Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4fm9; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- isomerase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.901 Å)
- Summary
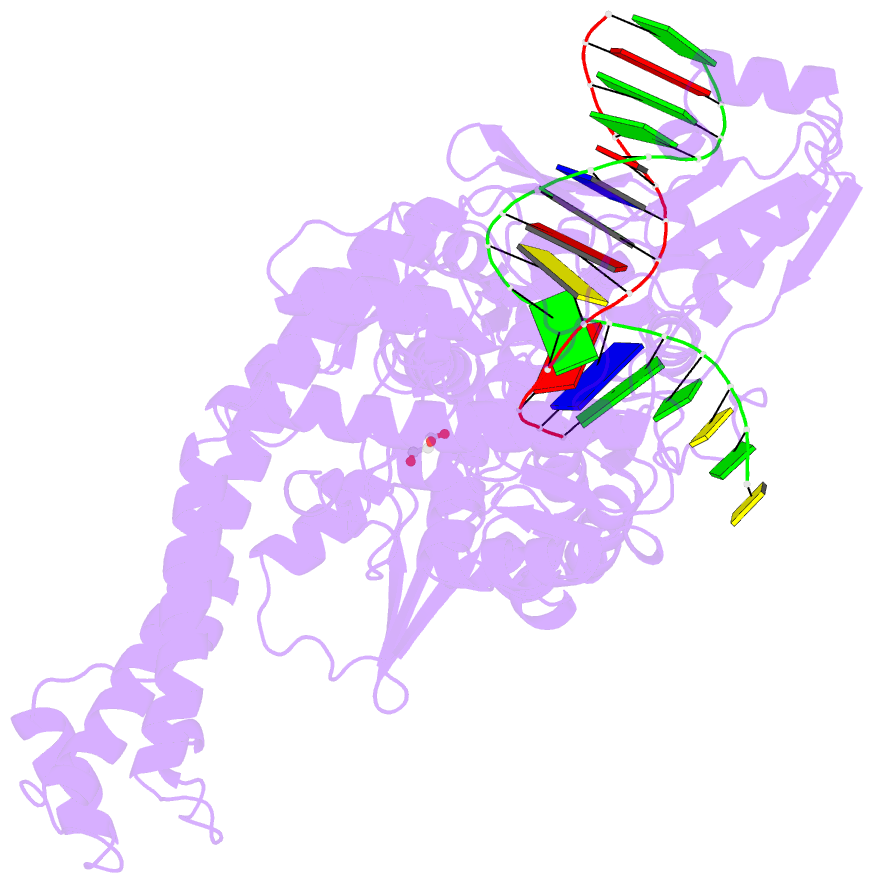
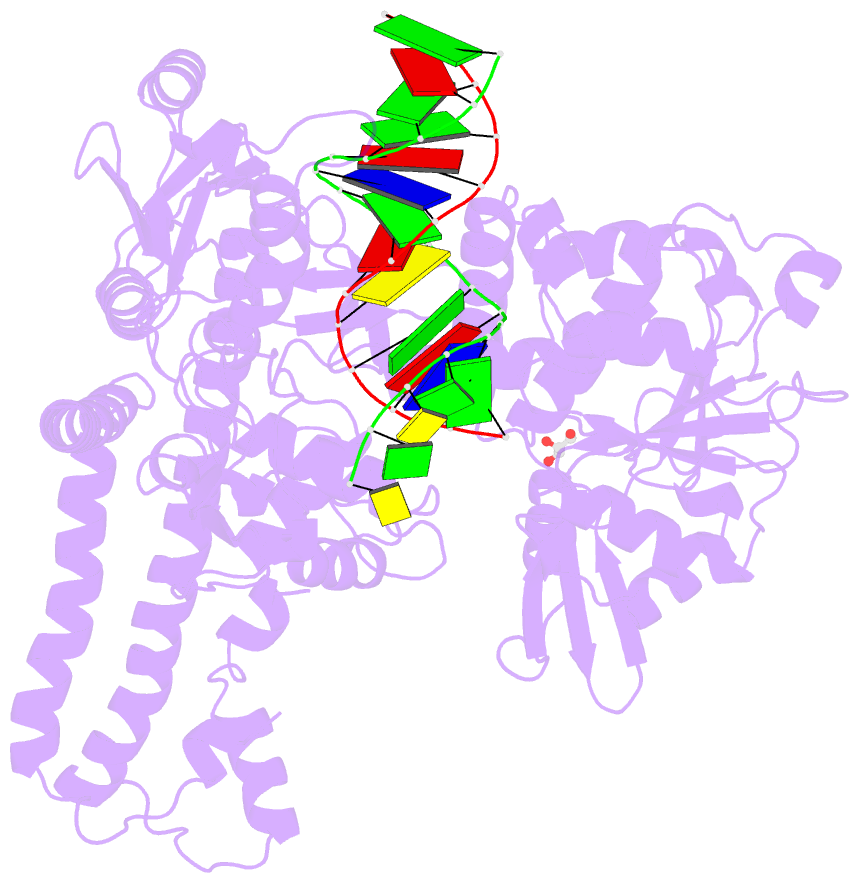
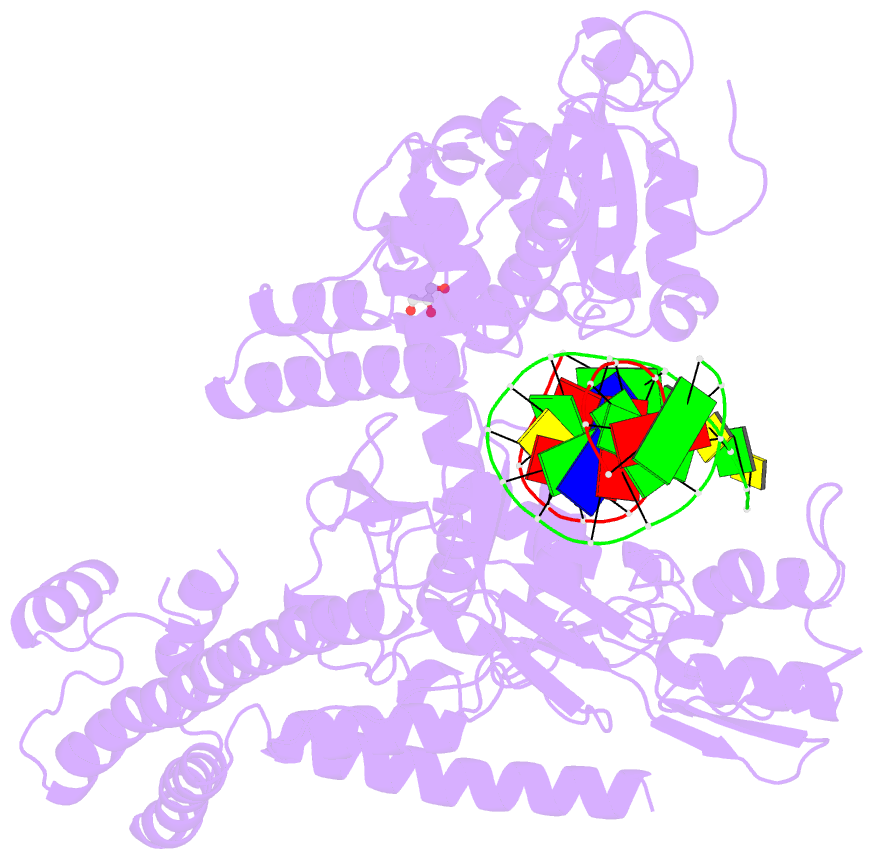
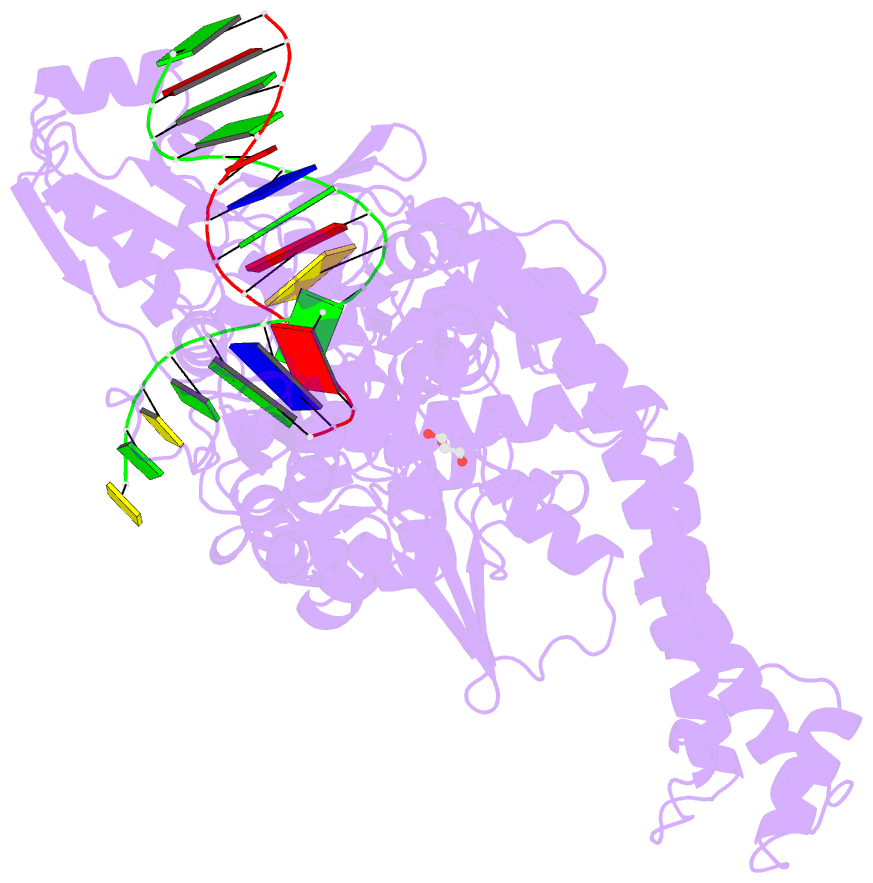
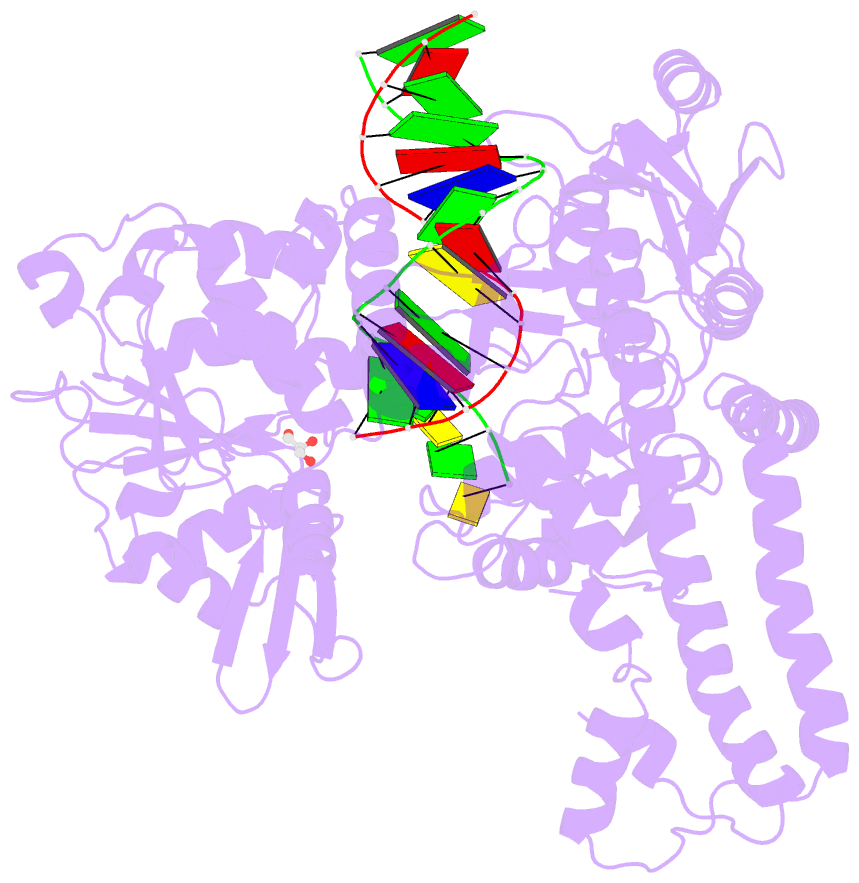
- Human topoisomerase ii alpha bound to DNA
- Reference
- Wendorff TJ, Schmidt BH, Heslop P, Austin CA, Berger JM (2012): "The Structure of DNA-Bound Human Topoisomerase II Alpha: Conformational Mechanisms for Coordinating Inter-Subunit Interactions with DNA Cleavage." J.Mol.Biol., 424, 109-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.07.014.
- Abstract
- Type II topoisomerases are required for the management of DNA superhelicity and chromosome segregation, and serve as frontline targets for a variety of small-molecule therapeutics. To better understand how these enzymes act in both contexts, we determined the 2.9-Å-resolution structure of the DNA cleavage core of human topoisomerase IIα (TOP2A) bound to a doubly nicked, 30-bp duplex oligonucleotide. In accord with prior biochemical and structural studies, TOP2A significantly bends its DNA substrate using a bipartite, nucleolytic center formed at an N-terminal dimerization interface of the cleavage core. However, the protein also adopts a global conformation in which the second of its two inter-protomer contact points, one at the C-terminus, has separated. This finding, together with comparative structural analyses, reveals that the principal site of DNA engagement undergoes highly quantized conformational transitions between distinct binding, cleavage, and drug-inhibited states that correlate with the control of subunit-subunit interactions. Additional consideration of our TOP2A model in light of an etoposide-inhibited complex of human topoisomerase IIβ (TOP2B) suggests possible modification points for developing paralog-specific inhibitors to overcome the tendency of topoisomerase II-targeting chemotherapeutics to generate secondary malignancies.