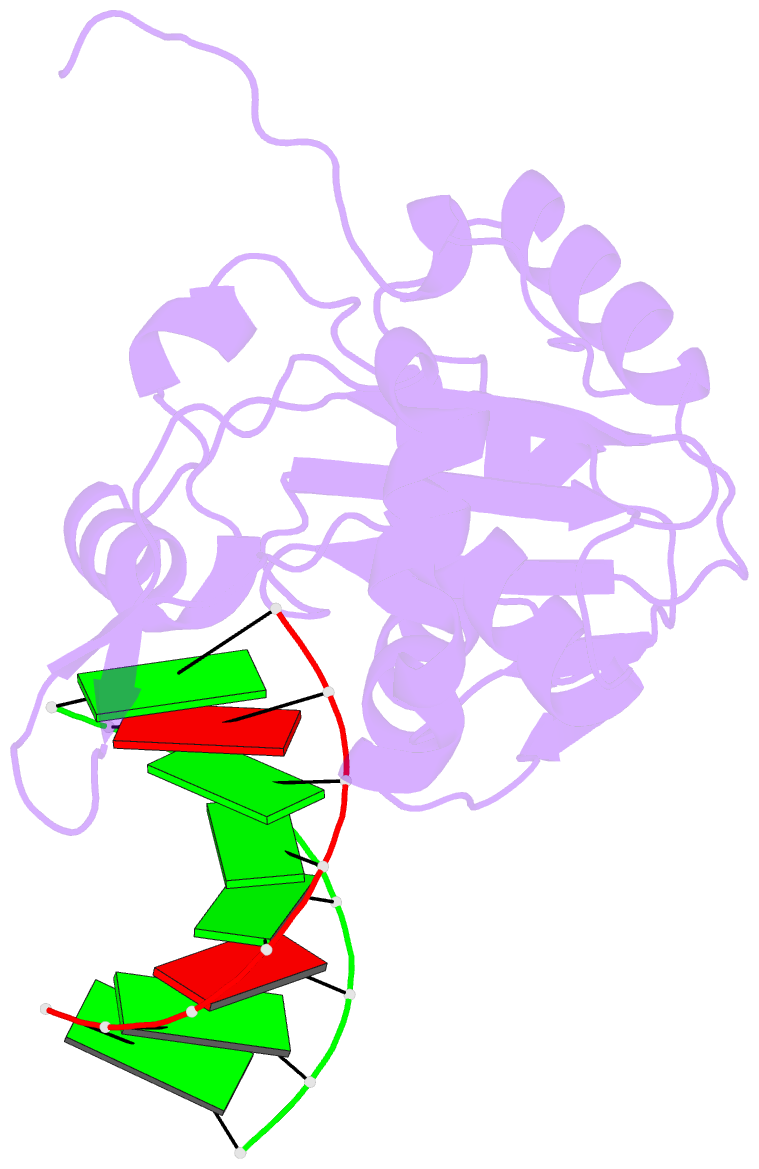
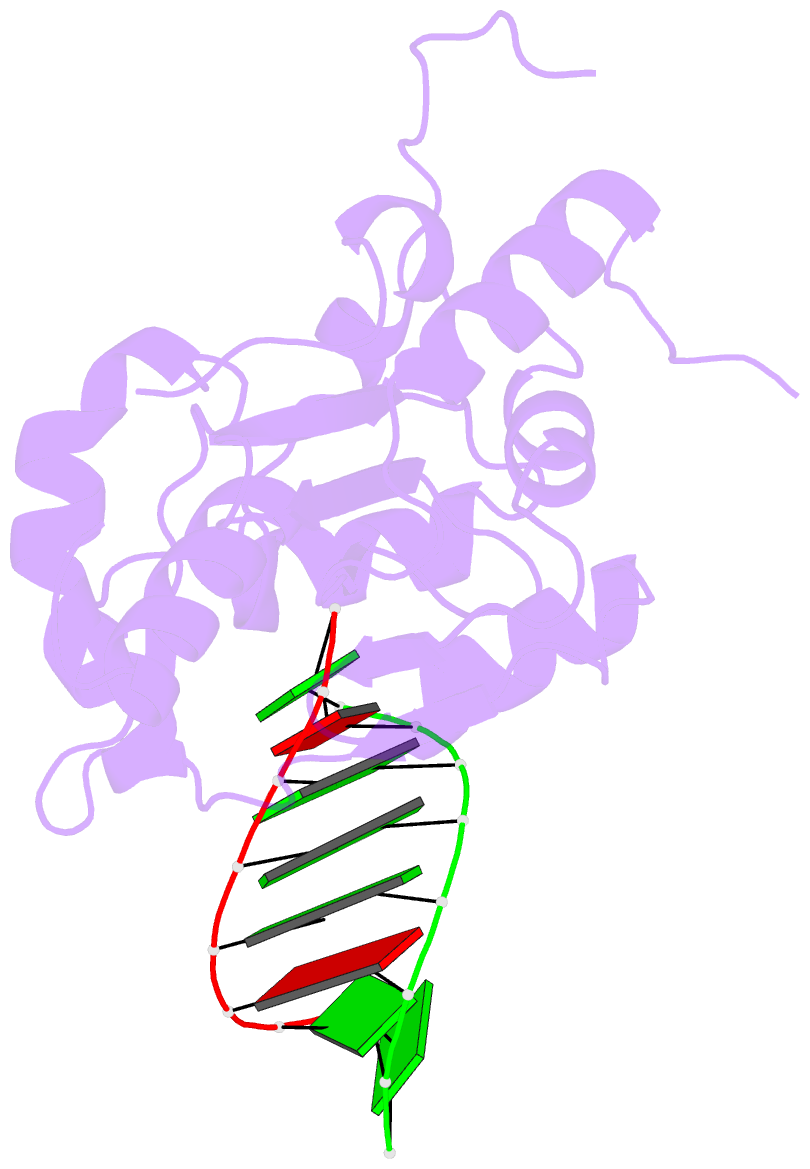
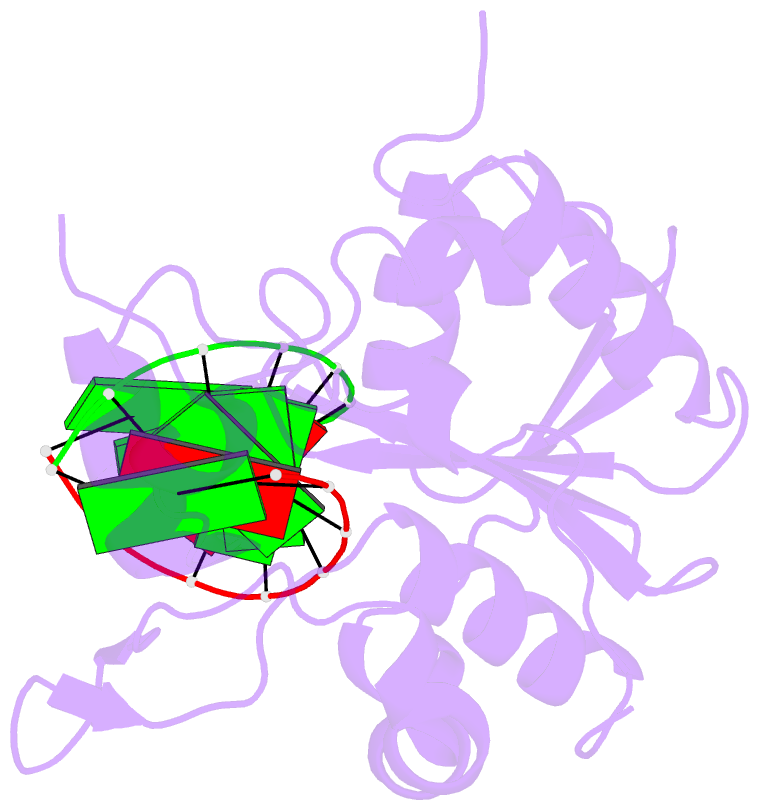
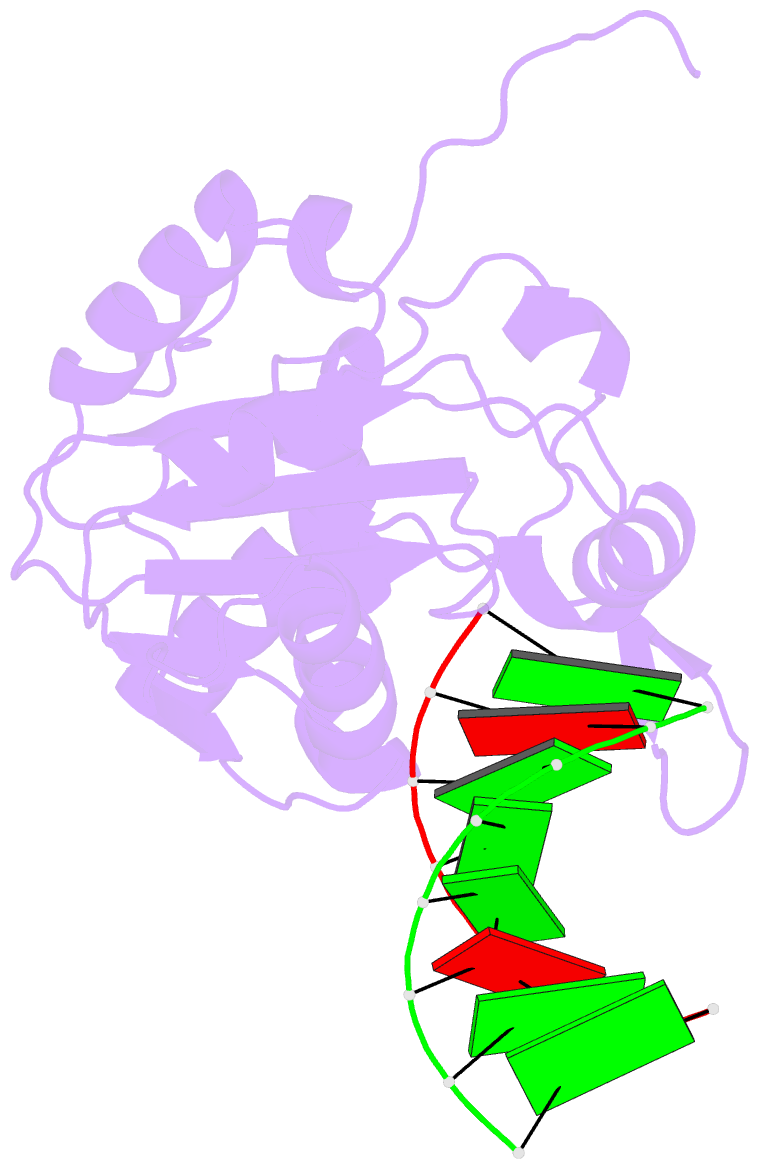
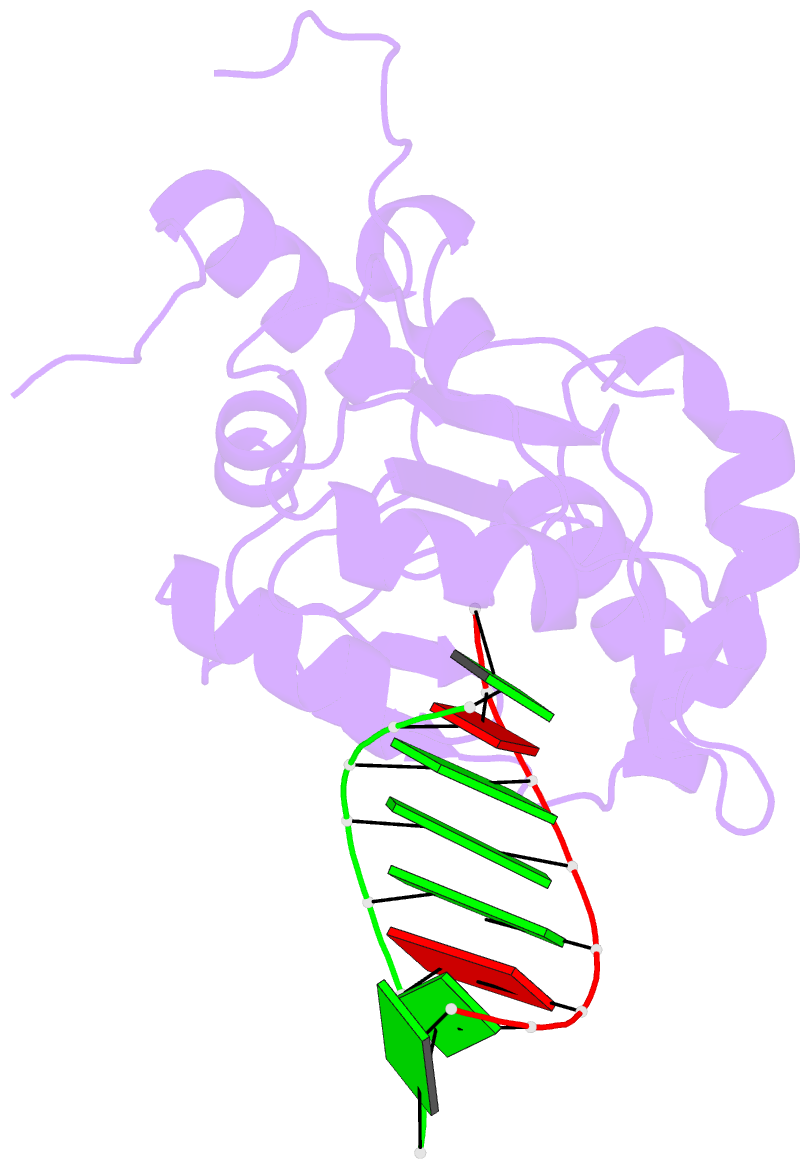
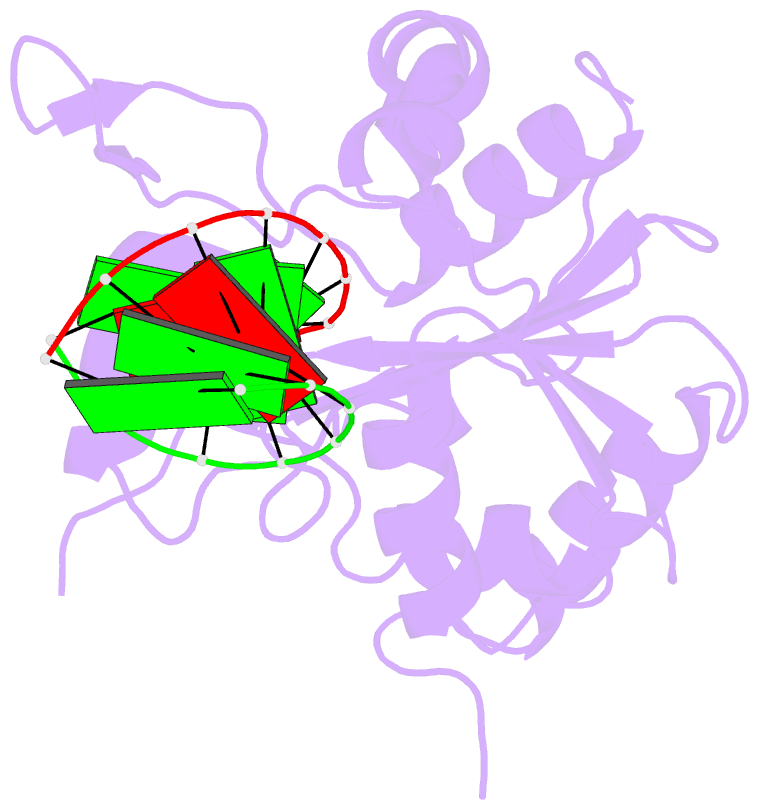
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
4fvu;
DSSR-derived features in text and
JSON formats; DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.91 Å)
- Summary
- Structural basis for the dsrna specificity of the lassa
virus np exonuclease
- Reference
-
Hastie KM, King LB, Zandonatti MA, Saphire EO (2012):
"Structural
