Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4ifd; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.805 Å)
- Summary
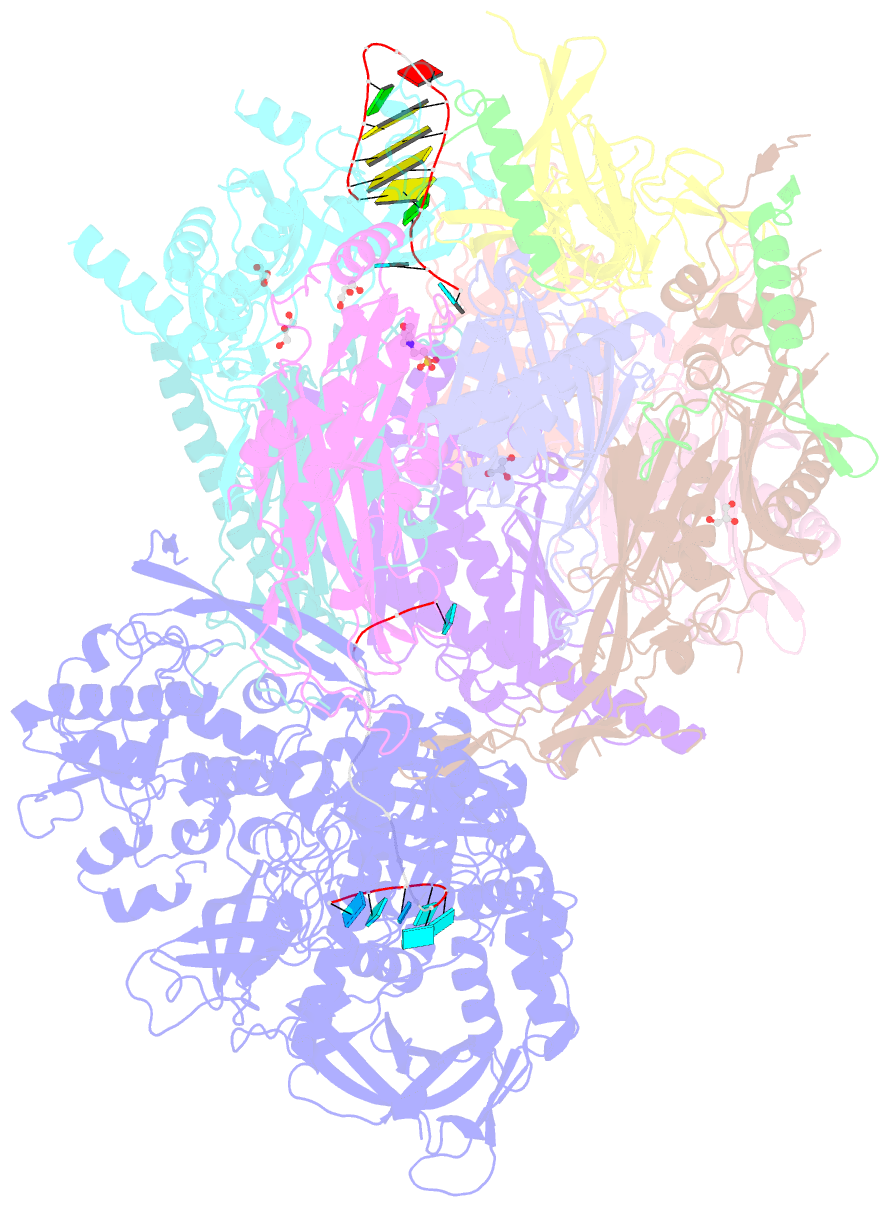
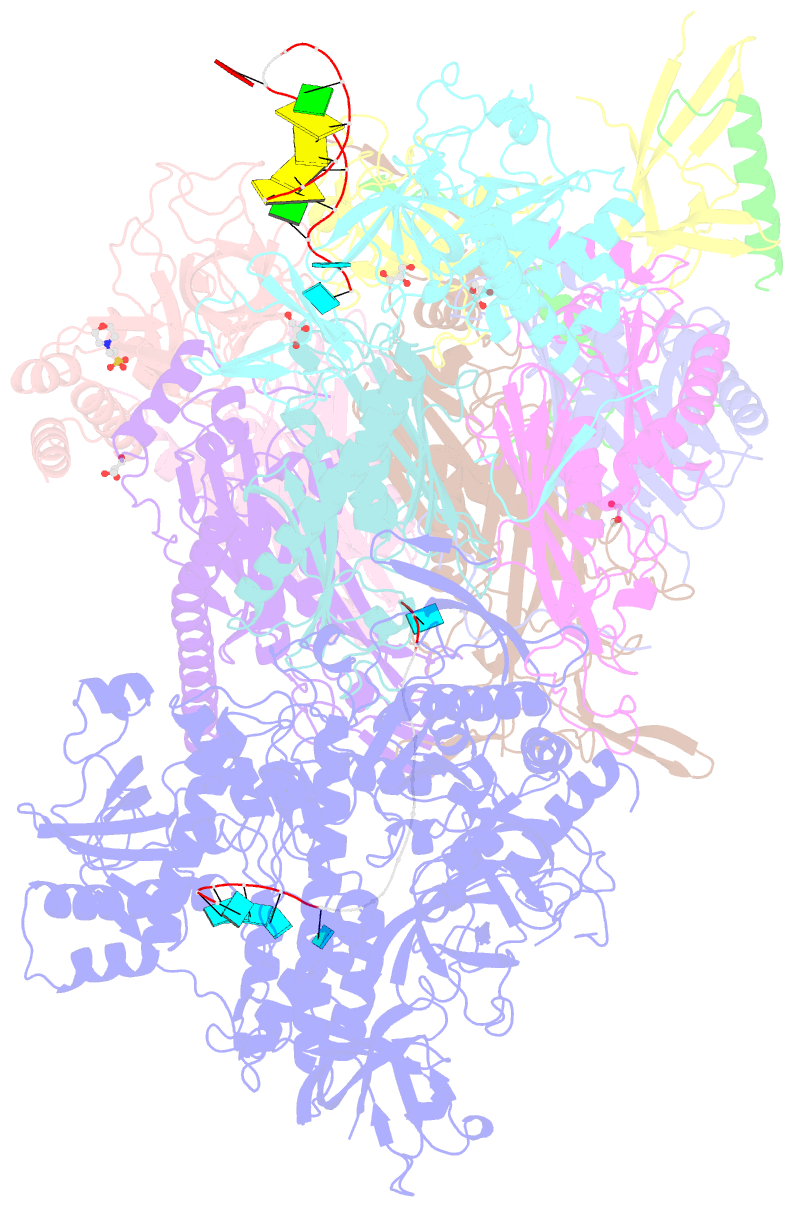
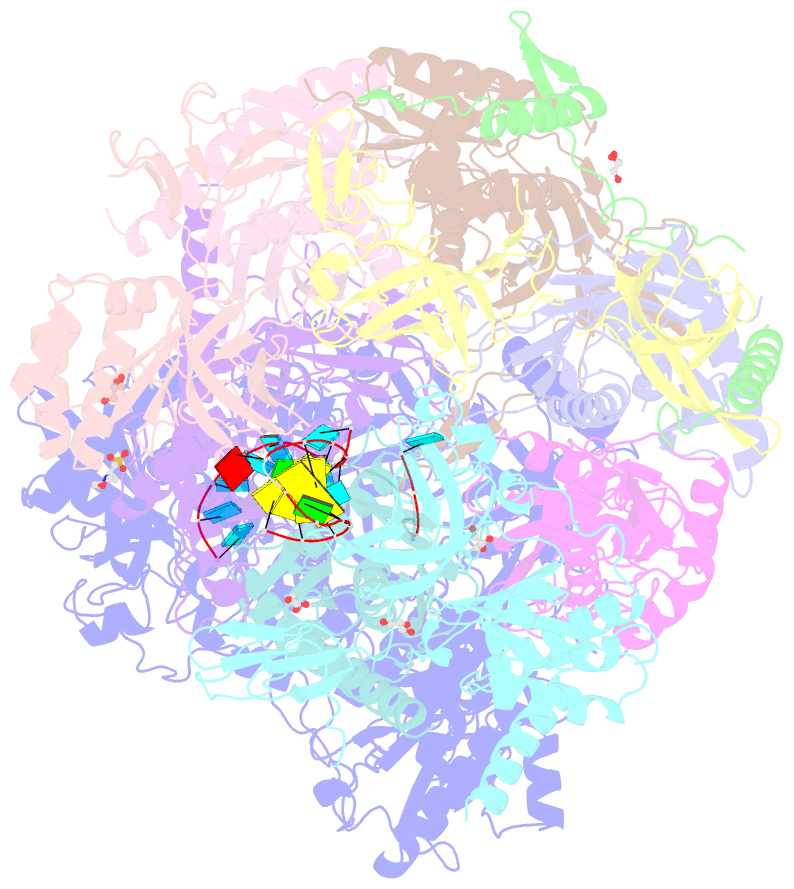
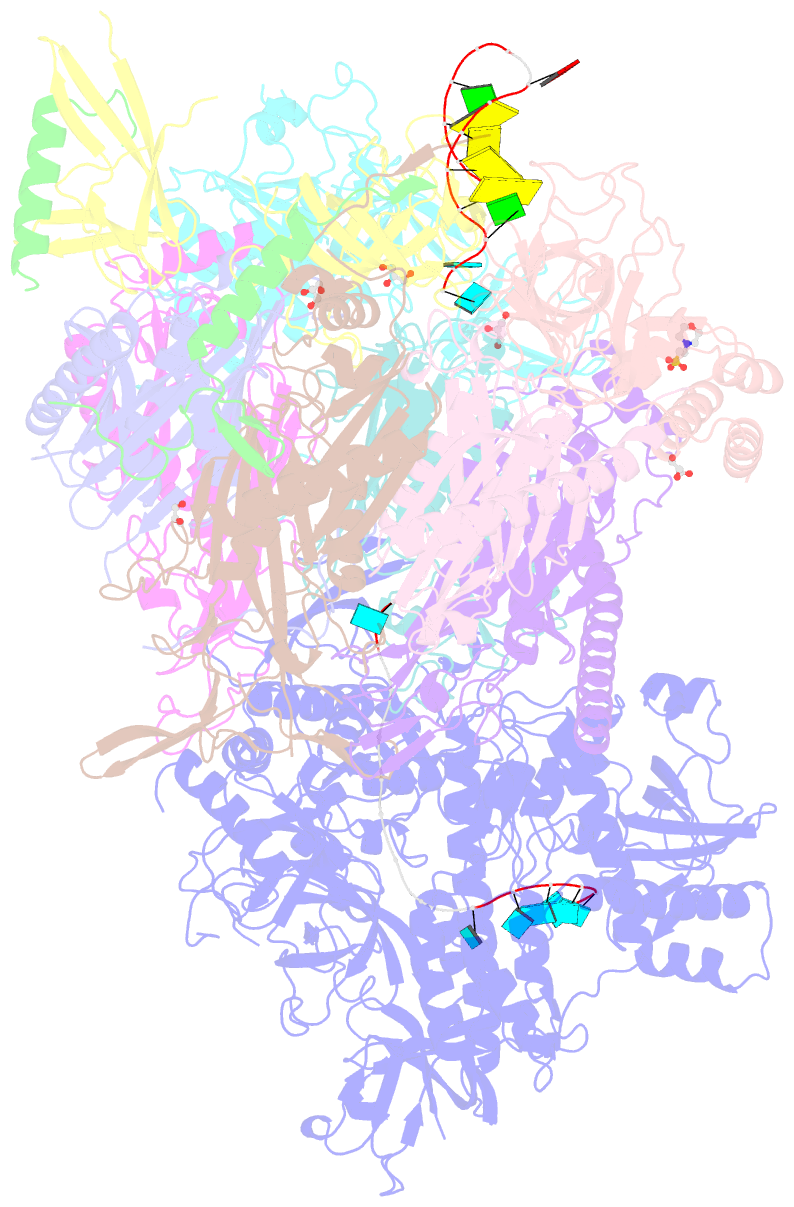
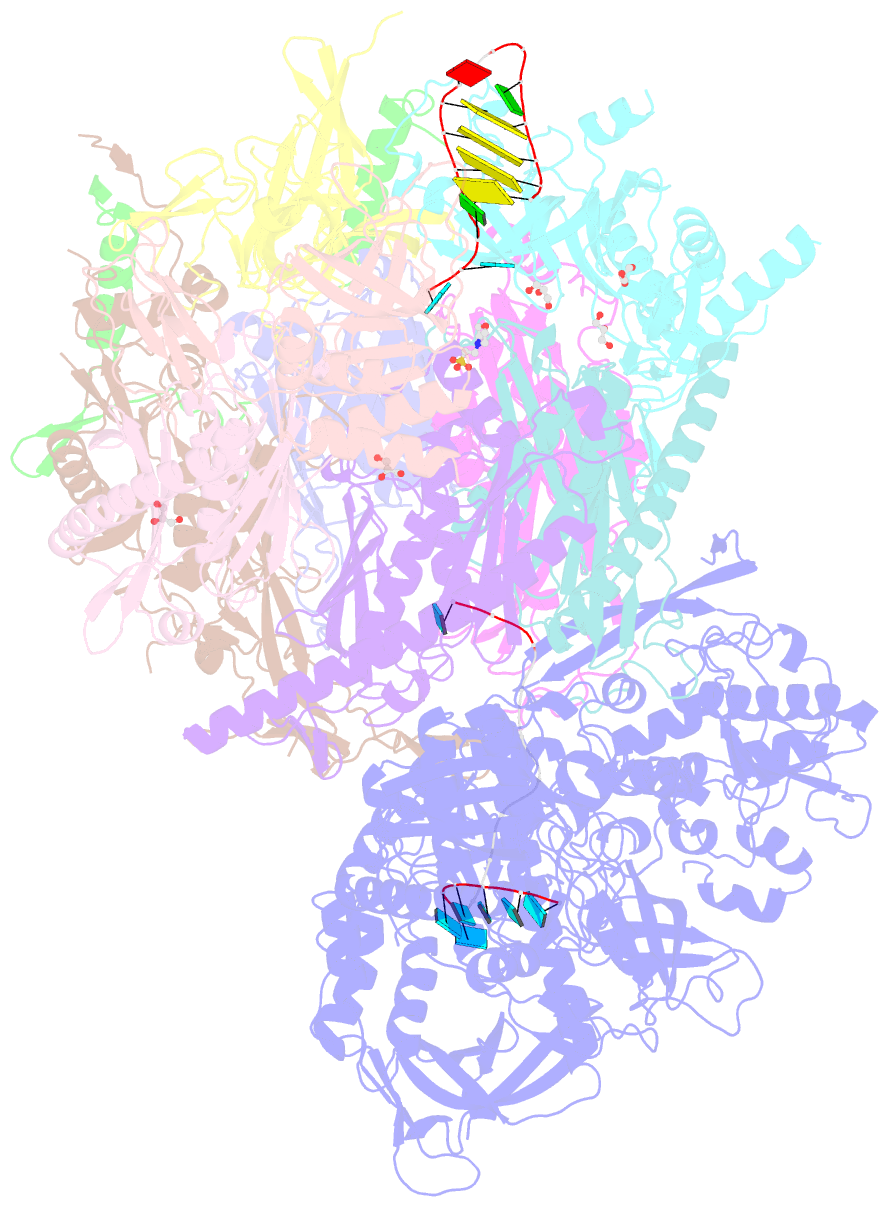
- Crystal structure of an 11-subunit eukaryotic exosome complex bound to RNA
- Reference
- Makino DL, Baumgartner M, Conti E (2013): "Crystal structure of an RNA-bound 11-subunit eukaryotic exosome complex." Nature, 495, 70-75. doi: 10.1038/nature11870.
- Abstract
- The exosome is the major 3'-5' RNA-degradation complex in eukaryotes. The ubiquitous core of the yeast exosome (Exo-10) is formed by nine catalytically inert subunits (Exo-9) and a single active RNase, Rrp44. In the nucleus, the Exo-10 core recruits another nuclease, Rrp6. Here we crystallized an approximately 440-kilodalton complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Exo-10 bound to a carboxy-terminal region of Rrp6 and to an RNA duplex with a 3'-overhang of 31 ribonucleotides. The 2.8 Å resolution structure shows how RNA is funnelled into the Exo-9 channel in a single-stranded conformation by an unwinding pore. Rrp44 adopts a closed conformation and captures the RNA 3'-end that exits from the side of Exo-9. Exo-9 subunits bind RNA with sequence-unspecific interactions reminiscent of archaeal exosomes. The substrate binding and channelling mechanisms of 3'-5' RNA degradation complexes are conserved in all kingdoms of life.