Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4xjn; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.11 Å)
- Summary
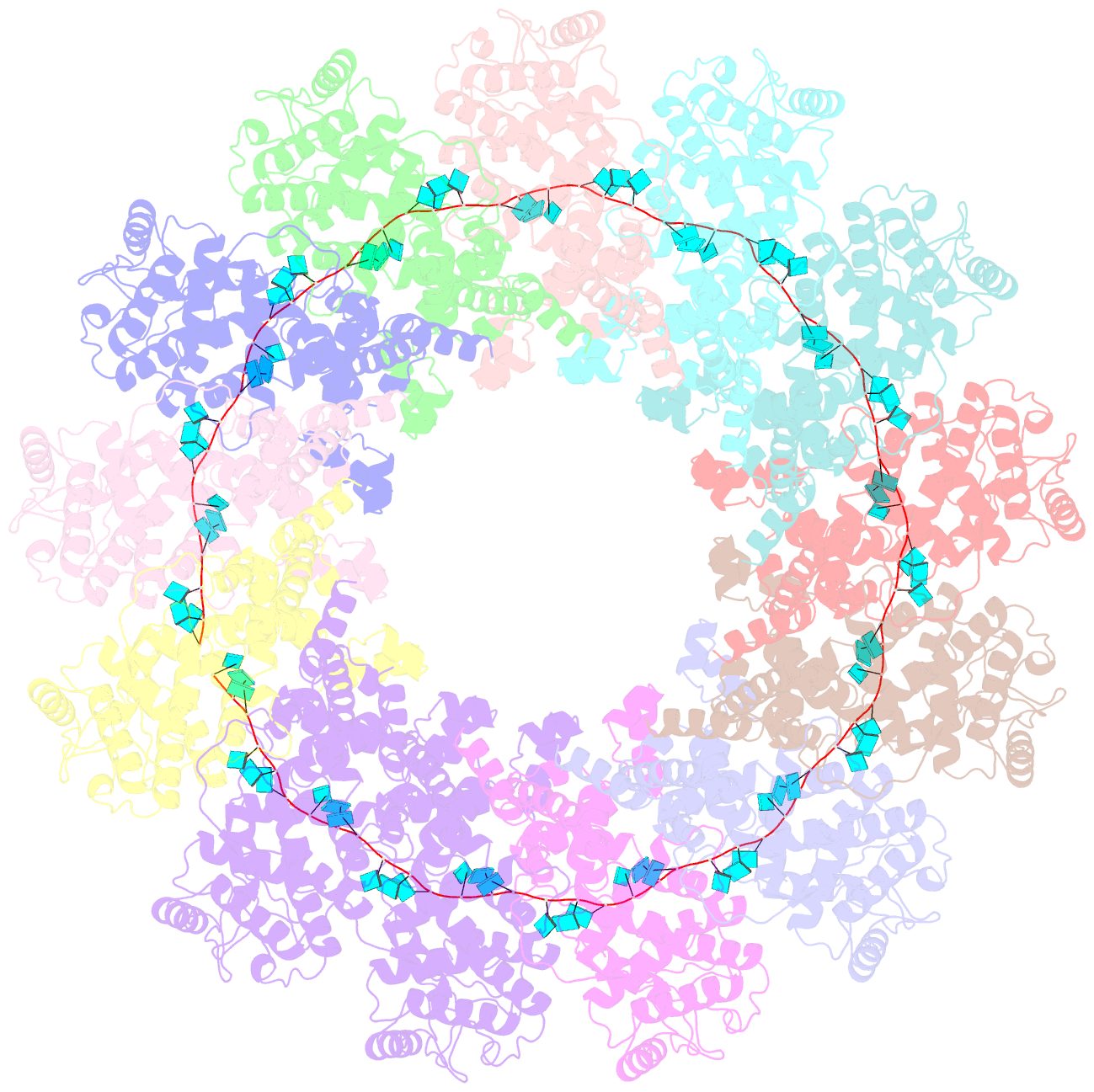
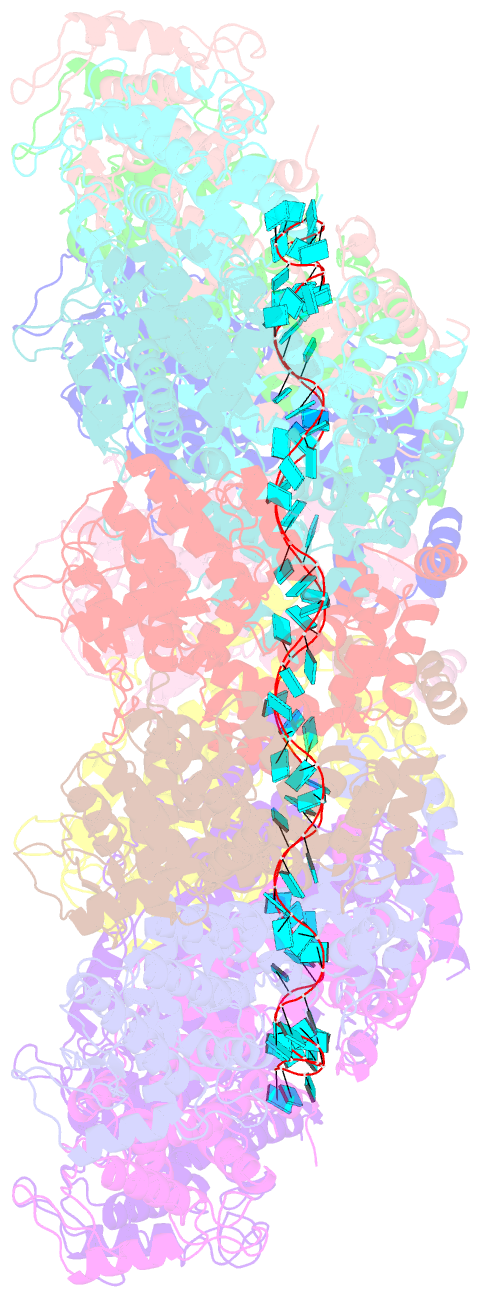
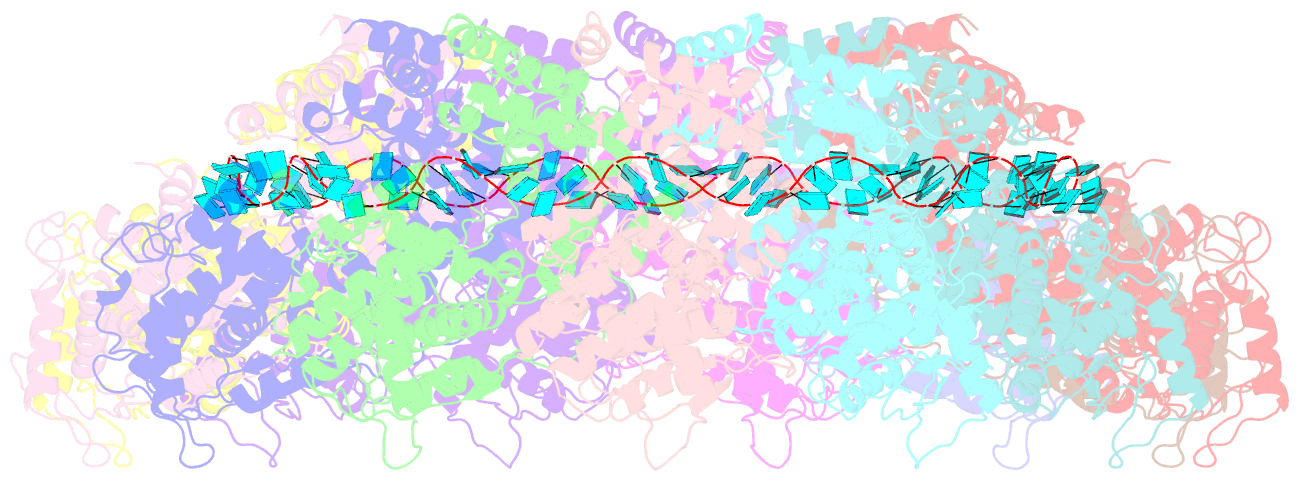
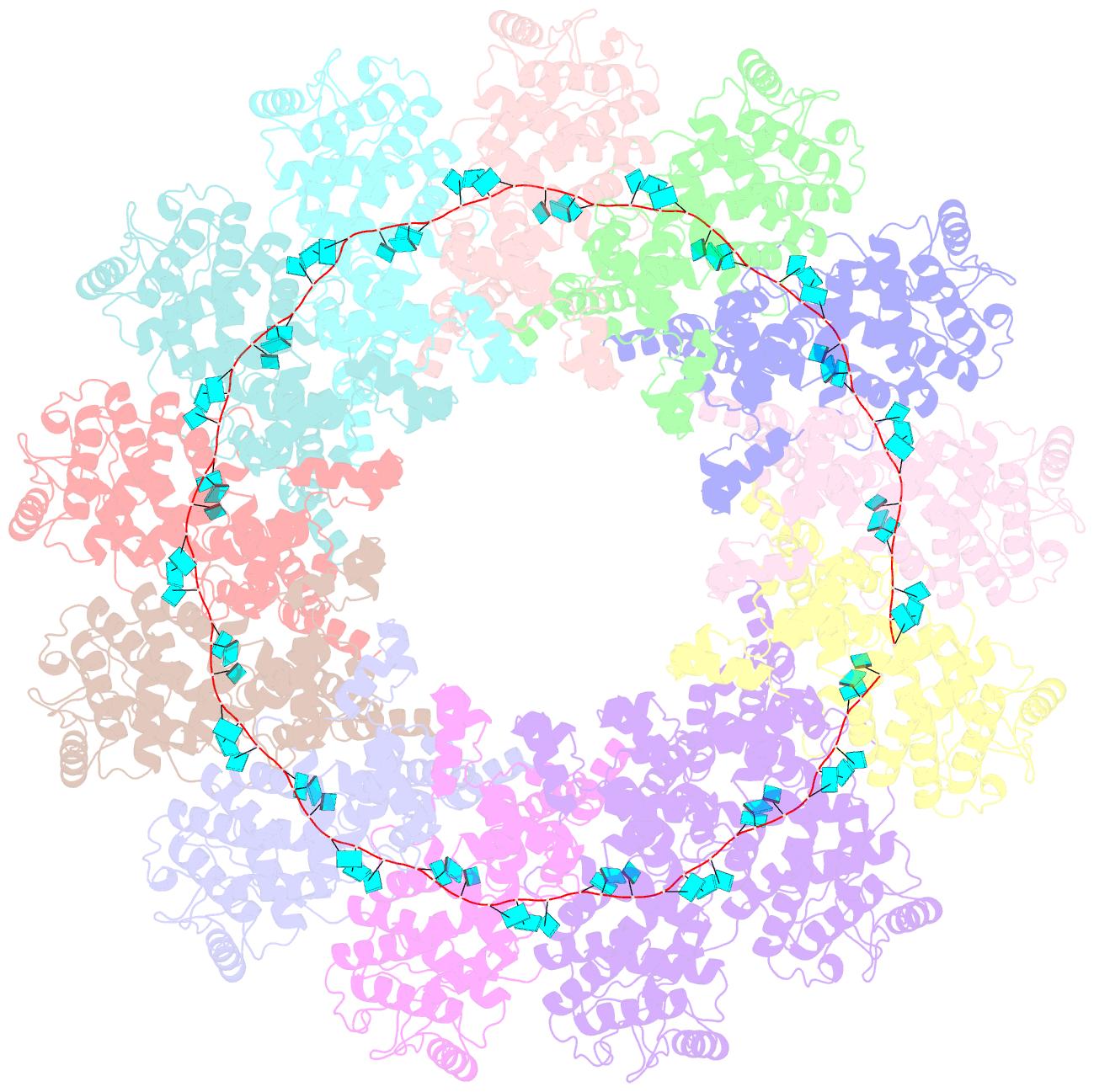
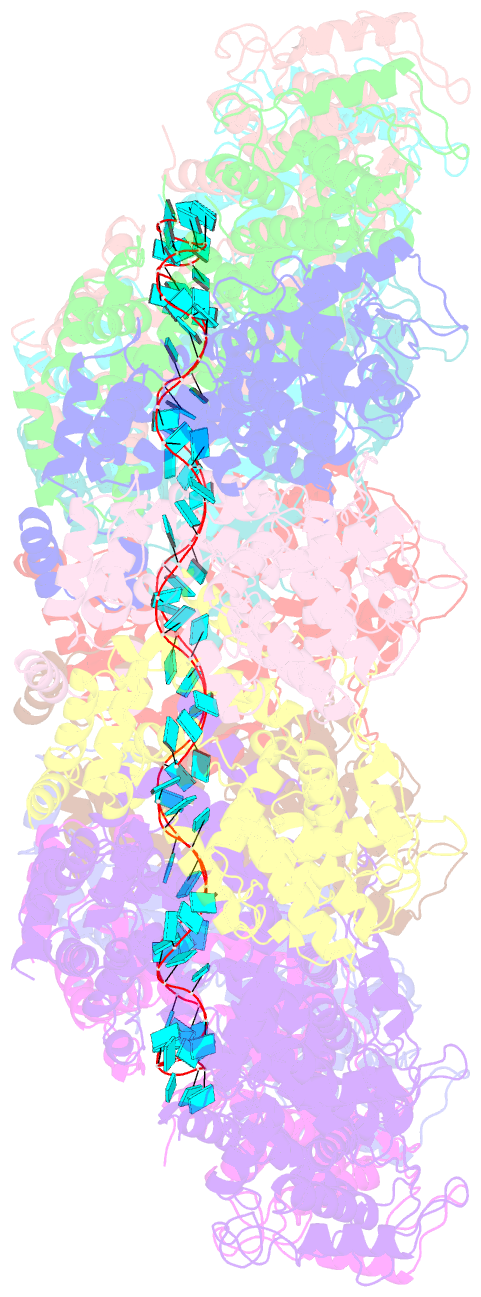
