Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4fxd; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.0 Å)
- Summary
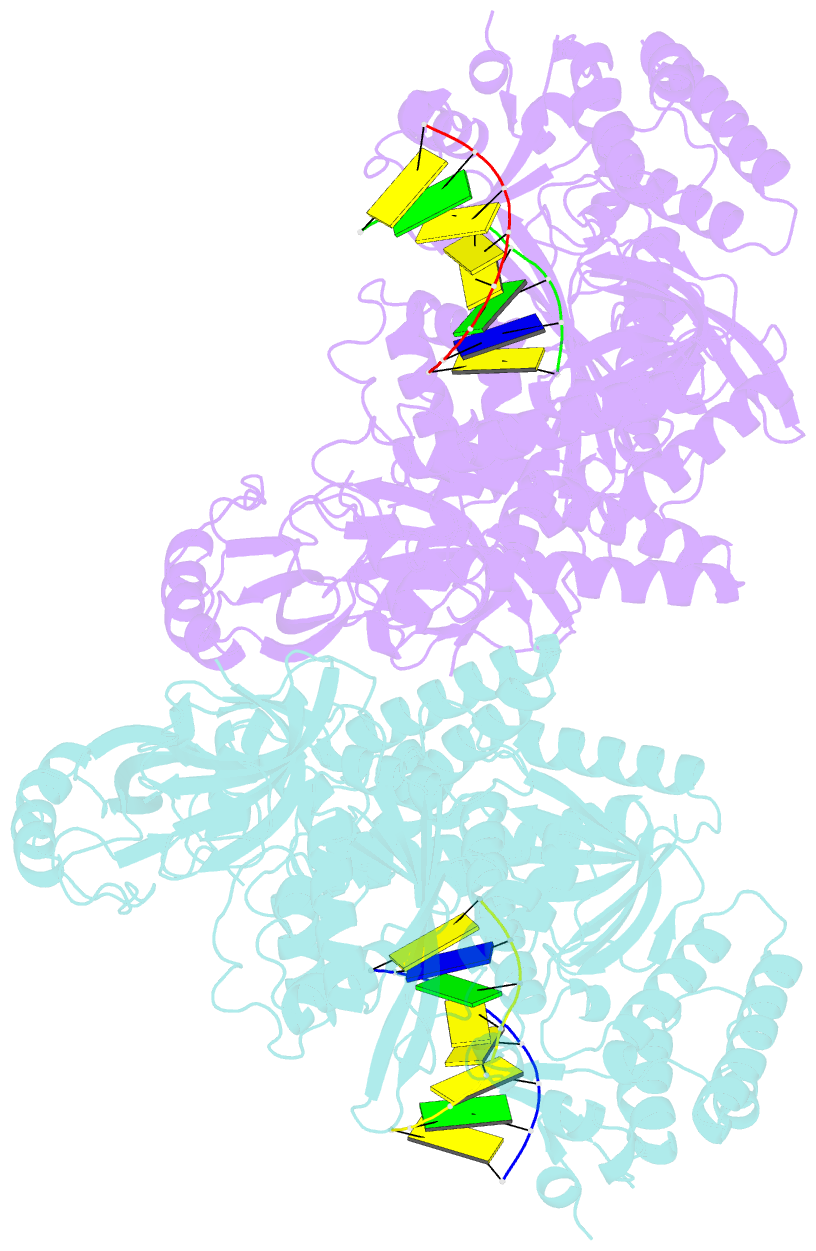
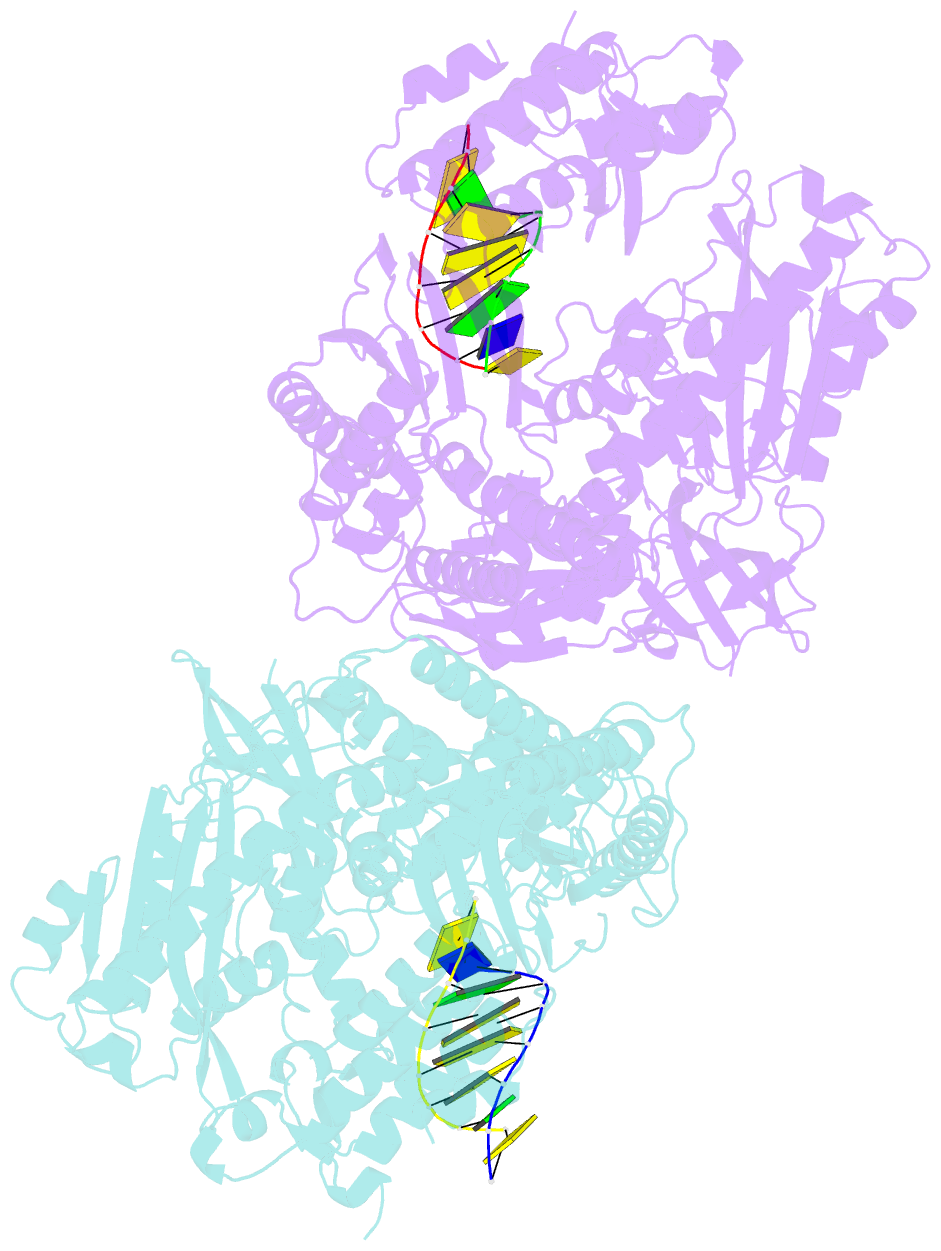
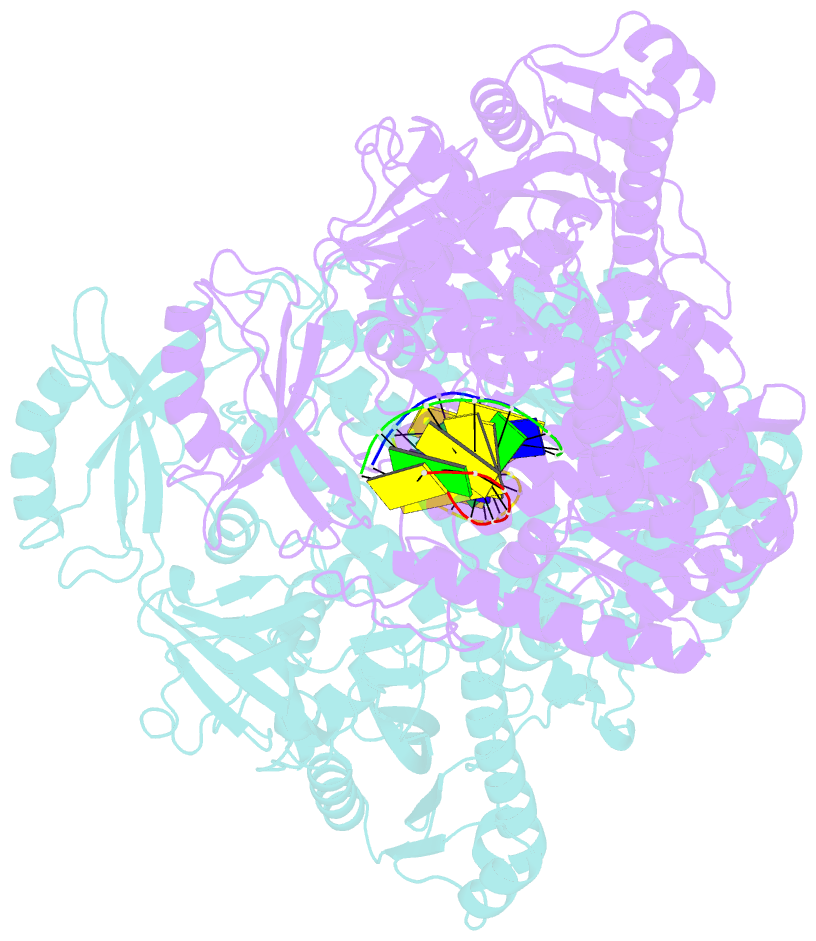
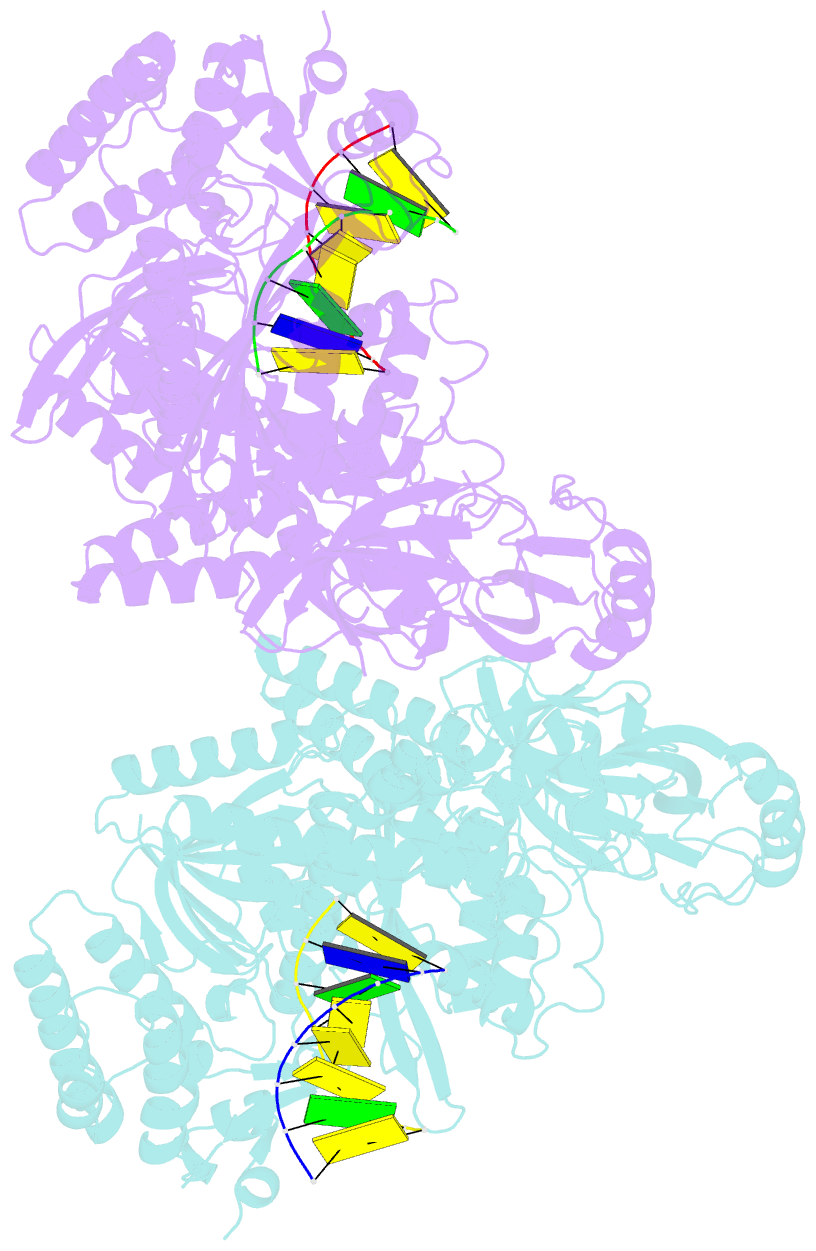
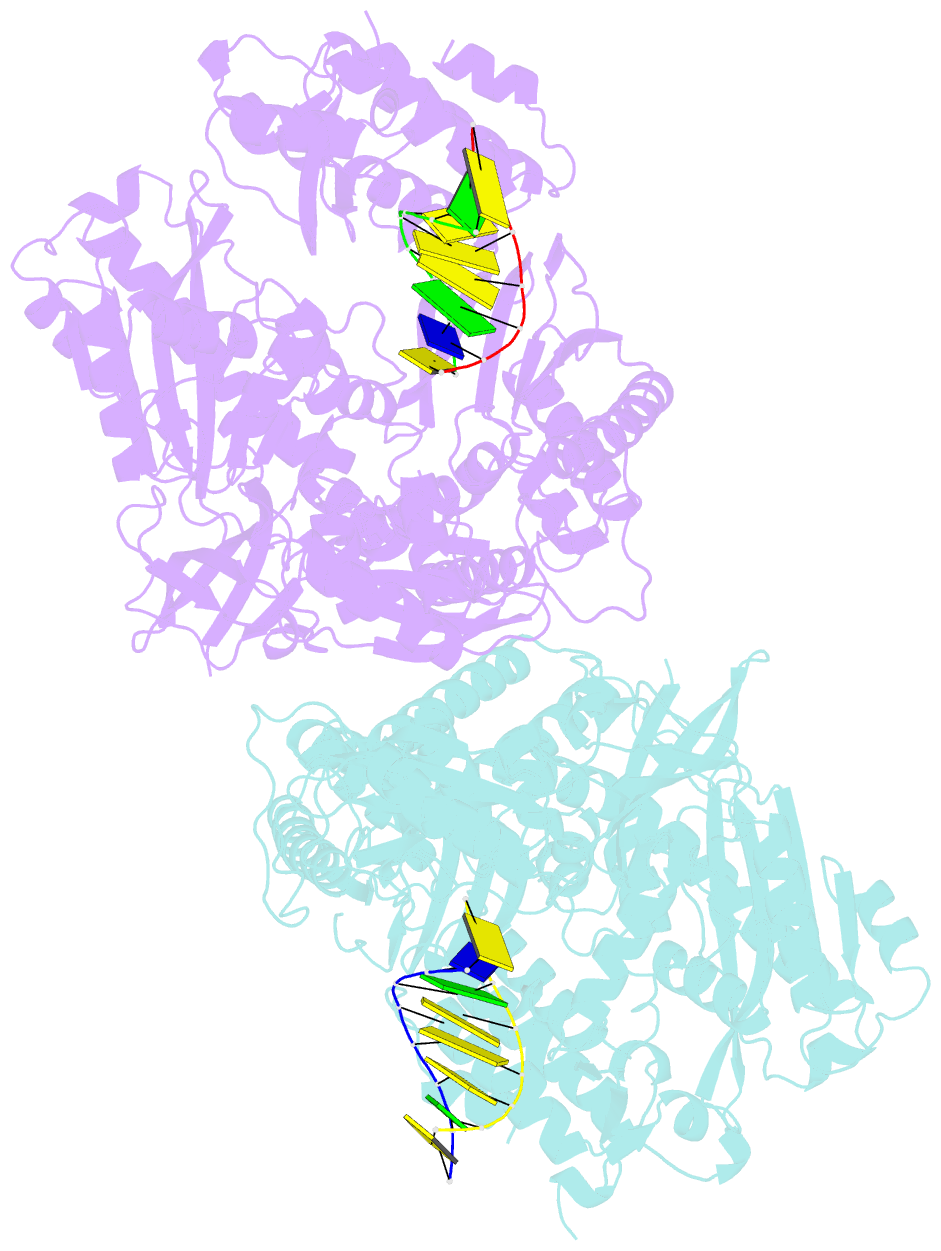
