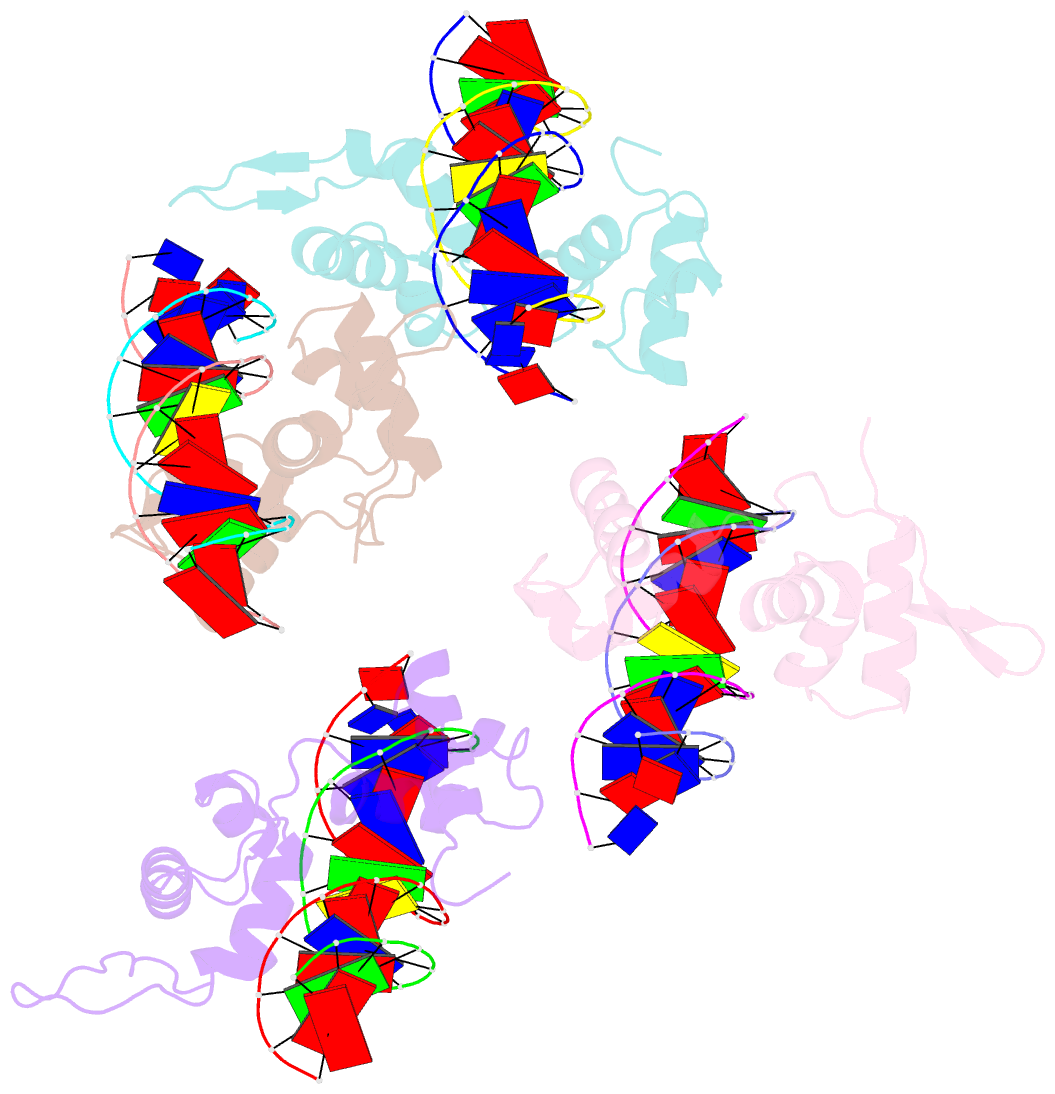
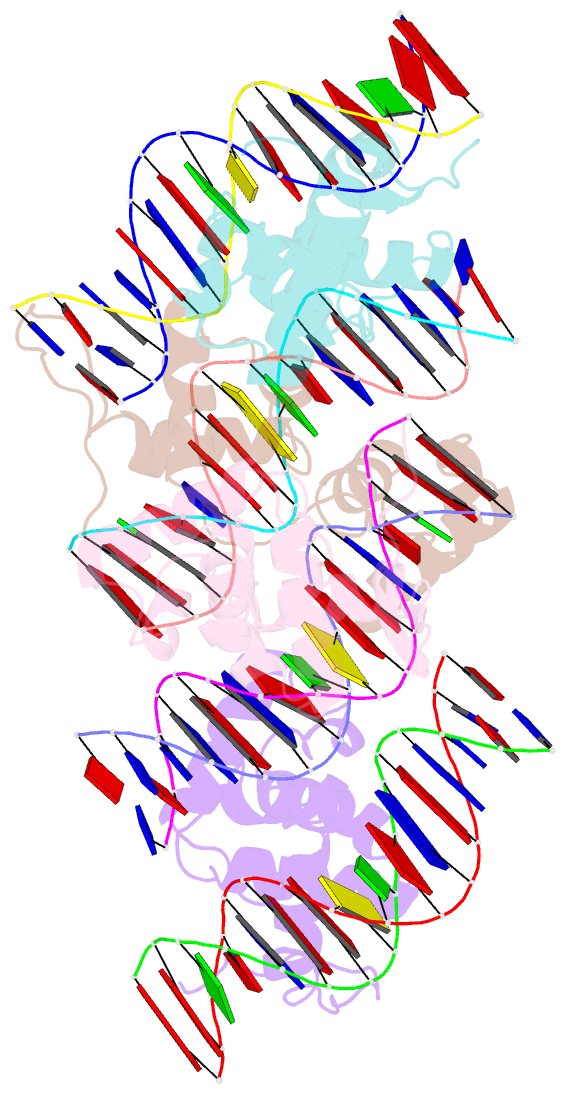
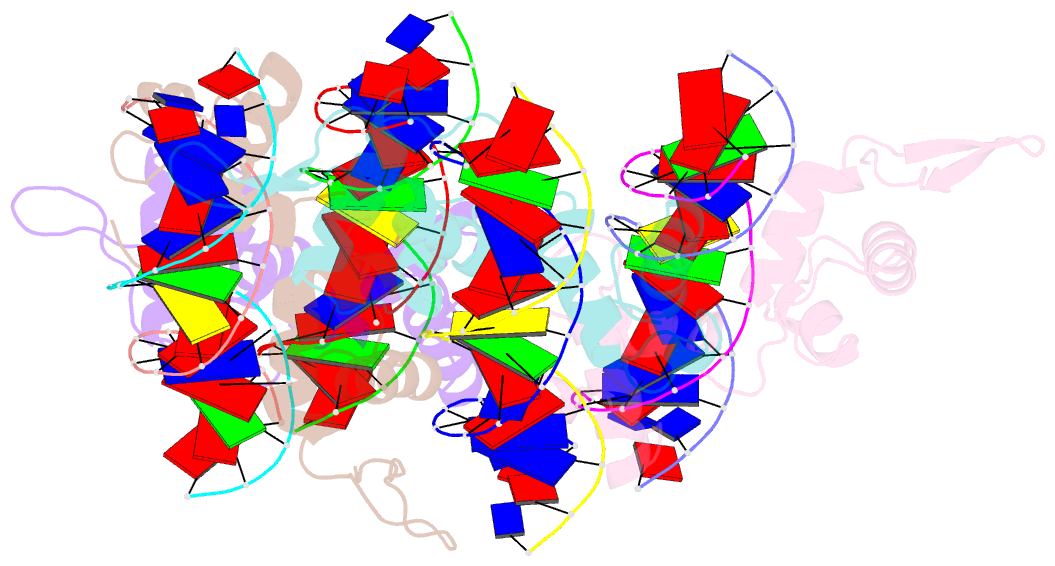
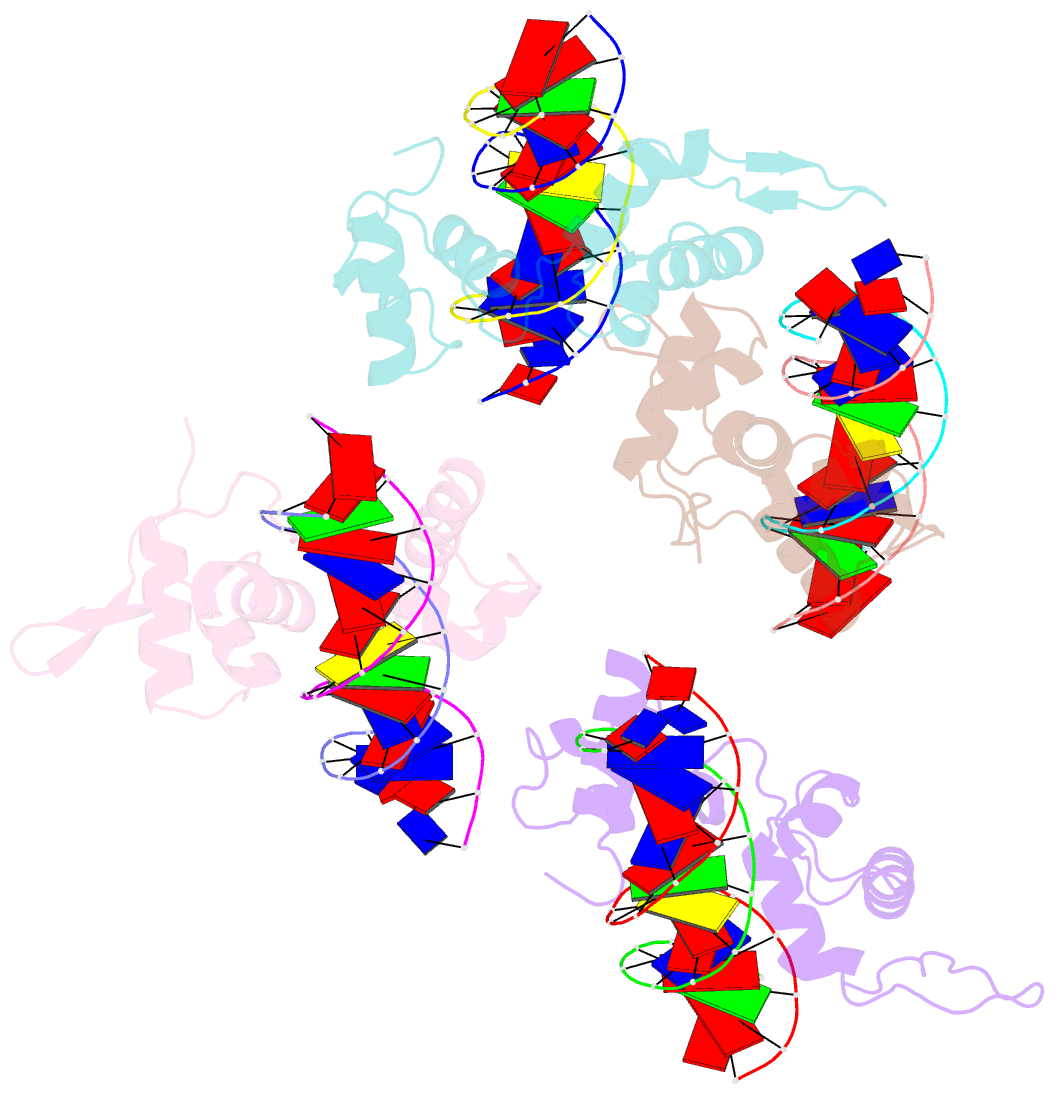
- Structure of the trichomonas vaginalis myb3 DNA-binding domain bound to a promoter sequence reveals a unique c-terminal beta-hairpin conformation
- Reference
- Wei S-Y, Lou Y-C, Tsai J-Y, Ho MR, Chou CC, Rajasekaran M, Hsu H-M, Tai J-H, Hsiao C-D, Chen C (2012): "Structure of the Trichomonas Vaginalis Myb3 DNA-Binding Domain Bound to a Promoter Sequence Reveals a Unique C-Terminal Beta-Hairpin Conformation." Nucleic Acids Res., 40, 449. doi: 10.1093/NAR/GKR707.
- Abstract
- Trichomonas vaginalis Myb3 transcription factor (tvMyb3) recognizes the MRE-1 promoter sequence and regulates ap65-1 gene, which encodes a hydrogenosomal malic enzyme that may play a role in the cytoadherence of the parasite. Here, we identified tvMyb3(53-180) as the essential fragment for DNA recognition and report the crystal structure of tvMyb3(53-180) bound to MRE-1 DNA. The N-terminal fragment adopts the classical conformation of an Myb DNA-binding domain, with the third helices of R2 and R3 motifs intercalating in the major groove of DNA. The C-terminal extension forms a β-hairpin followed by a flexible tail, which is stabilized by several interactions with the R3 motif and is not observed in other Myb proteins. Interestingly, this unique C-terminal fragment does not stably connect with DNA in the complex structure but is involved in DNA binding, as demonstrated by NMR chemical shift perturbation, (1)H-(15)N heteronuclear-nuclear Overhauser effect and intermolecular paramagnetic relaxation enhancement. Site-directed mutagenesis also revealed that this C-terminal fragment is crucial for DNA binding, especially the residue Arg(153) and the fragment K(170)KRK(173). We provide a structural basis for MRE-1 DNA recognition and suggest a possible post-translational regulation of tvMyb3 protein.