Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4o6a; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.859 Å)
- Summary
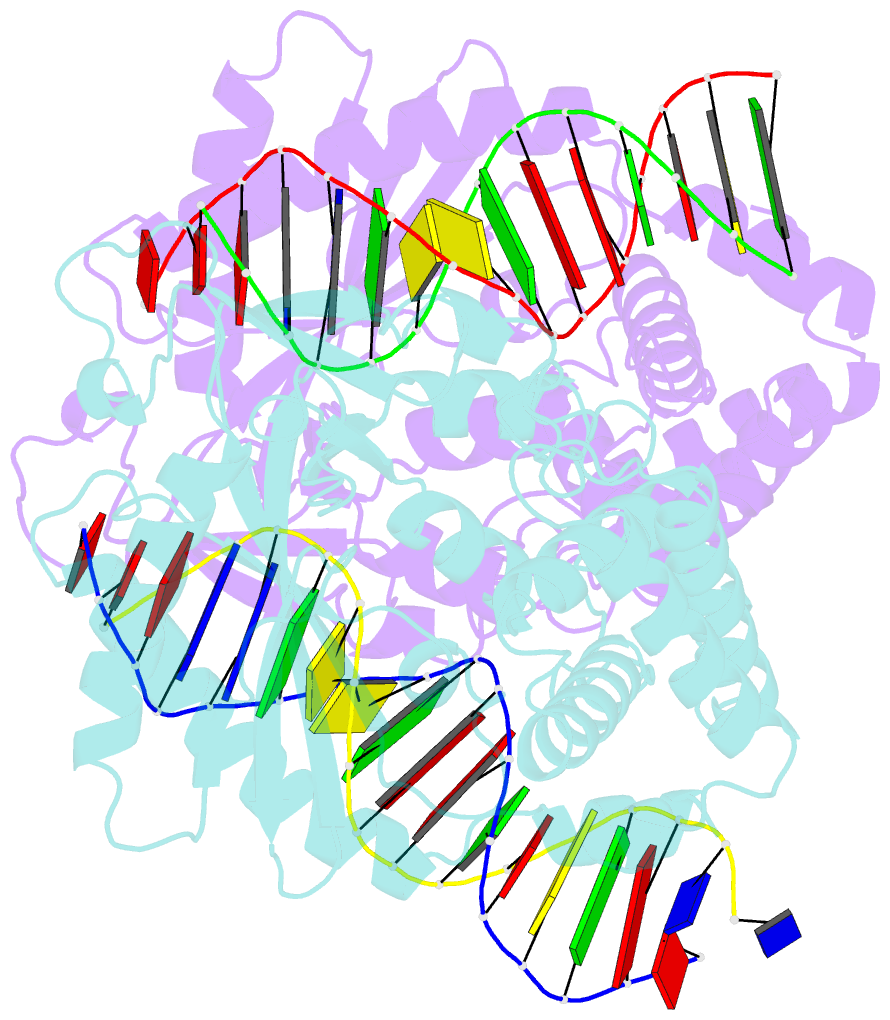
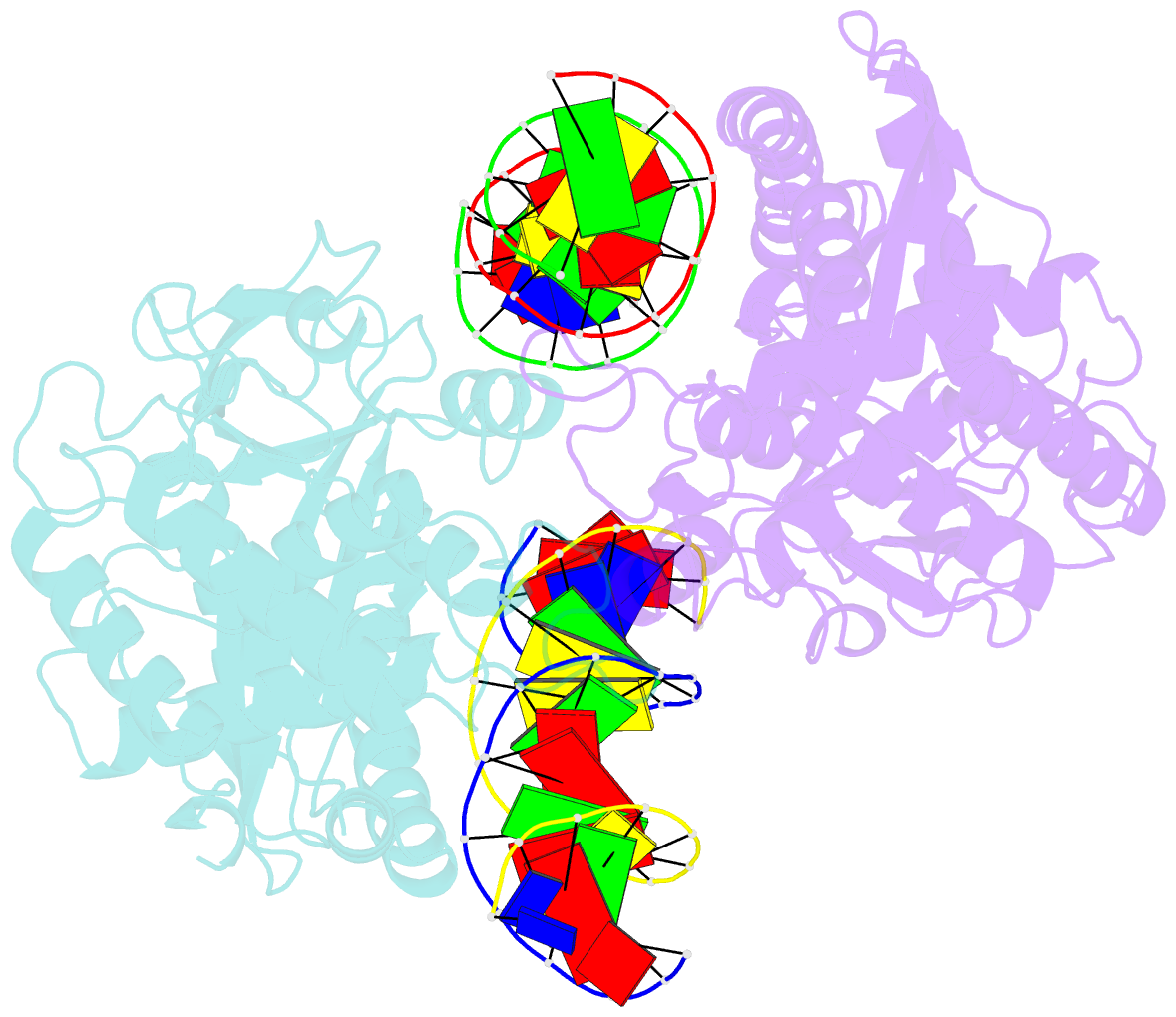
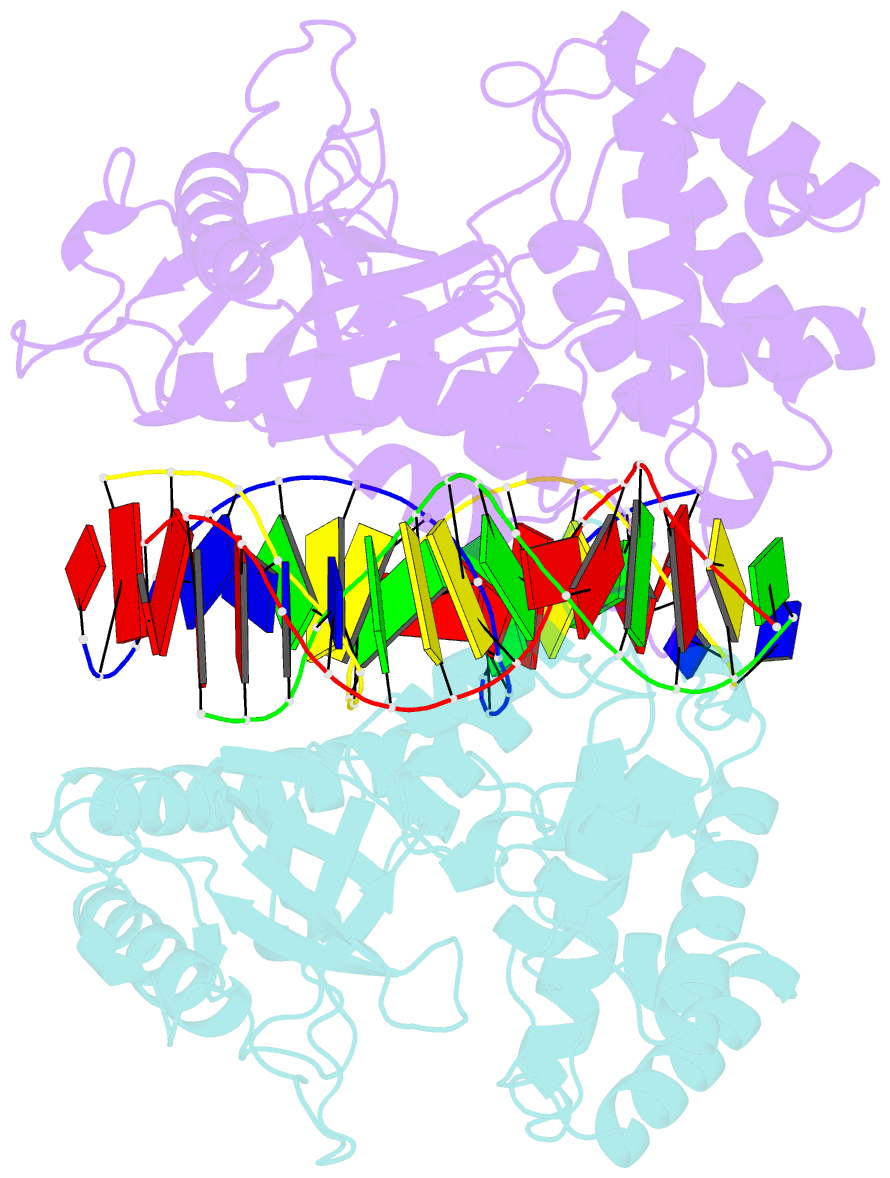
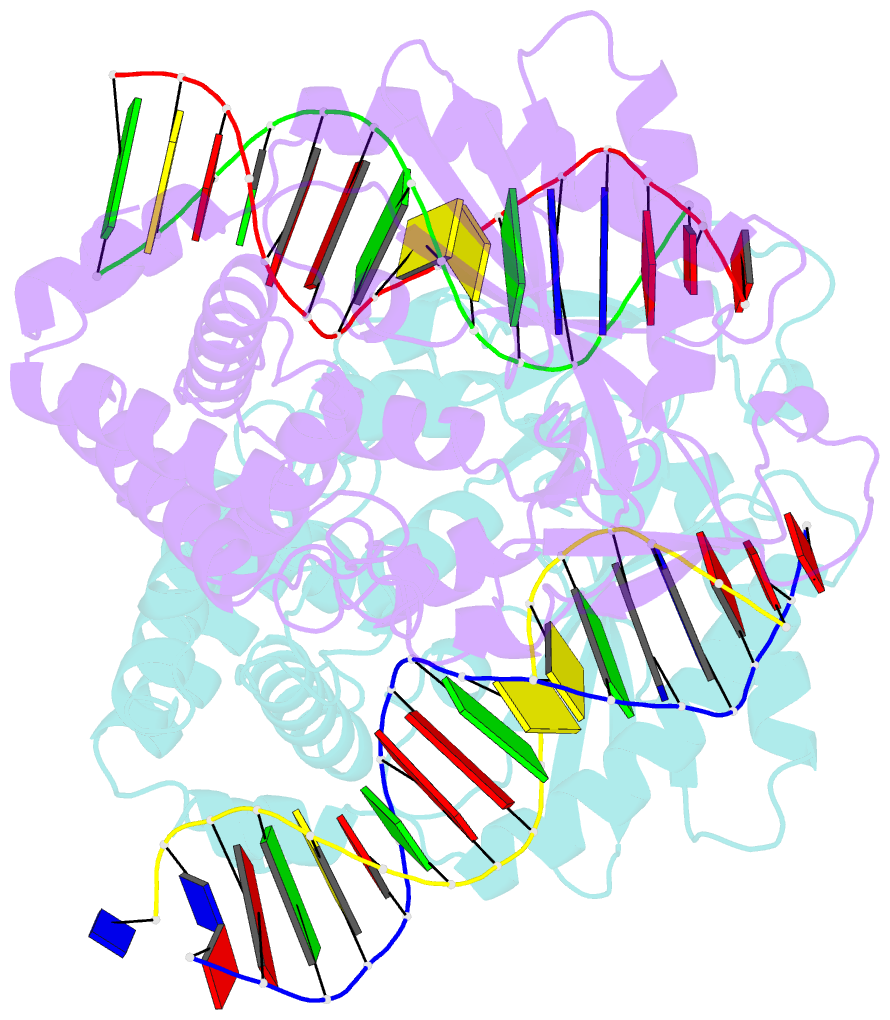
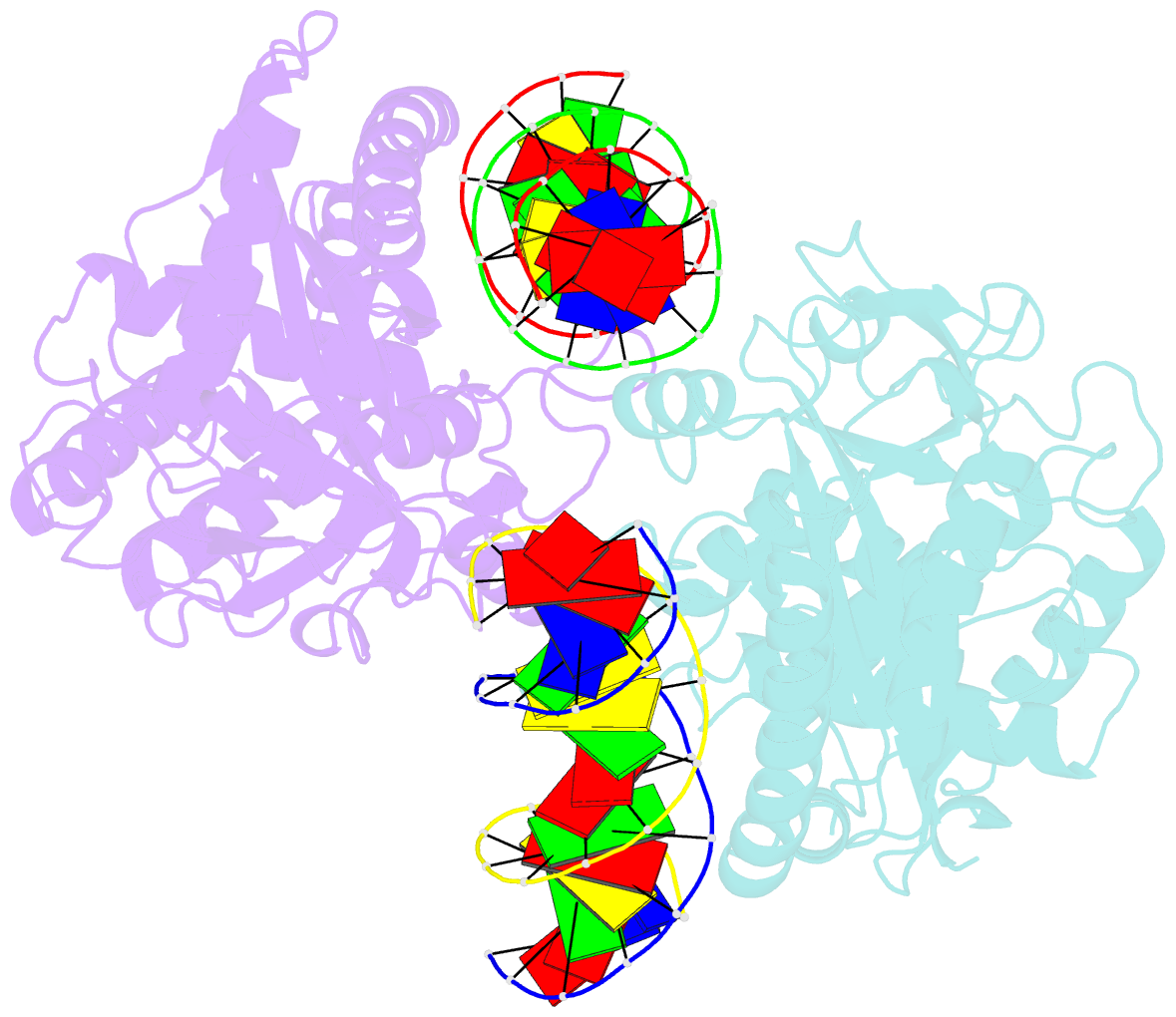
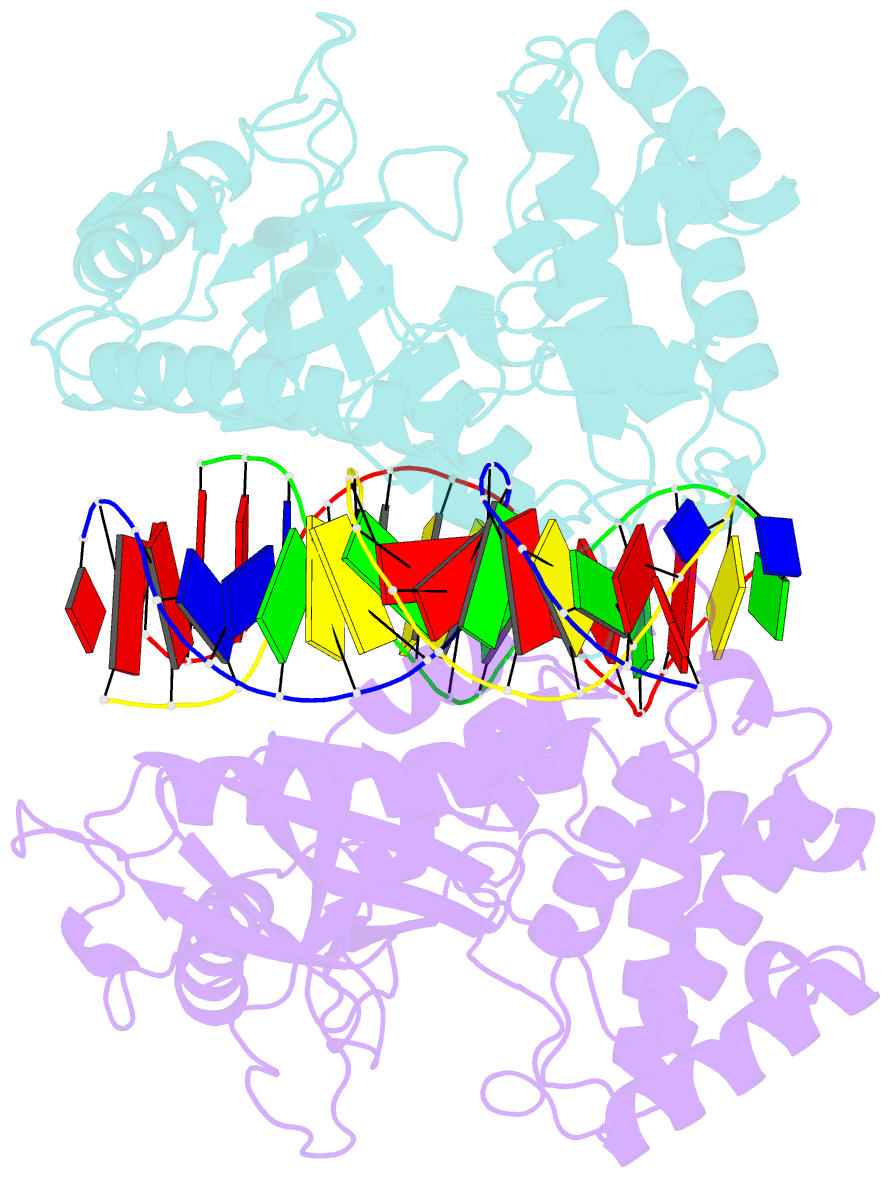
