Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4bxo; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.15 Å)
- Summary
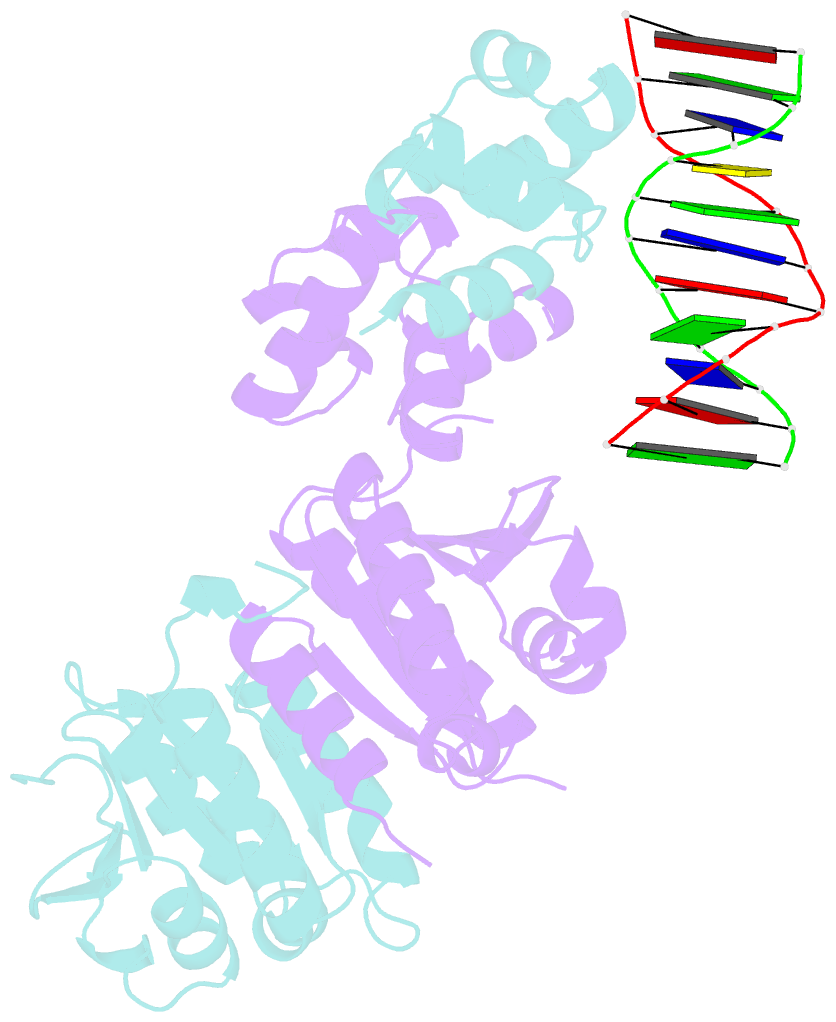
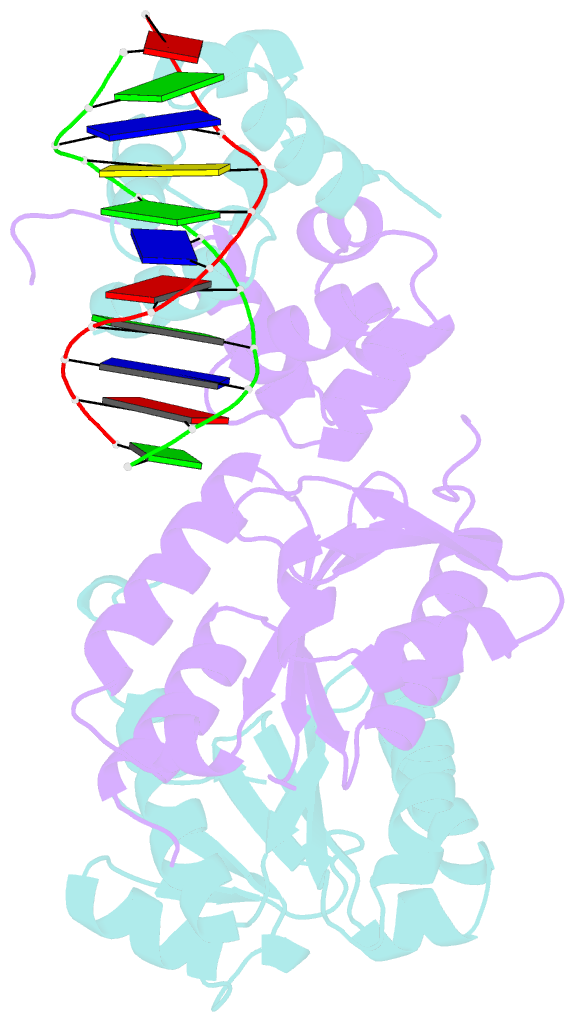
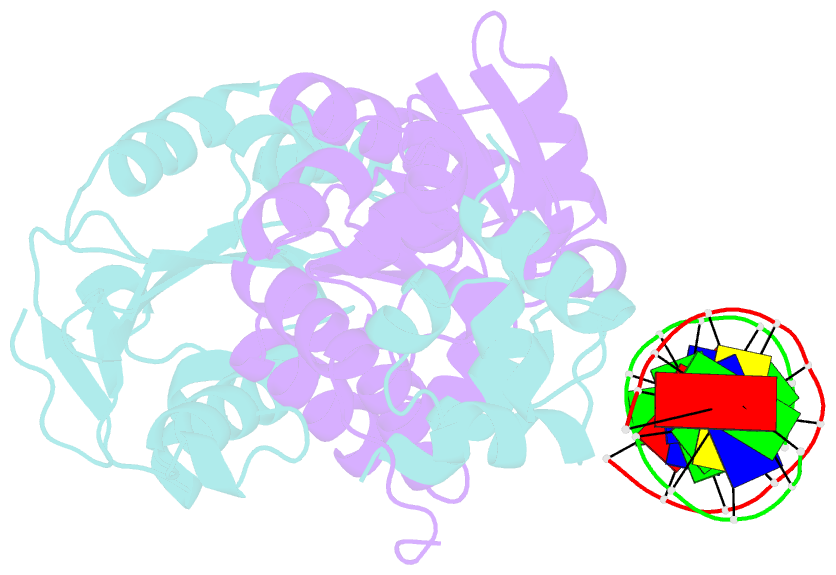
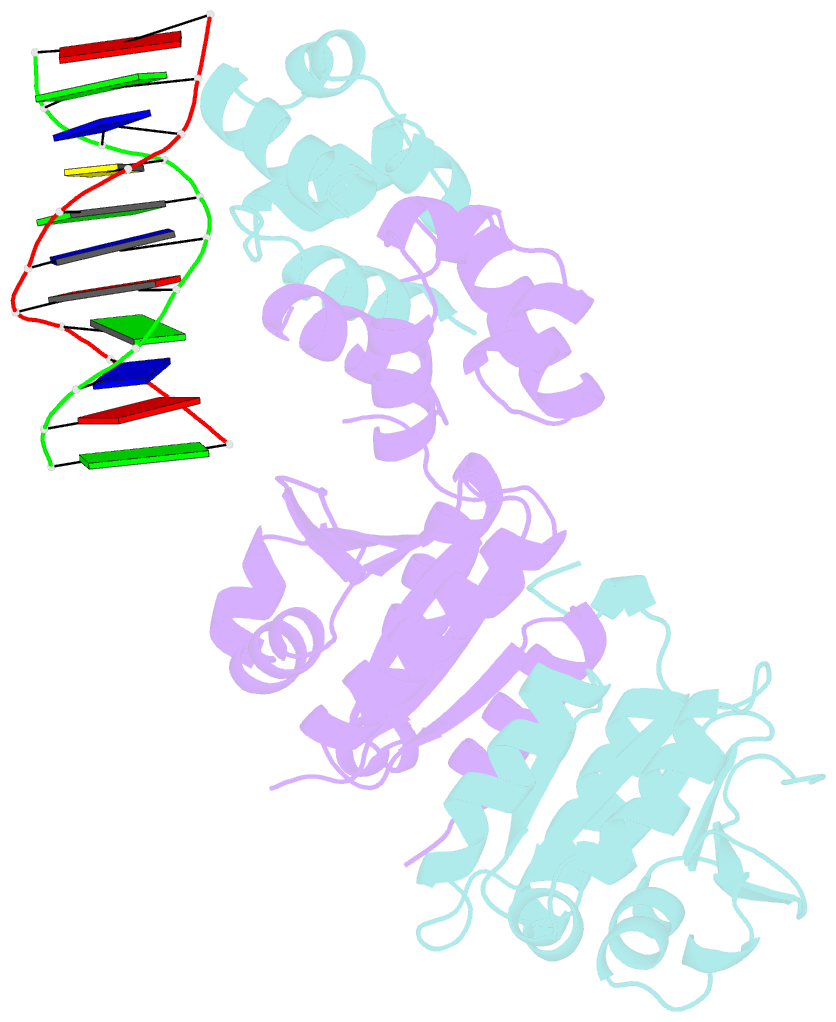
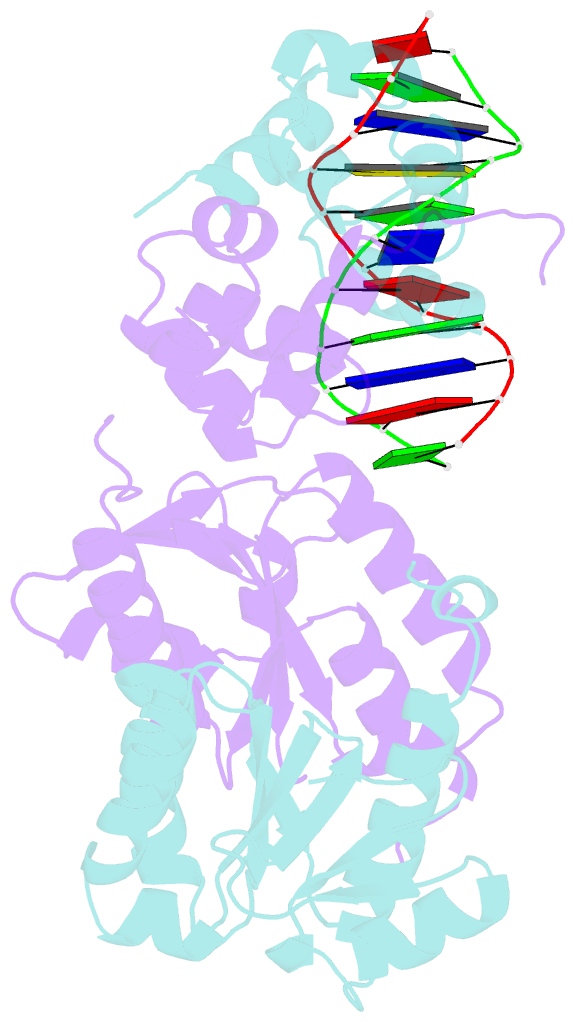
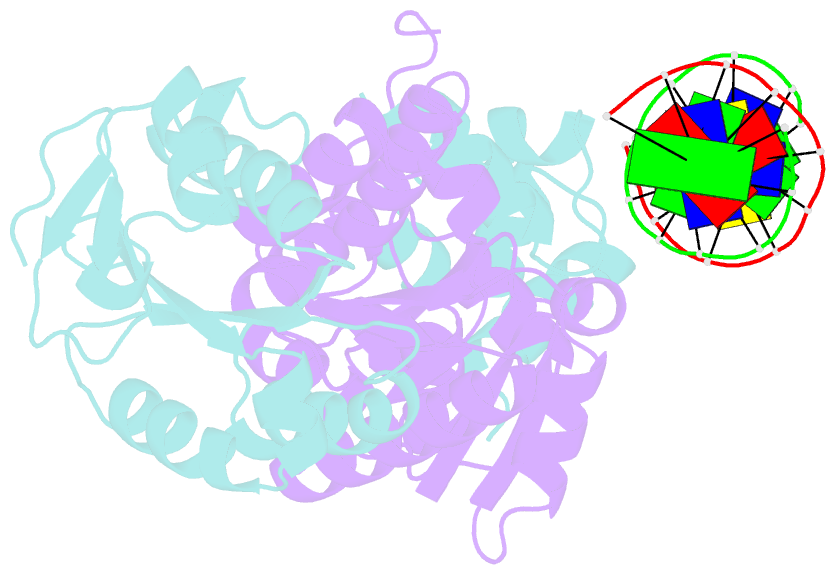
- Architecture and DNA recognition elements of the fanconi anemia fancm- faap24 complex
- Reference
- Coulthard R, Deans AJ, Swuec P, Bowles M, Costa A, West SC, Mcdonald NQ (2013): "Architecture and DNA Recognition Elements of the Fanconi Anemia Fancm-Faap24 Complex." Structure, 21, 1648. doi: 10.1016/J.STR.2013.07.006.
- Abstract
- Fanconi anemia (FA) is a disorder associated with a failure in DNA repair. FANCM (defective in FA complementation group M) and its partner FAAP24 target other FA proteins to sites of DNA damage. FANCM-FAAP24 is related to XPF/MUS81 endonucleases but lacks endonucleolytic activity. We report a structure of an FANCM C-terminal fragment (FANCMCTD) bound to FAAP24 and DNA. This S-shaped structure reveals the FANCM (HhH)2 domain is buried, whereas the FAAP24 (HhH)2 domain engages DNA. We identify a second DNA contact and a metal center within the FANCM pseudo-nuclease domain and demonstrate that mutations in either region impair double-stranded DNA binding in vitro and FANCM-FAAP24 function in vivo. We show the FANCM translocase domain lies in proximity to FANCMCTD by electron microscopy and that binding fork DNA structures stimulate its ATPase activity. This suggests a tracking model for FANCM-FAAP24 until an encounter with a stalled replication fork triggers ATPase-mediated fork remodeling.