Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4csf; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.598 Å)
- Summary
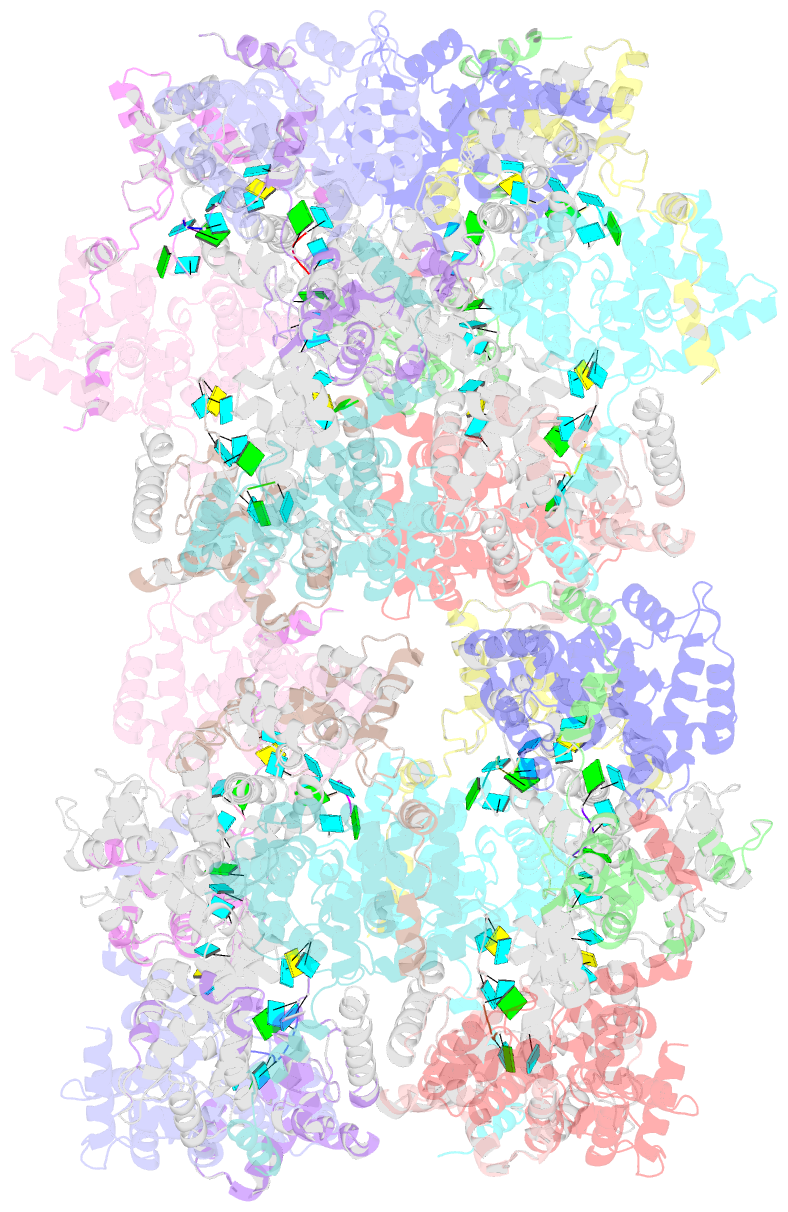
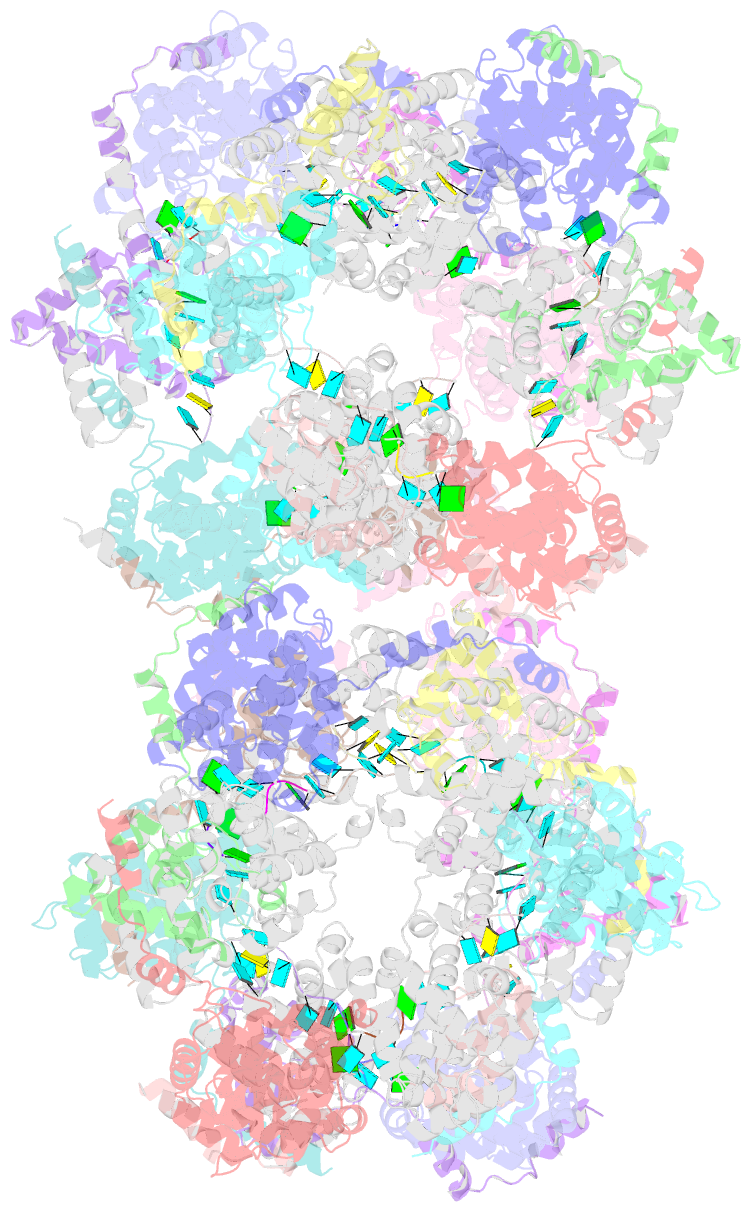
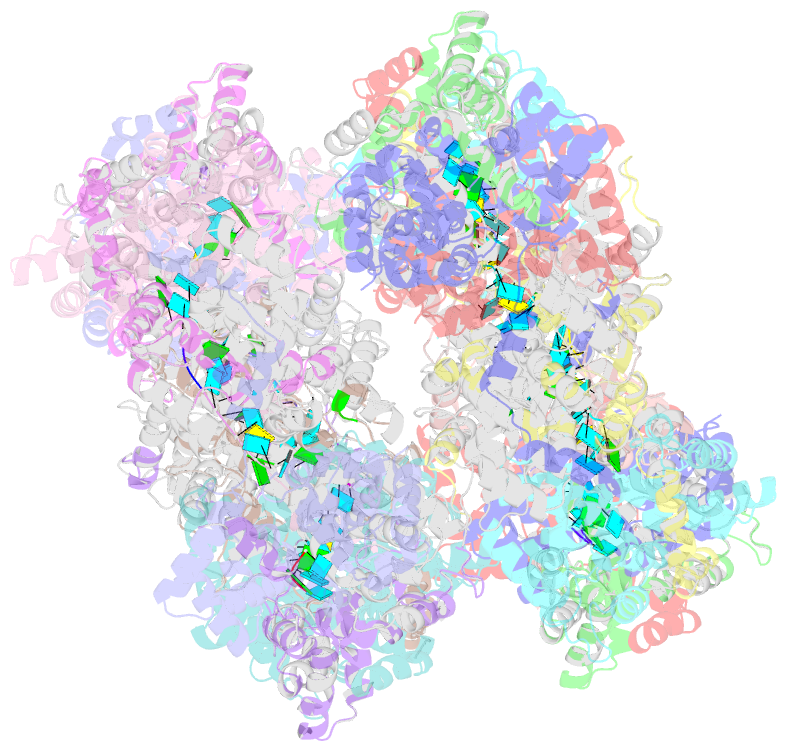
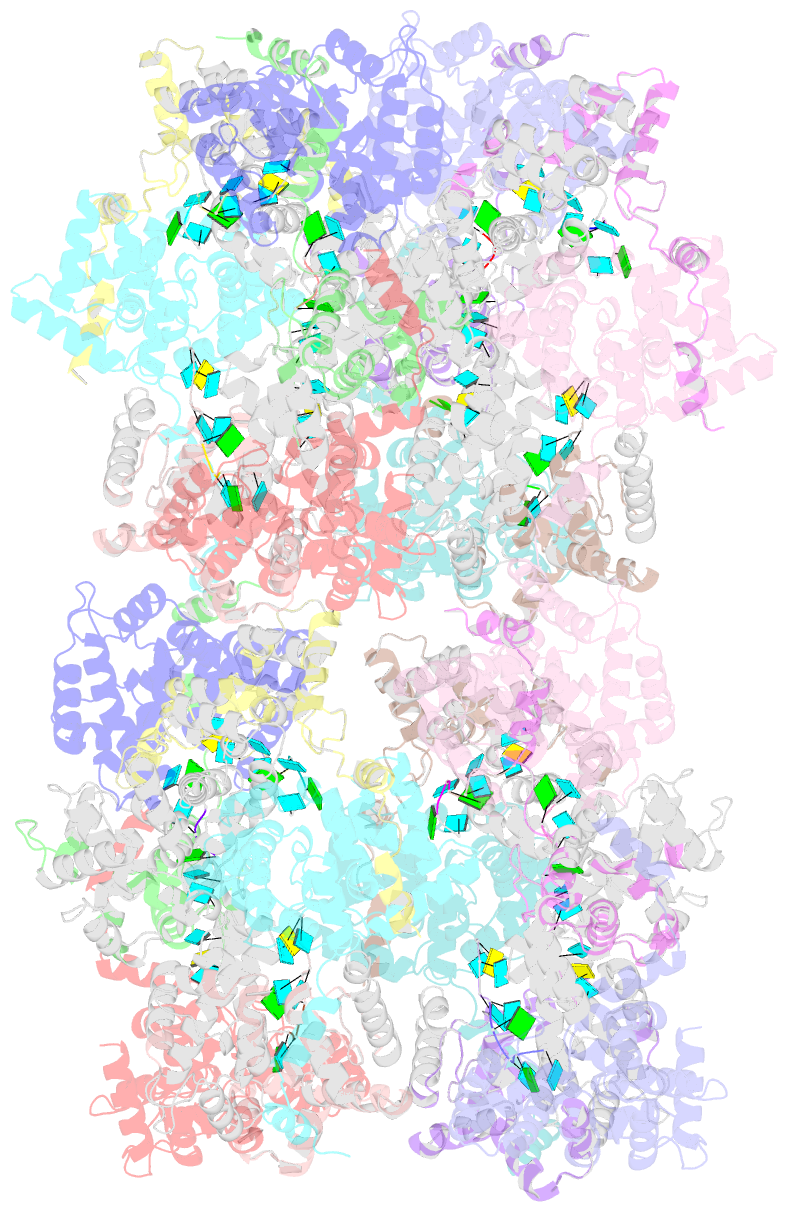
- Structural insights into toscana virus RNA encapsidation
- Reference
- Olal D, Dick A, Woods VL, Liu T, Li S, Devignot S, Weber F, Saphire EO, Daumke O (2014): "Structural Insights Into RNA Encapsidation and Helical Assembly of the Toscana Virus Nucleoprotein." Nucleic Acids Res., 42, 6025. doi: 10.1093/NAR/GKU229.
- Abstract
- Toscana virus is an emerging bunyavirus in Mediterranean Europe where it accounts for 80% of pediatric meningitis cases during the summer. The negative-strand ribonucleic acid (RNA) genome of the virus is wrapped around the virally encoded nucleoprotein N to form the ribonucleoprotein complex (RNP). We determined crystal structures of hexameric N alone (apo) and in complex with a nonameric single-stranded RNA. RNA is sequestered in a sequence-independent fashion in a deep groove inside the hexamer. At the junction between two adjacent copies of Ns, RNA binding induced an inter-subunit rotation, which opened the RNA-binding tunnel and created a new assembly interface at the outside of the hexamer. Based on these findings, we suggest a structural model for how binding of RNA to N promotes the formation of helical RNPs, which are a characteristic hallmark of many negative-strand RNA viruses.