Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4awl; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.08 Å)
- Summary
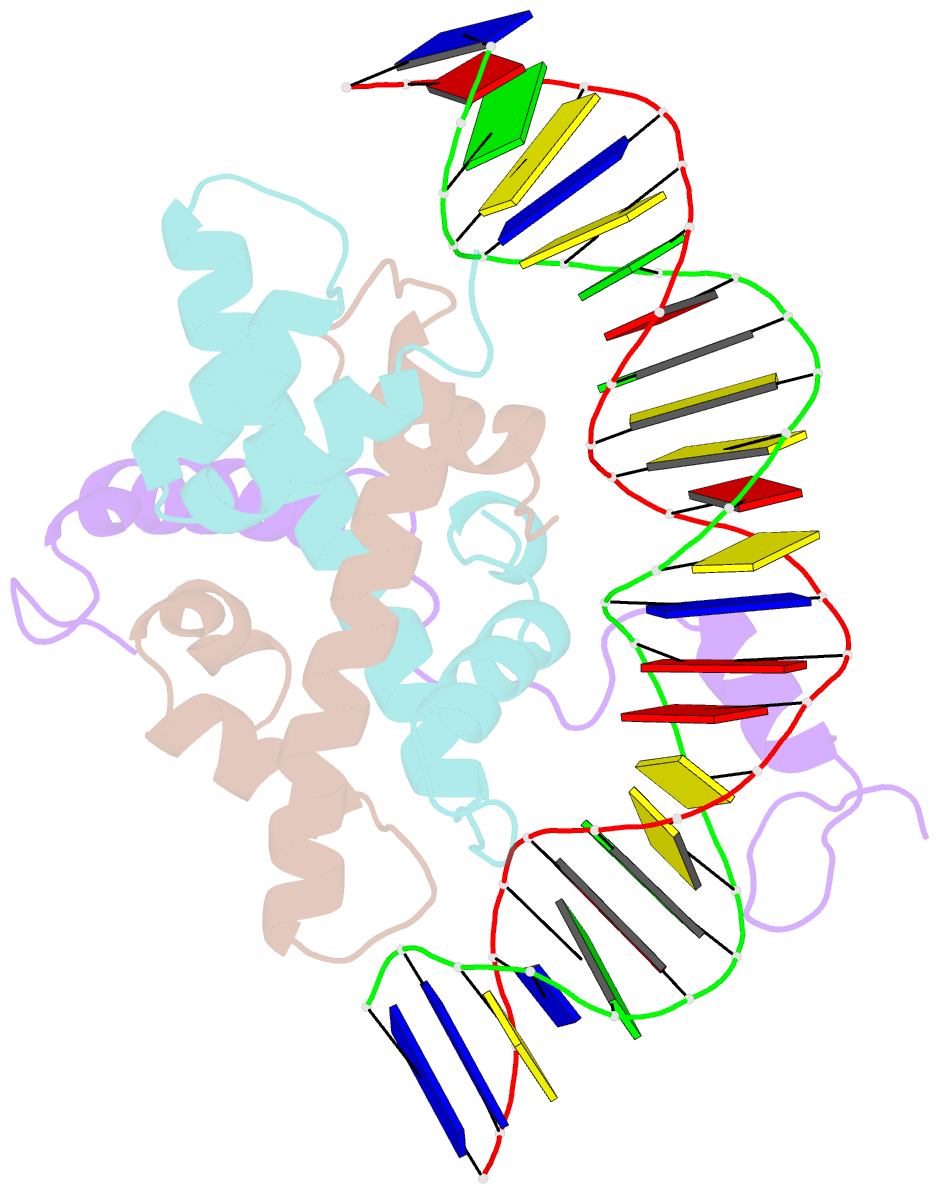
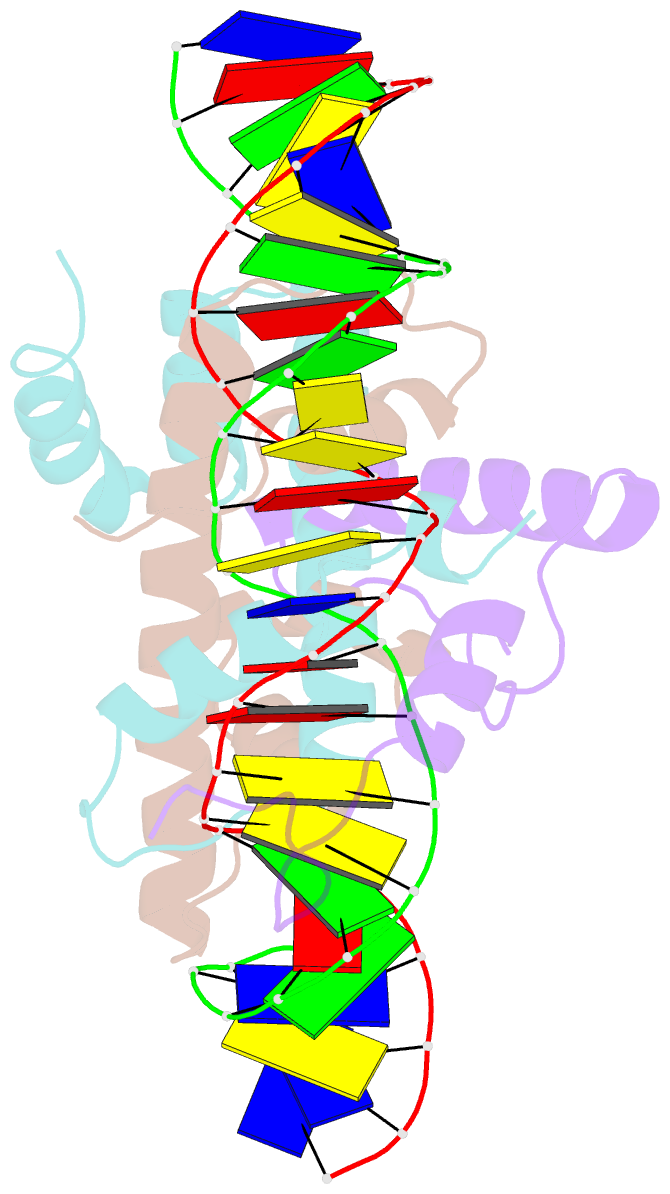
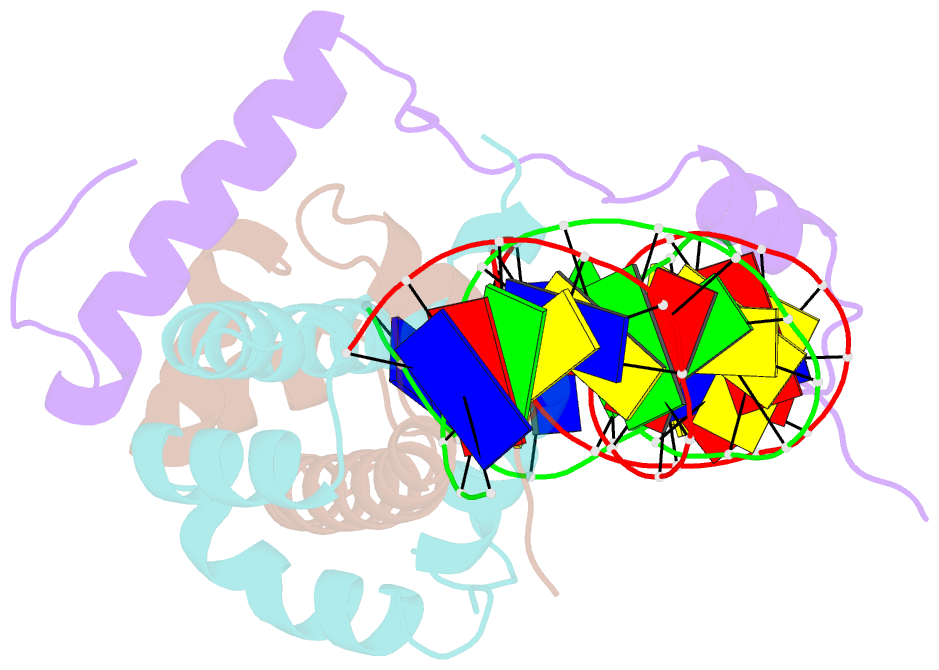
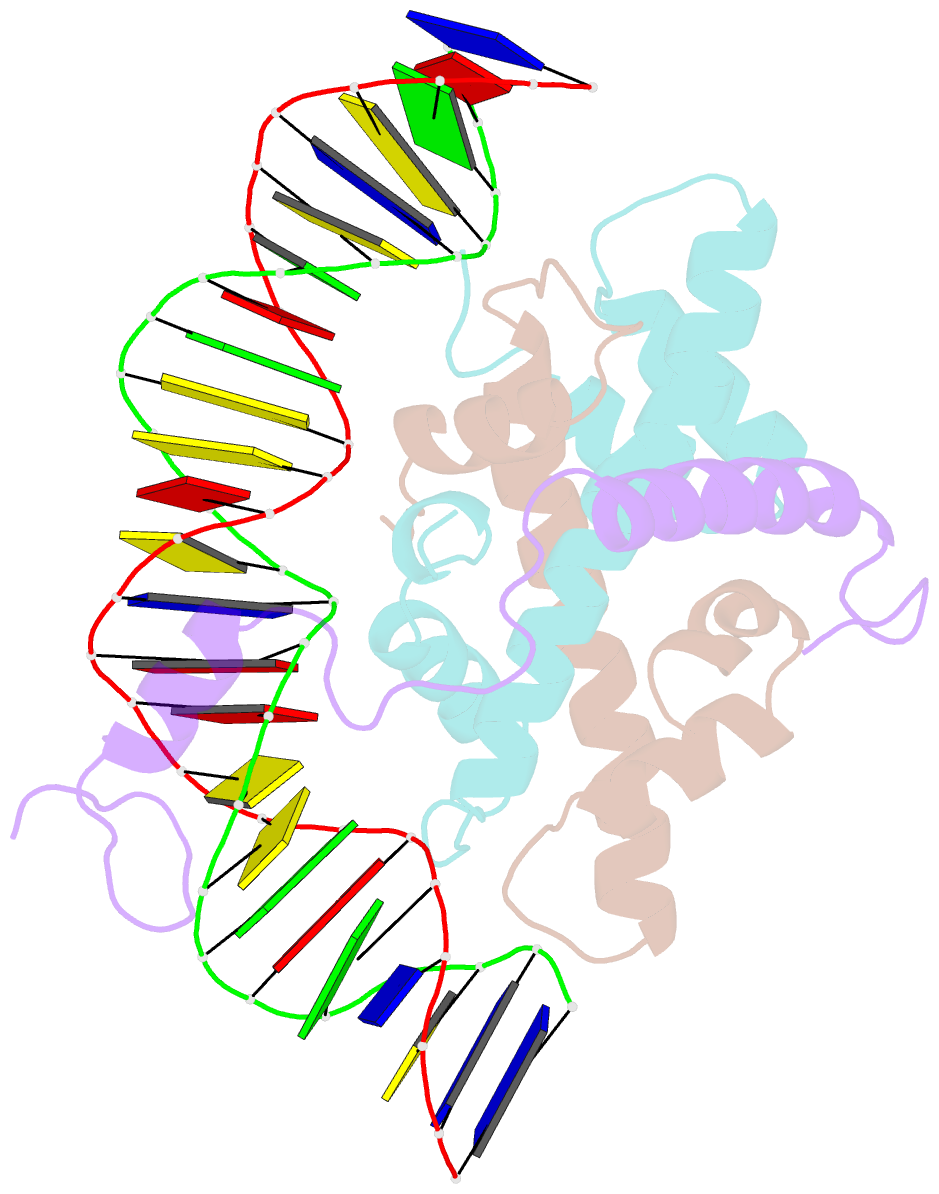
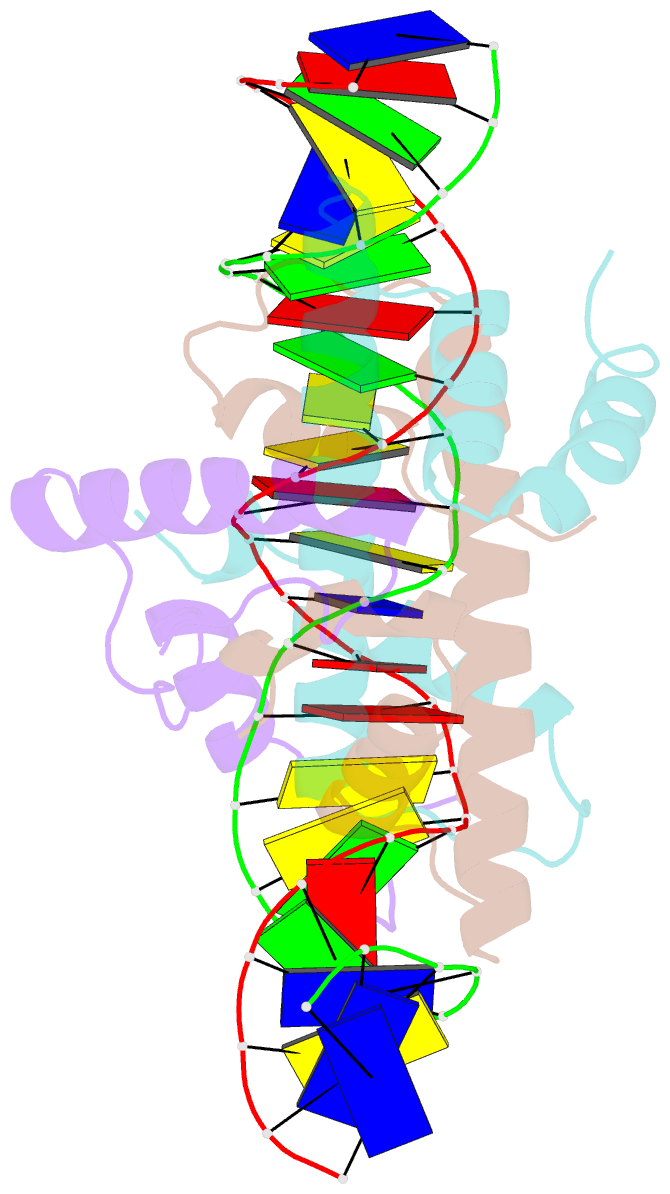
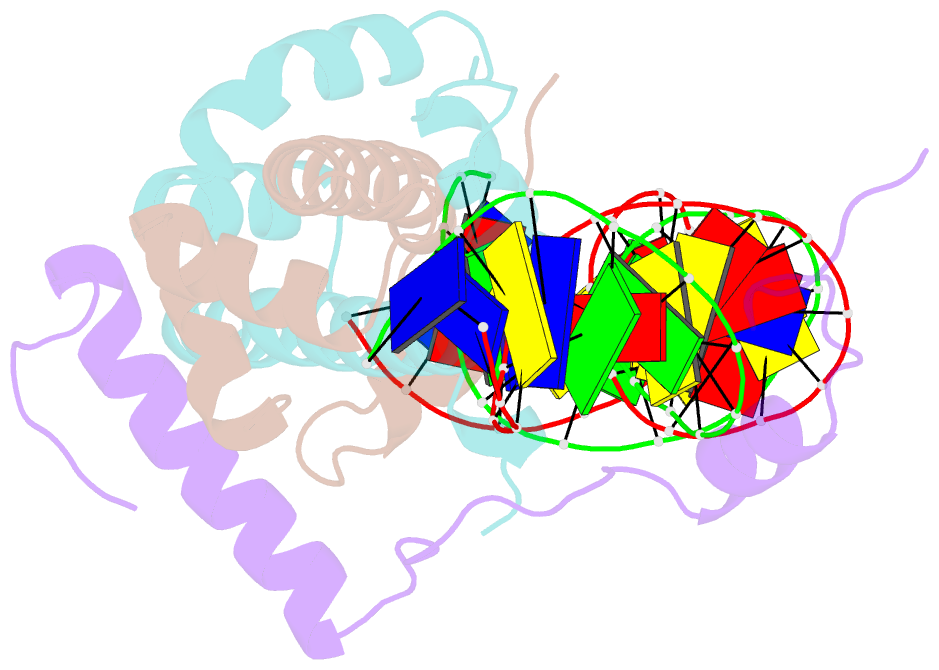
- The nf-y transcription factor is structurally and functionally a sequence specific histone
