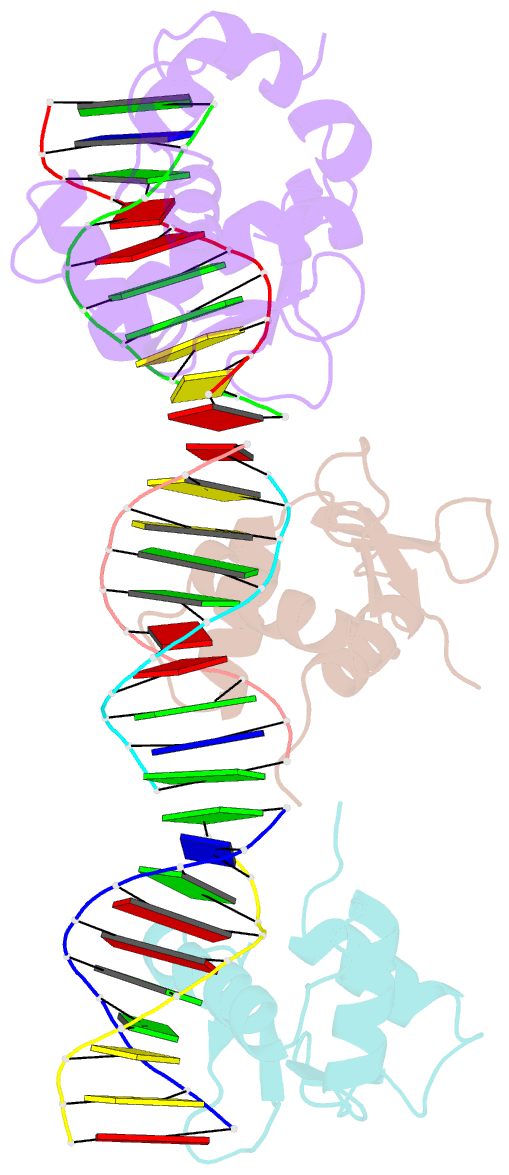
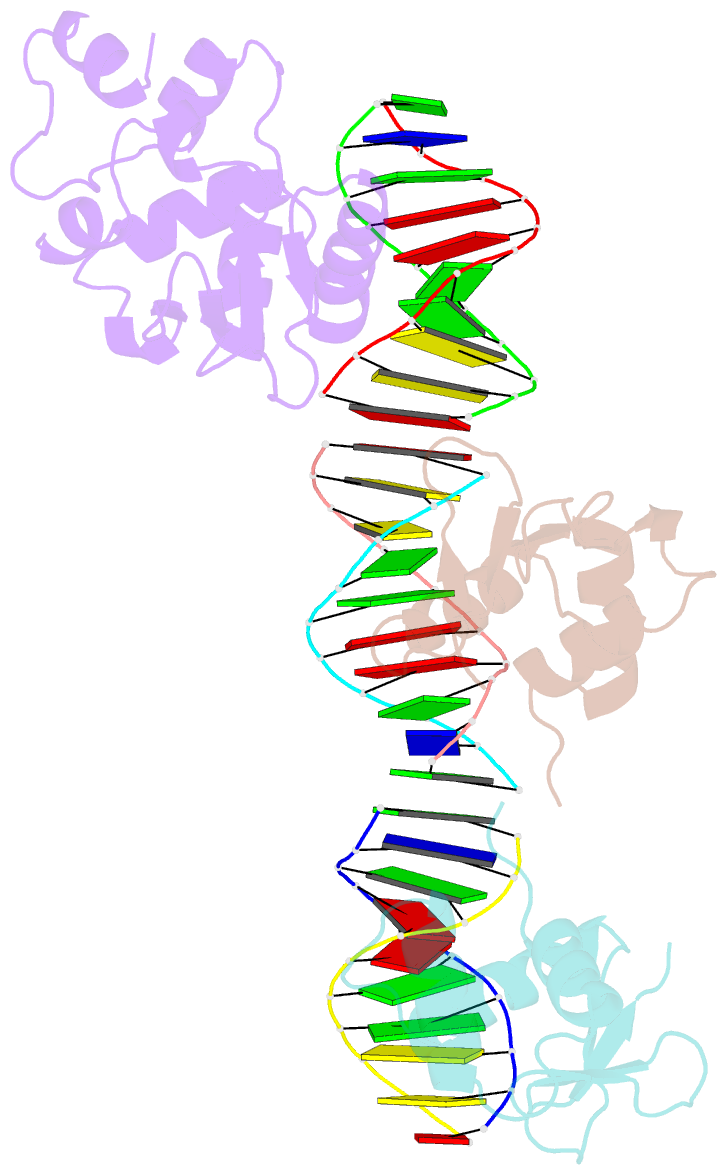
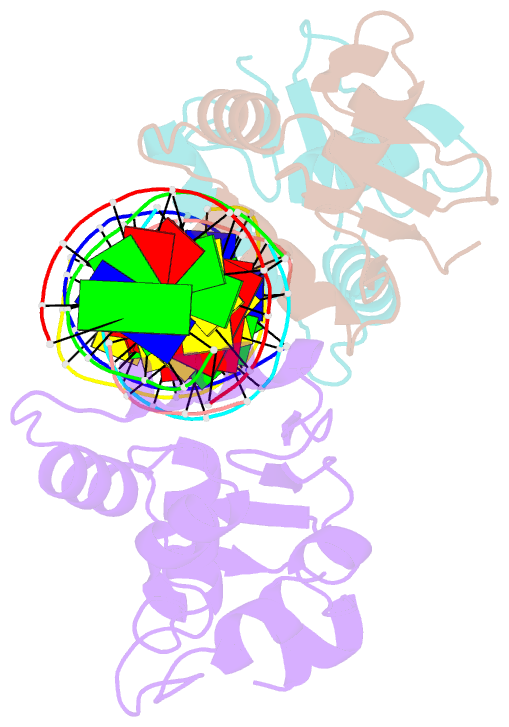
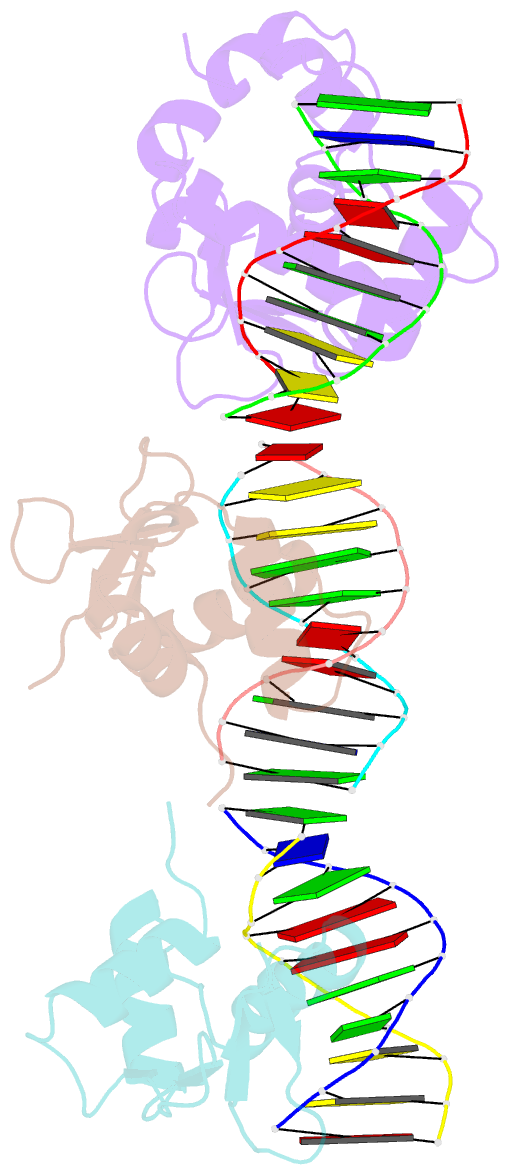
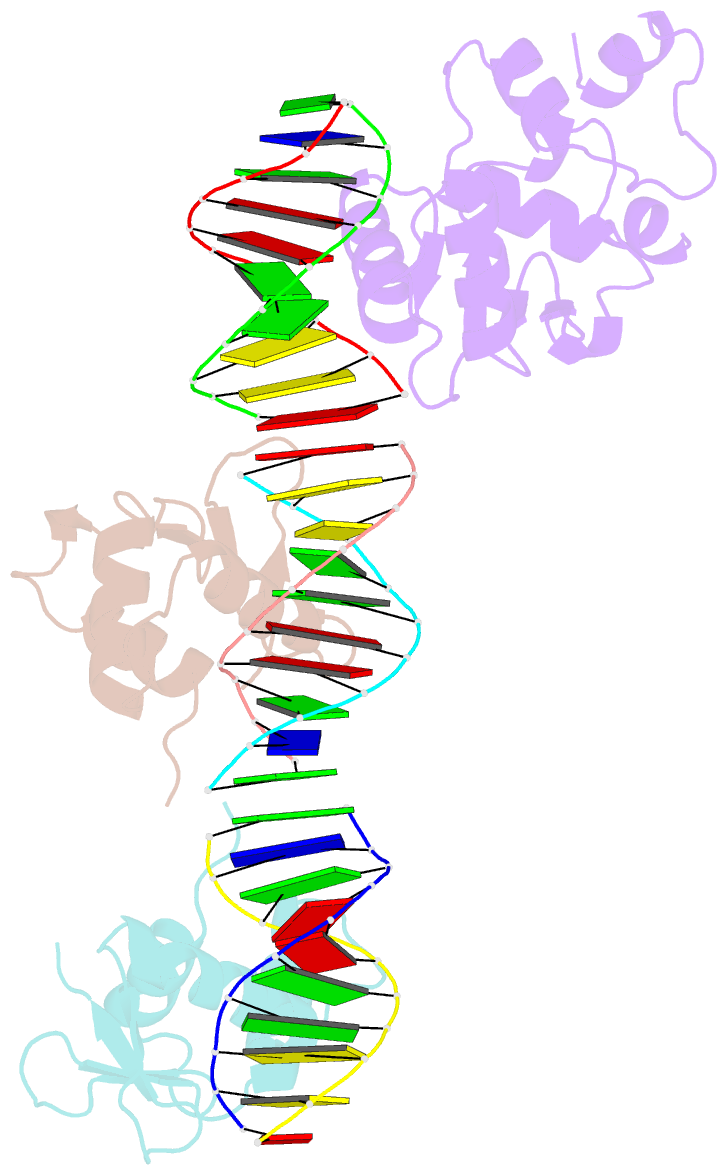
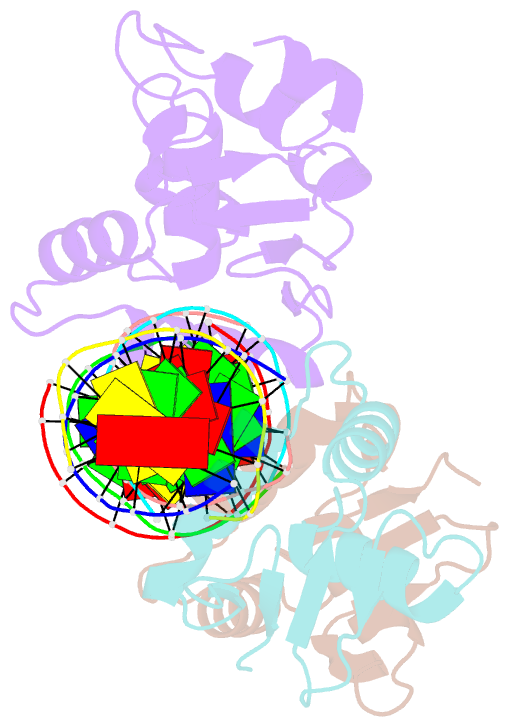
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4bqa; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of the ets domain of human ets2 in complex with DNA
- Reference
- Newman JA, Cooper CDO, Aitkenhead H, Gileadi O (2015): "Structural Insights Into the Autoregulation and Cooperativity of the Human Transcription Factor Ets-2." J.Biol.Chem., 290, 8539. doi: 10.1074/JBC.M114.619270.
- Abstract
- Ets-2, like its closely related homologue Ets-1, is a member of the Ets family of DNA binding transcription factors. Both proteins are subject to multiple levels of regulation of their DNA binding and transactivation properties. One such regulatory mechanism is the presence of an autoinhibitory module, which in Ets-1 allosterically inhibits the DNA binding activity. This inhibition can be relieved by interaction with protein partners or cooperative binding to closely separated Ets binding sites in a palindromic arrangement. In this study we describe the 2.5 Å resolution crystal structure of a DNA complex of the Ets-2 Ets domain. The Ets domain crystallized with two distinct species in the asymmetric unit, which closely resemble the autoinhibited and DNA bound forms of Ets-1. This discovery prompted us to re-evaluate the current model for the autoinhibitory mechanism and the structural basis for cooperative DNA binding. In contrast to Ets-1, in which the autoinhibition is caused by a combination of allosteric and steric mechanisms, we were unable to find clear evidence for the allosteric mechanism in Ets-2. We also demonstrated two possibly distinct types of cooperative binding to substrates with Ets binding motifs separated by four and six base pairs and suggest possible molecular mechanisms for this behavior.