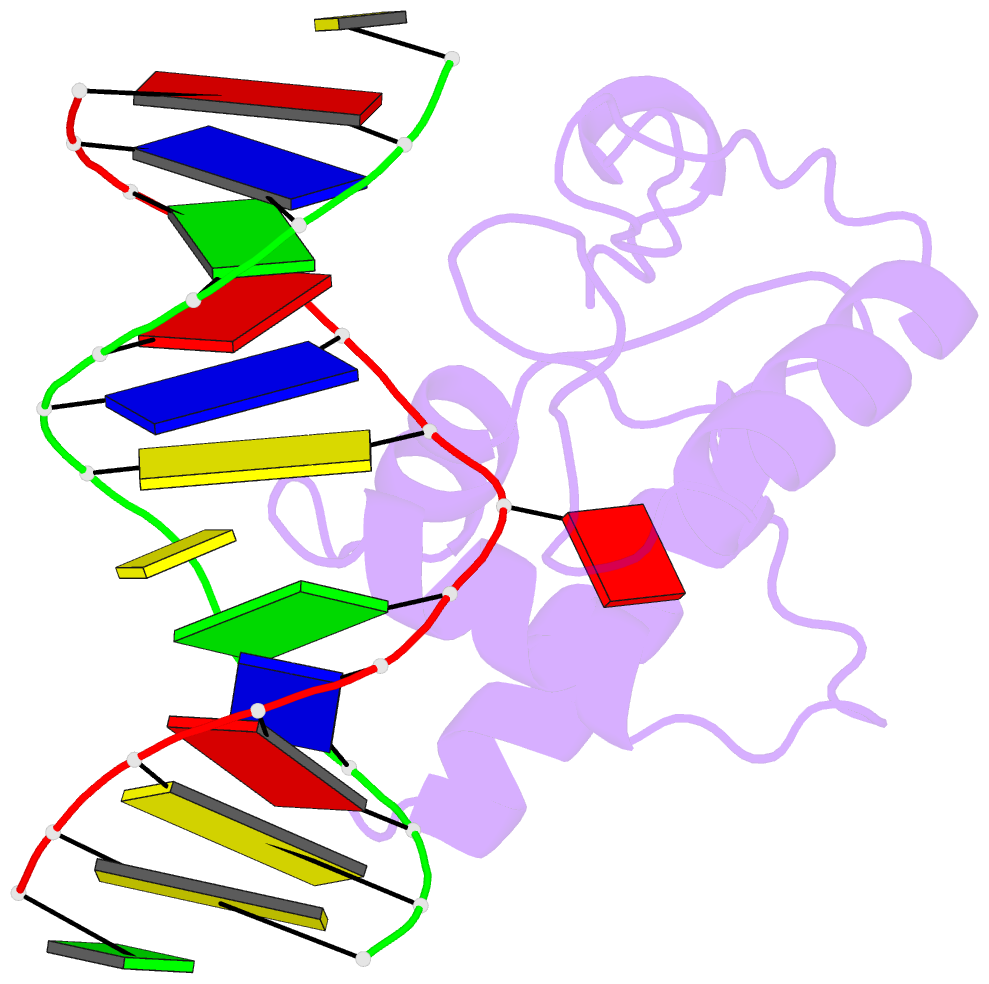
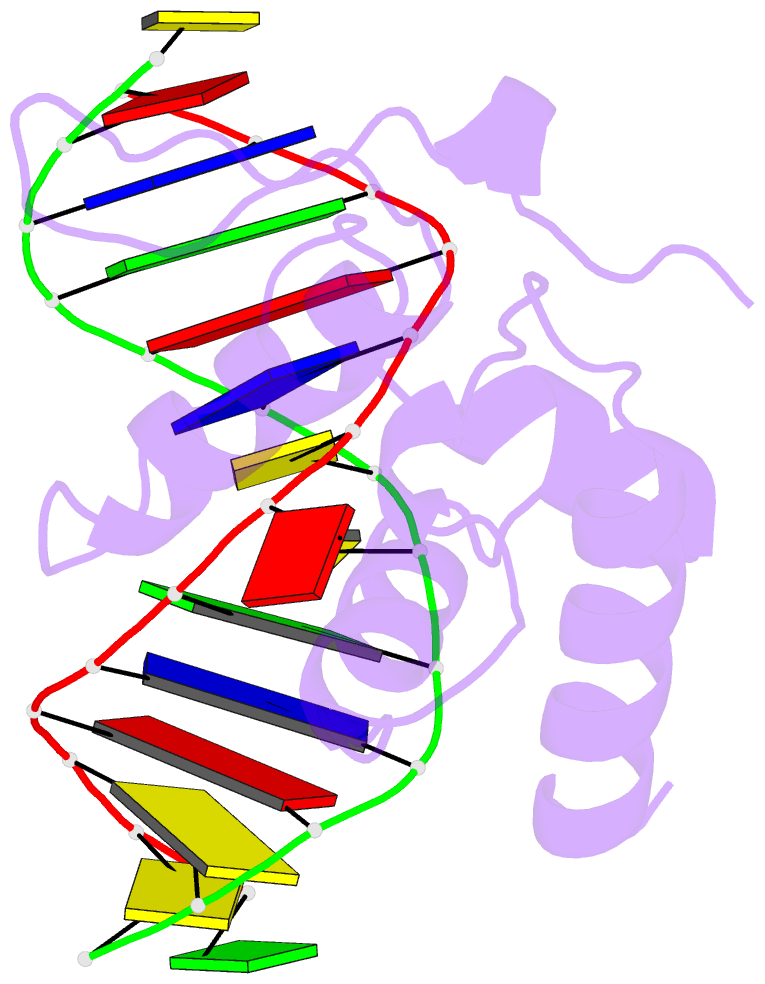
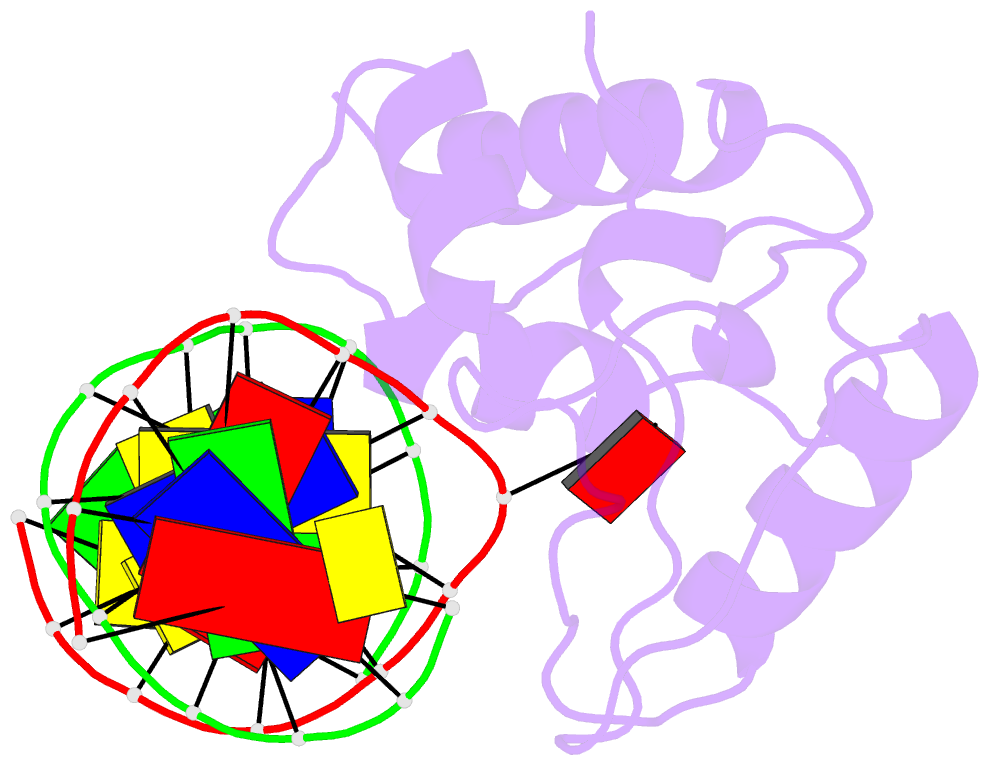
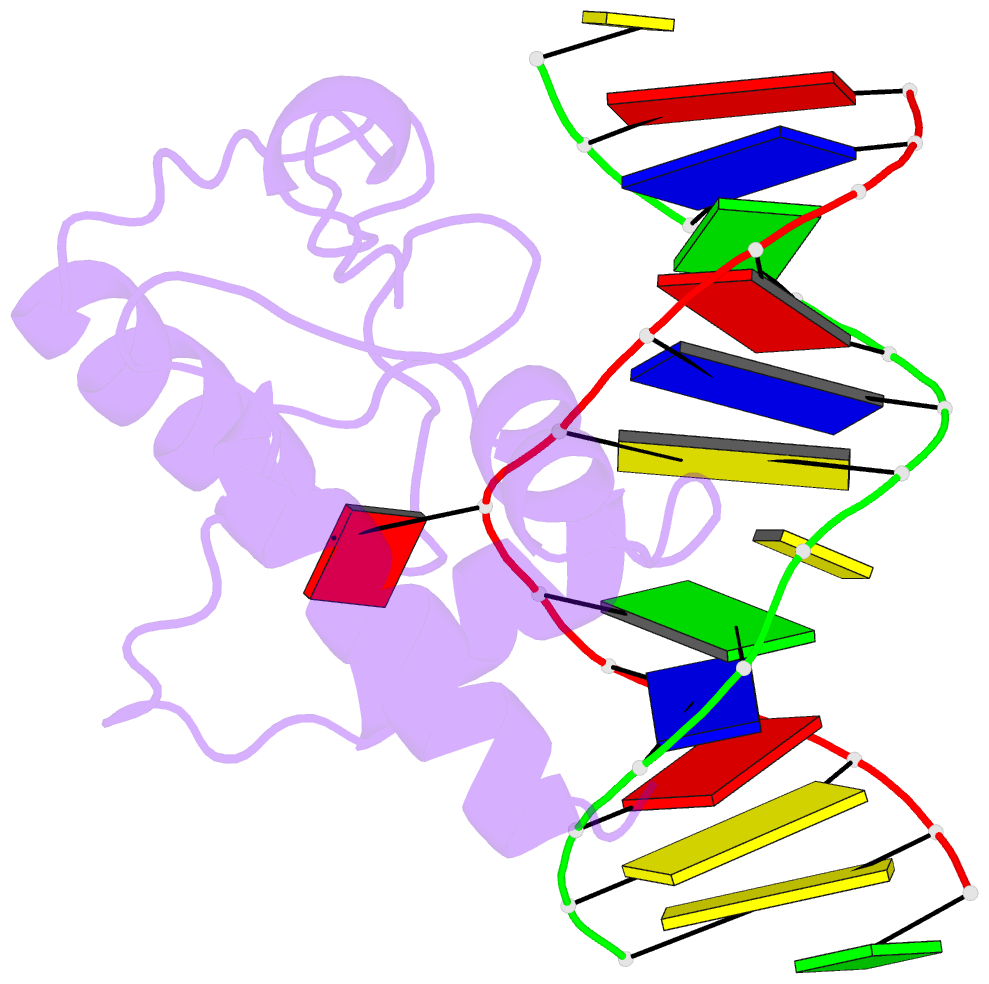
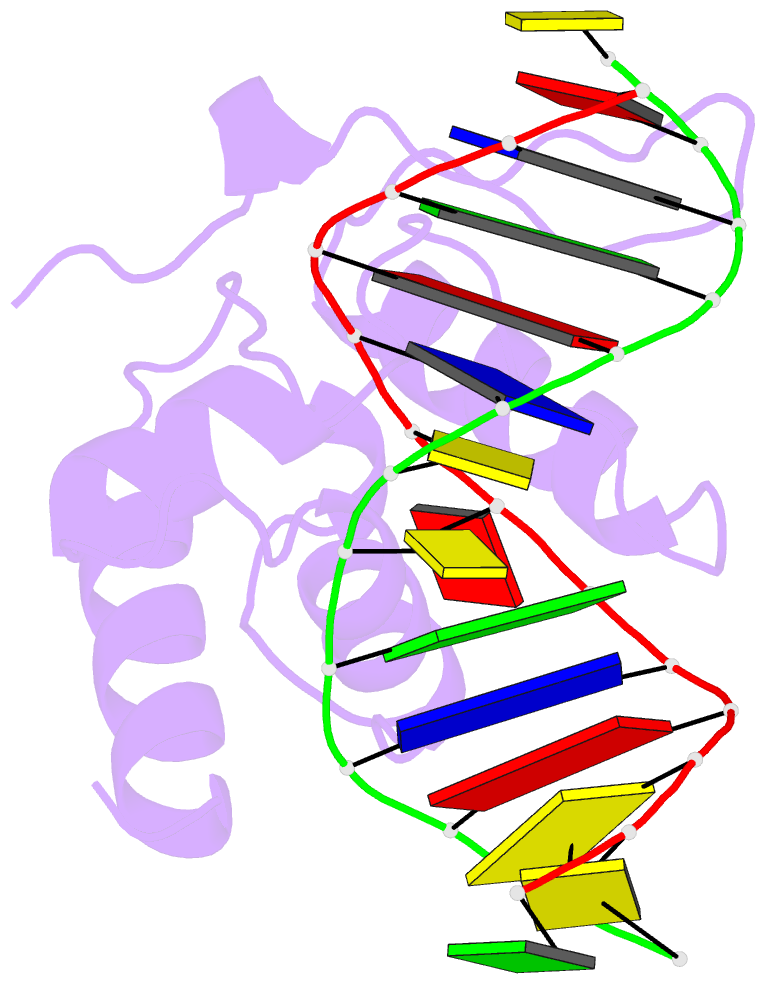
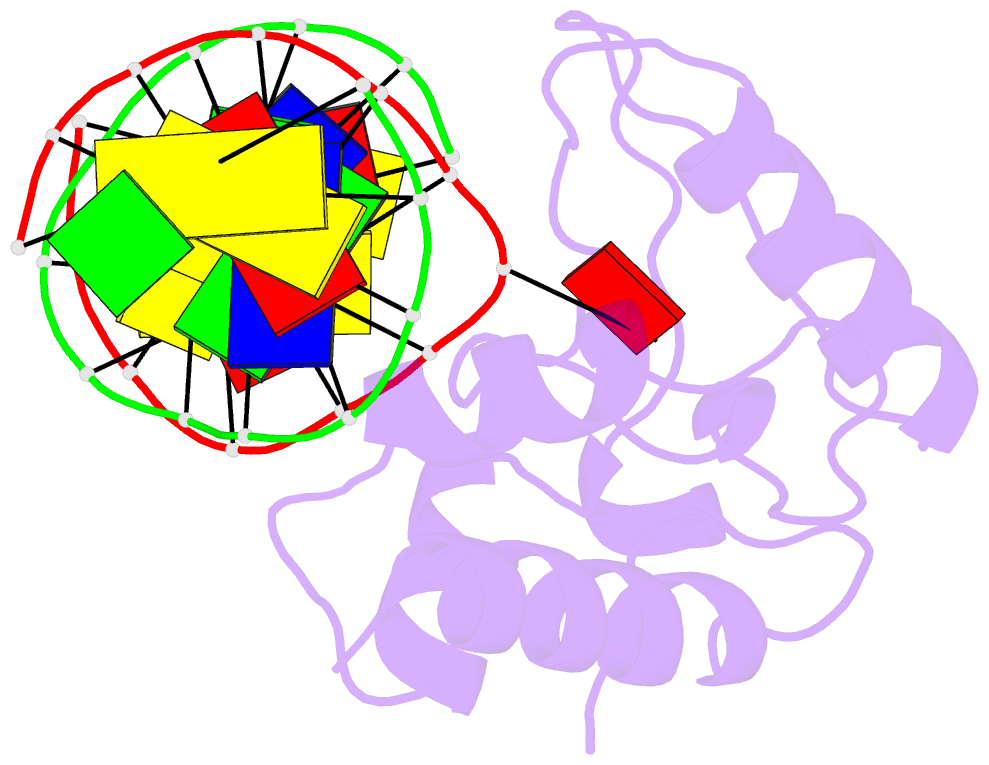
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4hdv; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.702 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of s. pombe atl1 in complex with damaged DNA containing 2,6-diaminopurine
- Reference
