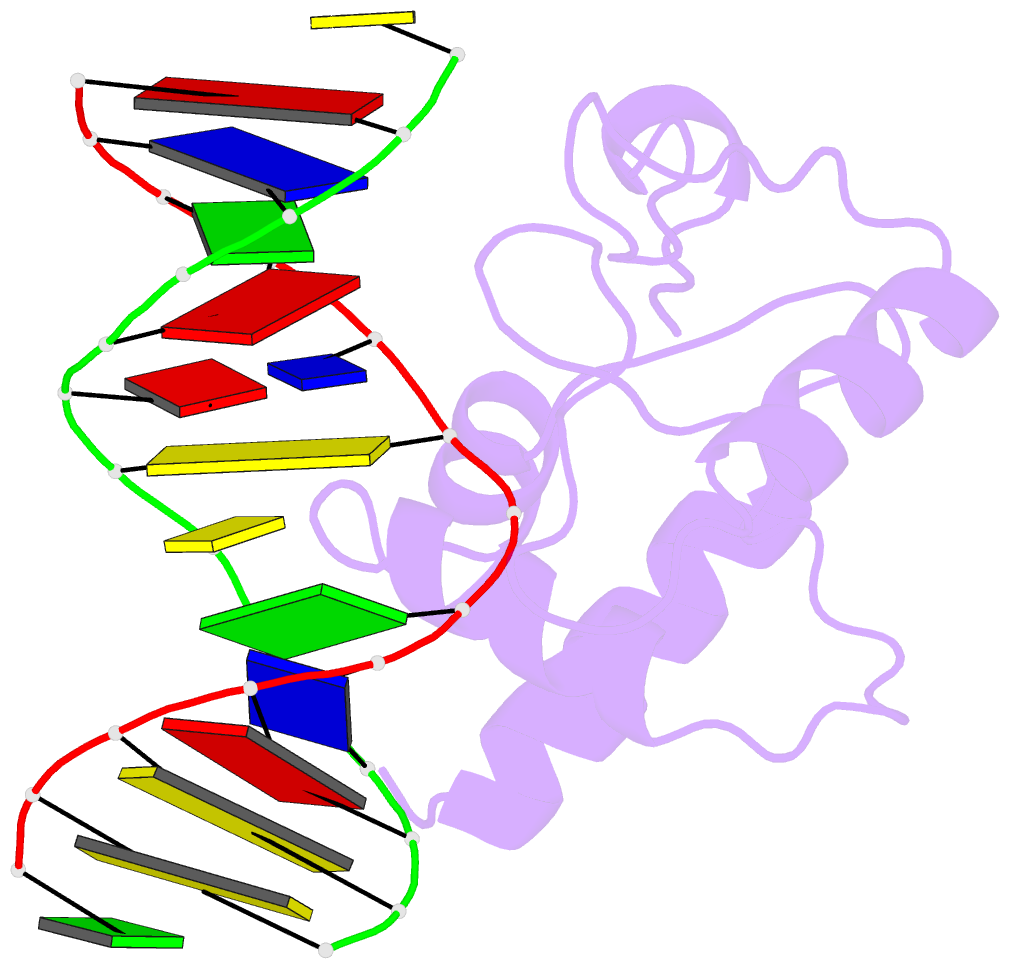
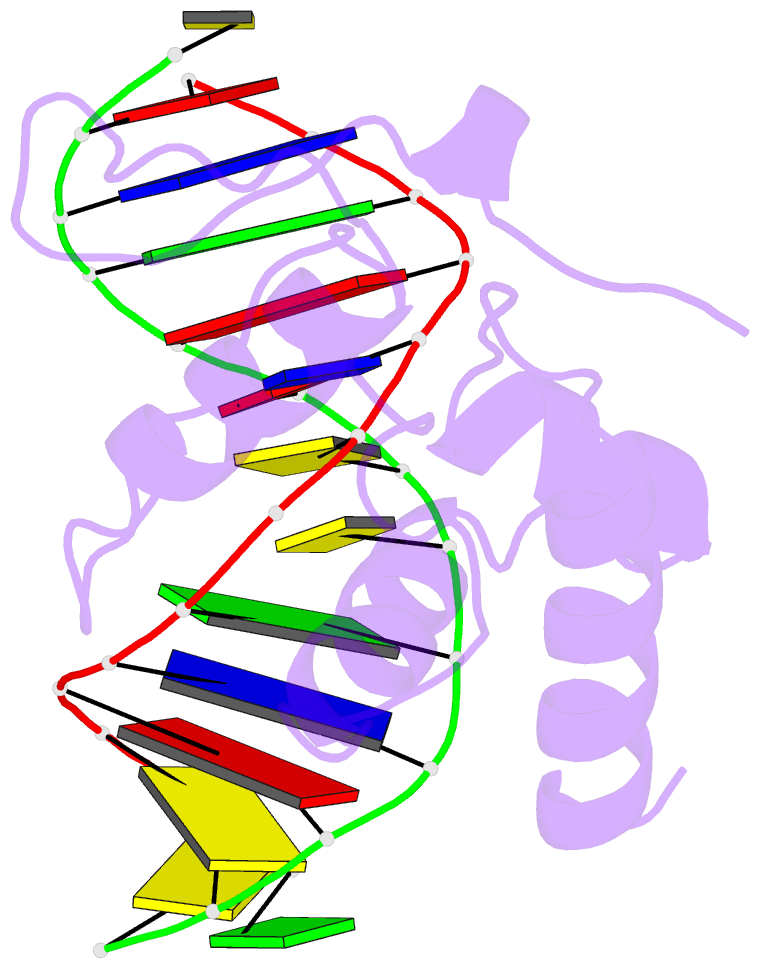
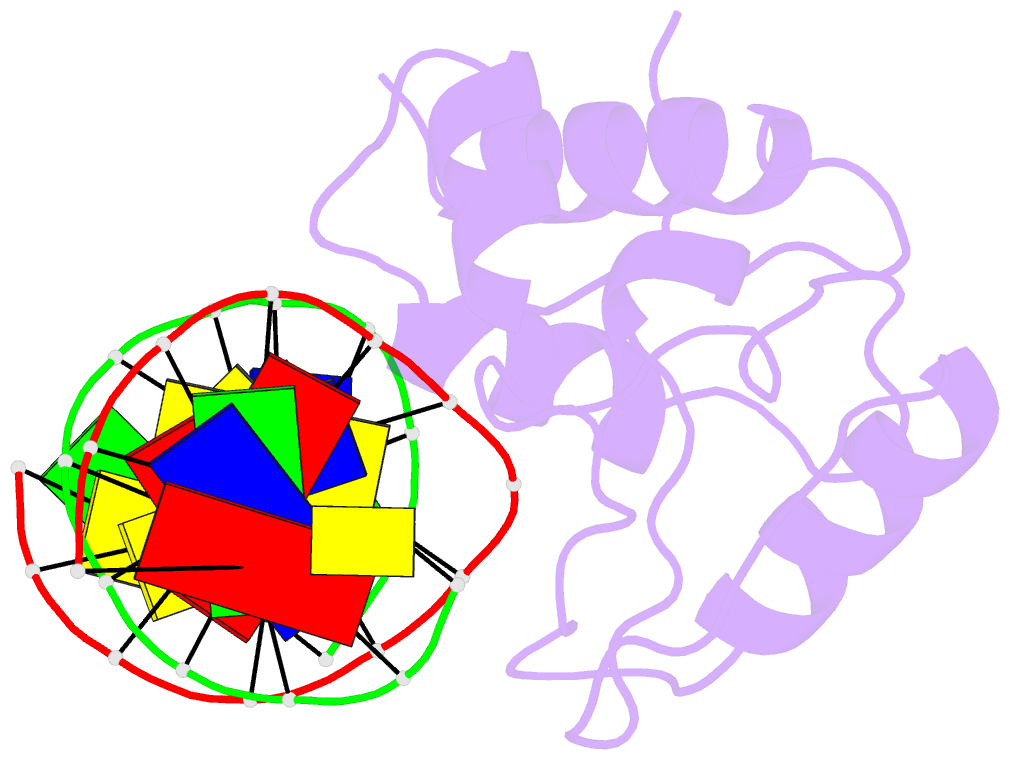
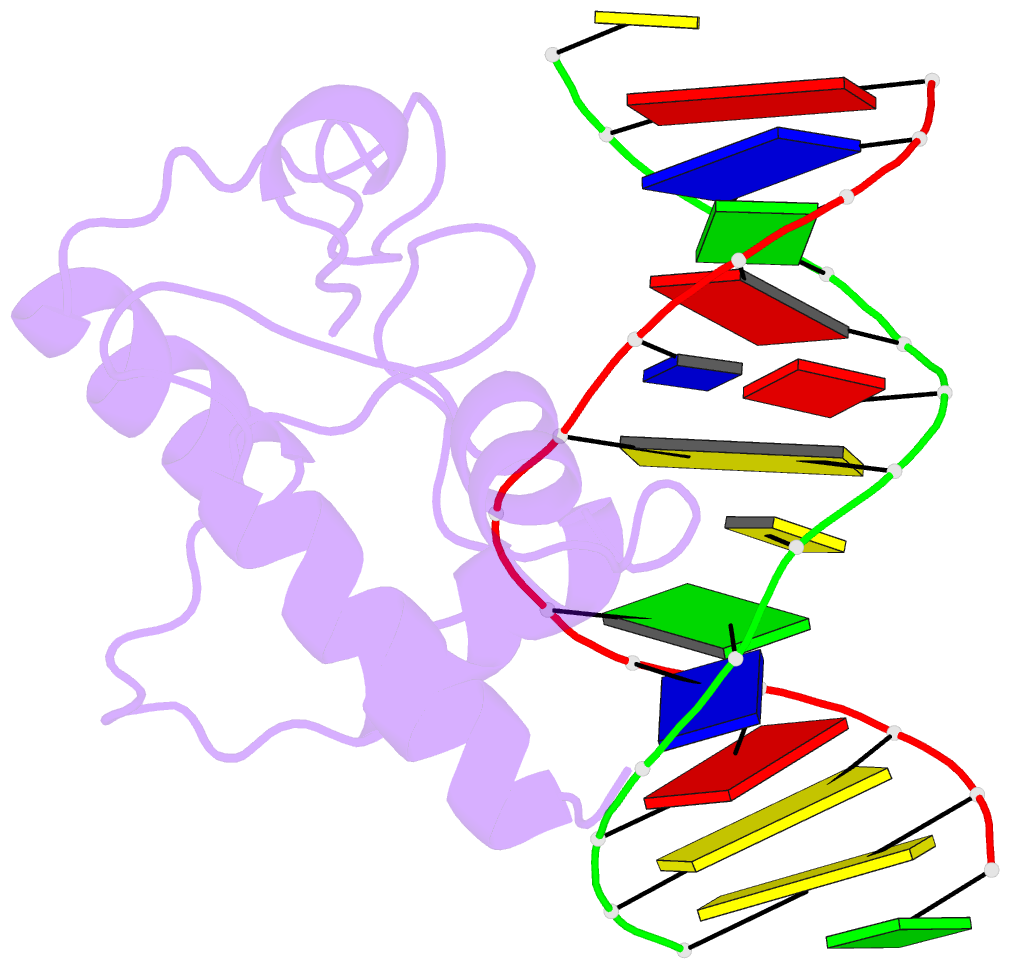
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4enm; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.84 Å)
- Summary
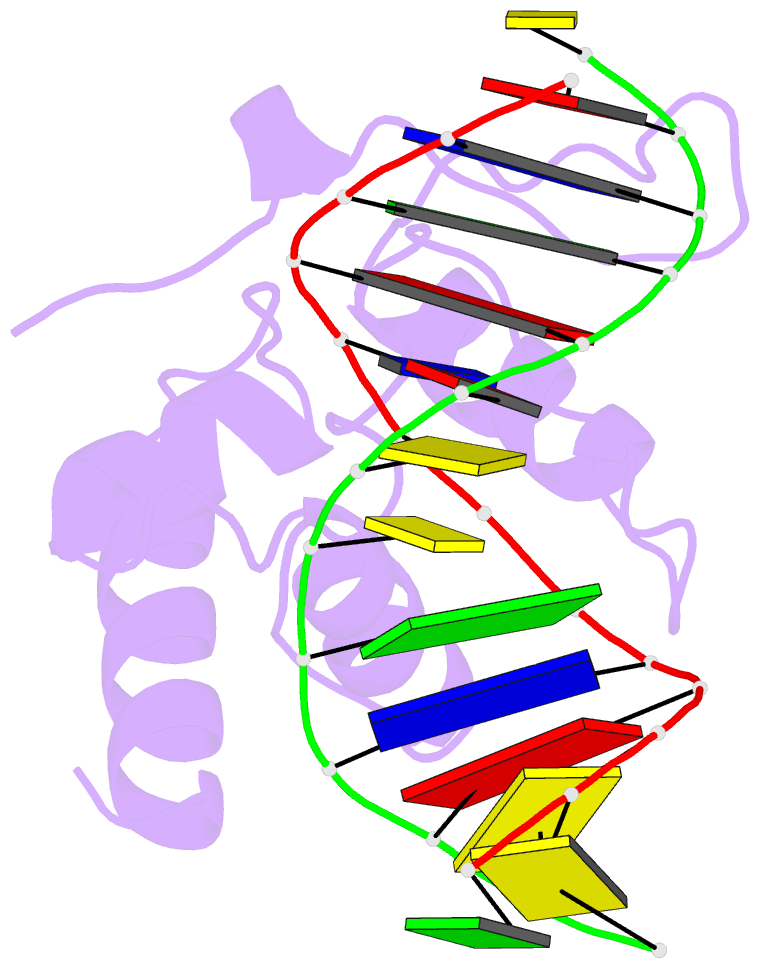
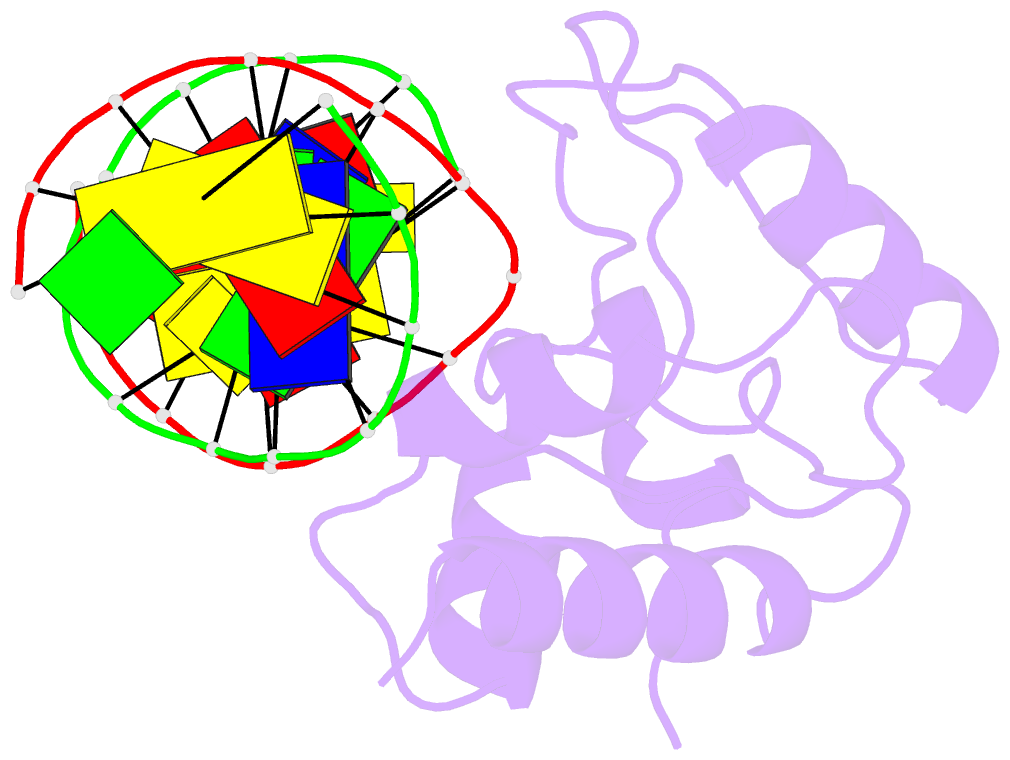
- Crystal structure of s. pombe atl1 in complex with damaged DNA containing o6-benzylguanine
- Reference
