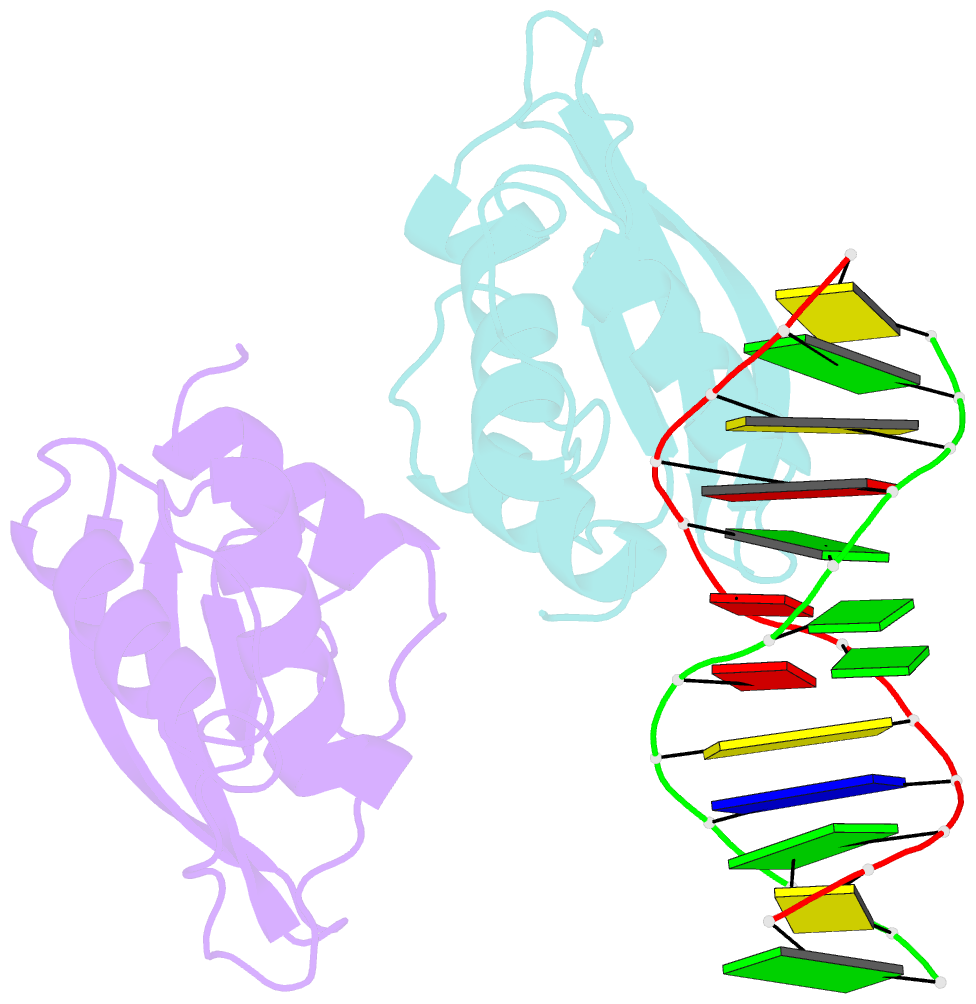
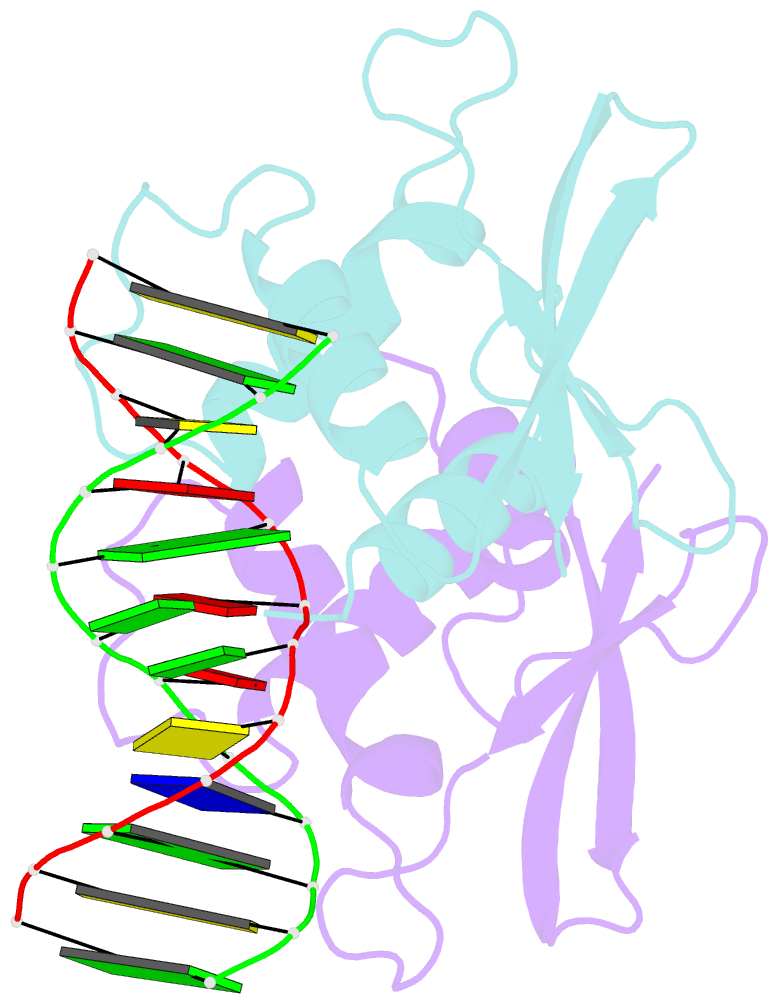
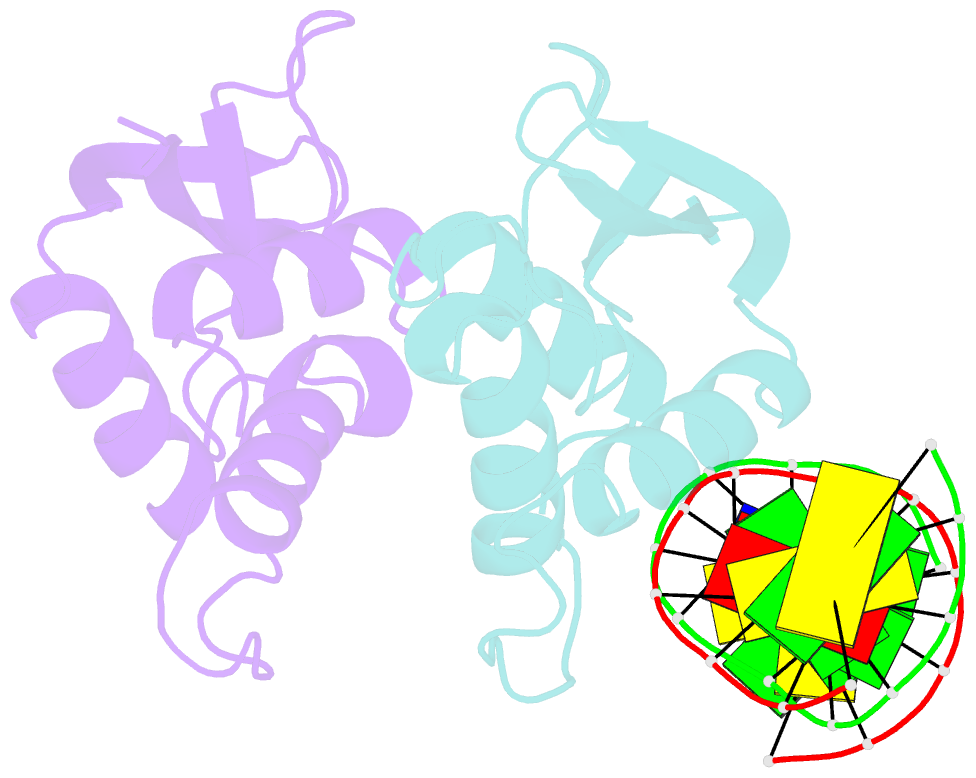
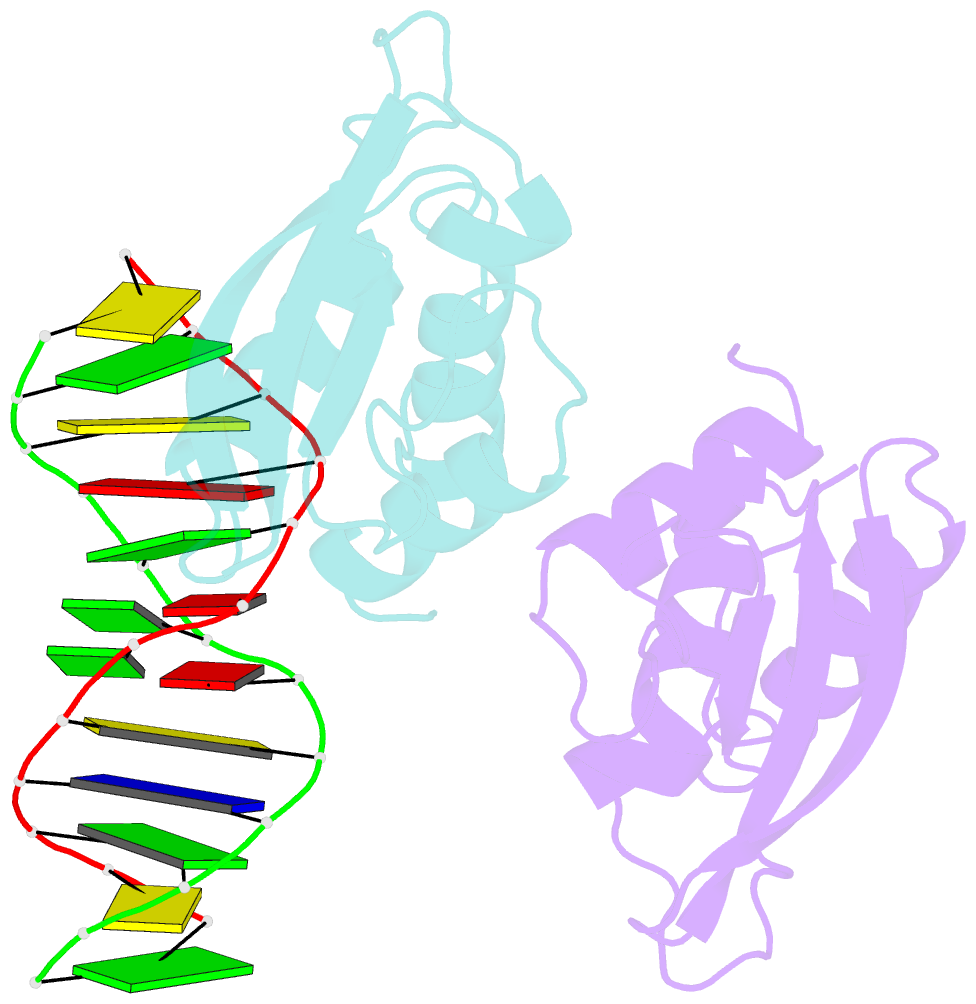
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4hly; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.48 Å)
- Summary
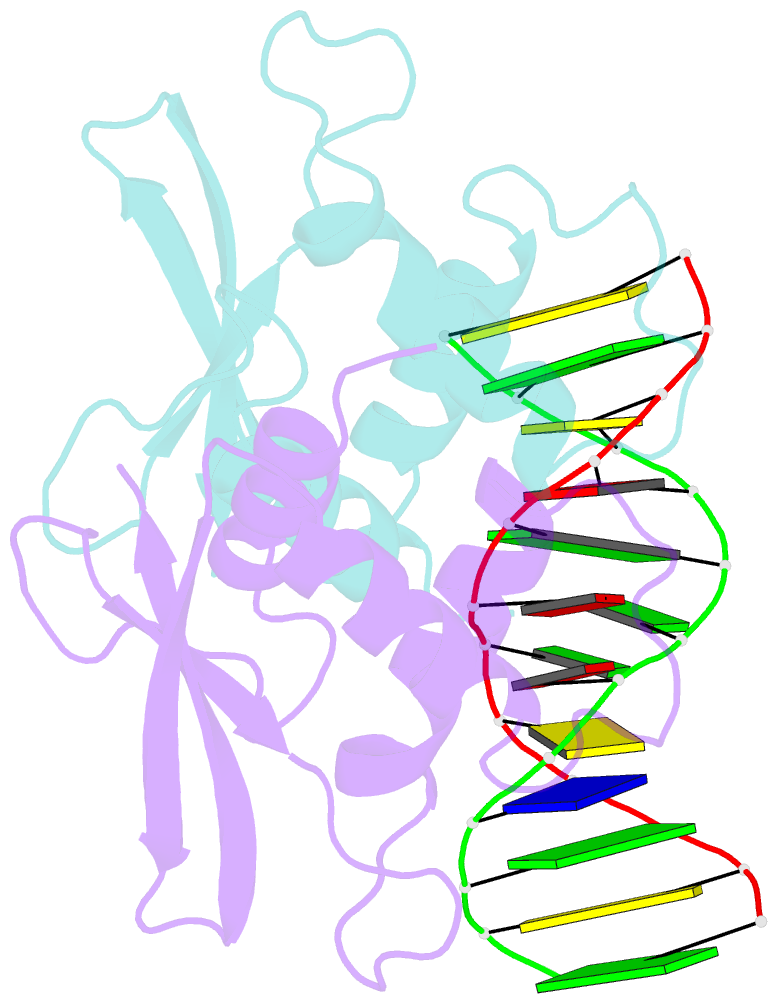
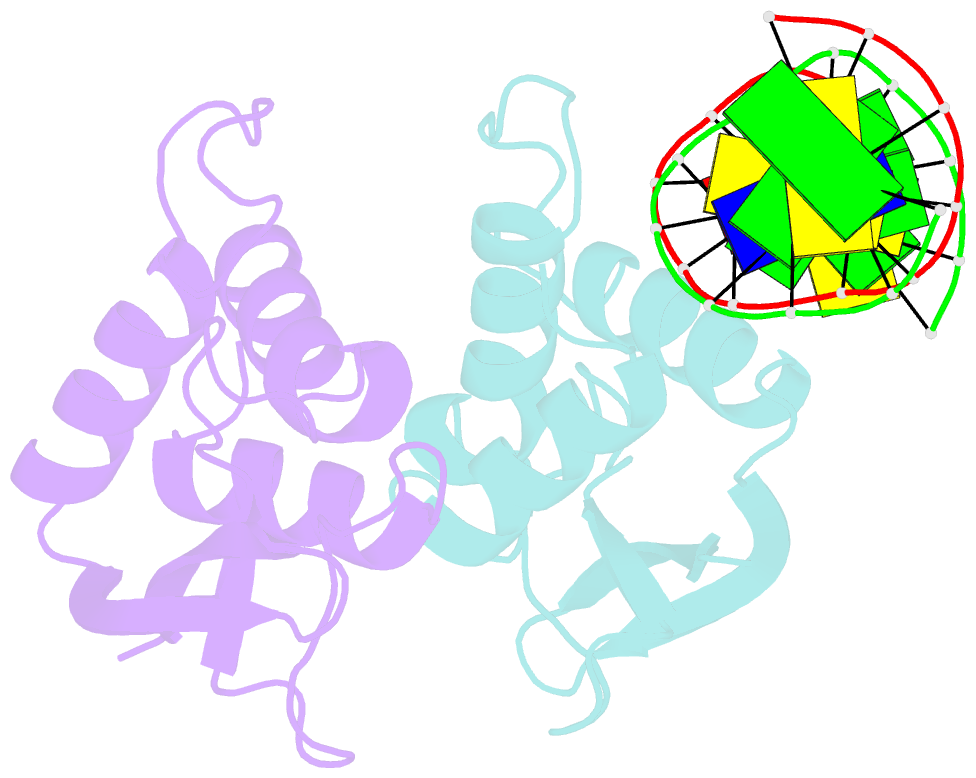
- The complex crystal structure of the DNA binding domain of virf-1 from the oncogenic kshv with DNA
- Reference