- Wilkinson OJ, Latypov V, Tubbs JL, Millington CL, Morita R, Blackburn H, Marriott A, McGown G, Thorncroft M, Watson AJ, Connolly BA, Grasby JA, Masui R, Hunter CA, Tainer JA, Margison GP, Williams DM (2012): "Alkyltransferase-like protein (Atl1) distinguishes alkylated guanines for DNA repair using cation-{pi} interactions." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 109, 18755-18760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209451109.
- Abstract
- Alkyltransferase-like (ATL) proteins in Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Atl1) and Thermus thermophilus (TTHA1564) protect against the adverse effects of DNA alkylation damage by flagging O(6)-alkylguanine lesions for nucleotide excision repair (NER). We show that both ATL proteins bind with high affinity to oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing O(6)-alkylguanines differing in size, polarity, and charge of the alkyl group. However, Atl1 shows a greater ability than TTHA1564 to distinguish between O(6)-alkylguanine and guanine and in an unprecedented mechanism uses Arg69 to probe the electrostatic potential surface of O(6)-alkylguanine, as determined using molecular mechanics calculations. An unexpected consequence of this feature is the recognition of 2,6-diaminopurine and 2-aminopurine, as confirmed in crystal structures of respective Atl1-DNA complexes. O(6)-Alkylguanine and guanine discrimination is diminished for Atl1 R69A and R69F mutants, and S. pombe R69A and R69F mutants are more sensitive toward alkylating agent toxicity, revealing the key role of Arg69 in identifying O(6)-alkylguanines critical for NER recognition.