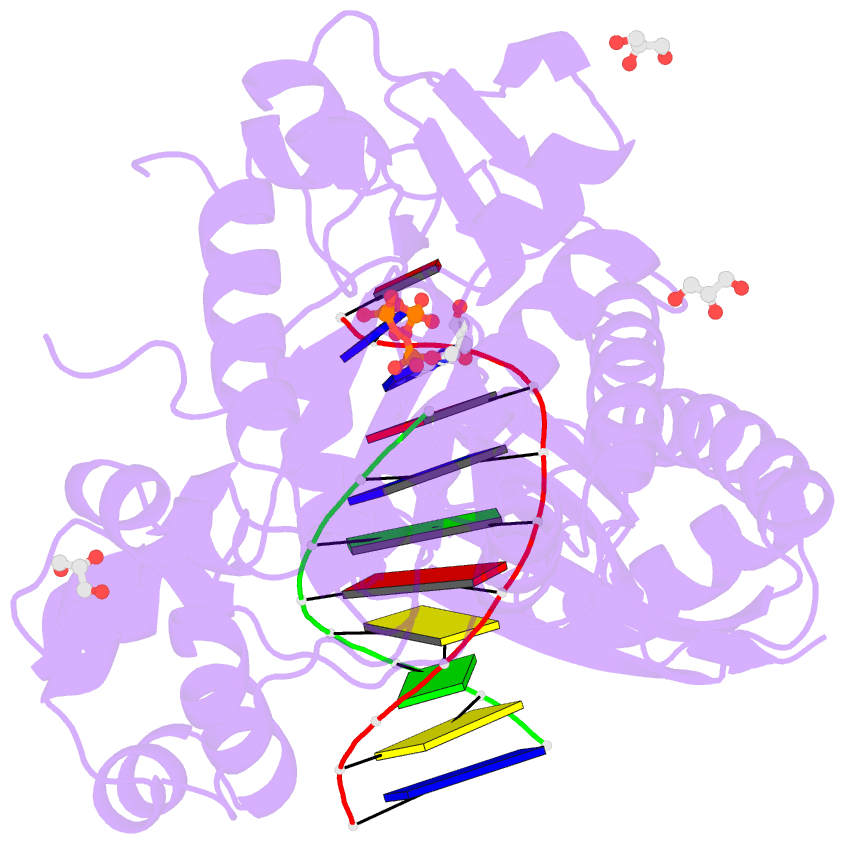
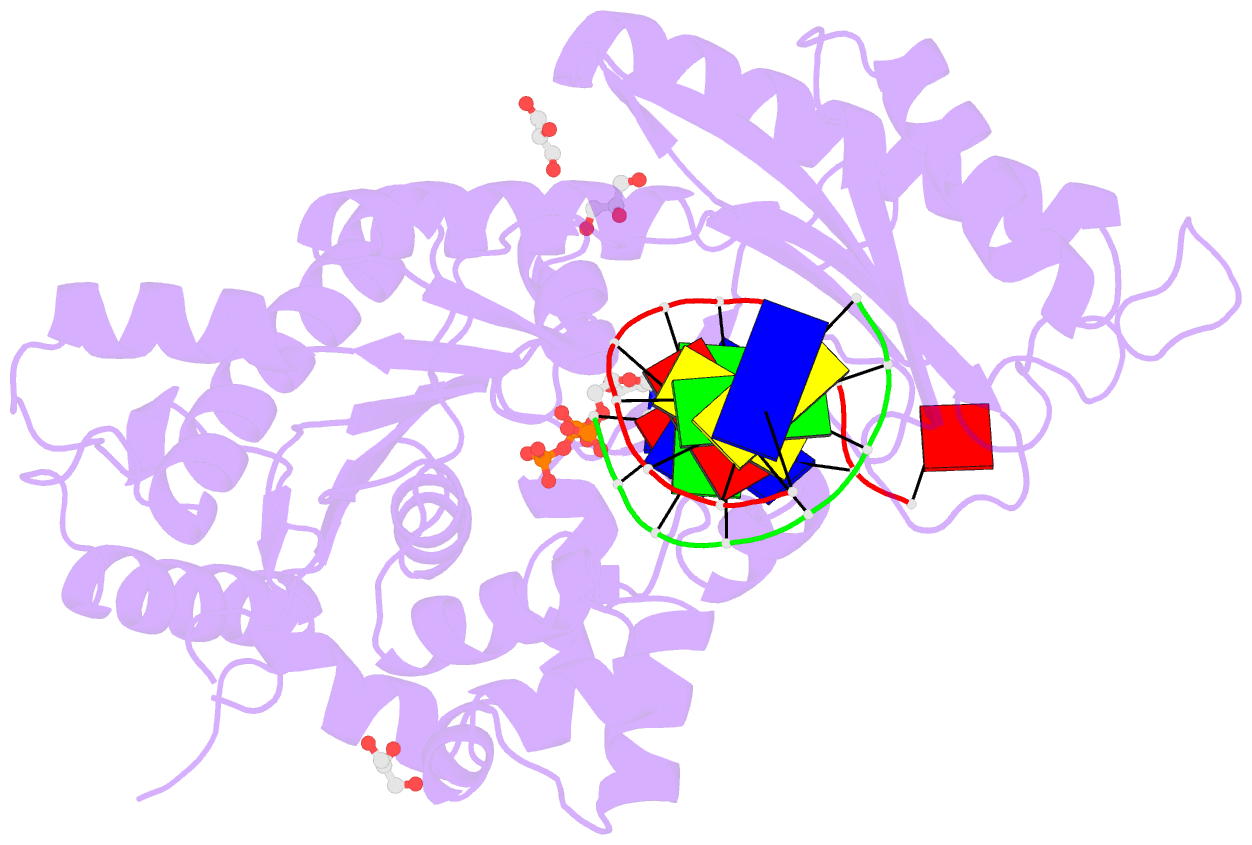
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4ecq; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.5 Å)
- Summary
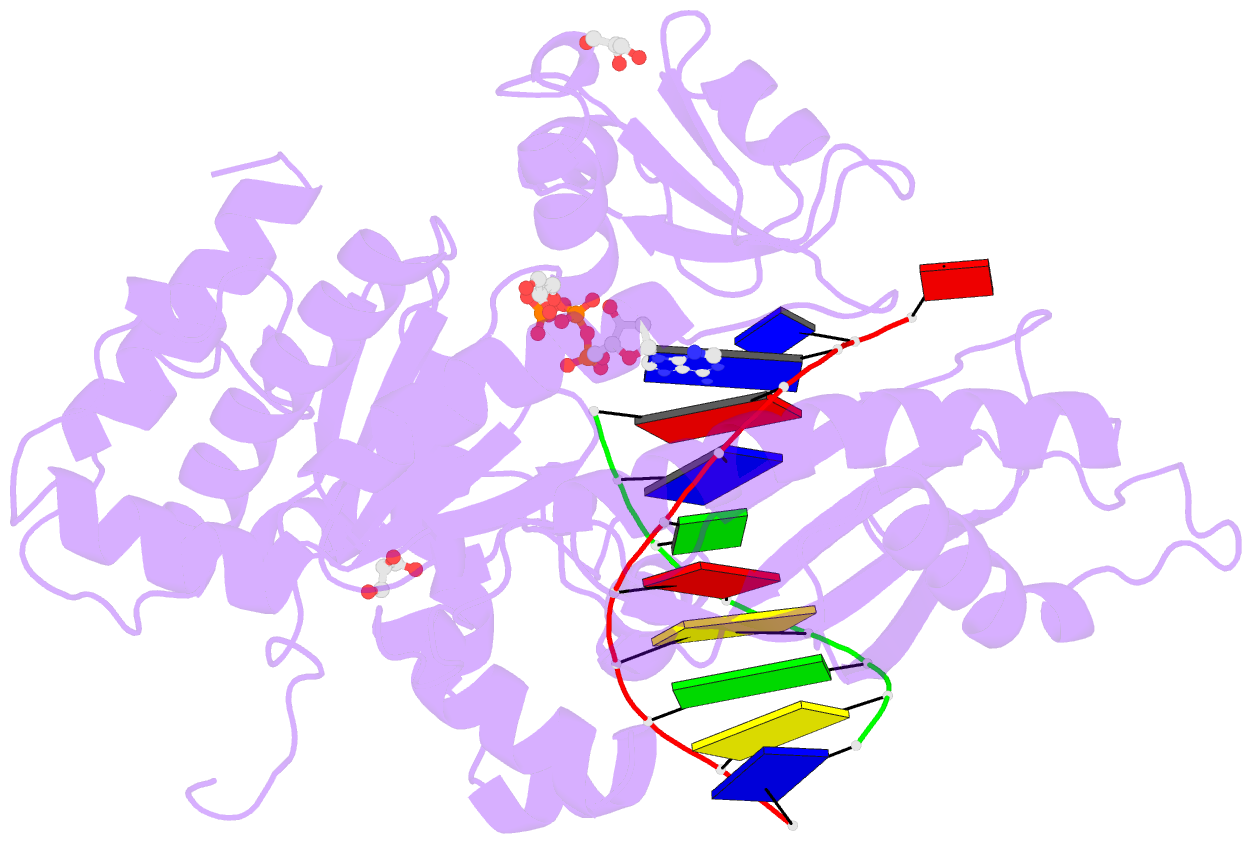
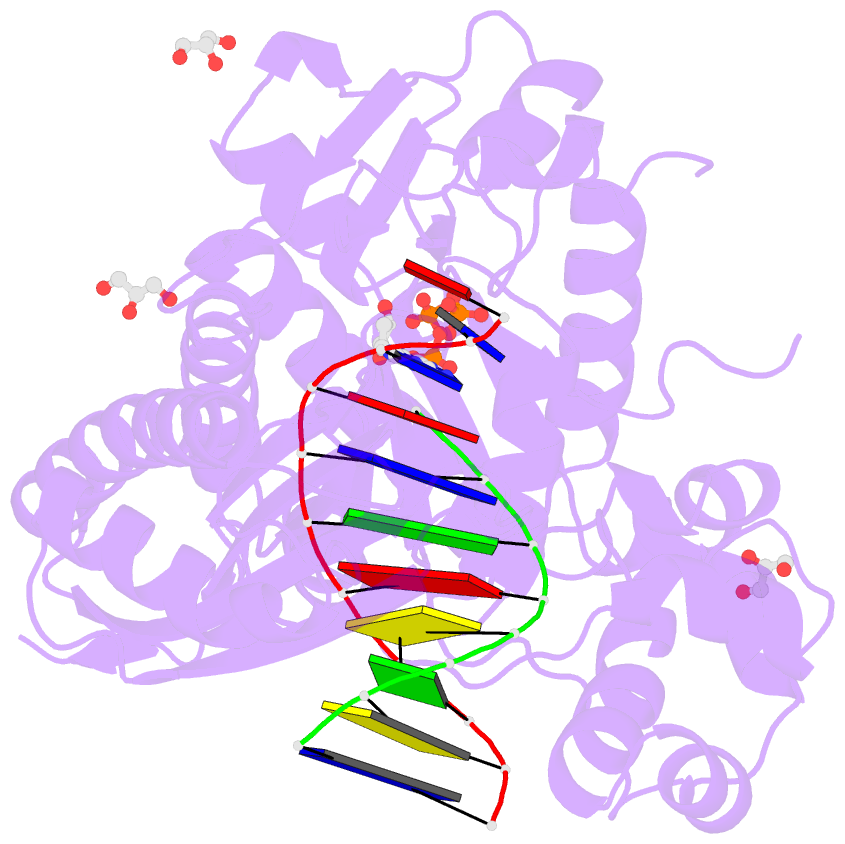
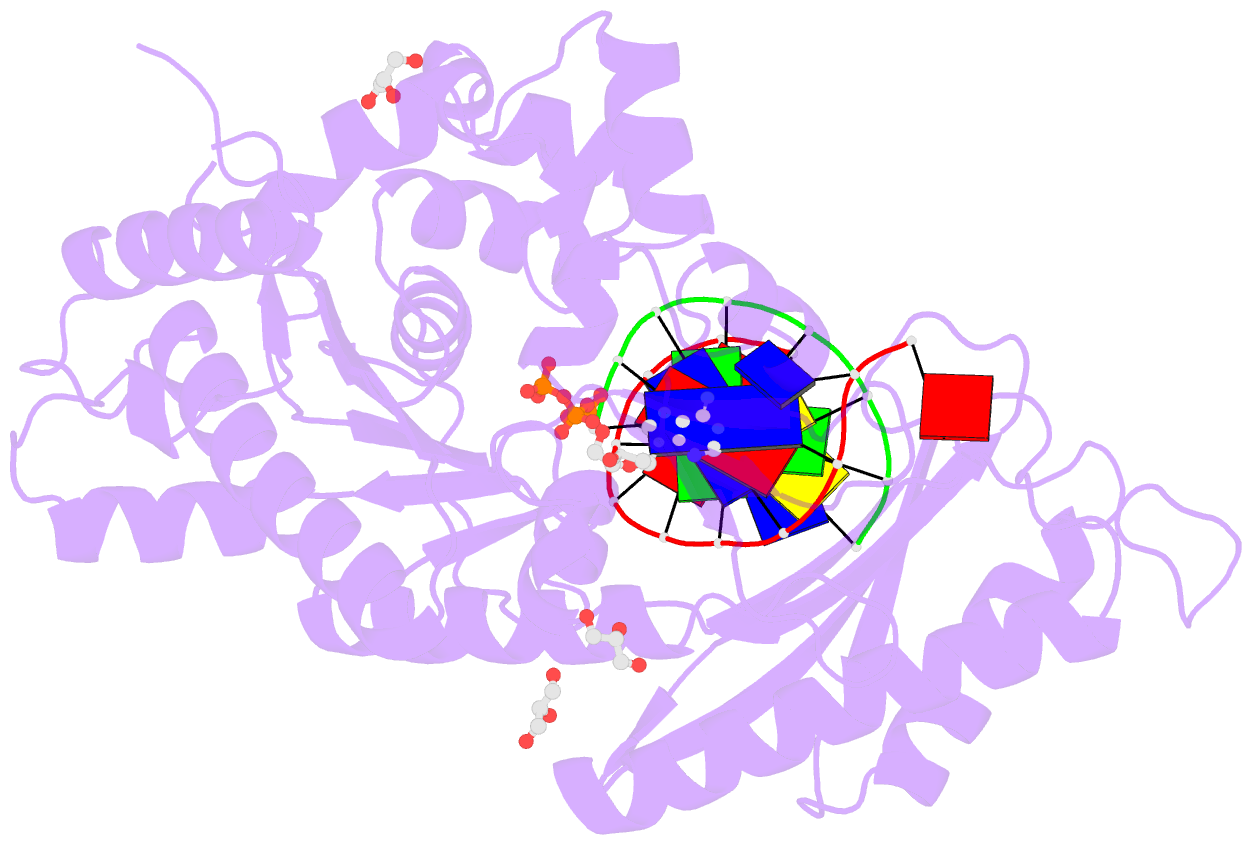
