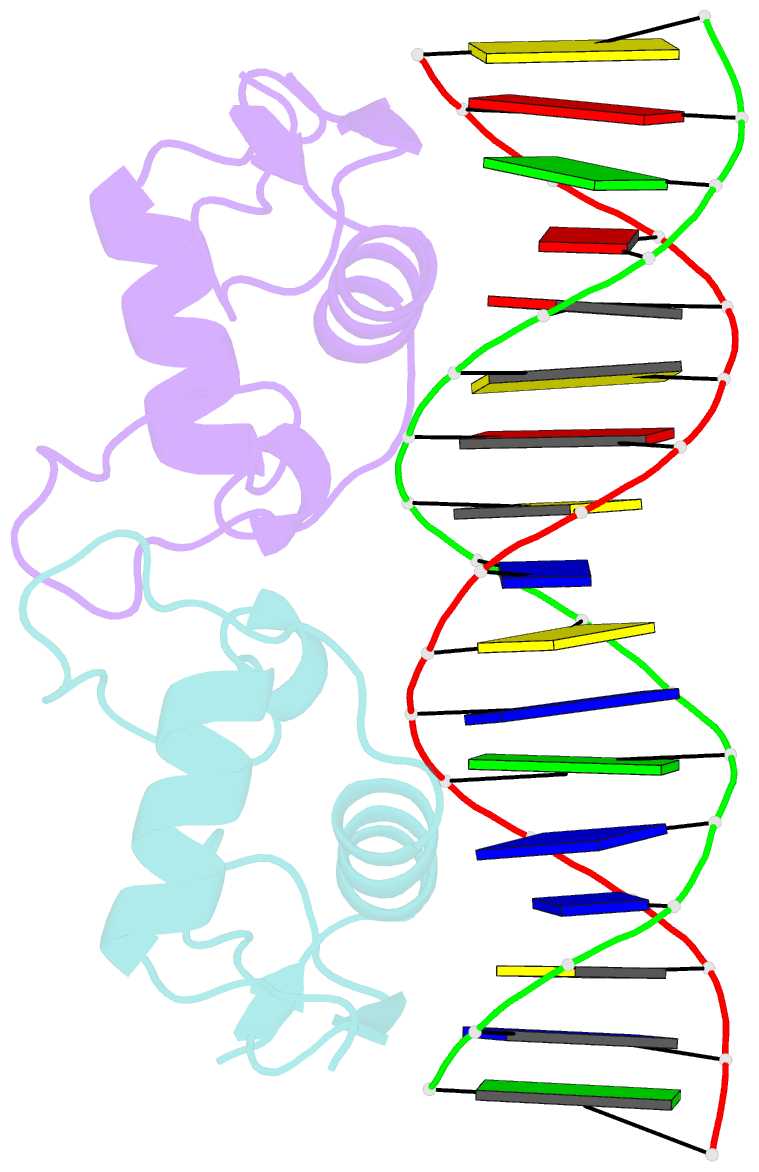
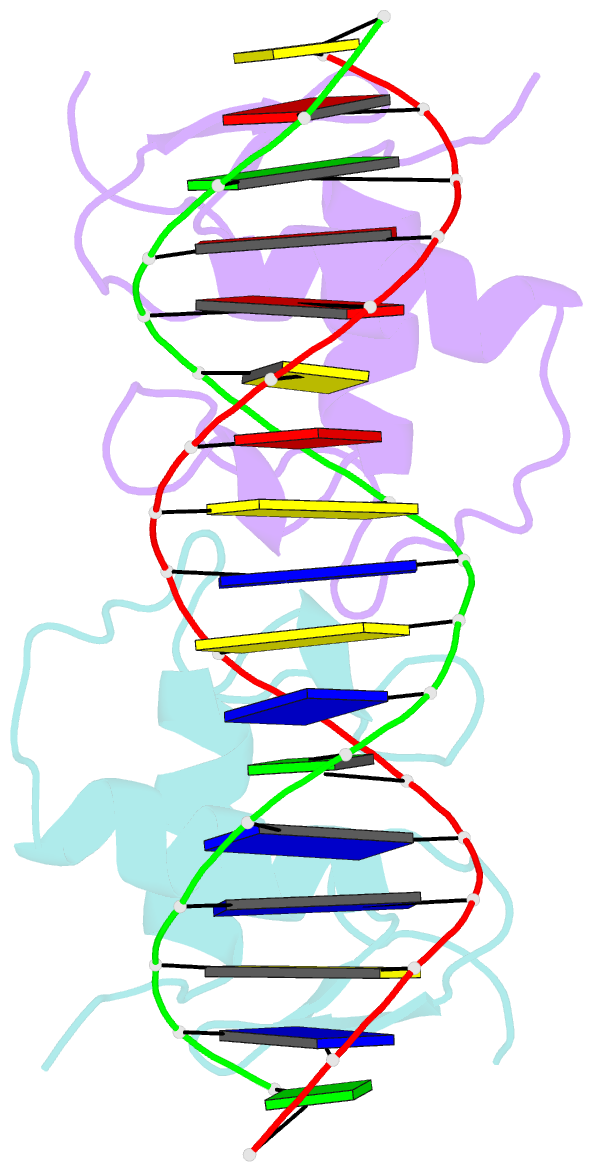
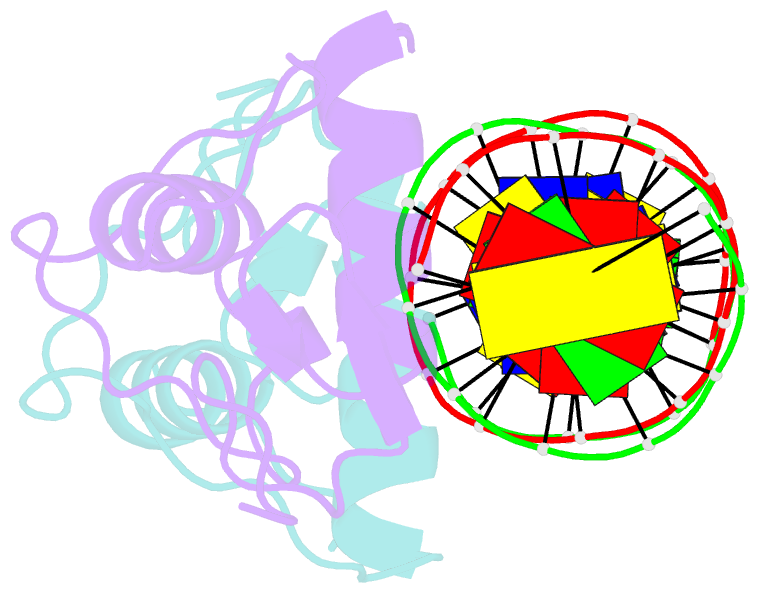
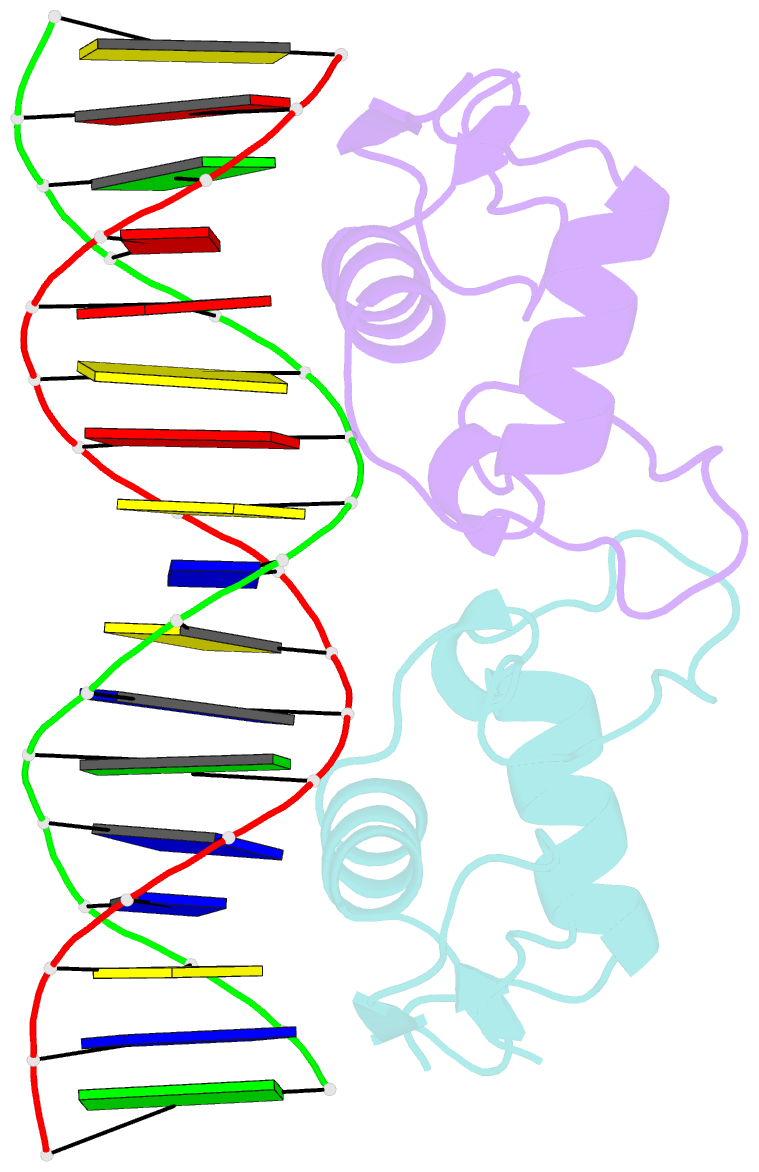
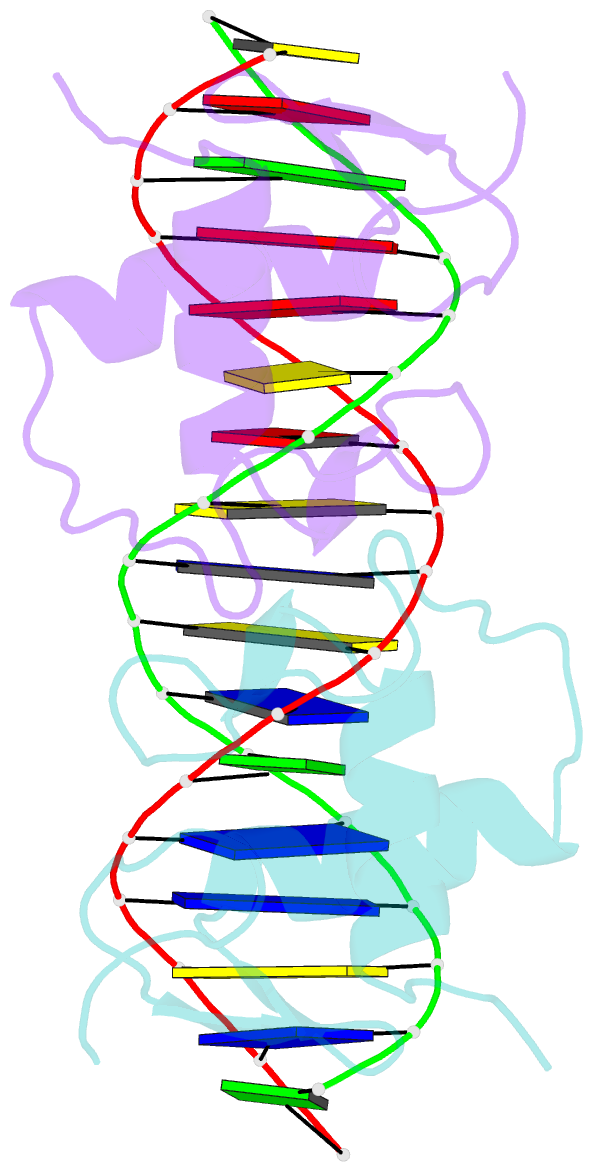
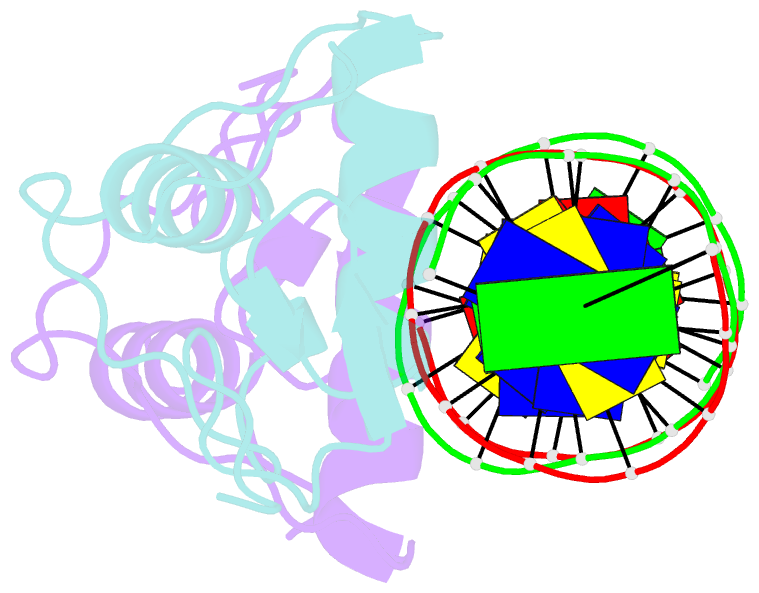
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4tnt; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.39 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of the human mineralocorticoid receptor in complex with DNA
- Reference
- Hudson WH, Youn C, Ortlund EA (2014): "Crystal structure of the mineralocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain in complex with DNA." Plos One, 9, e107000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107000.
- Abstract
- The steroid hormone receptors regulate important physiological functions such as reproduction, metabolism, immunity, and electrolyte balance. Mutations within steroid receptors result in endocrine disorders and can often drive cancer formation and progression. Despite the conserved three-dimensional structure shared among members of the steroid receptor family and their overlapping DNA binding preference, activation of individual steroid receptors drive unique effects on gene expression. Here, we present the first structure of the human mineralocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain, in complex with a canonical DNA response element. The overall structure is similar to the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain, but small changes in the mode of DNA binding and lever arm conformation may begin to explain the differential effects on gene regulation by the mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors. In addition, we explore the structural effects of mineralocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain mutations found in type I pseudohypoaldosteronism and multiple types of cancer.