- Hew K, Dahlroth SL, Venkatachalam R, Nasertorabi F, Lim BT, Cornvik T, Nordlund P (2013): "The crystal structure of the DNA-binding domain of vIRF-1 from the oncogenic KSHV reveals a conserved fold for DNA binding and reinforces its role as a transcription factor." Nucleic Acids Res., 41, 4295-4306. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt082.
- Abstract
- Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encodes four viral homologues to cellular interferon regulatory factors (IRFs), where the most studied is vIRF-1. Even though vIRF-1 shows sequence homology to the N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD) of human IRFs, a specific role for this domain in vIRF-1's function has remained uncertain. To provide insights into the function of the vIRF-1 DBD, we have determined the crystal structure of it in complex with DNA and in its apo-form. Using a thermal stability shift assay (TSSA), we show that the vIRF-1 DBD binds DNA, whereas full-length vIRF-1 does not, suggesting a cis-acting regulatory mechanism in similarity to human IRFs. The complex structure of vIRF-1 DBD reveals interactions with the DNA backbone and the positioning of two arginines for specific recognition in the major grove. A superimposition with human IRF-3 reveals a similar positioning of the two specificity-determining arginines, and additional TSSAs indicate binding of vIRF-1 to an IRF-3 operator consensus sequence. The results from this study, therefore, provide support that vIRF-1 has evolved to bind DNA and plays a role in DNA binding in the context of transcriptional regulation and might act on some of the many operator sequences controlled by human IRF-3.