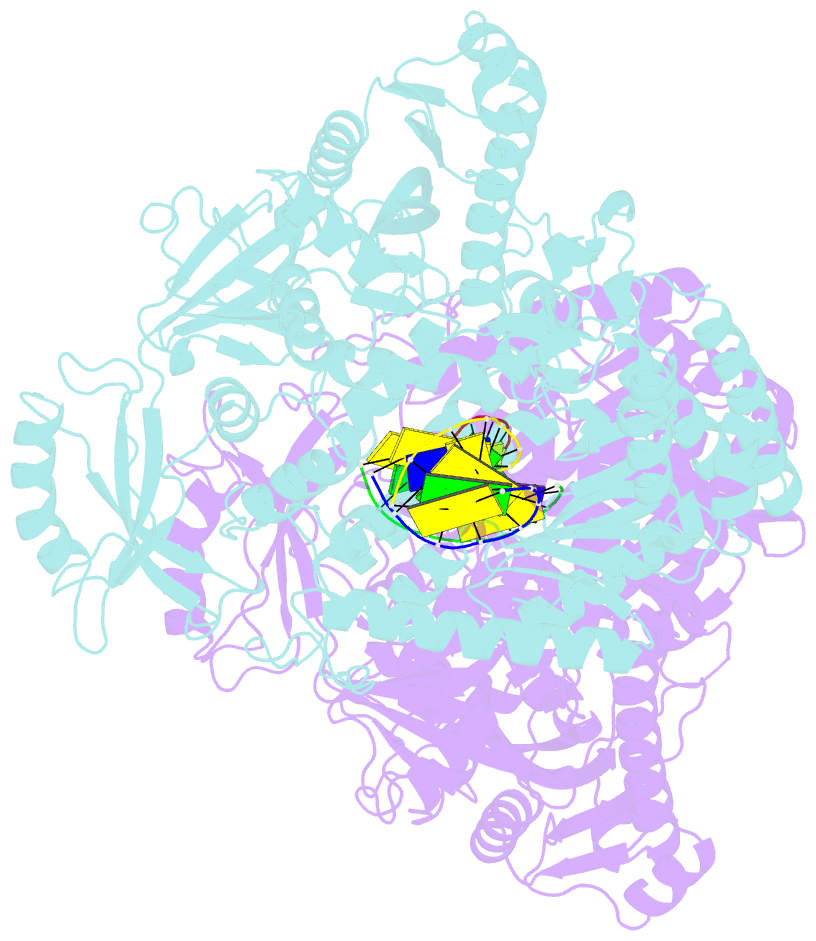
- Crystal structure of yeast DNA polymerase alpha bound to DNA-RNA
- Reference
- Perera RL, Torella R, Klinge S, Kilkenny ML, Maman JD, Pellegrini L (2013): "Mechanism for priming DNA synthesis by yeast DNA Polymerase alpha." eLife, 2, e00482. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00482.
- Abstract
- The DNA Polymerase α (Pol α)/primase complex initiates DNA synthesis in eukaryotic replication. In the complex, Pol α and primase cooperate in the production of RNA-DNA oligonucleotides that prime synthesis of new DNA. Here we report crystal structures of the catalytic core of yeast Pol α in unliganded form, bound to an RNA primer/DNA template and extending an RNA primer with deoxynucleotides. We combine the structural analysis with biochemical and computational data to demonstrate that Pol α specifically recognizes the A-form RNA/DNA helix and that the ensuing synthesis of B-form DNA terminates primer synthesis. The spontaneous release of the completed RNA-DNA primer by the Pol α/primase complex simplifies current models of primer transfer to leading- and lagging strand polymerases. The proposed mechanism of nucleotide polymerization by Pol α might contribute to genomic stability by limiting the amount of inaccurate DNA to be corrected at the start of each Okazaki fragment. DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00482.001.