Basis for the dsRNA Specificity of the Lassa Virus NP
Exonuclease." Plos One, 7,
e44211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044211.
- Abstract
- Lassa virus causes hemorrhagic fever characterized by
immunosuppression. The nucleoprotein of Lassa virus, termed
NP, binds the viral genome. It also has an additional
enzymatic activity as an exonuclease that specifically
digests double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). dsRNA is a strong
signal to the innate immune system of viral infection.
Digestion of dsRNA by the NP exonuclease activity appears
to cause suppression of innate immune signaling in the
infected cell. Although the fold of the NP enzyme is
conserved and the active site completely conserved with
other exonucleases in its DEDDh family, NP is atypical
among exonucleases in its preference for dsRNA and its
strict specificity for one substrate. Here, we present the
crystal structure of Lassa virus NP in complex with dsRNA.
We find that unlike the exonuclease in Klenow fragment, the
double-stranded nucleic acid in complex with Lassa NP
remains base-paired instead of splitting, and that binding
of the paired complementary strand is achieved by
"relocation" of a basic loop motif from its typical
exonuclease position. Further, we find that just one single
glycine that contacts the substrate strand and one single
tyrosine that stacks with a base of the complementary,
non-substrate strand are responsible for the unique
substrate specificity. This work thus provides templates
for development of antiviral drugs that would be specific
for viral, rather than host exonucleases of similar fold
and active site, and illustrates how a very few amino acid
changes confer alternate specificity and biological
phenotype to an enzyme.