- Reference
- Nardini M, Gnesutta N, Donati G, Gatta R, Forni C, Fossati A, Vonrhein C, Moras D, Romier C, Bolognesi M, Mantovani R (2013): "Sequence-Specific Transcription Factor NF-Y Displays Histone-Like DNA Binding and H2B-Like Ubiquitination." Cell(Cambridge,Mass.), 152, 132. doi: 10.1016/J.CELL.2012.11.047.
- Abstract
- The sequence-specific transcription factor NF-Y binds the CCAAT box, one of the sequence elements most frequently found in eukaryotic promoters. NF-Y is composed of the NF-YA and NF-YB/NF-YC subunits, the latter two hosting histone-fold domains (HFDs). The crystal structure of NF-Y bound to a 25 bp CCAAT oligonucleotide shows that the HFD dimer binds to the DNA sugar-phosphate backbone, mimicking the nucleosome H2A/H2B-DNA assembly. NF-YA both binds to NF-YB/NF-YC and inserts an α helix deeply into the DNA minor groove, providing sequence-specific contacts to the CCAAT box. Structural considerations and mutational data indicate that NF-YB ubiquitination at Lys138 precedes and is equivalent to H2B Lys120 monoubiquitination, important in transcriptional activation. Thus, NF-Y is a sequence-specific transcription factor with nucleosome-like properties of nonspecific DNA binding and helps establish permissive chromatin modifications at CCAAT promoters. Our findings suggest that other HFD-containing proteins may function in similar ways.