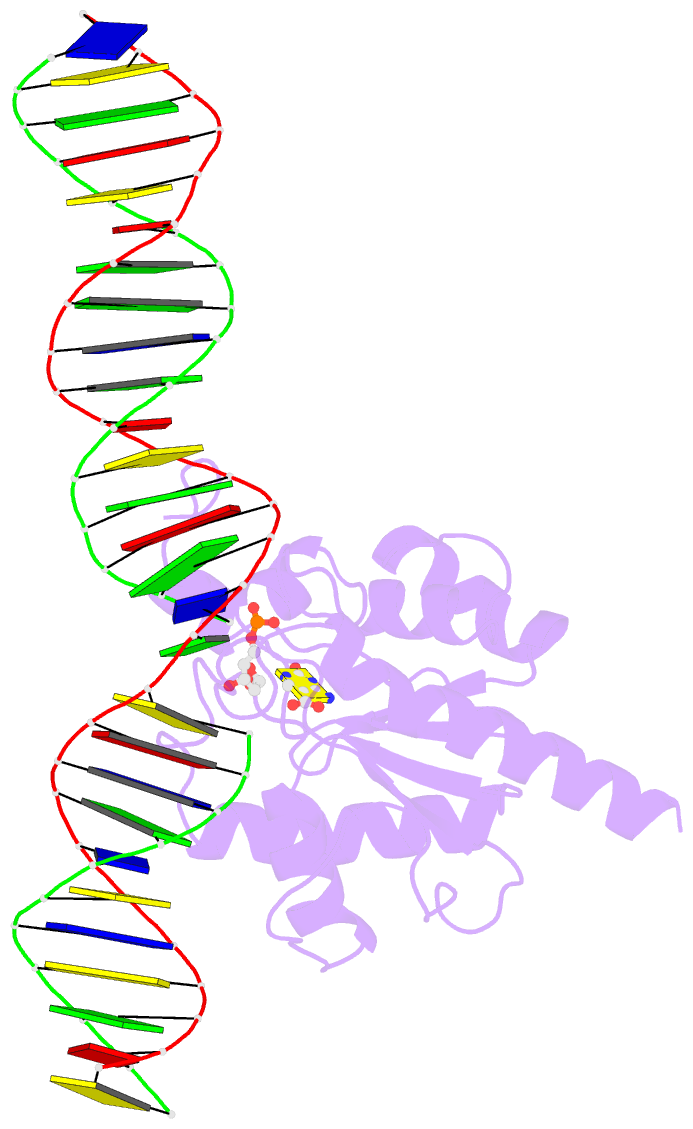
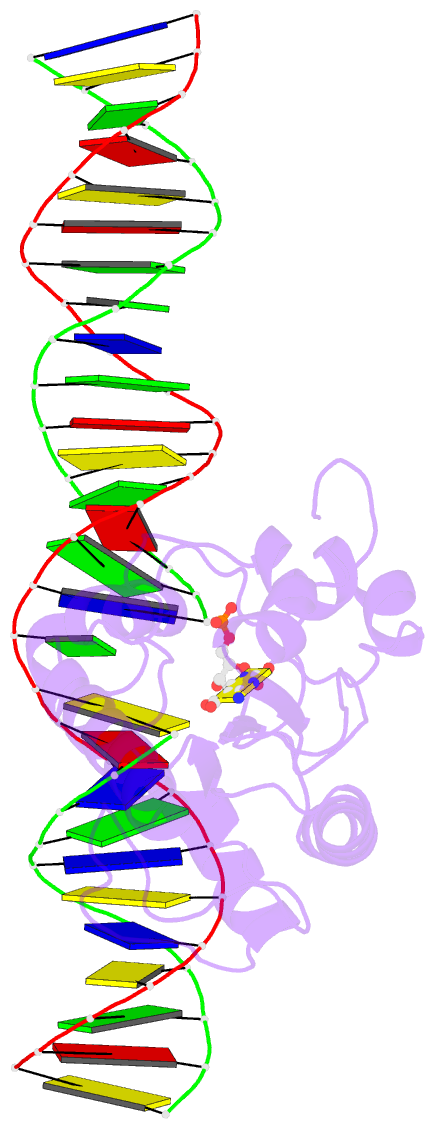
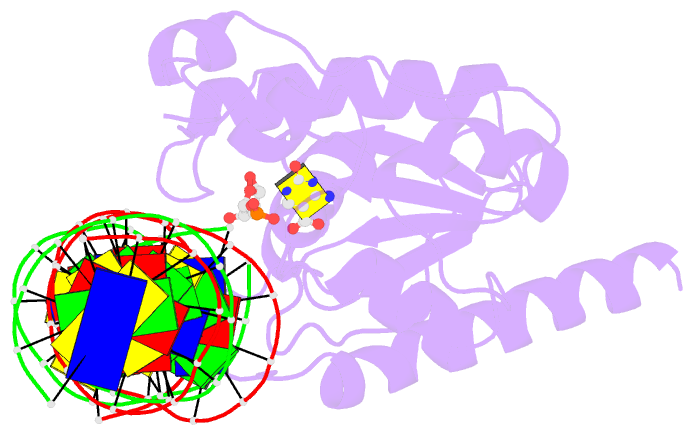
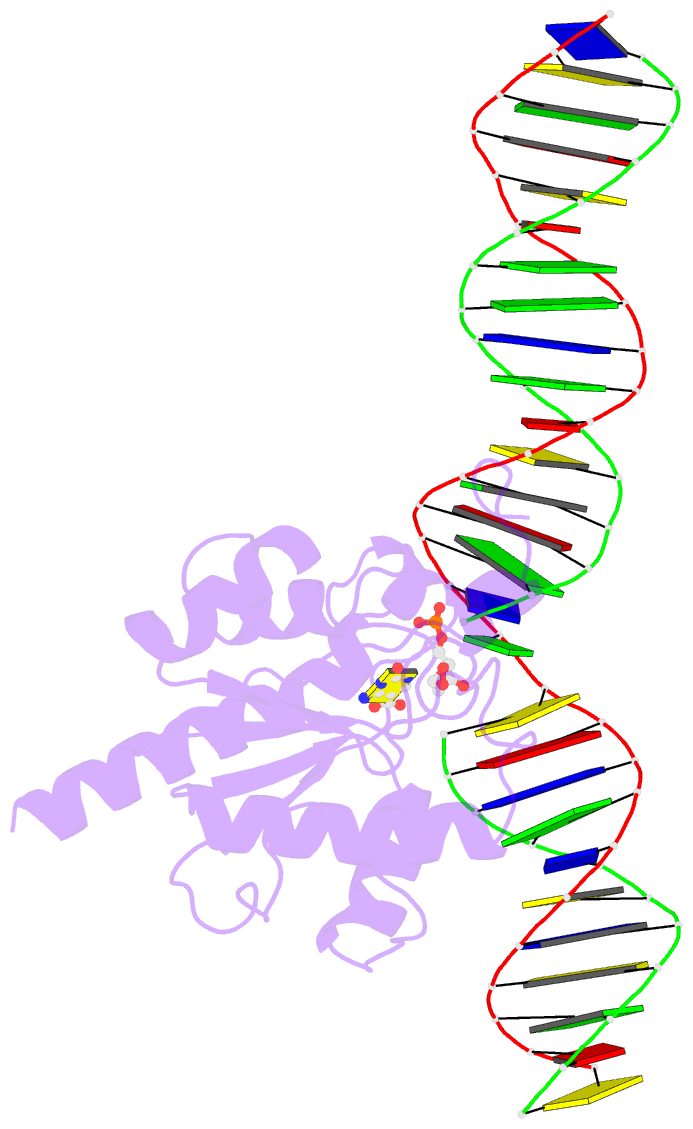
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4jgc; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.582 Å)
- Summary
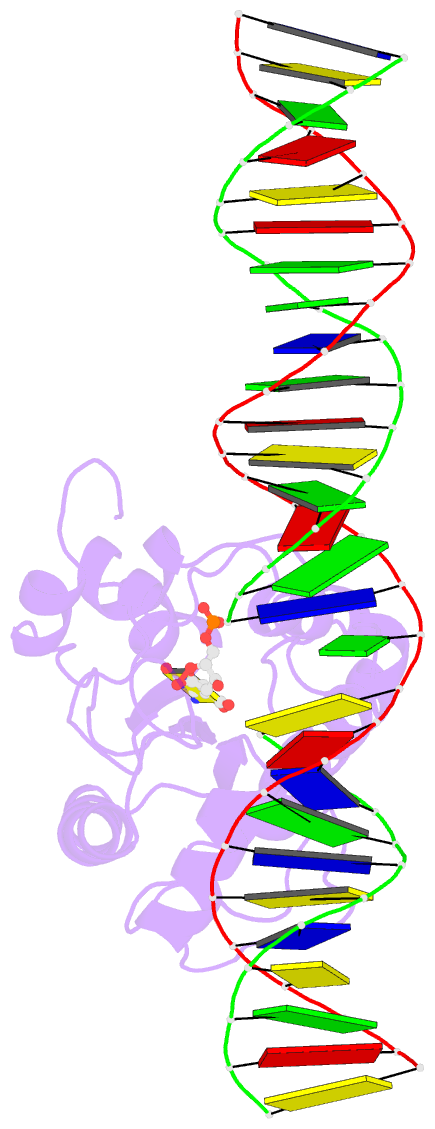
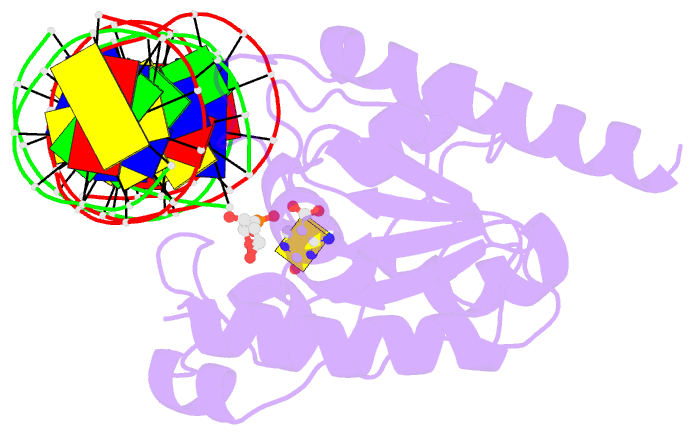
- Human tdg n140a mutant in a complex with 5-carboxylcytosine (5cac)
- Reference
- Hashimoto H, Zhang X, Cheng X (2013): "Activity and crystal structure of human thymine DNA glycosylase mutant N140A with 5-carboxylcytosine DNA at low pH." Dna Repair, 12, 535-540. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.04.003.
- Abstract
- The mammalian thymine DNA glycosylase (TDG) excises 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC) when paired with a guanine in a CpG sequence, in addition to mismatched bases. Here we present a complex structure of the human TDG catalytic mutant, asparagine 140 to alanine (N140A), with a 28-base pair DNA containing a G:5caC pair at pH 4.6. TDG interacts with the carboxylate moiety of target nucleotide 5caC using the side chain of asparagine 230 (N230), instead of asparagine 157 (N157) as previously reported. Mutation of either N157 or N230 residues to aspartate has minimal effect on G:5caC activity while significantly reducing activity on G:U substrate. Combination of both the asparagine-to-aspartate mutations (N157D/N230D) resulted in complete loss of activity on G:5caC while retaining measurable activity on G:U, implying that 5caC can adopt alternative conformations (either N157-interacting or N230-interacting) in the TDG active site to interact with either of the two asparagine side chain for 5caC excision.