Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4bs2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
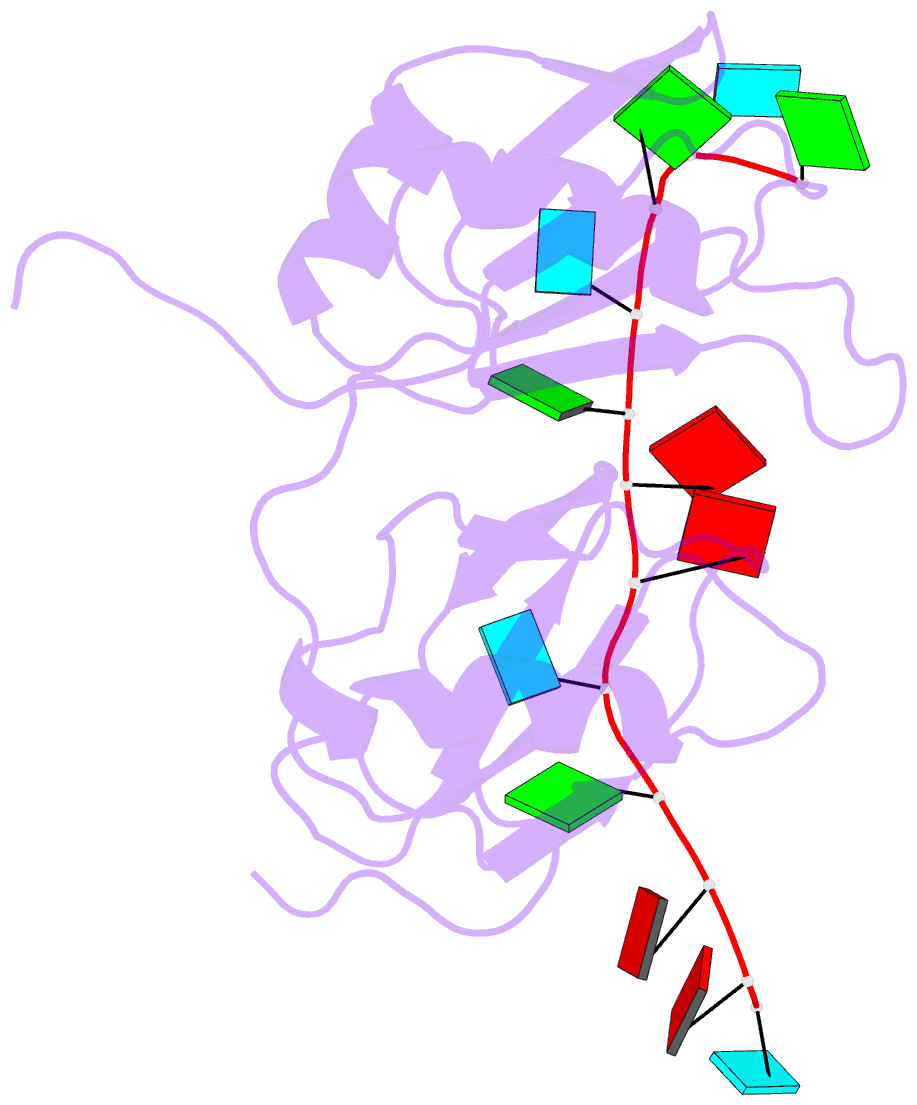
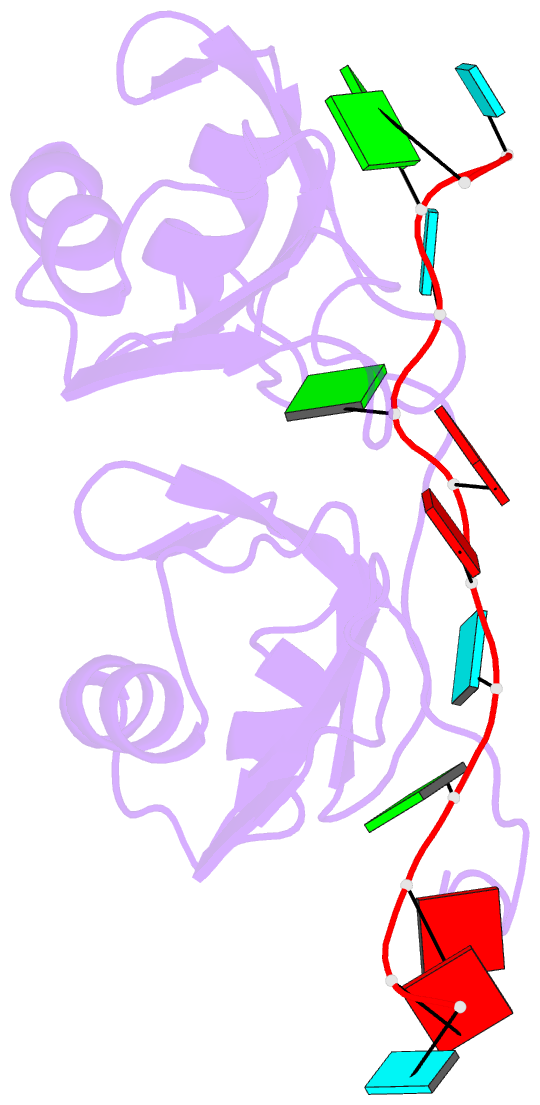
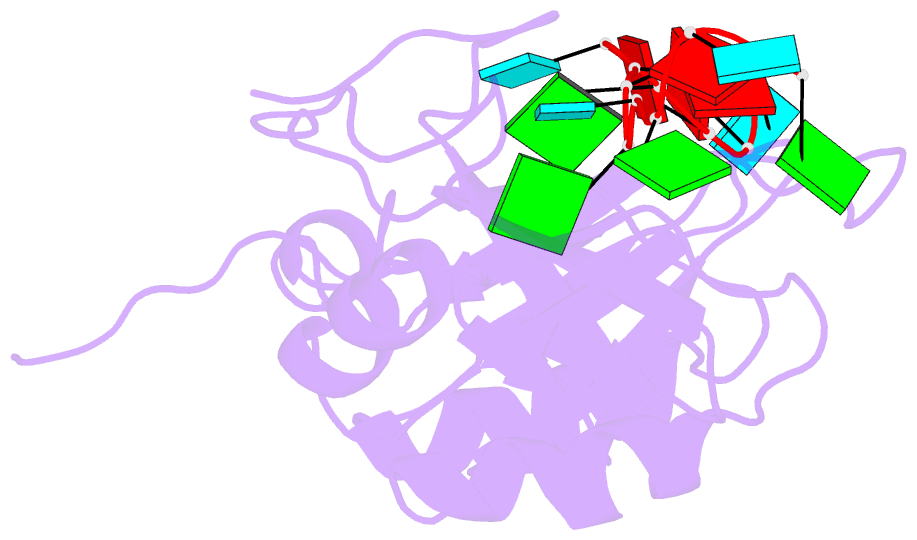
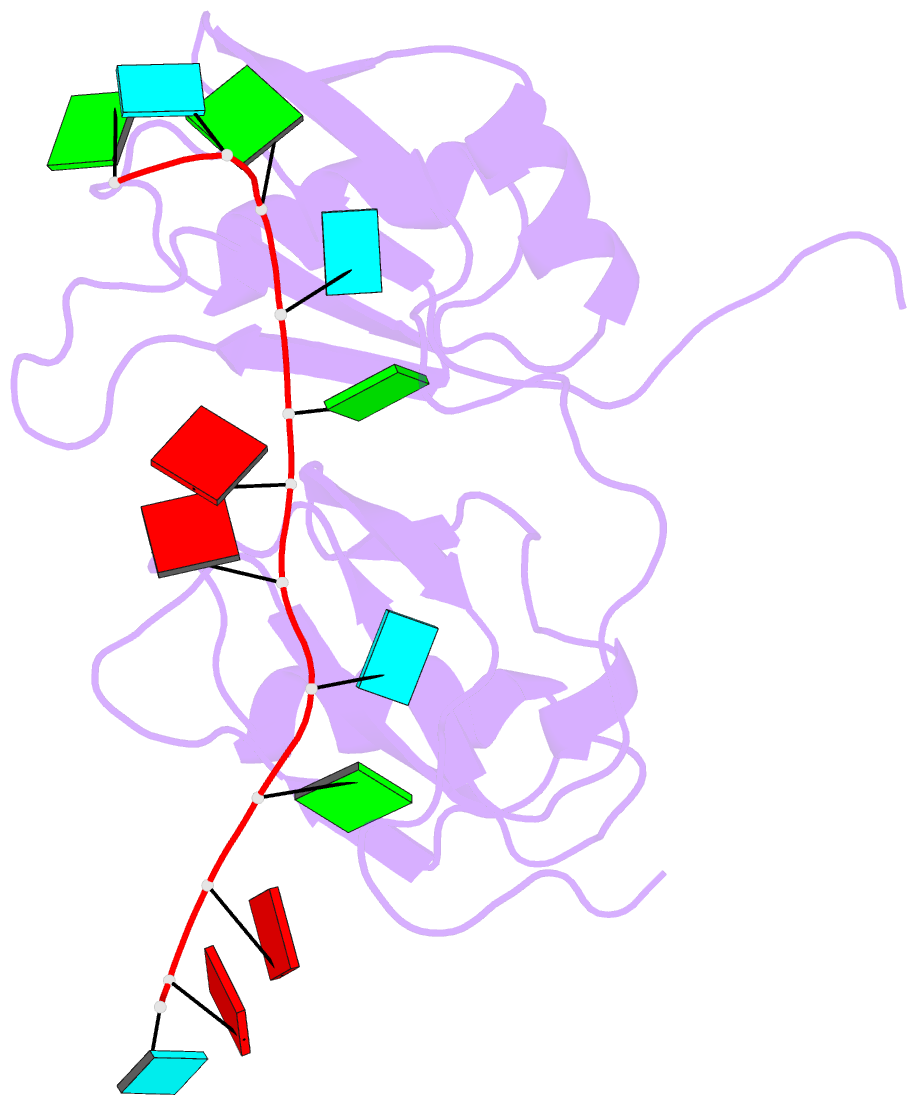
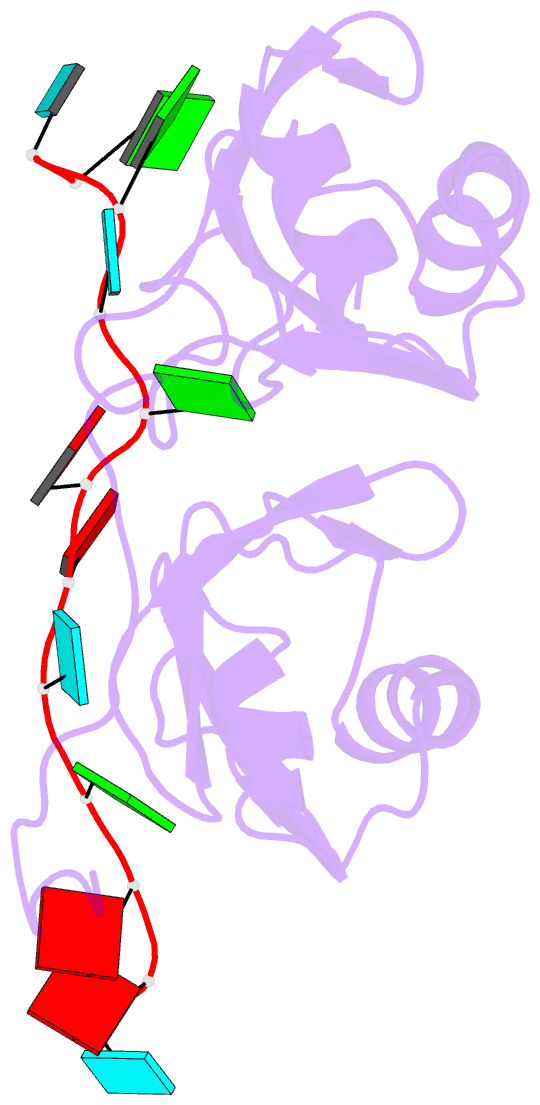
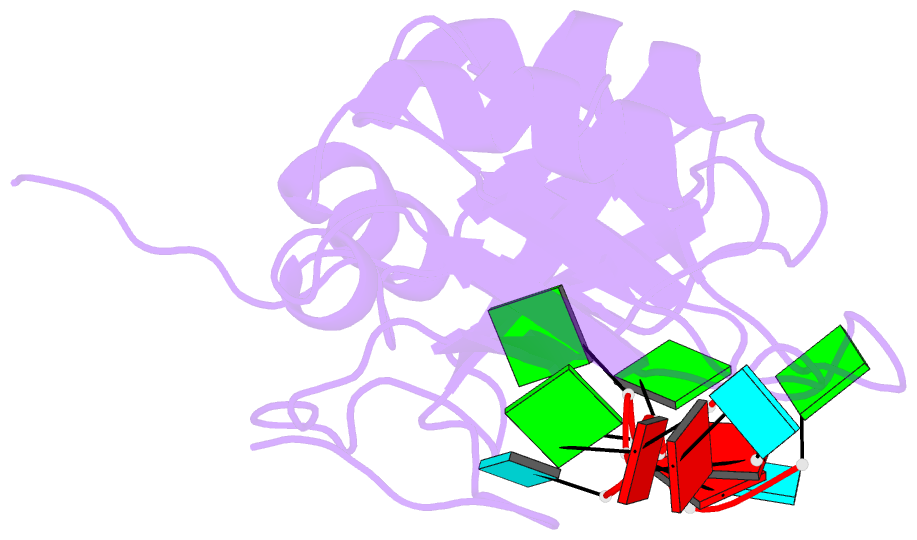
- NMR structure of human tdp-43 tandem rrms in complex with ug-rich RNA
- Reference
- Lukavsky PJ, Daujotyte D, Tollervey JR, Ule J, Stuani C, Buratti E, Baralle FE, Damberger FF, Allain FHT (2013): "Molecular Basis of Ug-Rich RNA Recognition by the Human Splicing Factor Tdp-43." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 20, 1443. doi: 10.1038/NSMB.2698.
- Abstract
- TDP-43 encodes an alternative-splicing regulator with tandem RNA-recognition motifs (RRMs). The protein regulates cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) exon 9 splicing through binding to long UG-rich RNA sequences and is found in cytoplasmic inclusions of several neurodegenerative diseases. We solved the solution structure of the TDP-43 RRMs in complex with UG-rich RNA. Ten nucleotides are bound by both RRMs, and six are recognized sequence specifically. Among these, a central G interacts with both RRMs and stabilizes a new tandem RRM arrangement. Mutations that eliminate recognition of this key nucleotide or crucial inter-RRM interactions disrupt RNA binding and TDP-43-dependent splicing regulation. In contrast, point mutations that affect base-specific recognition in either RRM have weaker effects. Our findings reveal not only how TDP-43 recognizes UG repeats but also how RNA binding-dependent inter-RRM interactions are crucial for TDP-43 function.