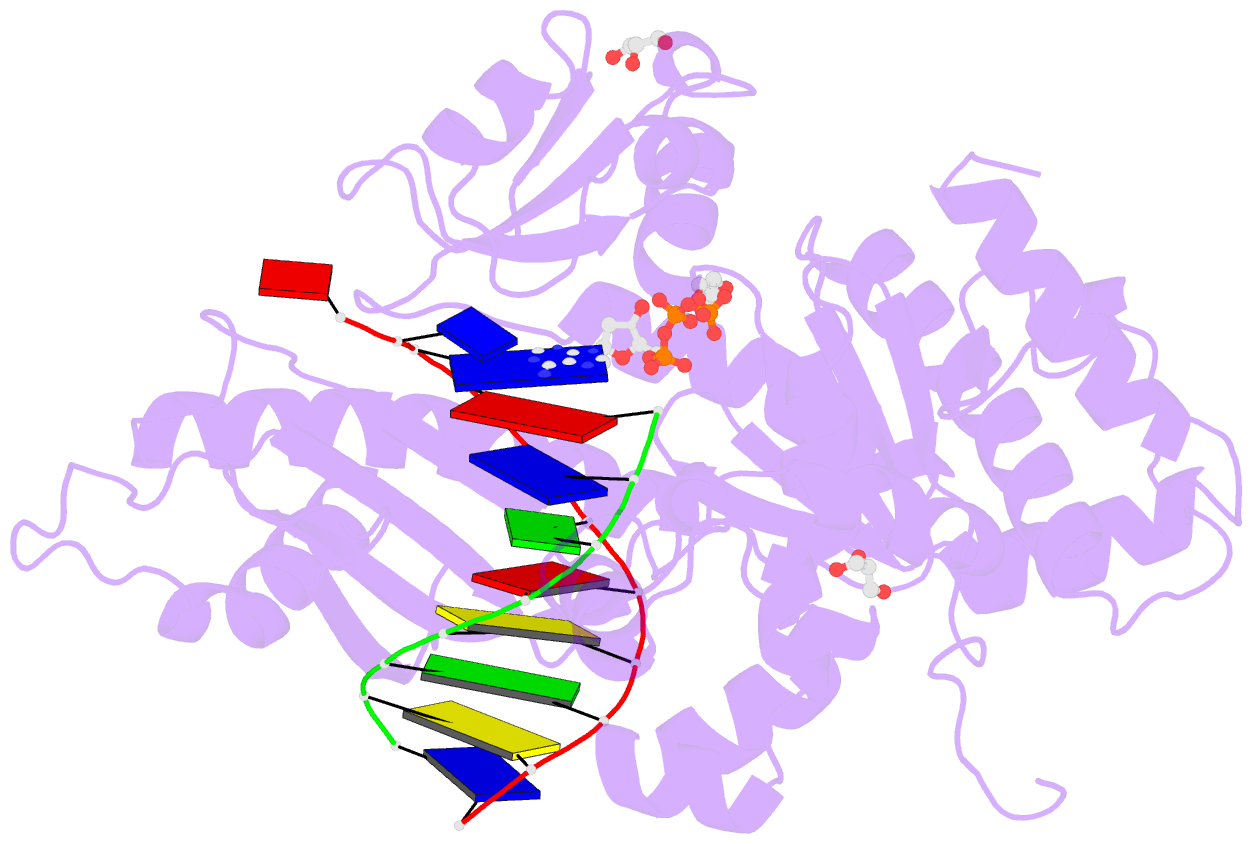
- Human DNA polymerase eta- DNA ternary complex: at crystal at ph6.8(k+ mes) with 1 ca2+ ion
- Reference
- Nakamura T, Zhao Y, Yamagata Y, Hua YJ, Yang W (2012): "Watching DNA polymerase eta make a phosphodiester bond." Nature, 487, 196-201. doi: 10.1038/nature11181.
- Abstract
- DNA synthesis has been extensively studied, but the chemical reaction itself has not been visualized. Here we follow the course of phosphodiester bond formation using time-resolved X-ray crystallography. Native human DNA polymerase η, DNA and dATP were co-crystallized at pH 6.0 without Mg(2+). The polymerization reaction was initiated by exposing crystals to 1 mM Mg(2+) at pH 7.0, and stopped by freezing at desired time points for structural analysis. The substrates and two Mg(2+) ions are aligned within 40 s, but the bond formation is not evident until 80 s. From 80 to 300 s structures show a mixture of decreasing substrate and increasing product of the nucleotidyl-transfer reaction. Transient electron densities indicate that deprotonation and an accompanying C2'-endo to C3'-endo conversion of the nucleophile 3'-OH are rate limiting. A third Mg(2+) ion, which arrives with the new bond and stabilizes the intermediate state, may be an unappreciated feature of the two-metal-ion mechanism.