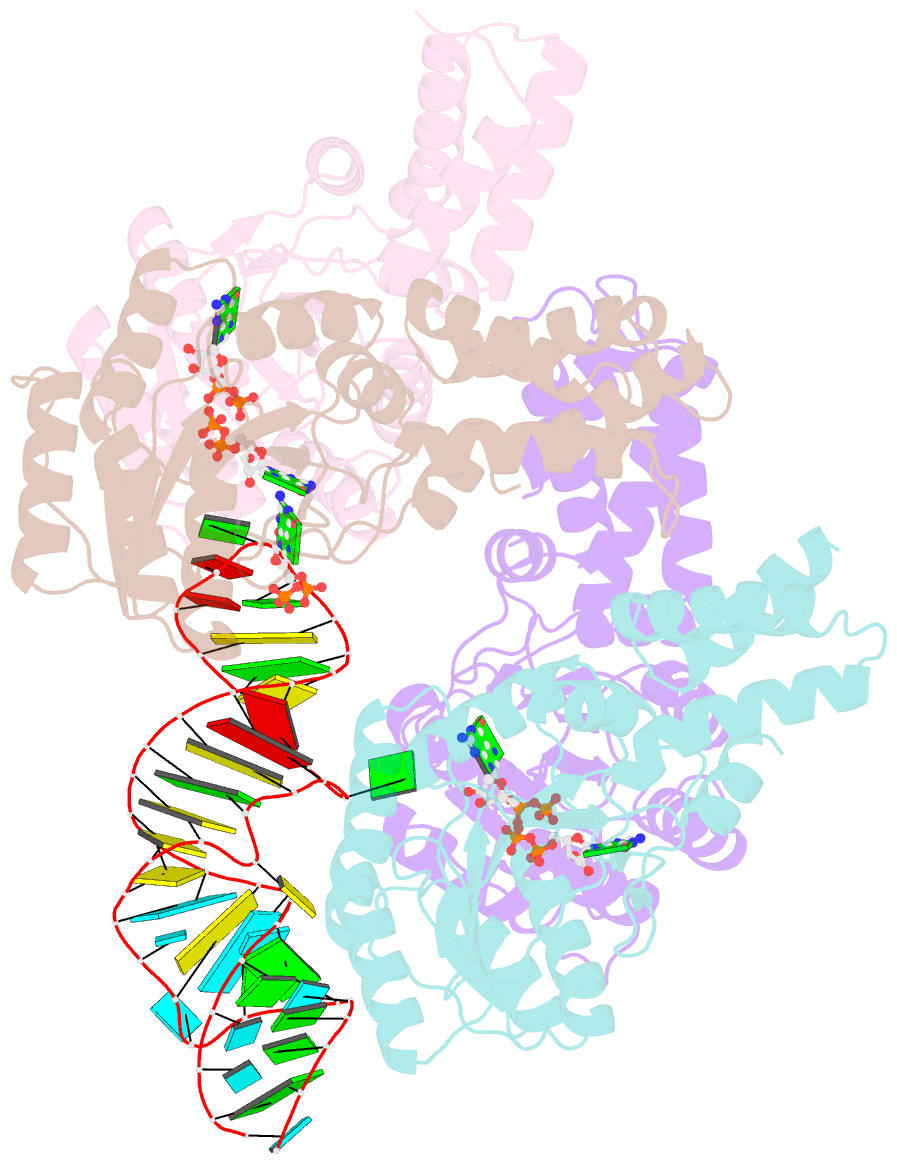
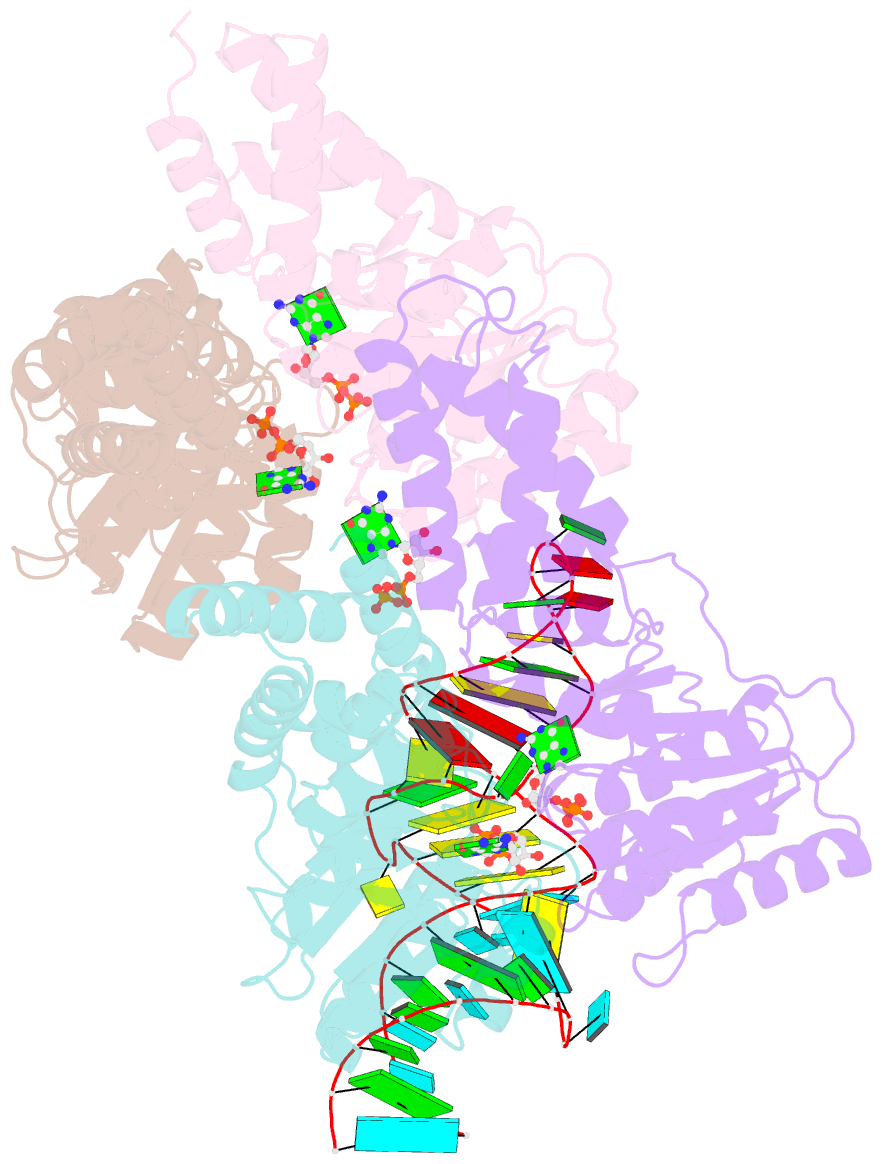
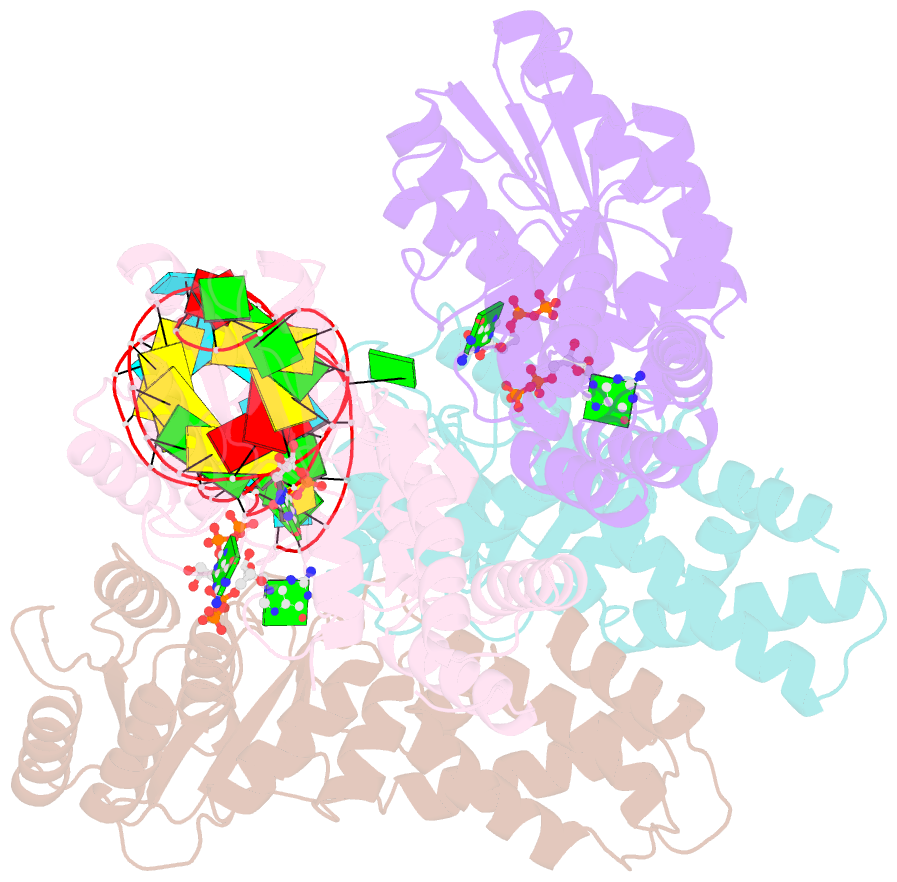
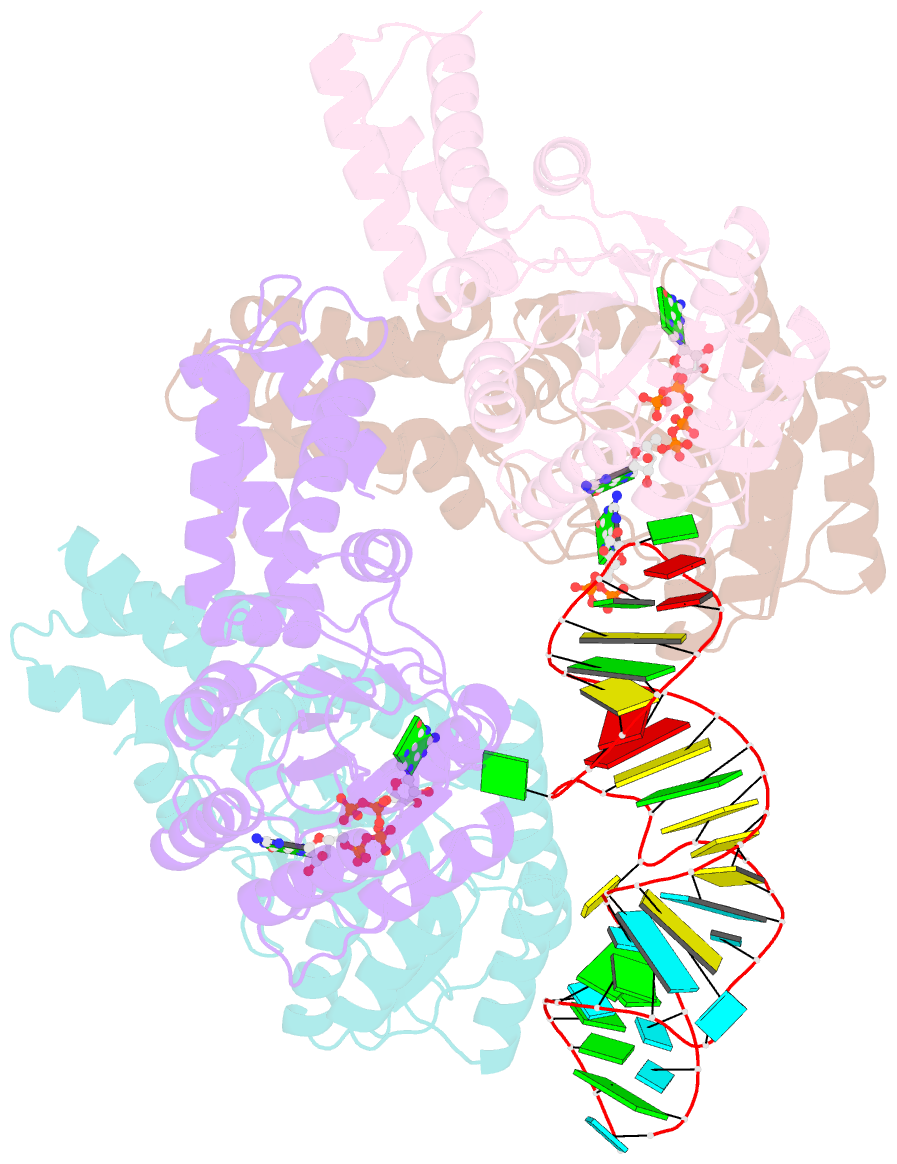
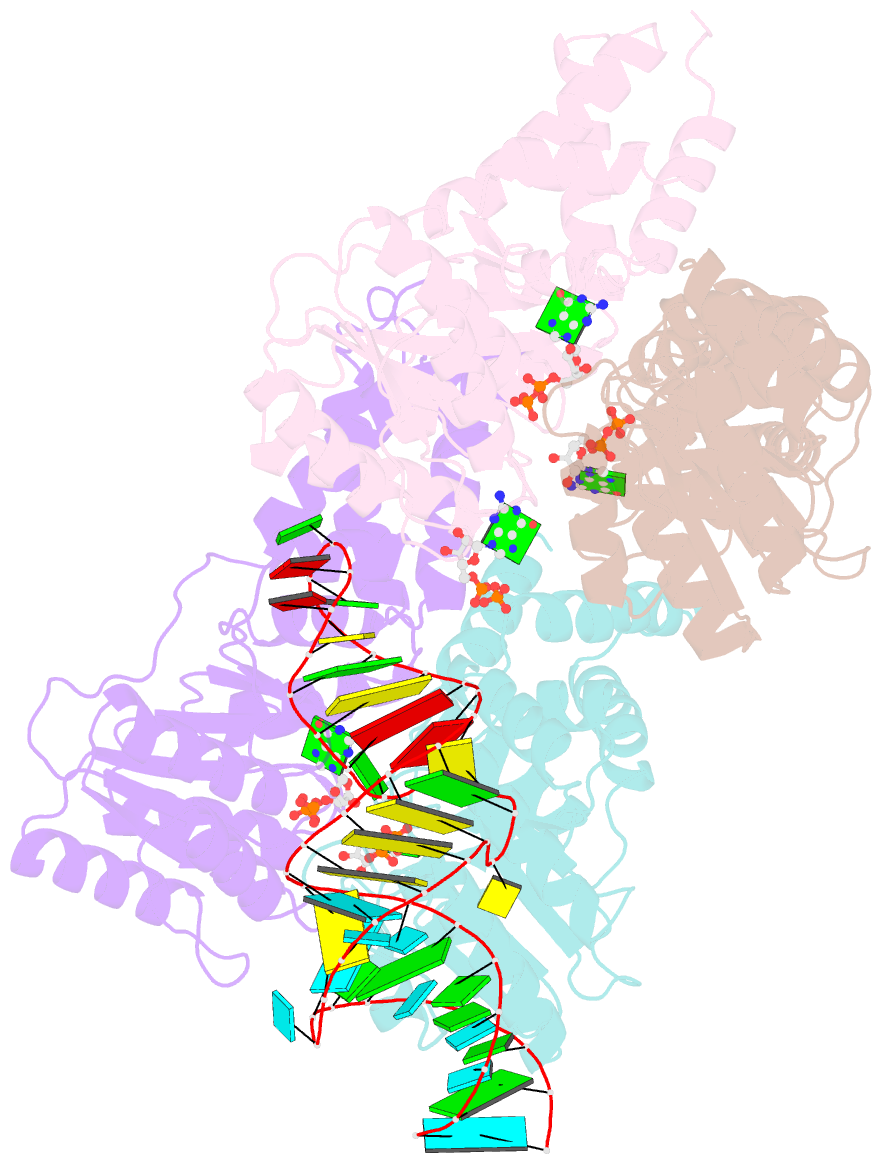
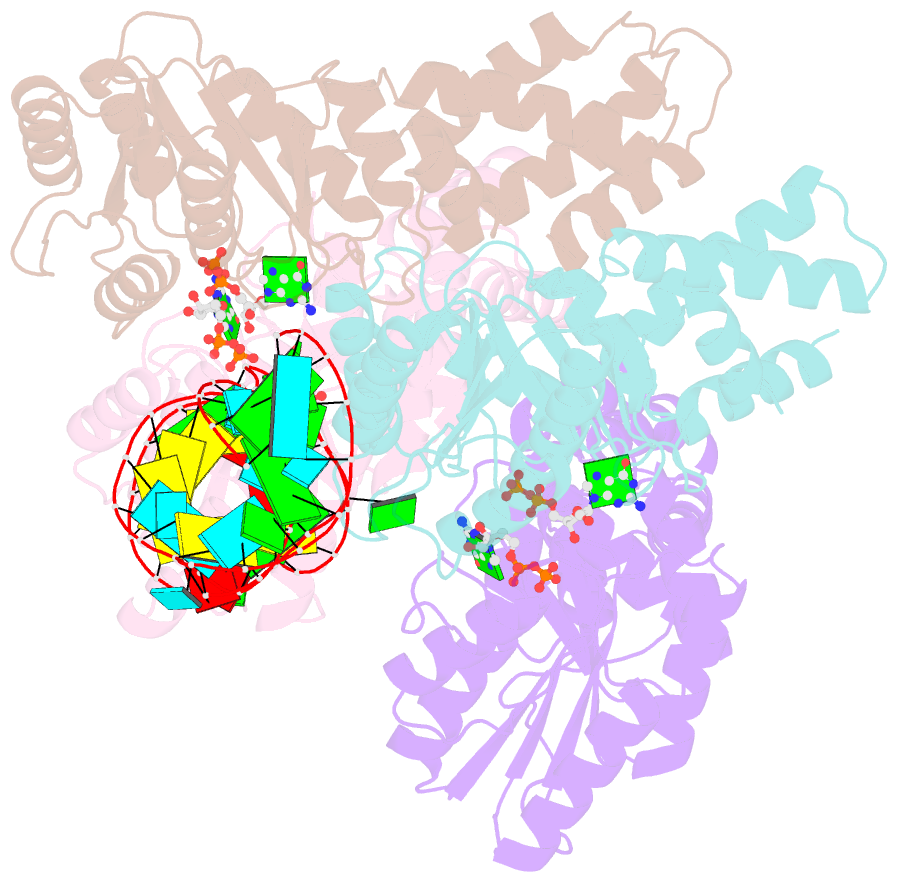
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4c7o; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- nuclear protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.6 Å)
- Summary
- The structural basis of ftsy recruitment and gtpase activation by srp RNA
- Reference
- Voigts-Hoffmann F, Schmitz N, Shen K, Shan SO, Ataide SF, Ban N (2013): "The Structural Basis of Ftsy Recruitment and Gtpase Activation by Srp RNA." Mol.Cell, 52, 643. doi: 10.1016/J.MOLCEL.2013.10.005.
- Abstract
- The universally conserved signal recognition particle (SRP) system mediates the targeting of membrane proteins to the translocon in a multistep process controlled by GTP hydrolysis. Here we present the 2.6 Å crystal structure of the GTPase domains of the E. coli SRP protein (Ffh) and its receptor (FtsY) in complex with the tetraloop and the distal region of SRP-RNA, trapped in the activated state in presence of GDP:AlF4. The structure reveals the atomic details of FtsY recruitment and, together with biochemical experiments, pinpoints G83 as the key RNA residue that stimulates GTP hydrolysis. Insertion of G83 into the FtsY active site orients a single glutamate residue provided by Ffh (E277), triggering GTP hydrolysis and complex disassembly at the end of the targeting cycle. The complete conservation of the key residues of the SRP-RNA and the SRP protein implies that the suggested chemical mechanism of GTPase activation is applicable across all kingdoms.