- Latypov VF, Tubbs JL, Watson AJ, Marriott AS, McGown G, Thorncroft M, Wilkinson OJ, Senthong P, Butt A, Arvai AS, Millington CL, Povey AC, Williams DM, Santibanez-Koref MF, Tainer JA, Margison GP (2012): "Atl1 Regulates Choice between Global Genome and Transcription-Coupled Repair of O(6)-Alkylguanines." Mol.Cell, 47, 50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.04.028.
- Abstract
- Nucleotide excision repair (NER) has long been known to remove DNA lesions induced by chemical carcinogens, and the molecular mechanism has been partially elucidated. Here we demonstrate that in Schizosaccharomyces pombe a DNA recognition protein, alkyltransferase-like 1 (Atl1), can play a pivotal role in selecting a specific NER pathway, depending on the nature of the DNA modification. The relative ease of dissociation of Atl1 from DNA containing small O(6)-alkylguanines allows accurate completion of global genome repair (GGR), whereas strong Atl1 binding to bulky O(6)-alkylguanines blocks GGR, stalls the transcription machinery, and diverts the damage to transcription-coupled repair. Our findings redraw the initial stages of the NER process in those organisms that express an alkyltransferase-like gene and raise the question of whether or not O(6)-alkylguanine lesions that are poor substrates for the alkyltransferase proteins in higher eukaryotes might, by analogy, signal such lesions for repair by NER.