Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4erd; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.589 Å)
- Summary
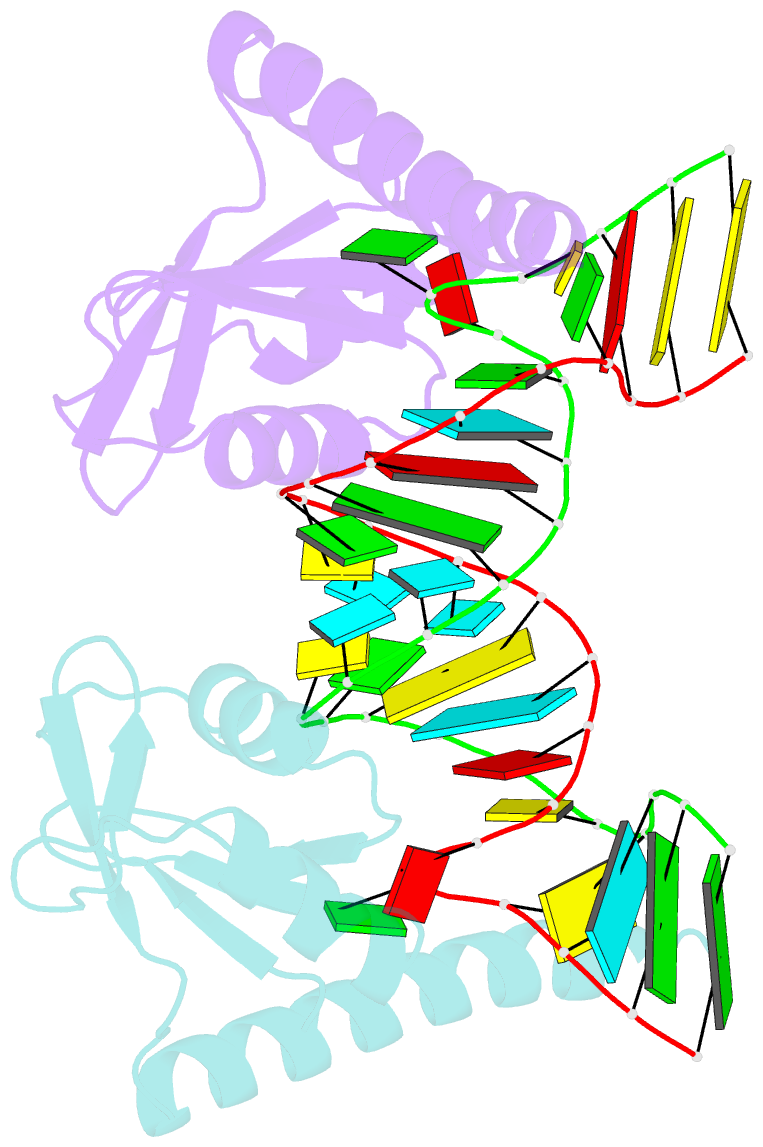
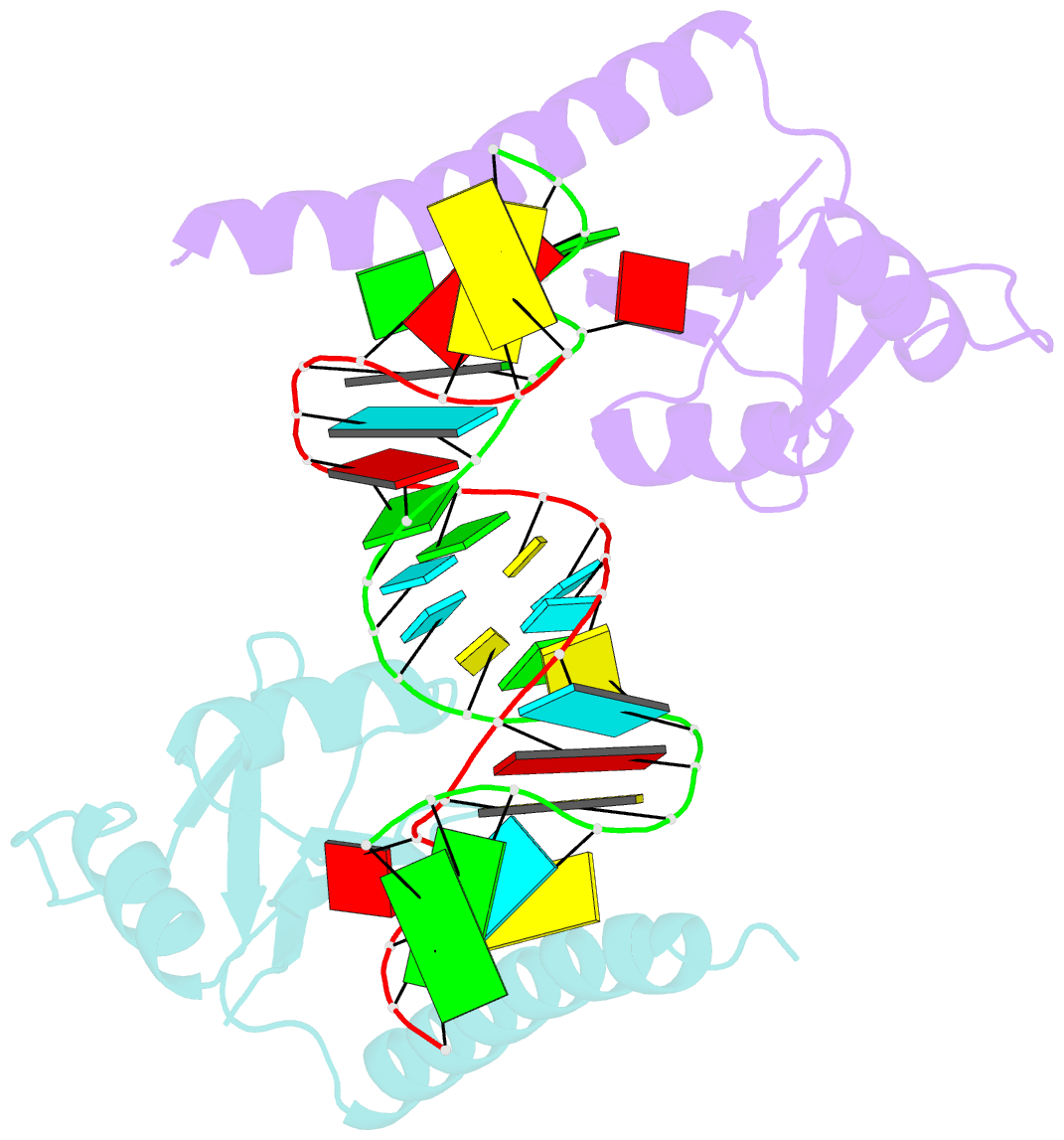
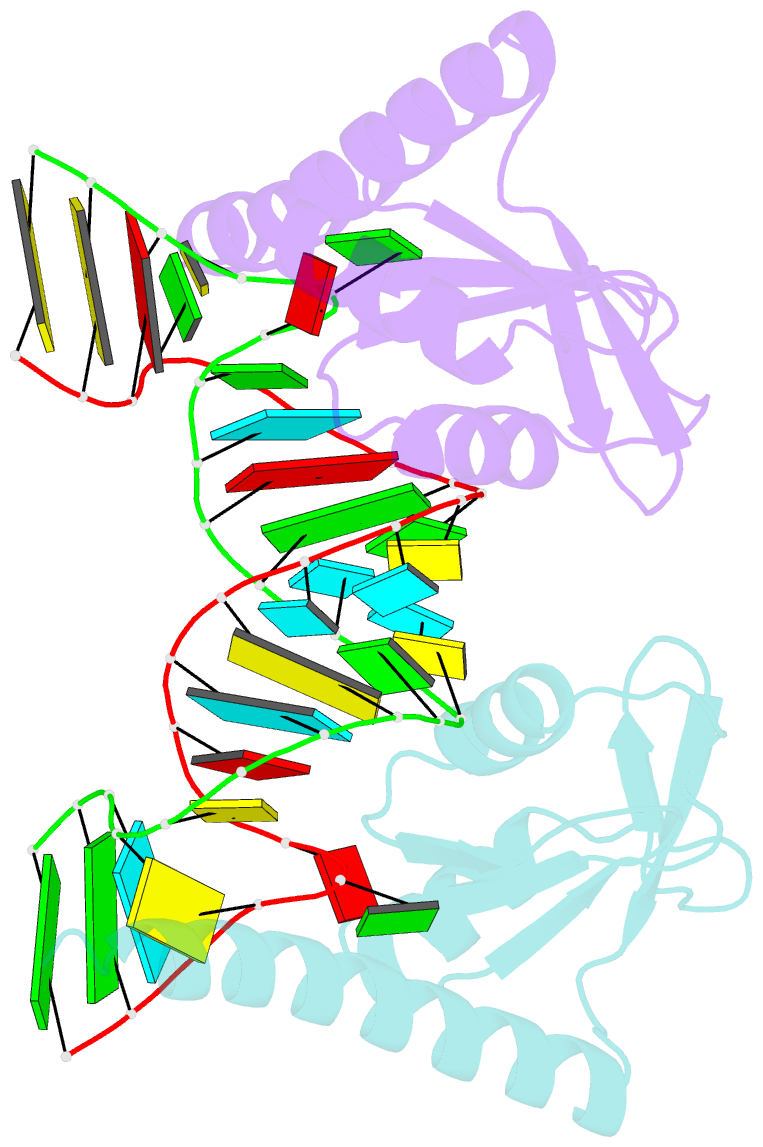
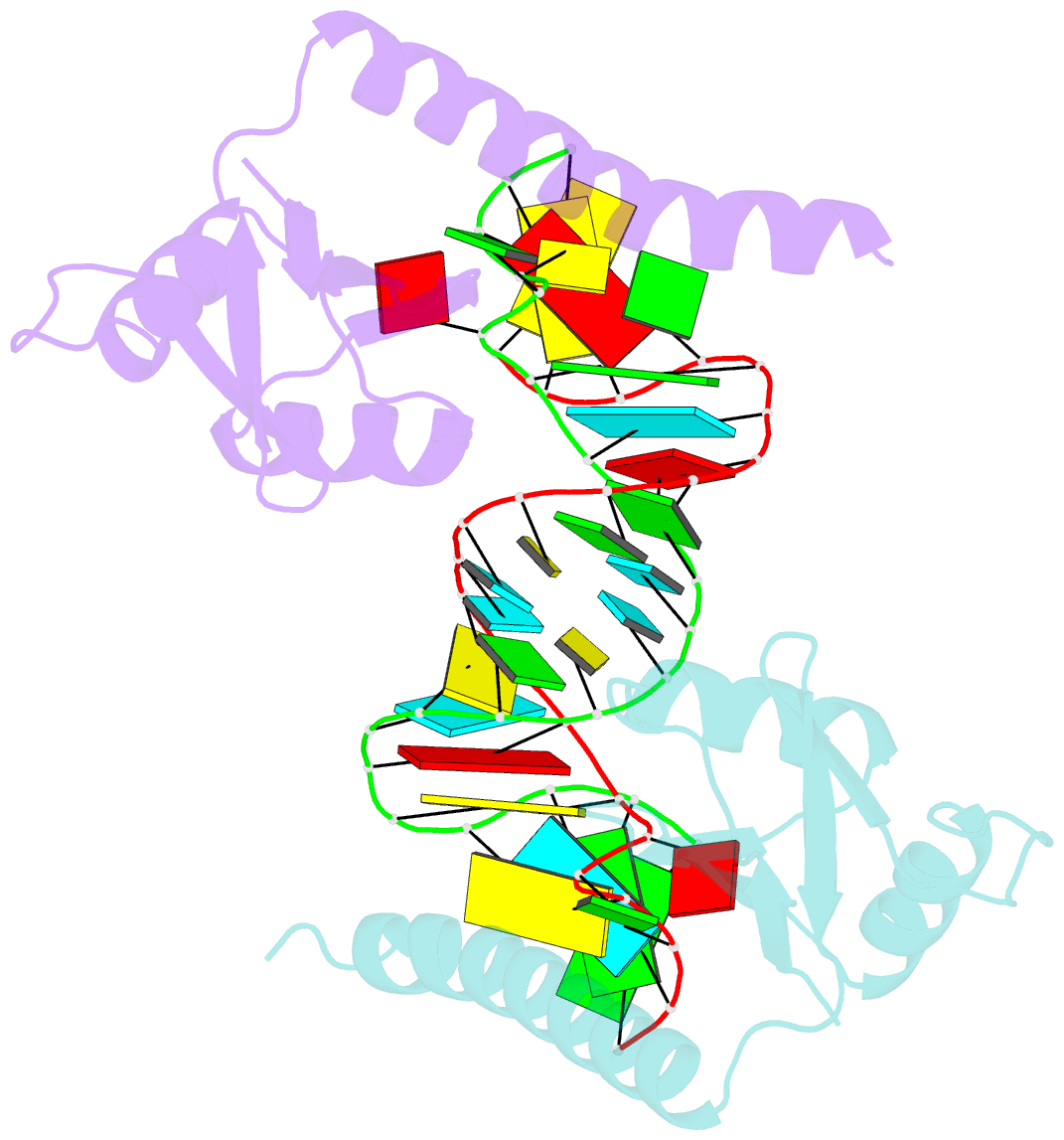
- Crystal structure of the c-terminal domain of tetrahymena telomerase protein p65 in complex with stem iv of telomerase RNA
- Reference
- Singh M, Wang Z, Koo BK, Patel A, Cascio D, Collins K, Feigon J (2012): "Structural Basis for Telomerase RNA Recognition and RNP Assembly by the Holoenzyme La Family Protein p65." Mol.Cell, 47, 16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.018.
- Abstract
- Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein complex essential for maintenance of telomere DNA at linear chromosome ends. The catalytic core of Tetrahymena telomerase comprises a ternary complex of telomerase RNA (TER), telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), and the essential La family protein p65. NMR and crystal structures of p65 C-terminal domain and its complex with stem IV of TER reveal that RNA recognition is achieved by a combination of single- and double-stranded RNA binding, which induces a 105° bend in TER. The domain is a cryptic, atypical RNA recognition motif with a disordered C-terminal extension that forms an α helix in the complex necessary for hierarchical assembly of TERT with p65-TER. This work provides the first structural insight into biogenesis and assembly of TER with a telomerase-specific protein. Additionally, our studies define a structurally homologous domain (xRRM) in genuine La and LARP7 proteins and suggest a general mode of RNA binding for biogenesis of their diverse RNA targets.