Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4tzv; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
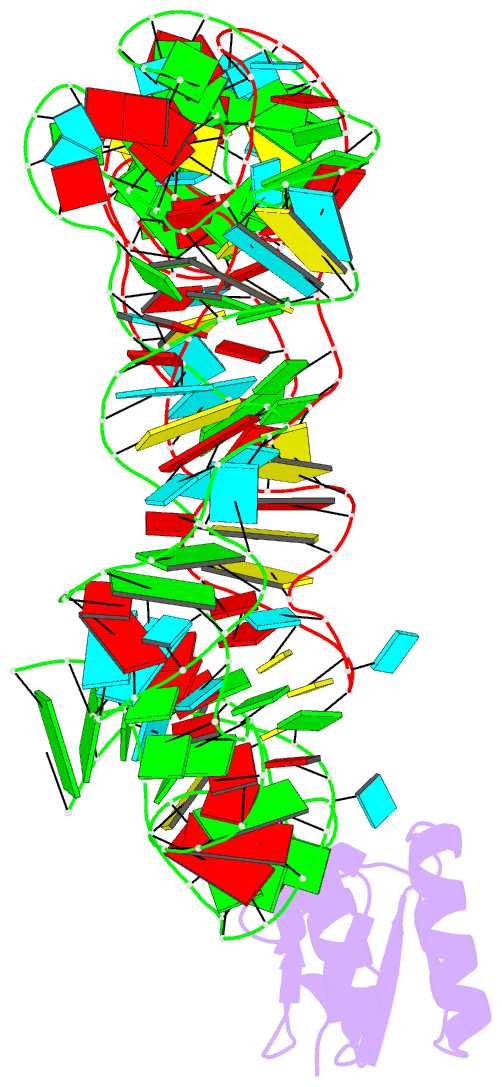
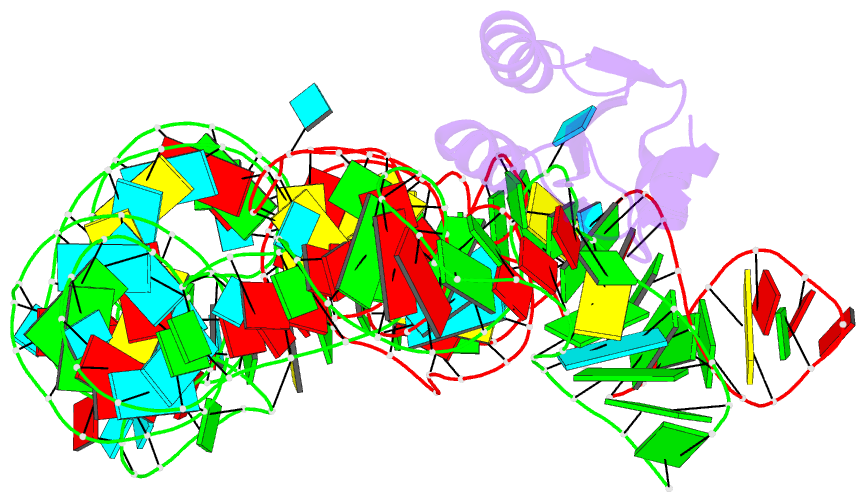
- ribosomal protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (5.03 Å)
- Summary
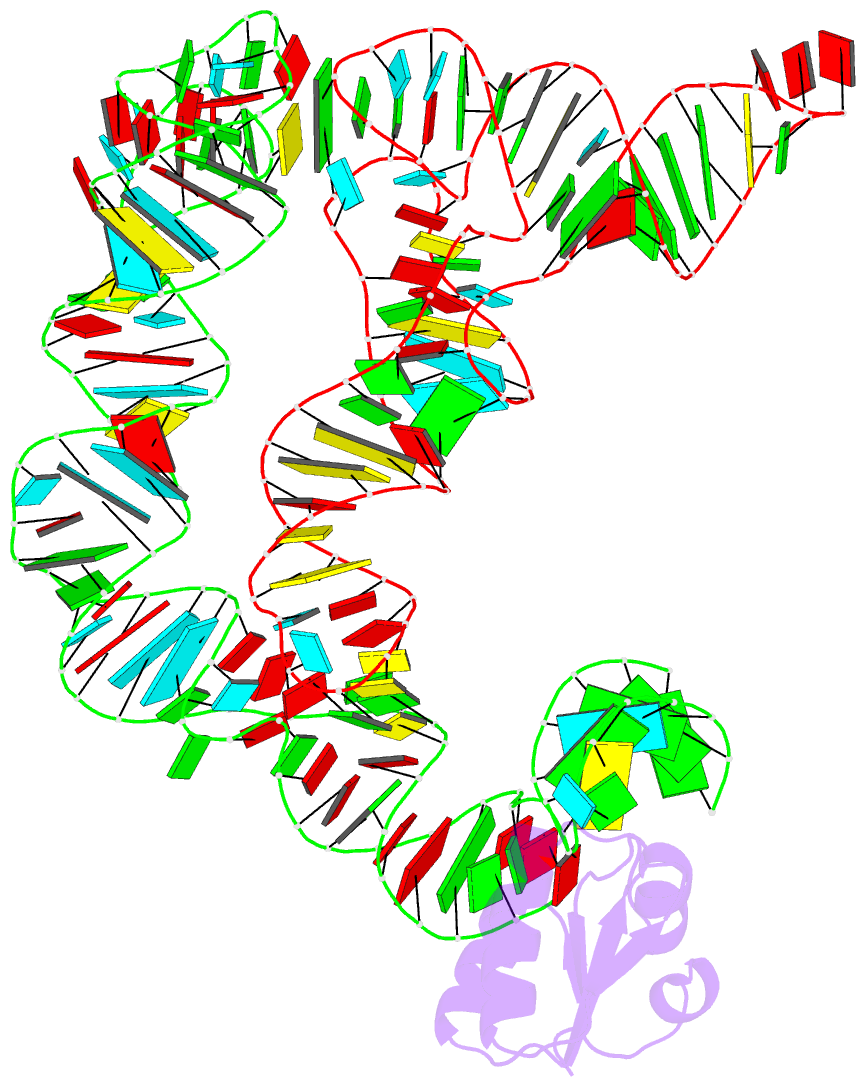
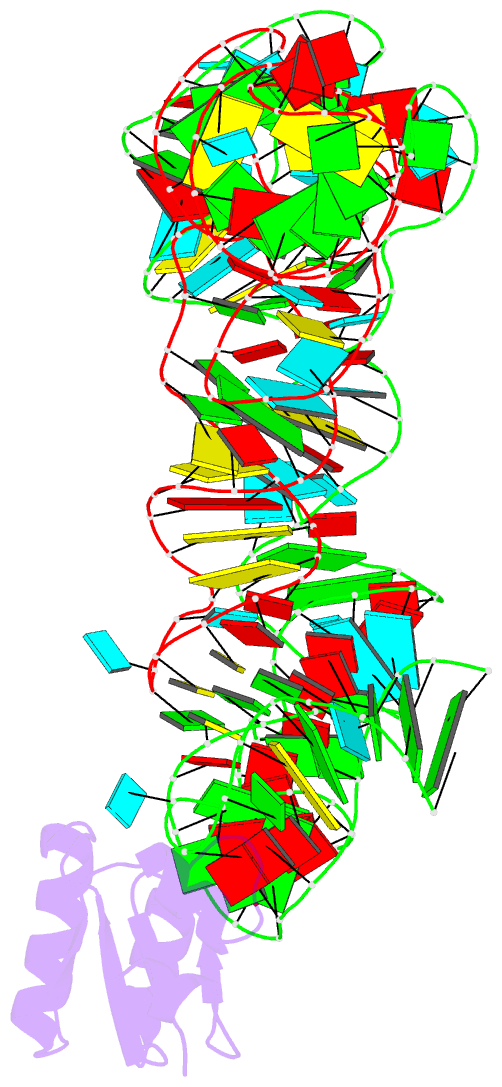
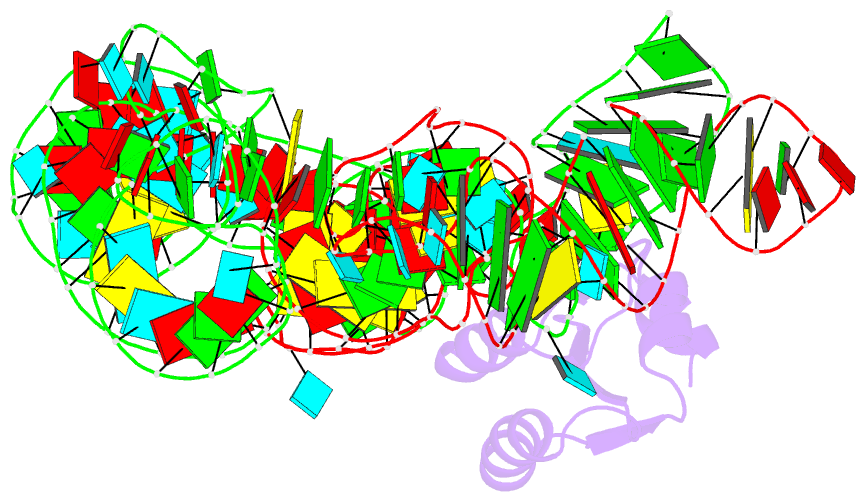
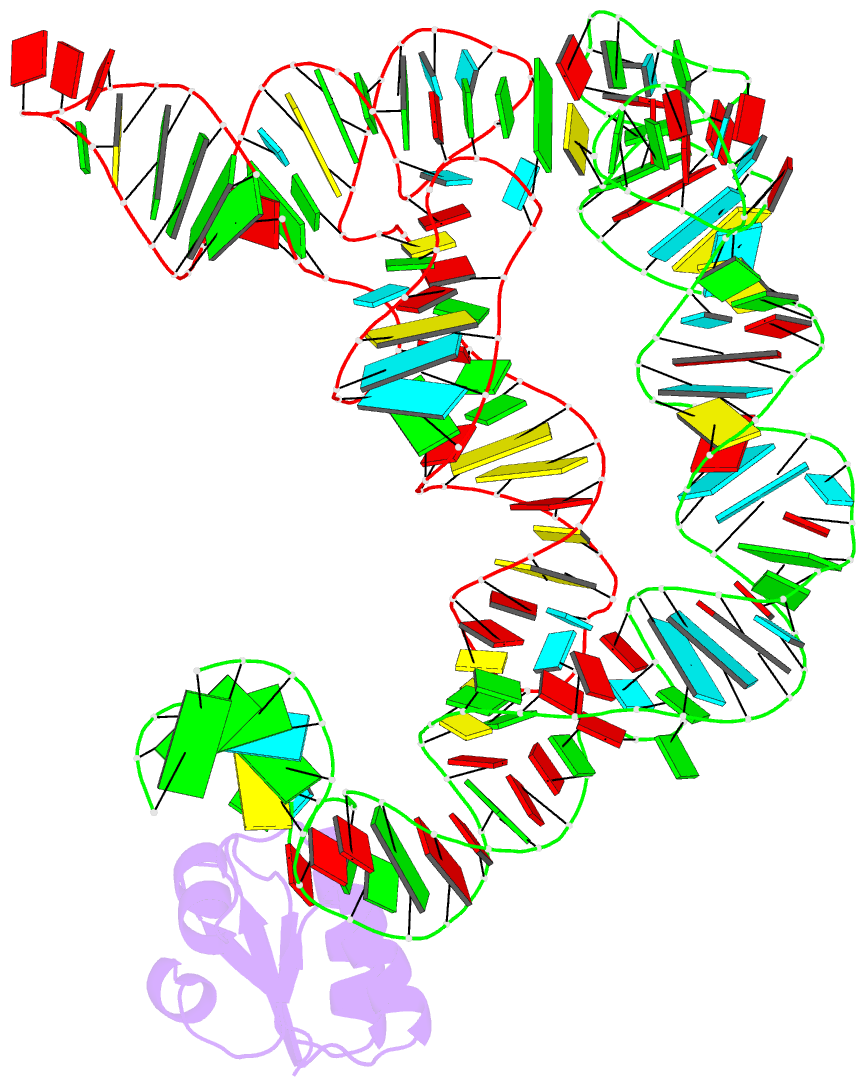
- Co-crystals of the ternary complex containing a t-box stem i RNA, its cognate trnagly, and b. subtilis ybxf protein, treated by removing lithium sulfate post crystallization
- Reference
- Zhang J, Ferre-D'Amare AR (2014): "Dramatic Improvement of Crystals of Large RNAs by Cation Replacement and Dehydration." Structure, 22, 1363-1371. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.07.011.
- Abstract
- Compared to globular proteins, RNAs with complex 3D folds are characterized by poorly differentiated molecular surfaces dominated by backbone phosphates, sparse tertiary contacts stabilizing global architecture, and conformational flexibility. The resulting generally poor order of crystals of large RNAs and their complexes frequently hampers crystallographic structure determination. We describe and rationalize a postcrystallization treatment strategy that exploits the importance of solvation and counterions for RNA folding. Replacement of Li(+) and Mg(2+) needed for growth of crystals of a tRNA-riboswitch-protein complex with Sr(2+), coupled with dehydration, dramatically improved the resolution limit (8.5-3.2 Å) and data quality, enabling structure determination. The soft Sr(2+) ion forms numerous stabilizing intermolecular contacts. Comparison of pre- and posttreatment structures reveals how RNA assemblies redistribute as quasi-rigid bodies to yield improved crystal packing. Cation exchange complements previously reported postcrystallization dehydration of protein crystals and represents a potentially general strategy for improving crystals of large RNAs.