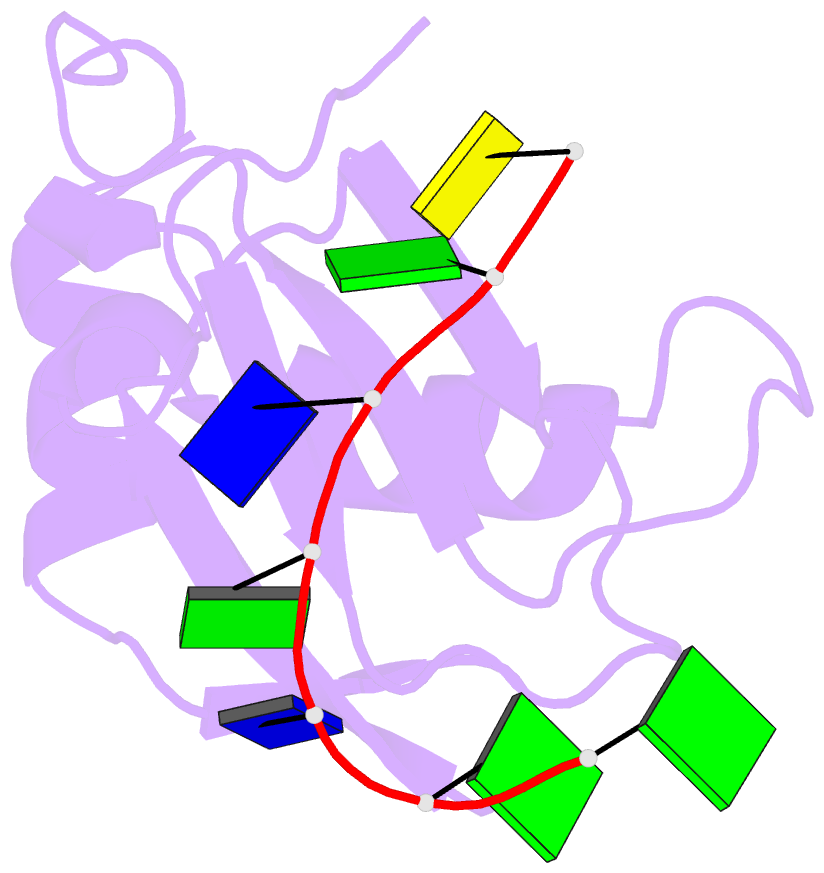
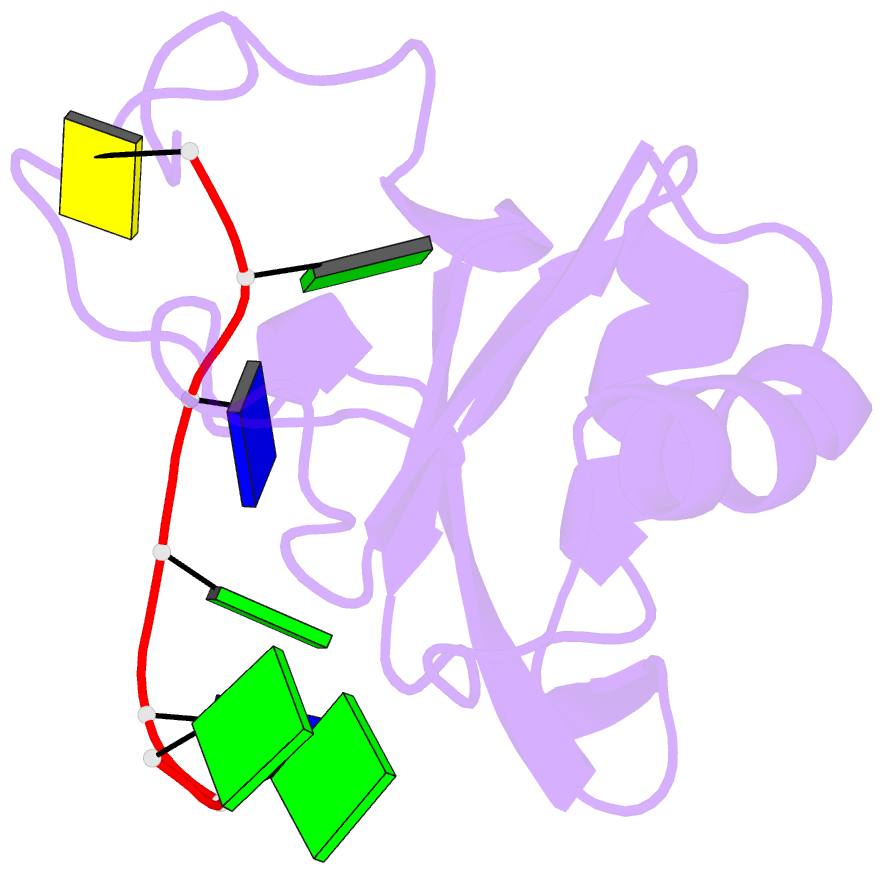
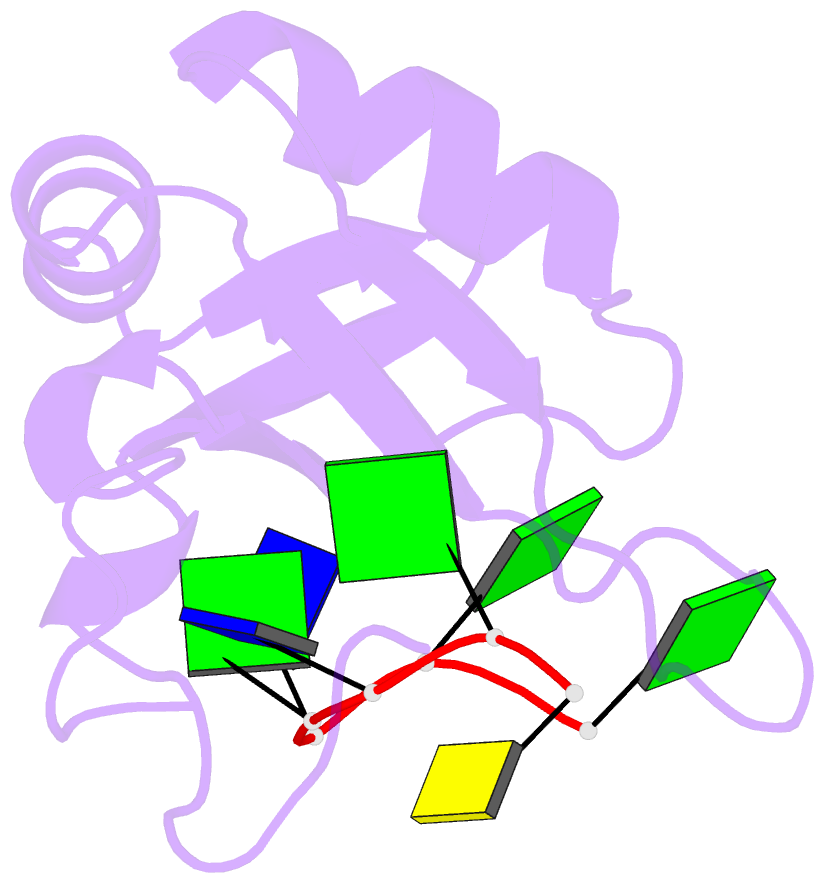
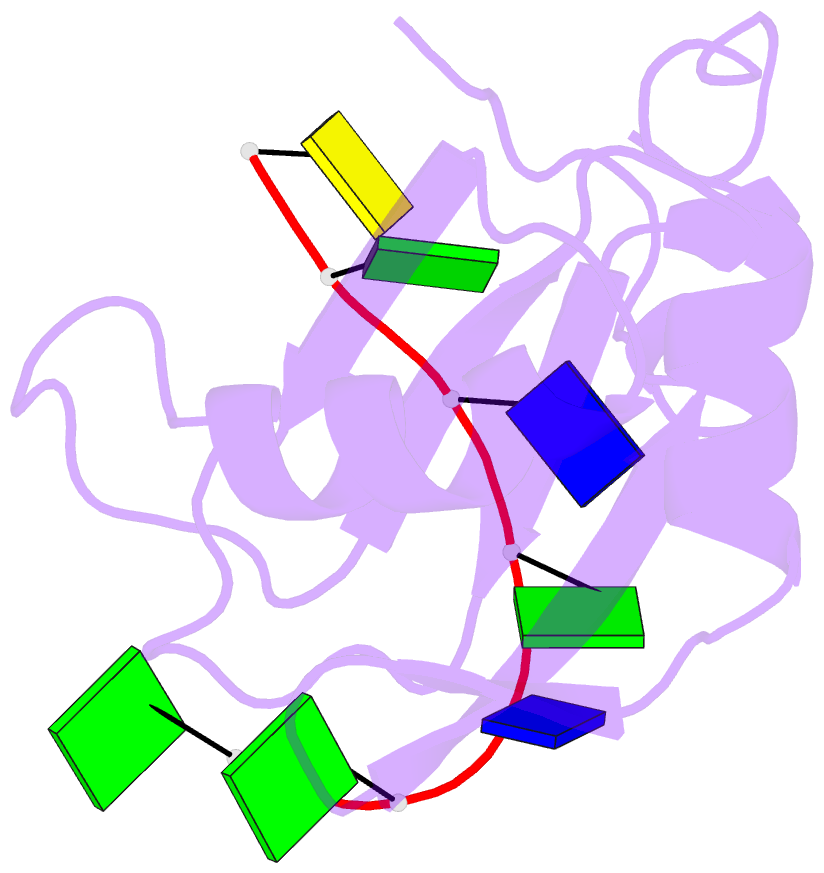
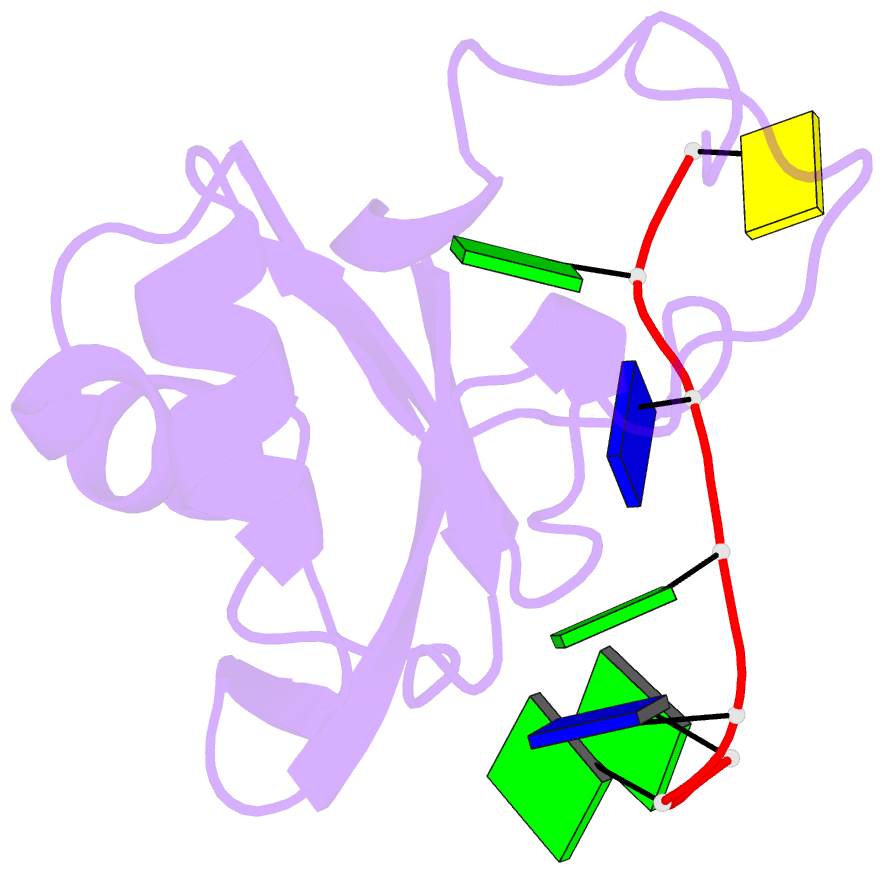
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4ch1; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- Rrm domain from c. elegans sup-12 bound to ggtgtgc DNA
- Reference
- Amrane S, Rebora K, Zniber I, Dupuy D, Mackereth CD (2014): "Backbone-Independent Nucleic Acid Binding by Splicing Factor Sup-12 Reveals Key Aspects of Molecular Recognition." Nat.Commun., 5, 4595. doi: 10.1038/NCOMMS5595.
- Abstract
- Cellular differentiation is frequently accompanied by alternative splicing, enabled by the expression of tissue-specific factors which bind to pre-mRNAs and regulate exon choice. During Caenorhabditis elegans development, muscle-specific expression of the splicing factor SUP-12, together with a member of the Fox-1 family of splicing proteins, generates a functionally distinct isoform of the fibroblast growth factor receptor EGL-15. Using a combination of NMR spectroscopy and isothermal titration calorimetry, we determined the mode of nucleic acid binding by the RNA recognition motif domain of SUP-12. The calculated structures provide the first atomic details of RNA and DNA binding by the family of proteins that include SUP-12, RBM24, RBM38/RNPC1, SEB-4 and XSeb4R. This information was further used to design strategic mutations to probe the interaction with ASD-1 and to quantitatively perturb splicing in vivo.