Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4alp; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- chaperone-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.48 Å)
- Summary
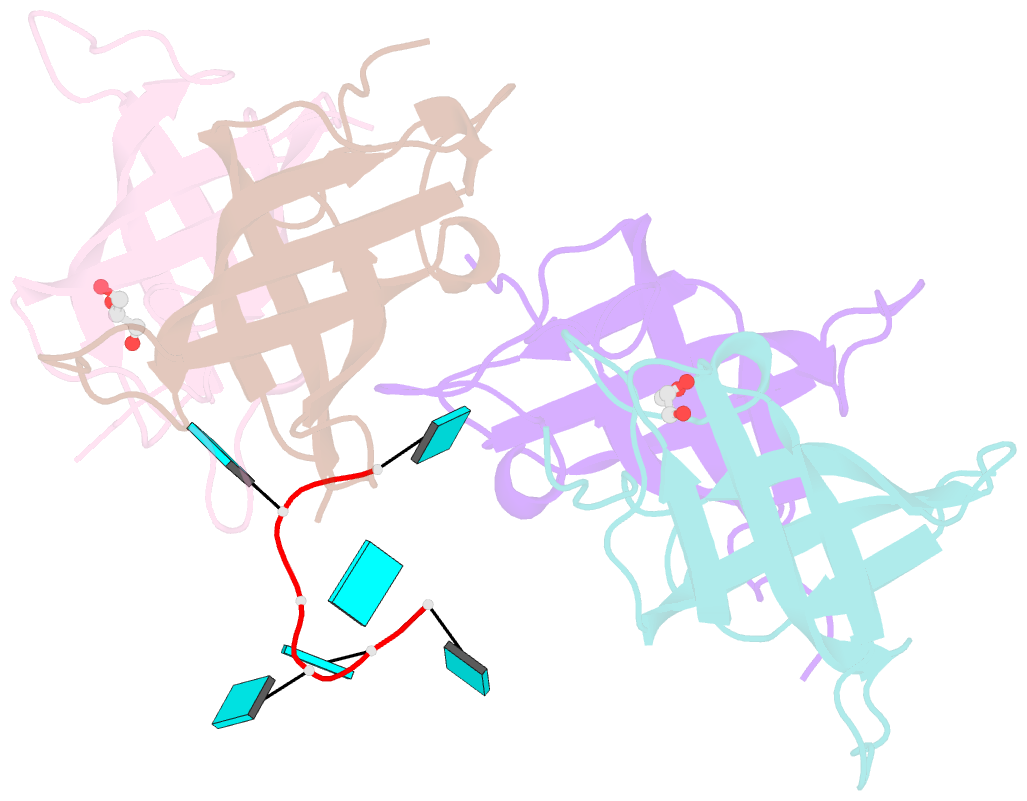
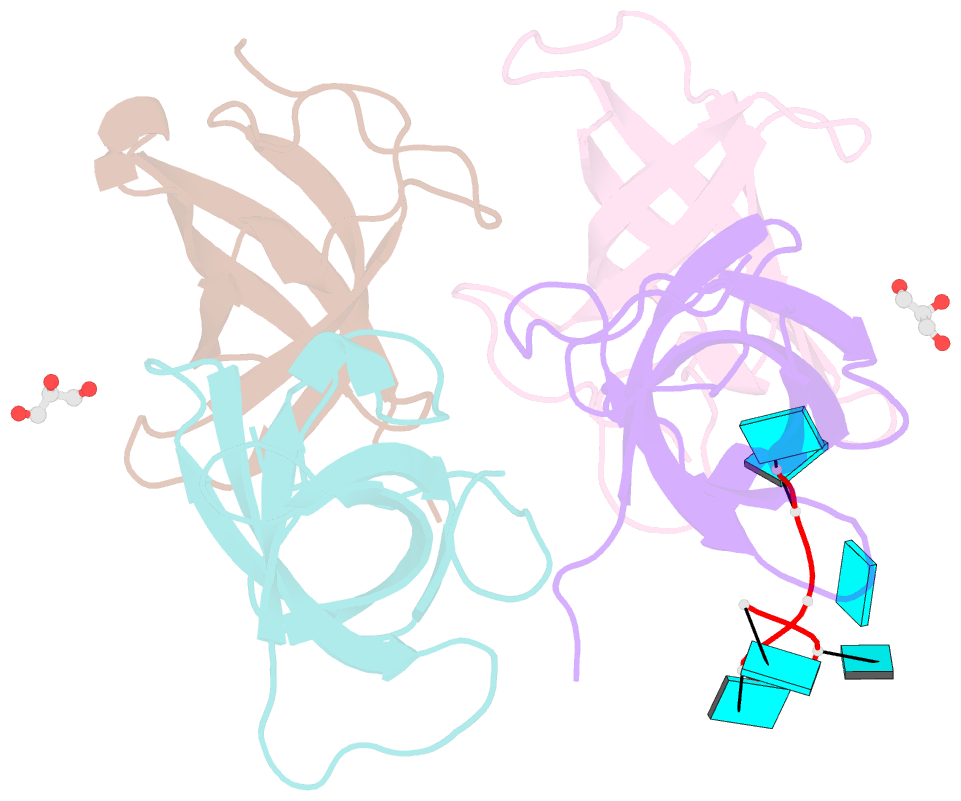
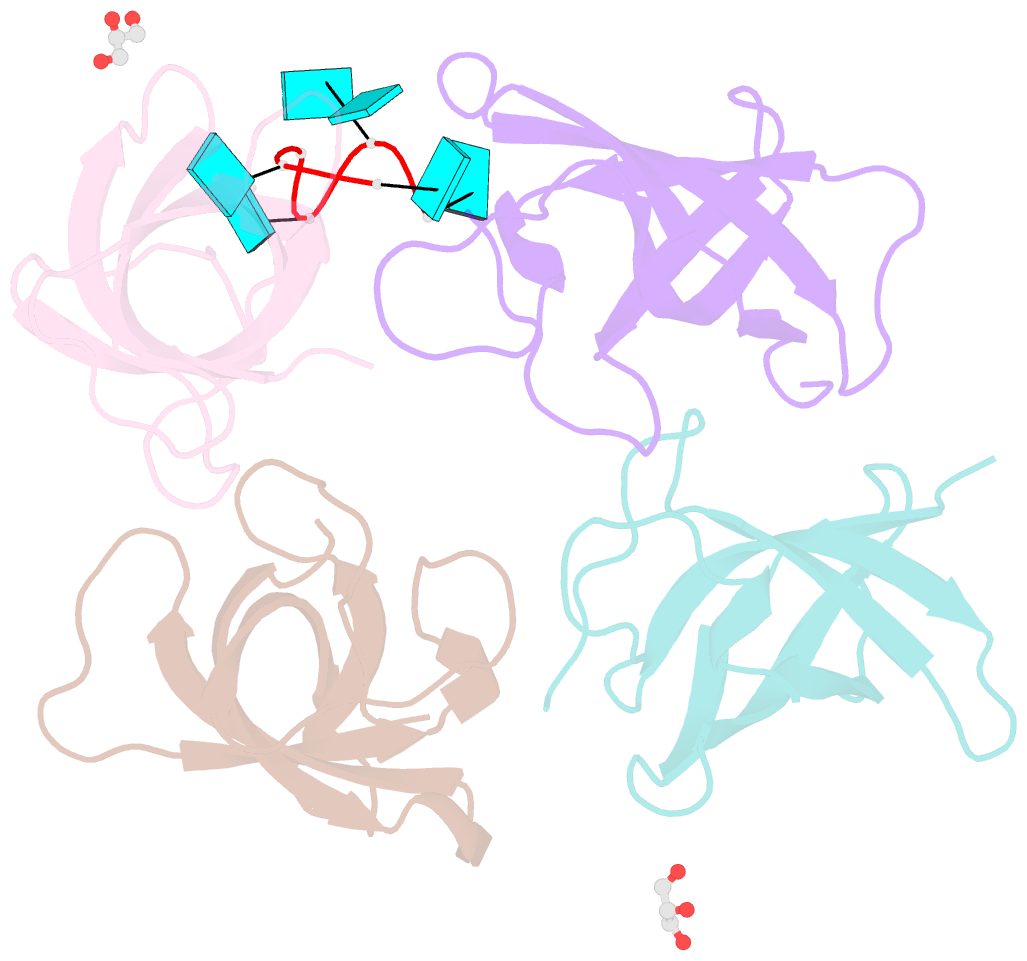
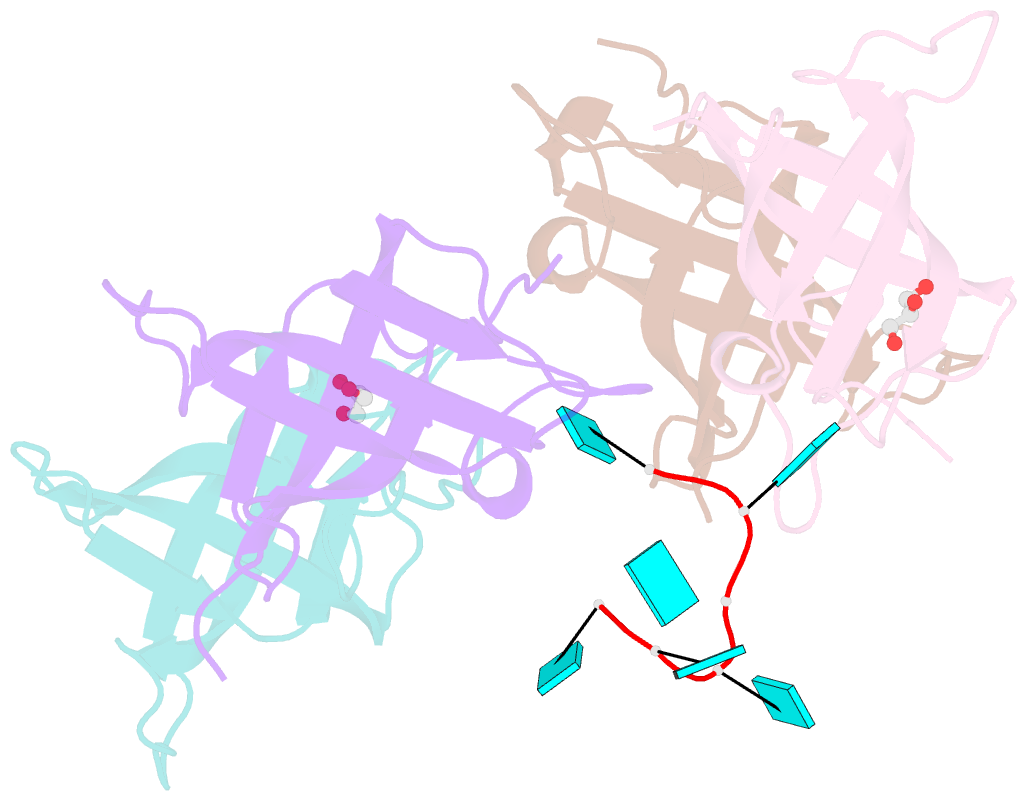
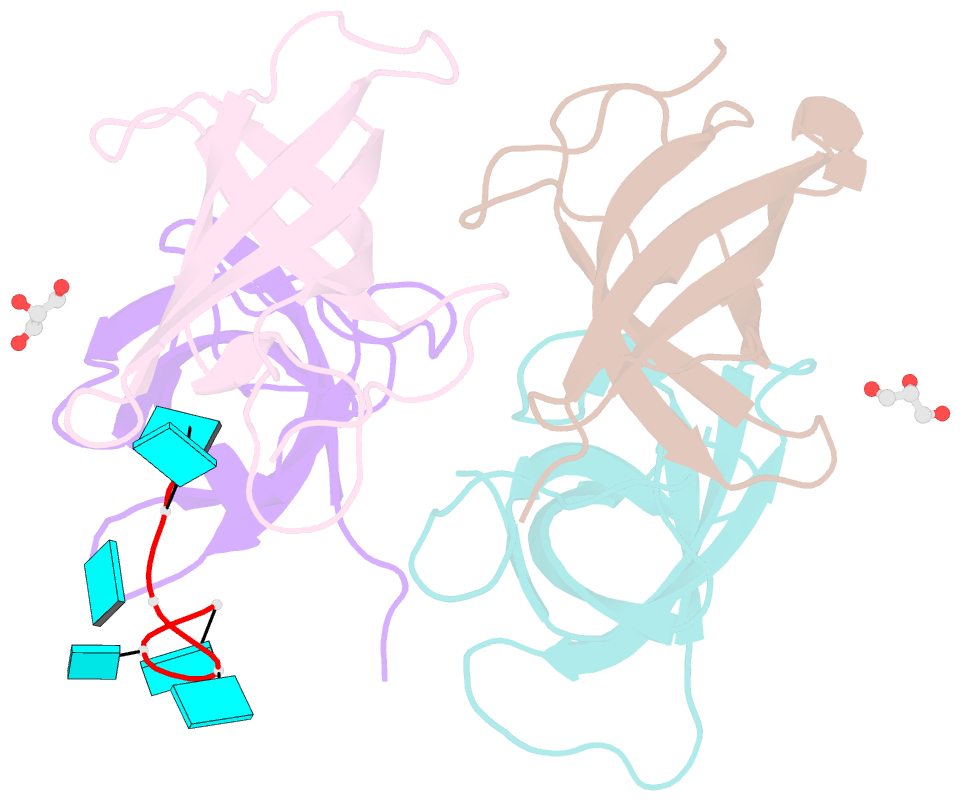
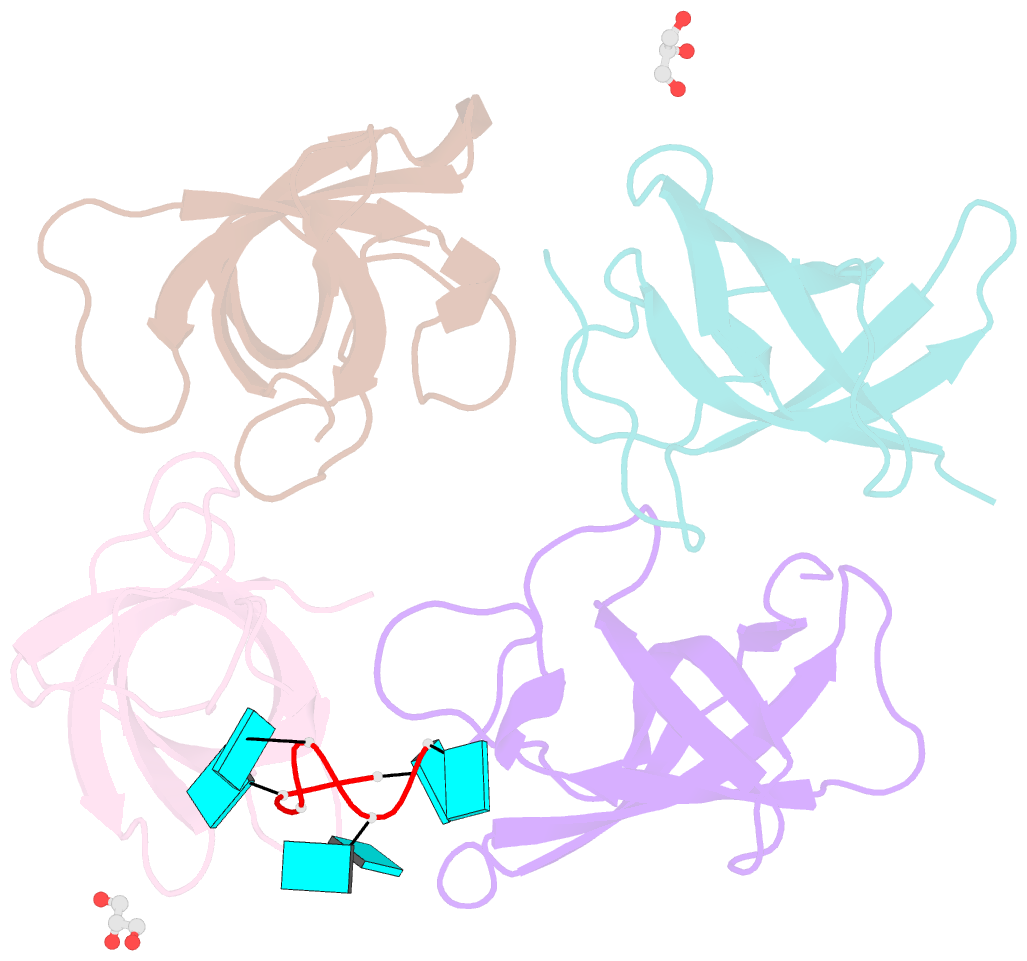
- The lin28b cold shock domain in complex with hexauridine
