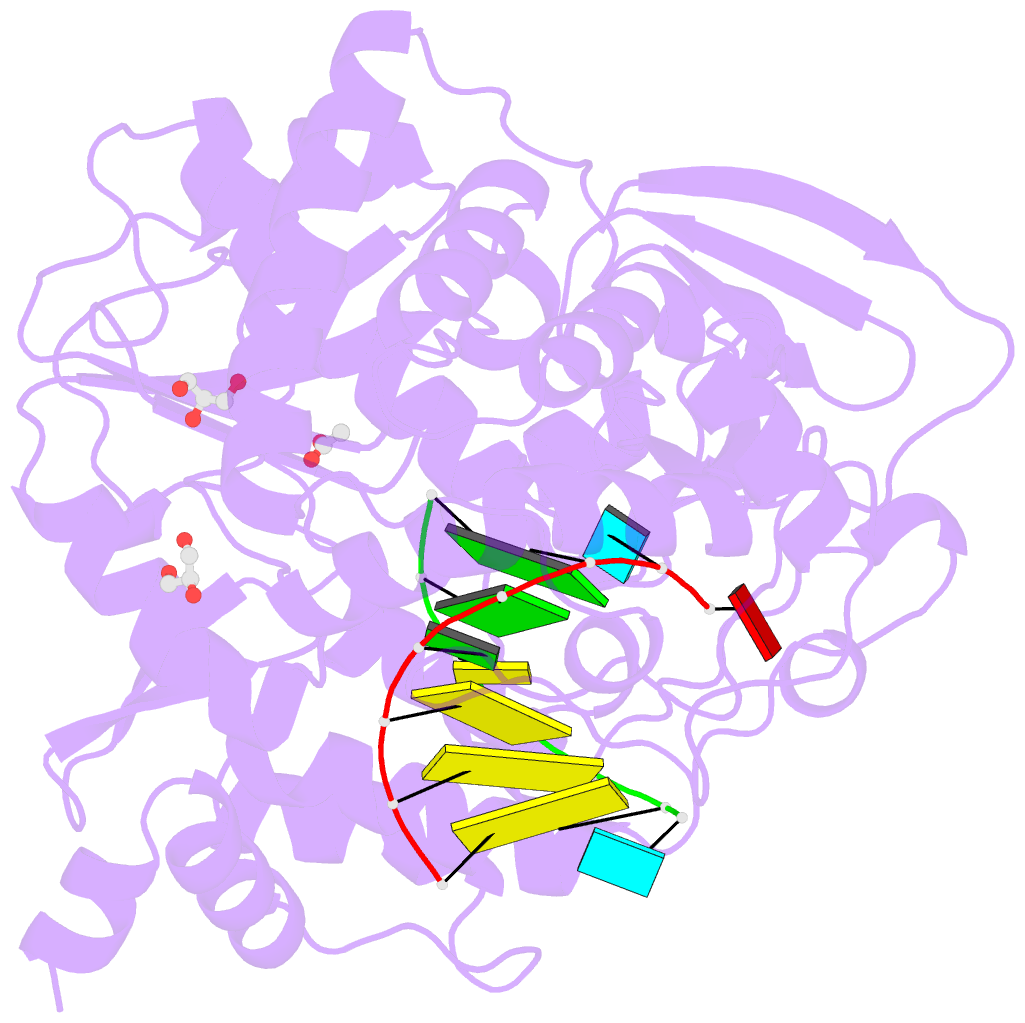
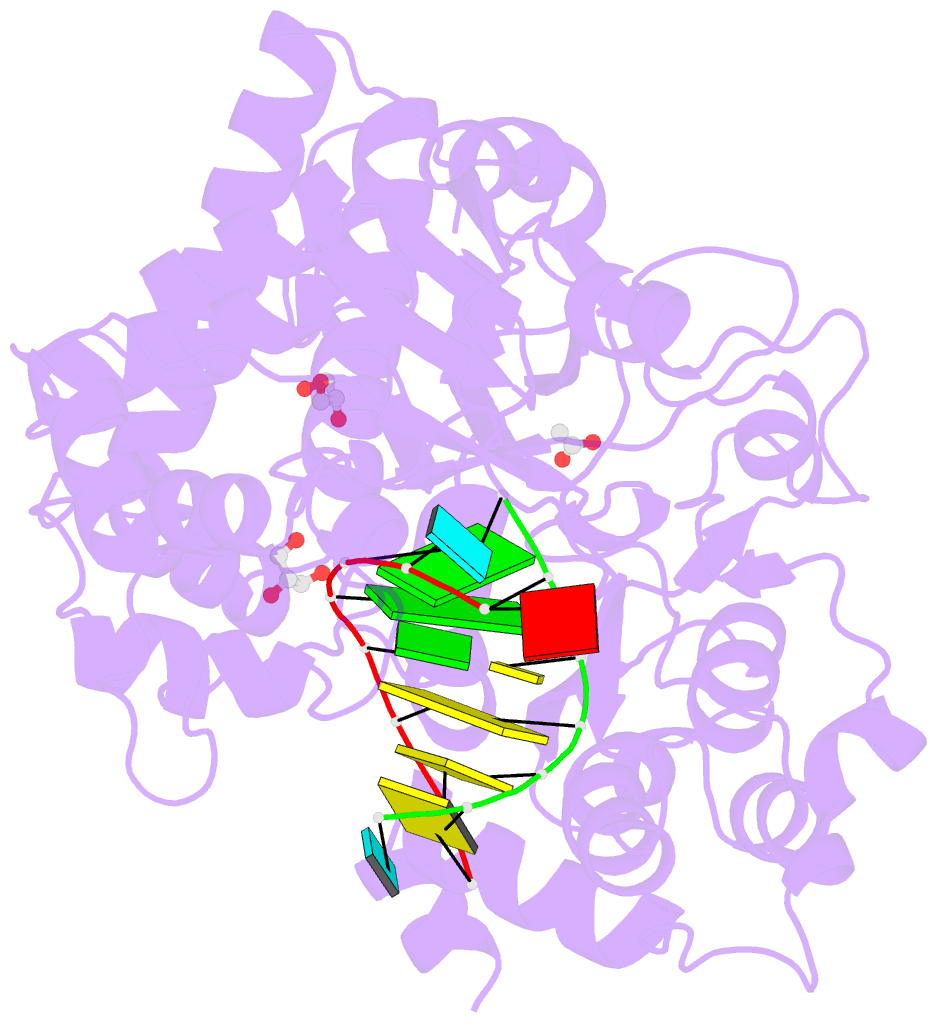
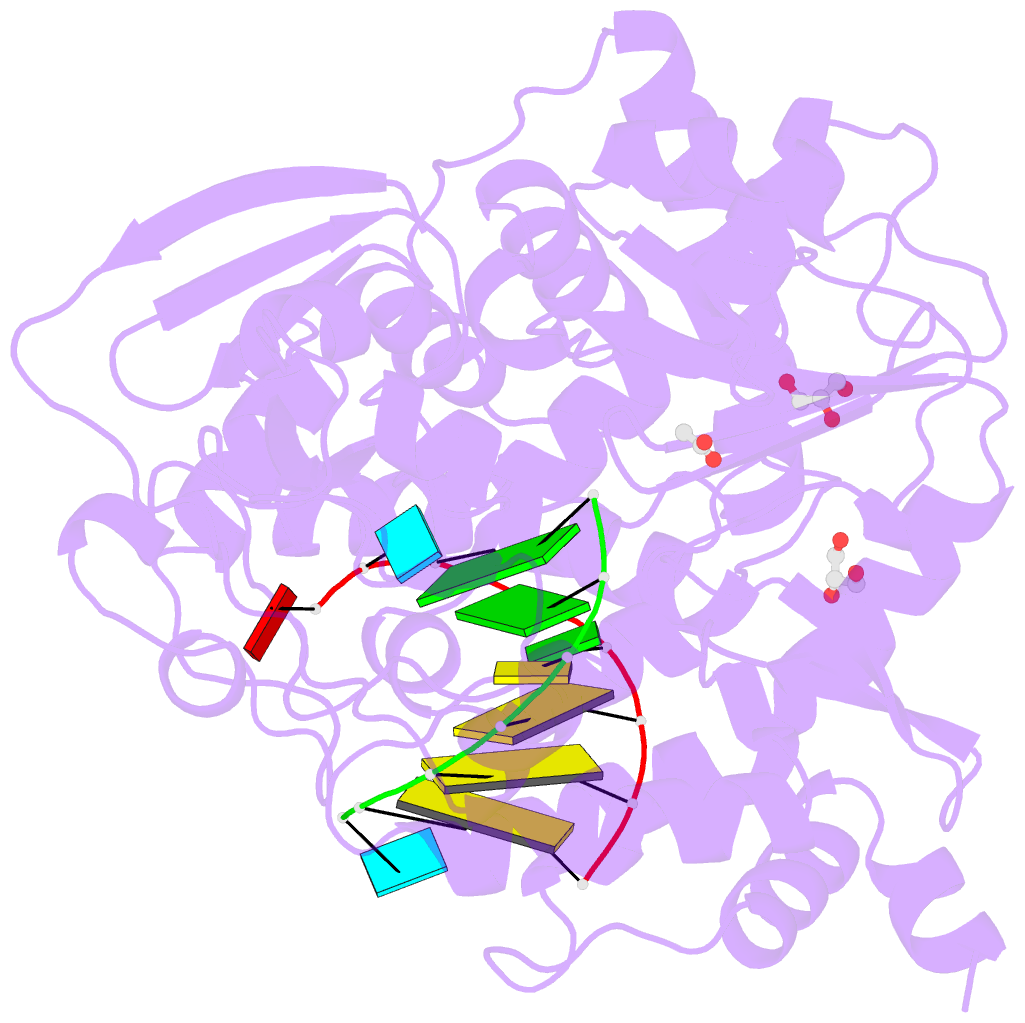
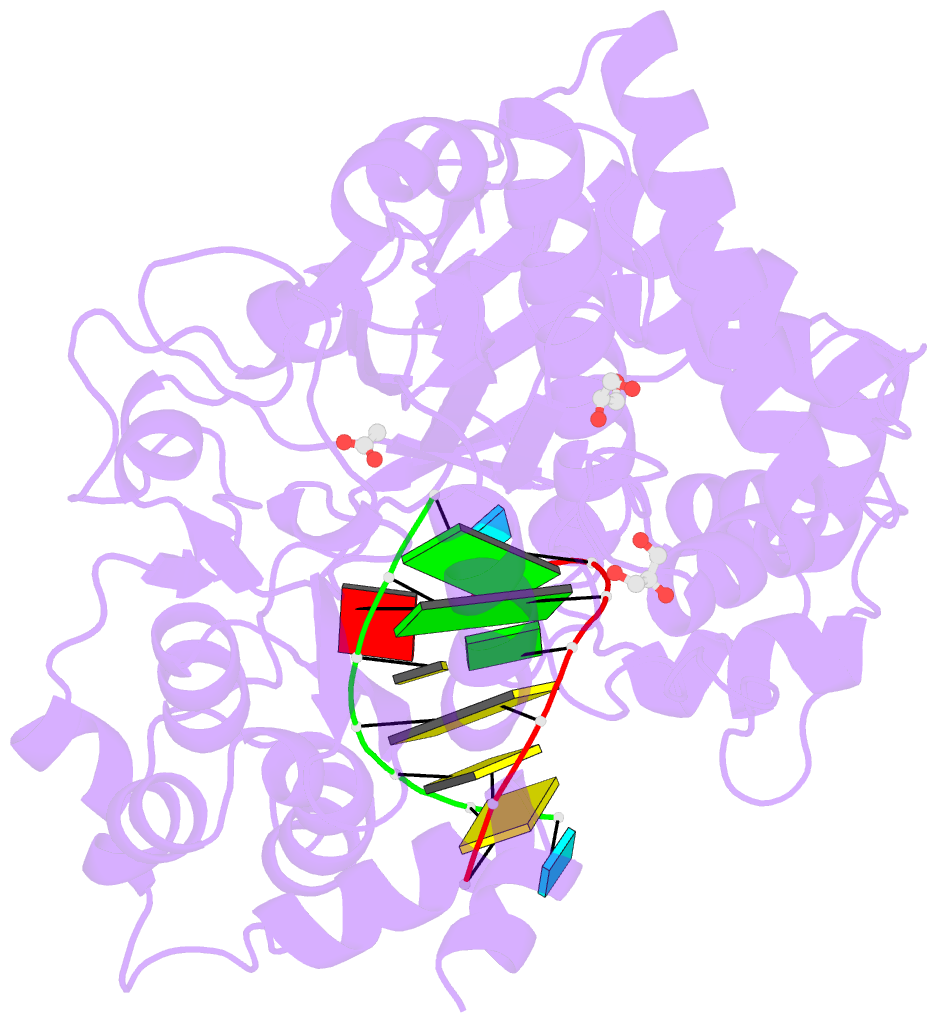
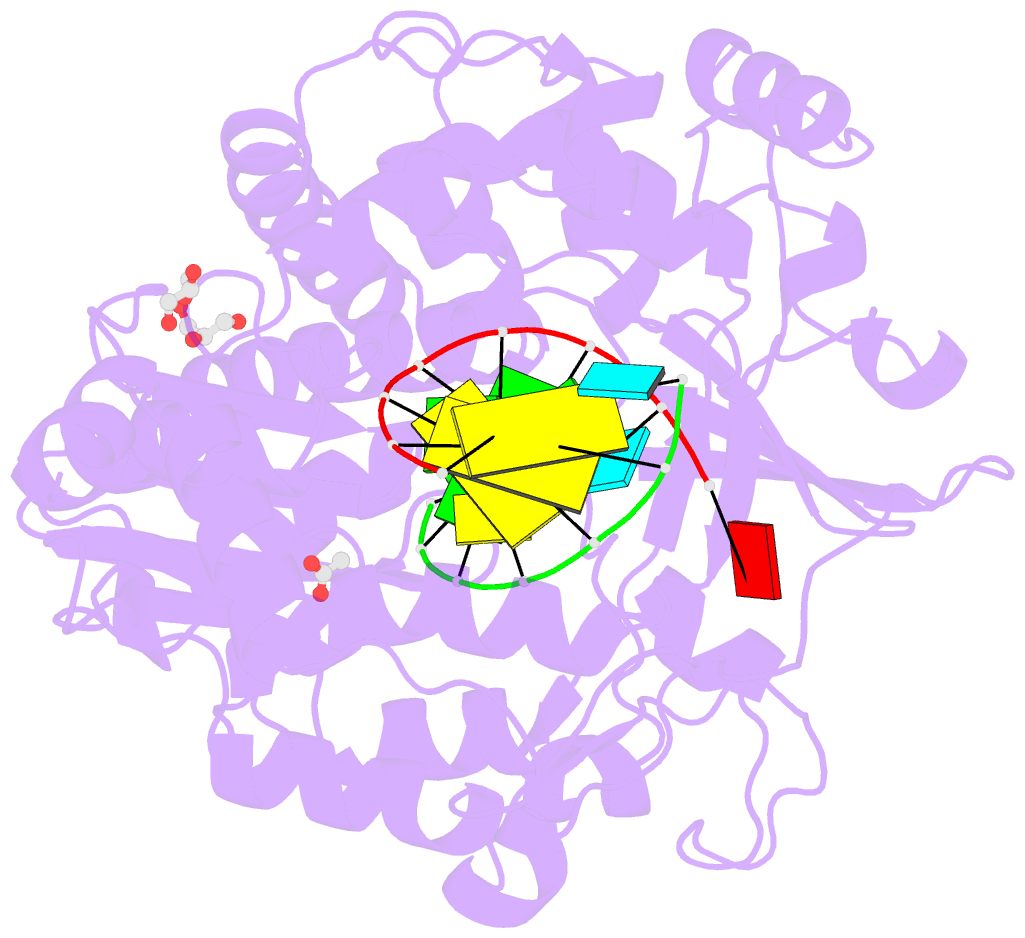
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4wzm; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase
- Method
- X-ray (2.52 Å)
- Summary
- Mutant k18e of RNA dependent RNA polymerase from foot-and-mouth disease virus complexed with RNA
- Reference
- Ferrer-Orta C, de la Higuera I, Caridi F, Sanchez-Aparicio MT, Moreno E, Perales C, Singh K, Sarafianos SG, Sobrino F, Domingo E, Verdaguer N (2015): "Multifunctionality of a picornavirus polymerase domain: nuclear localization signal and nucleotide recognition." J.Virol., 89, 6848-6859. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03283-14.
- Abstract
-