- Mouse cyclic gmp-amp synthase (cgas) in complex with DNA
- Reference
- Zhang X, Wu J, Du F, Xu H, Sun L, Chen Z, Brautigam CA, Zhang X, Chen ZJ (2014): "The Cytosolic DNA Sensor cGAS Forms an Oligomeric Complex with DNA and Undergoes Switch-like Conformational Changes in the Activation Loop." Cell Rep, 6, 421-430. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.01.003.
- Abstract
- The presence of DNA in the cytoplasm is a danger signal that triggers immune and inflammatory responses. Cytosolic DNA binds to and activates cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS), which produces the second messenger cGAMP. cGAMP binds to the adaptor protein STING and activates a signaling cascade that leads to the production of type I interferons and other cytokines. Here, we report the crystal structures of human cGAS in its apo form, representing its autoinhibited conformation as well as in its cGAMP- and sulfate-bound forms. These structures reveal switch-like conformational changes of an activation loop that result in the rearrangement of the catalytic site. The structure of DNA-bound cGAS reveals a complex composed of dimeric cGAS bound to two molecules of DNA. Functional analyses of cGAS mutants demonstrate that both the protein-protein interface and the two DNA binding surfaces are critical for cGAS activation. These results provide insights into the mechanism of DNA sensing by cGAS.