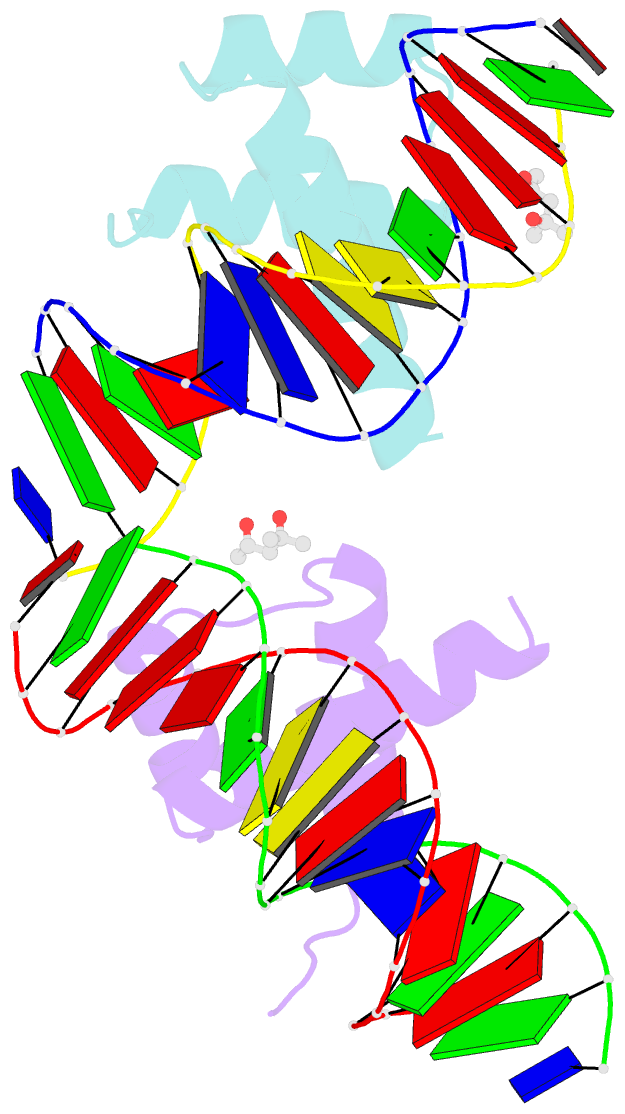
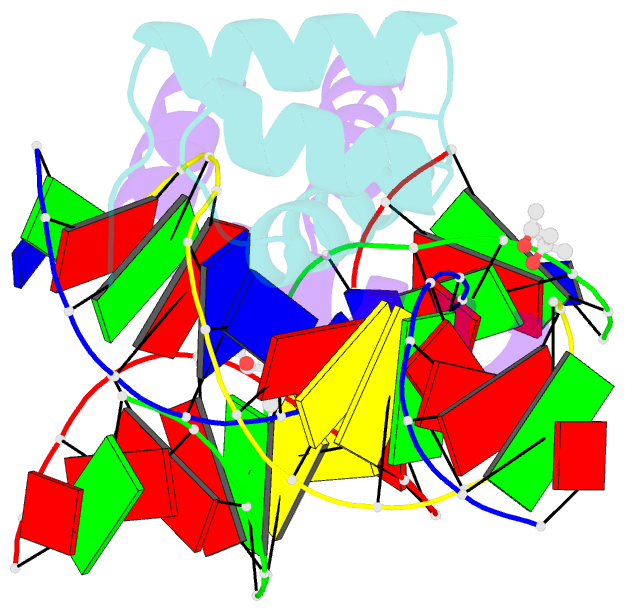
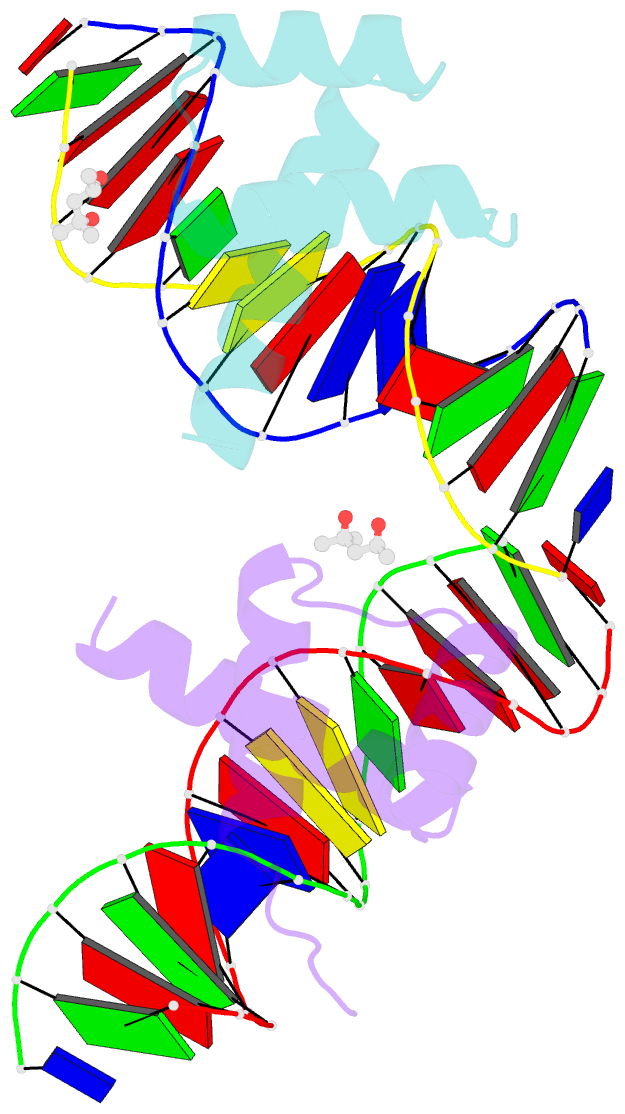
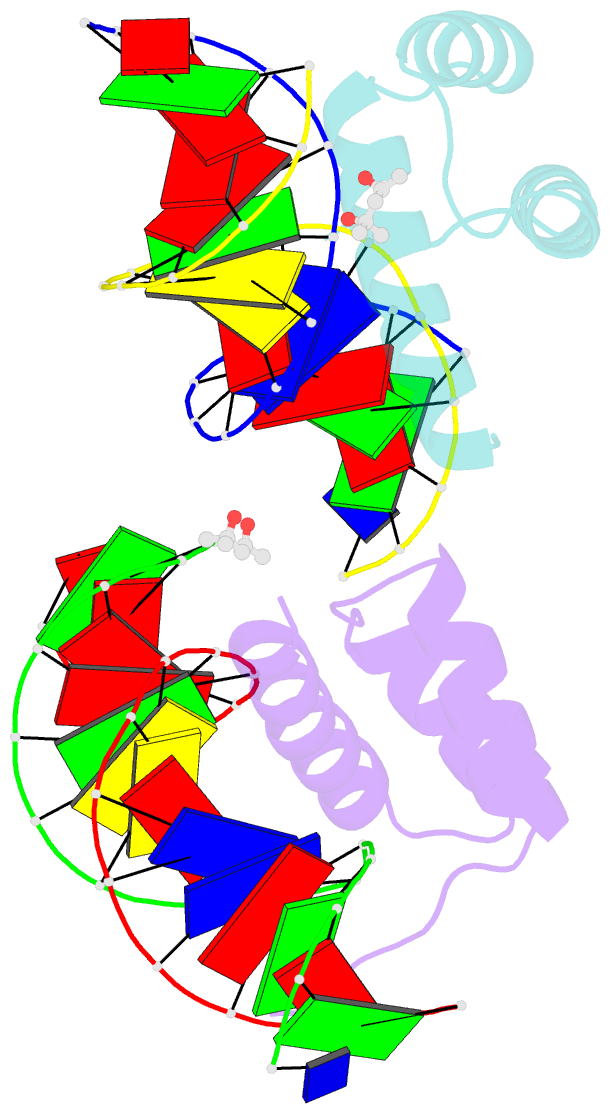
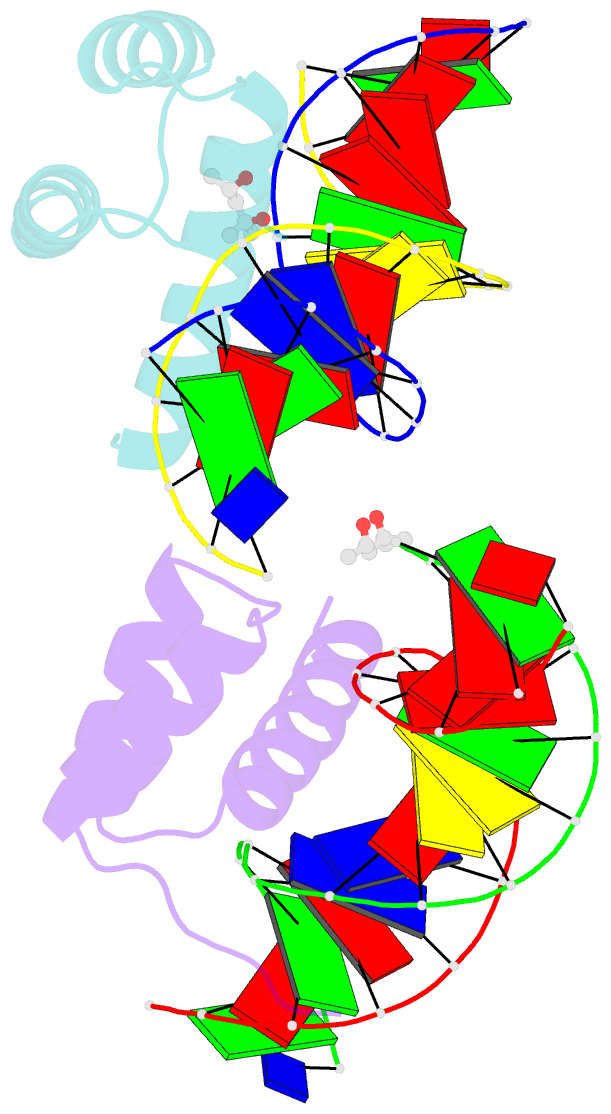
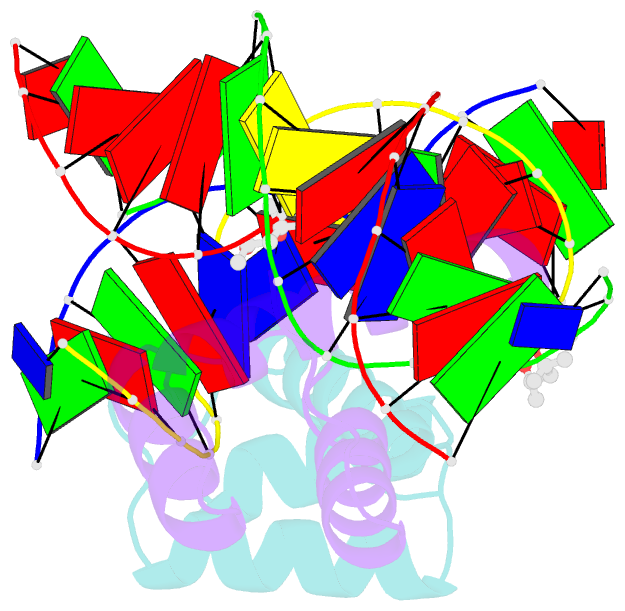
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4xid; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription regulator-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.701 Å)
- Summary
- Antphd with 15bp DNA duplex
- Reference
- Zandarashvili L, Nguyen D, Anderson KM, White MA, Gorenstein DG, Iwahara J (2015): "Entropic Enhancement of Protein-DNA Affinity by Oxygen-to-Sulfur Substitution in DNA Phosphate." Biophys.J., 109, 1026-1037. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.07.032.
- Abstract
- Dithioation of DNA phosphate is known to enhance binding affinities, at least for some proteins. We mechanistically characterized this phenomenon for the Antennapedia homeodomain-DNA complex by integrated use of fluorescence, isothermal titration calorimetry, NMR spectroscopy, and x-ray crystallography. By fluorescence and isothermal titration calorimetry, we found that this affinity enhancement is entropy driven. By NMR, we investigated the ionic hydrogen bonds and internal motions of lysine side-chain NH3(+) groups involved in ion pairs with DNA. By x-ray crystallography, we compared the structures of the complexes with and without dithioation of the phosphate. Our NMR and x-ray data show that the lysine side chain in contact with the DNA phosphate becomes more dynamic upon dithioation. Our thermodynamic, structural, and dynamic investigations collectively suggest that the affinity enhancement by the oxygen-to-sulfur substitution in DNA phosphate is largely due to an entropic gain arising from mobilization of the intermolecular ion pair at the protein-DNA interface.