Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4q9r; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA-immune system
- Method
- X-ray (3.12 Å)
- Summary
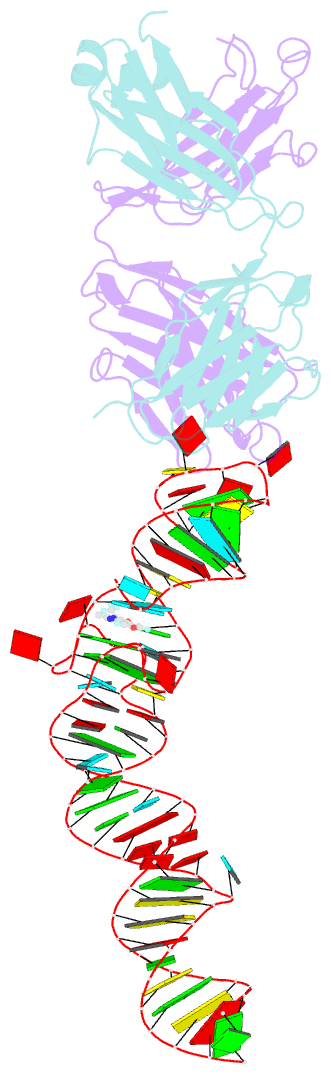
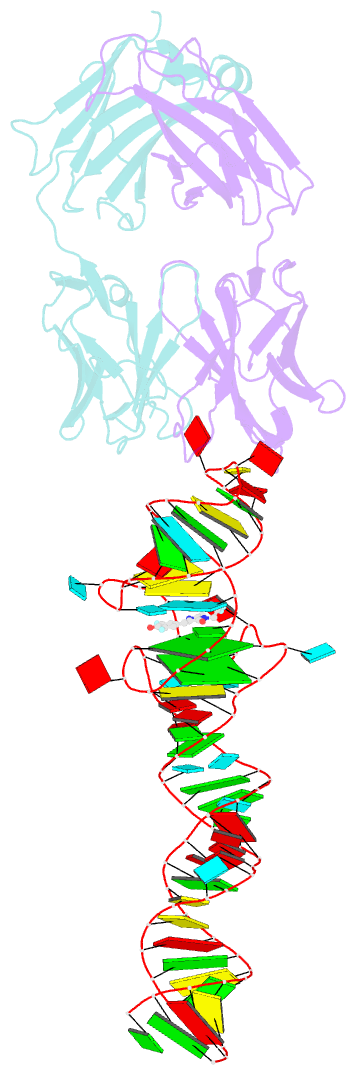
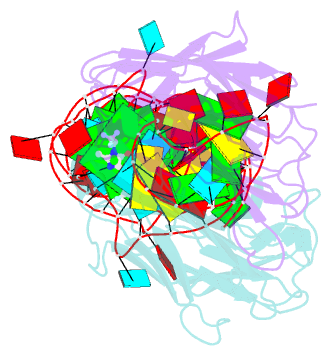
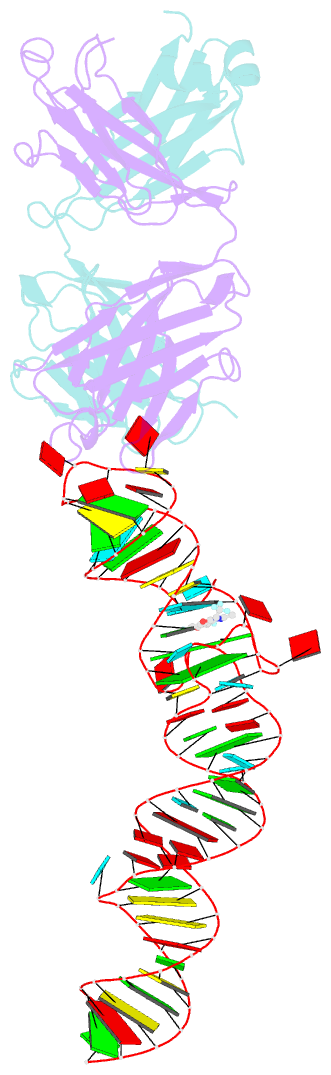
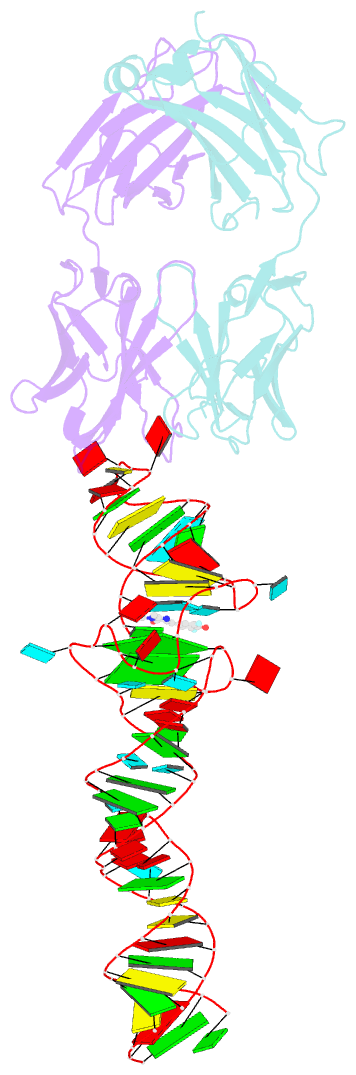
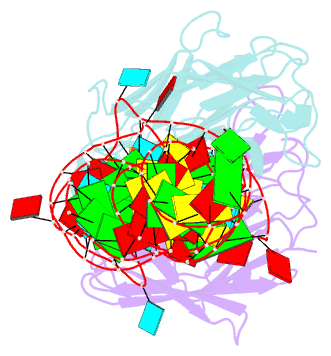
- Crystal structure of an RNA aptamer bound to trifluoroethyl-ligand analog in complex with fab
- Reference
- Huang H, Suslov NB, Li NS, Shelke SA, Evans ME, Koldobskaya Y, Rice PA, Piccirilli JA (2014): "A G-quadruplex-containing RNA activates fluorescence in a GFP-like fluorophore." Nat.Chem.Biol., 10, 686-691. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1561.
- Abstract
- Spinach is an in vitro-selected RNA aptamer that binds a GFP-like ligand and activates its green fluorescence. Spinach is thus an RNA analog of GFP and has potentially widespread applications for in vivo labeling and imaging. We used antibody-assisted crystallography to determine the structures of Spinach both with and without bound fluorophore at 2.2-Å and 2.4-Å resolution, respectively. Spinach RNA has an elongated structure containing two helical domains separated by an internal bulge that folds into a G-quadruplex motif of unusual topology. The G-quadruplex motif and adjacent nucleotides comprise a partially preformed binding site for the fluorophore. The fluorophore binds in a planar conformation and makes extensive aromatic stacking and hydrogen bond interactions with the RNA. Our findings provide a foundation for structure-based engineering of new fluorophore-binding RNA aptamers.