Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4oav; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.1 Å)
- Summary
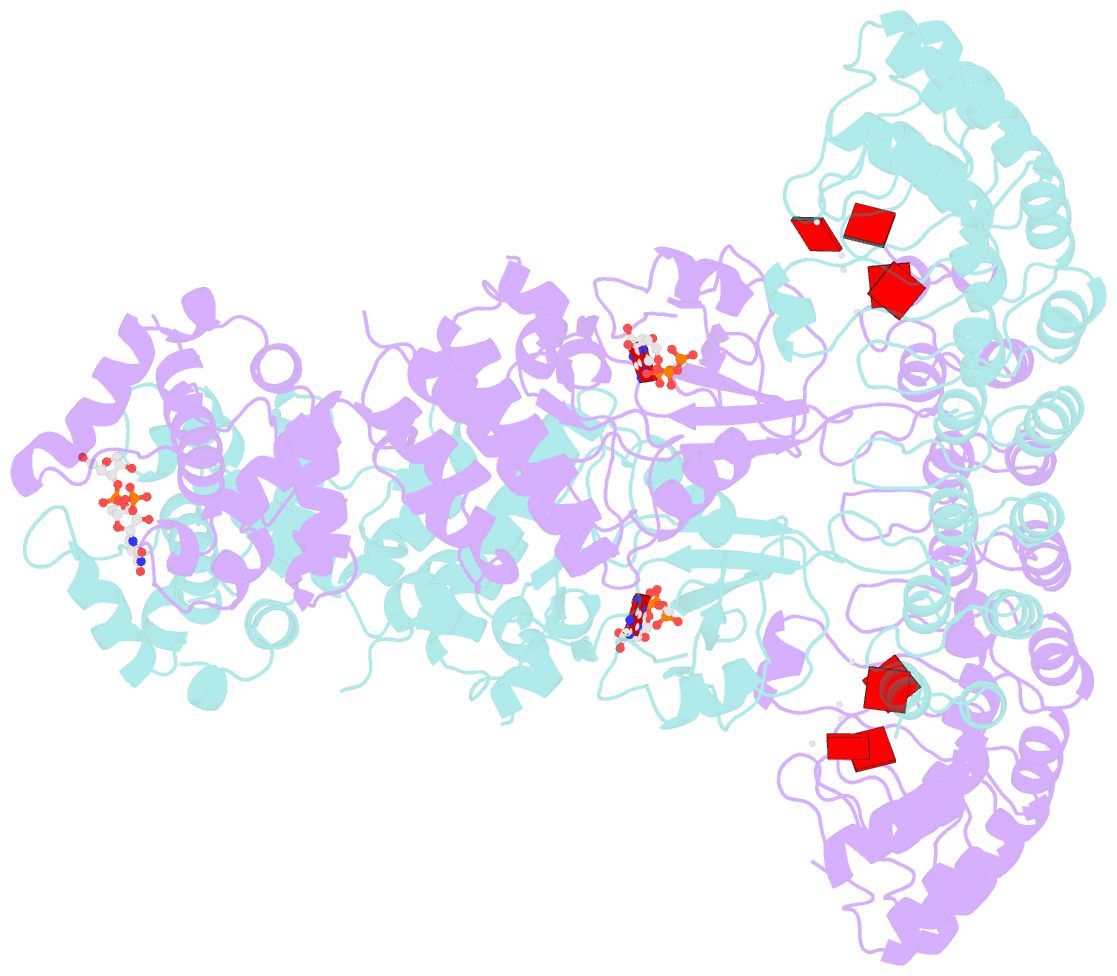
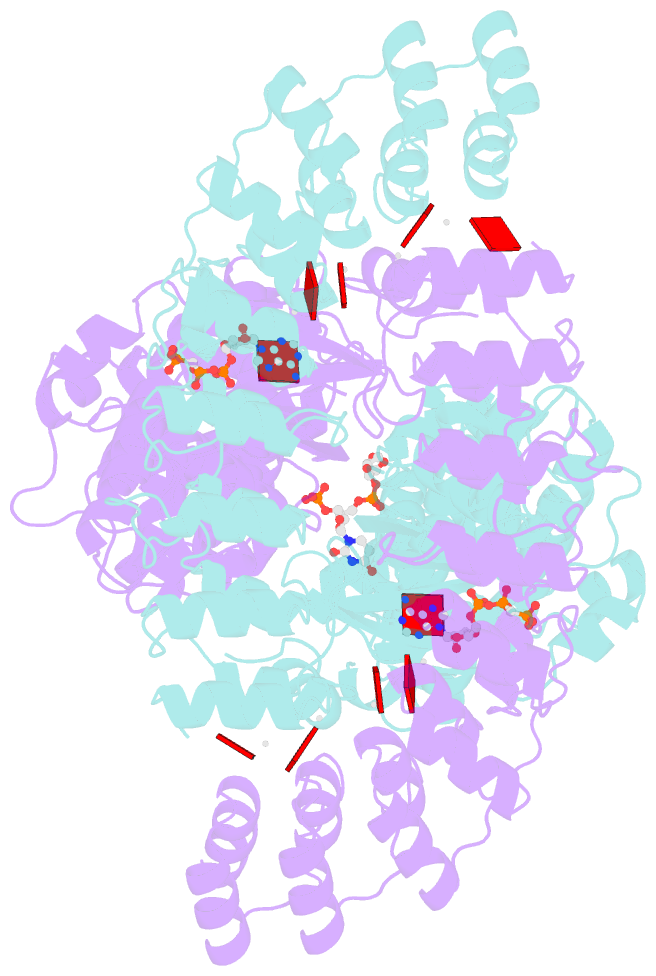
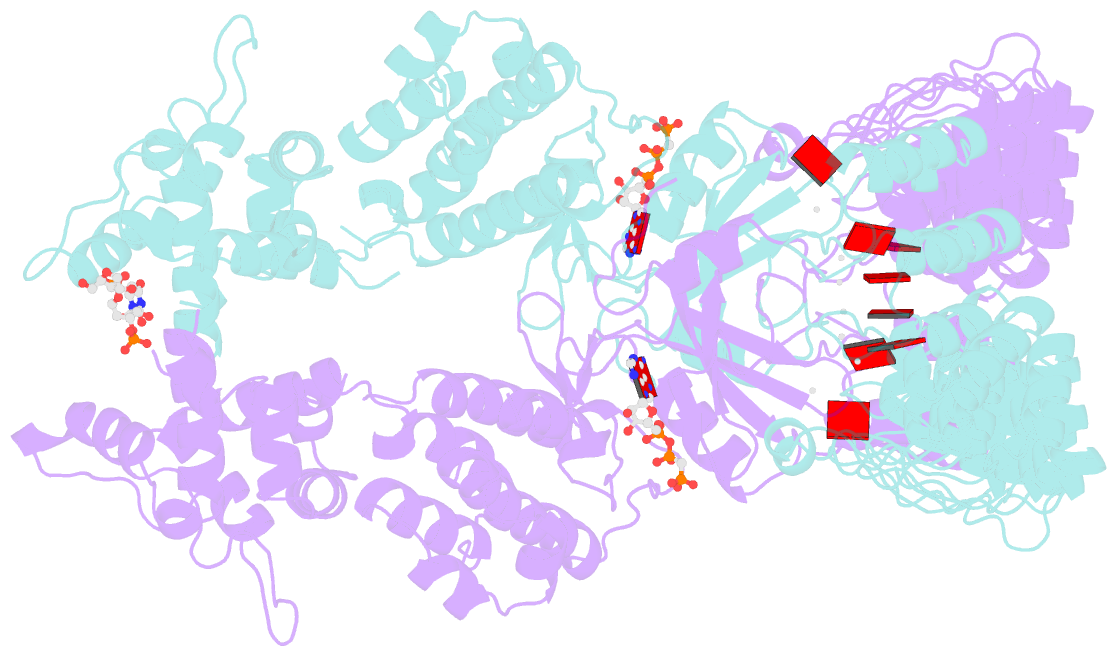
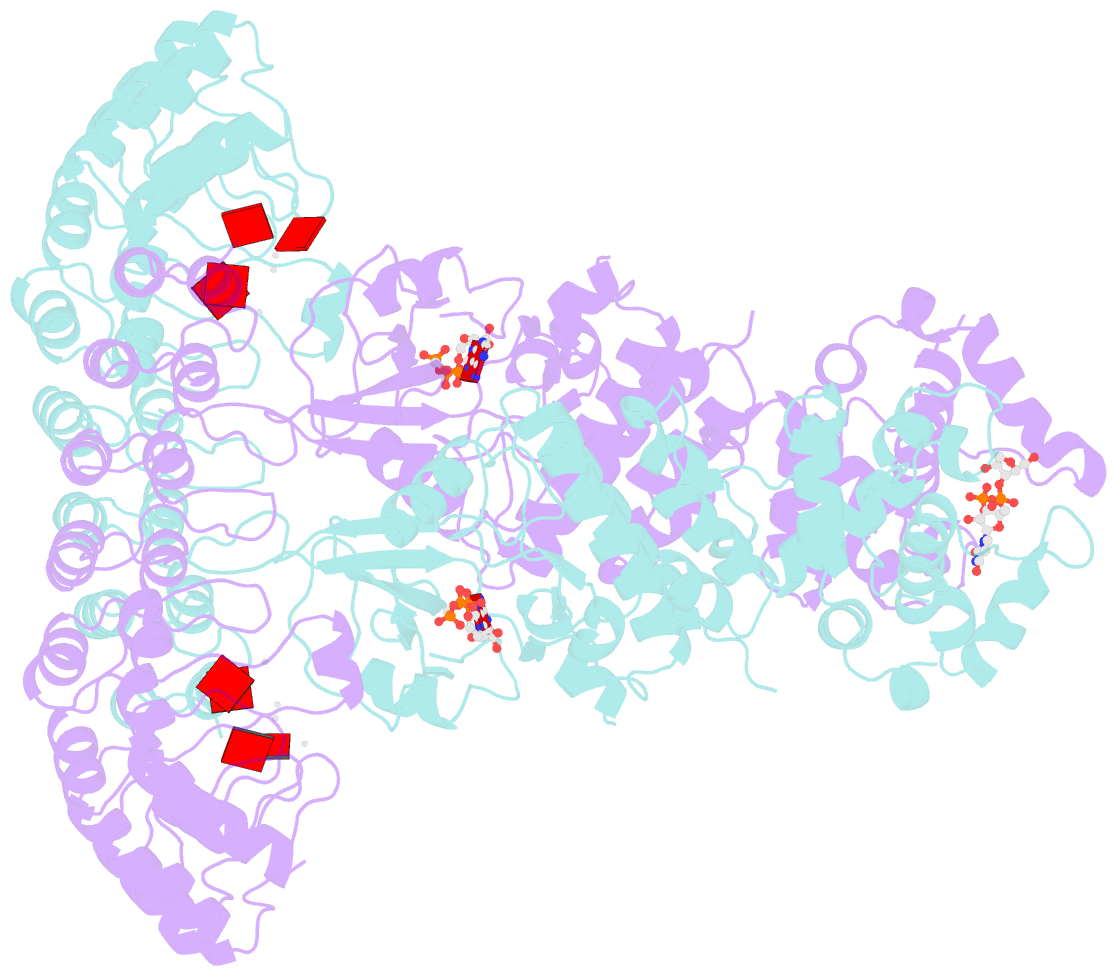
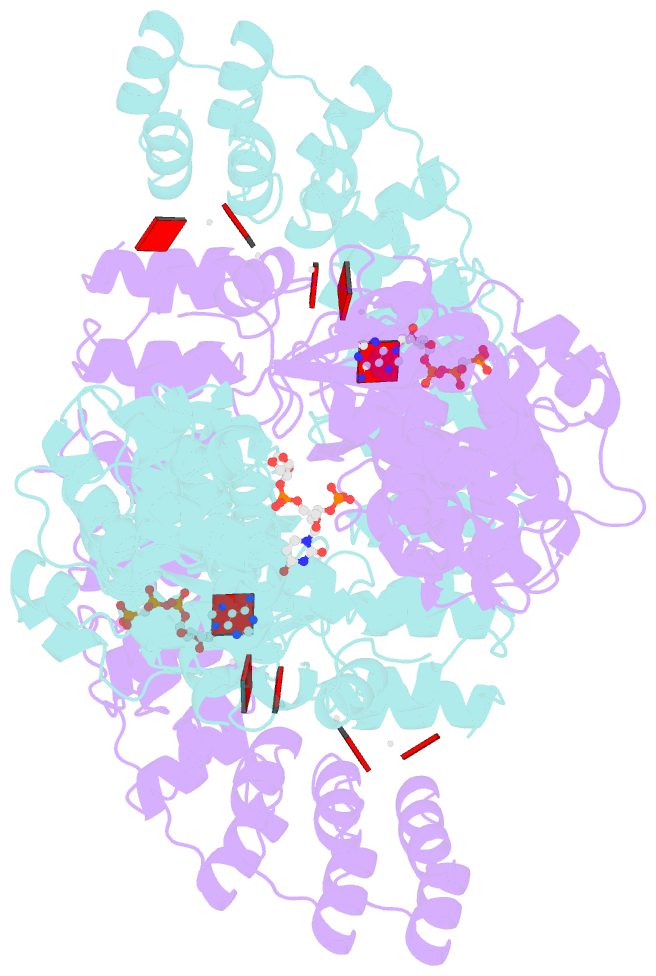
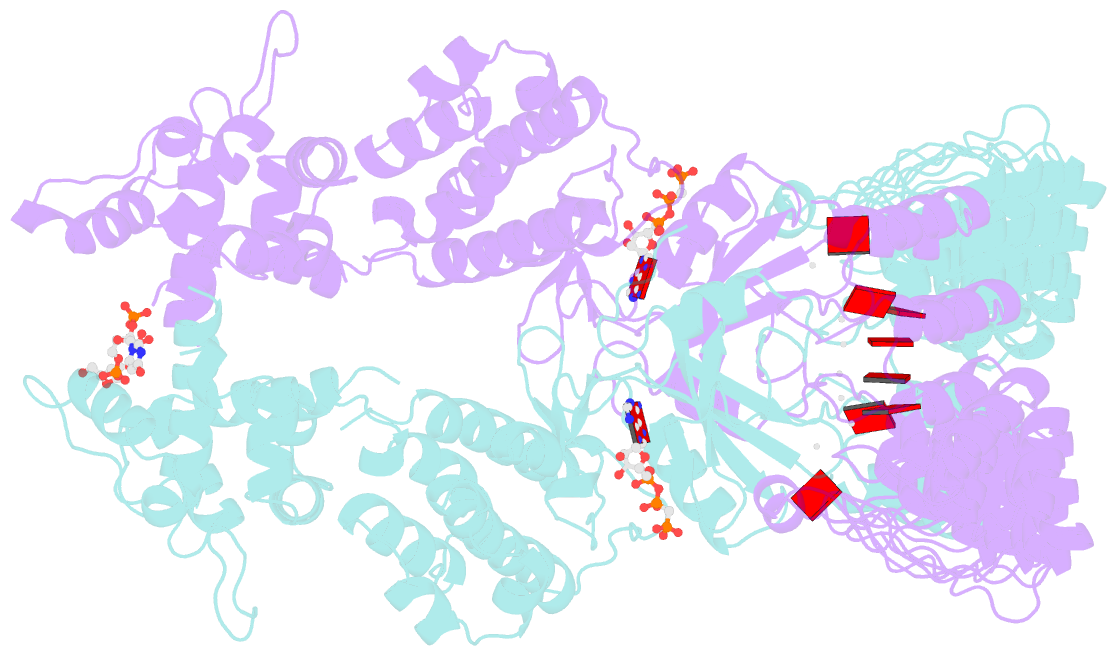
- Complete human rnase l in complex with 2-5a (5'-ppp heptamer), amppcp and RNA substrate.
- Reference
- Han Y, Donovan J, Rath S, Whitney G, Chitrakar A, Korennykh A (2014): "Structure of human RNase L reveals the basis for regulated RNA decay in the IFN response." Science, 343, 1244-1248. doi: 10.1126/science.1249845.
- Abstract
- One of the hallmark mechanisms activated by type I interferons (IFNs) in human tissues involves cleavage of intracellular RNA by the kinase homology endoribonuclease RNase L. We report 2.8 and 2.1 angstrom crystal structures of human RNase L in complexes with synthetic and natural ligands and a fragment of an RNA substrate. RNase L forms a crossed homodimer stabilized by ankyrin (ANK) and kinase homology (KH) domains, which positions two kinase extension nuclease (KEN) domains for asymmetric RNA recognition. One KEN protomer recognizes an identity nucleotide (U), whereas the other protomer cleaves RNA between nucleotides +1 and +2. The coordinated action of the ANK, KH, and KEN domains thereby provides regulated, sequence-specific cleavage of viral and host RNA targets by RNase L.
Cartoon-block schematics in six views