- Reference
- Mayr F, Schutz A, Doge N, Heinemann U (2012): "The Lin28 Cold-Shock Domain Remodels Pre-Let-7 Microrna." Nucleic Acids Res., 40, 7492. doi: 10.1093/NAR/GKS355.
- Abstract
- The RNA-binding protein Lin28 regulates the processing of a developmentally important group of microRNAs, the let-7 family. Lin28 blocks the biogenesis of let-7 in embryonic stem cells and thereby prevents differentiation. It was shown that both RNA-binding domains (RBDs) of this protein, the cold-shock domain (CSD) and the zinc-knuckle domain (ZKD) are indispensable for pri- or pre-let-7 binding and blocking its maturation. Here, we systematically examined the nucleic acid-binding preferences of the Lin28 RBDs and determined the crystal structure of the Lin28 CSD in the absence and presence of nucleic acids. Both RNA-binding domains bind to single-stranded nucleic acids with the ZKD mediating specific binding to a conserved GGAG motif and the CSD showing only limited sequence specificity. However, only the isolated Lin28 CSD, but not the ZKD, can bind with a reasonable affinity to pre-let-7 and thus is able to remodel the terminal loop of pre-let-7 including the Dicer cleavage site. Further mutagenesis studies reveal that the Lin28 CSD induces a conformational change in the terminal loop of pre-let-7 and thereby facilitates a subsequent specific binding of the Lin28 ZKD to the conserved GGAG motif.