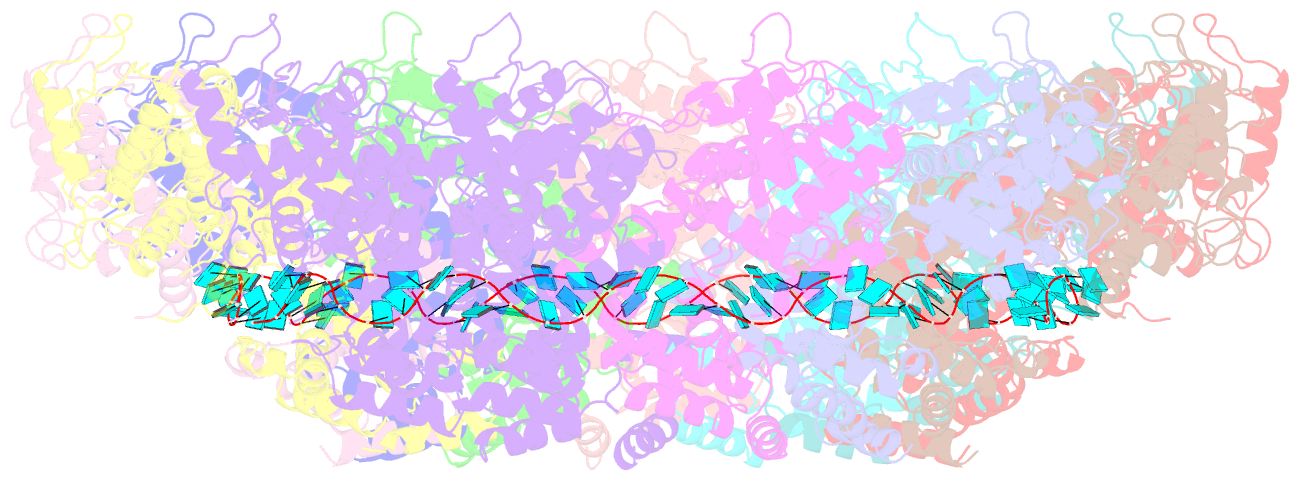
- Structure of the parainfluenza virus 5 nucleocapsid-RNA complex: an insight into paramyxovirus polymerase activity
- Reference
- Alayyoubi M, Leser GP, Kors CA, Lamb RA (2015): "Structure of the paramyxovirus parainfluenza virus 5 nucleoprotein-RNA complex." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 112, E1792-E1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503941112.
- Abstract
- Parainfluenza virus 5 (PIV5) is a member of the Paramyxoviridae family of membrane-enveloped viruses with a negative-sense RNA genome that is packaged and protected by long filamentous nucleocapsid-helix structures (RNPs). These RNPs, consisting of ∼2,600 protomers of nucleocapsid (N) protein, form the template for viral transcription and replication. We have determined the 3D X-ray crystal structure of the nucleoprotein (N)-RNA complex from PIV5 to 3.11-Å resolution. The structure reveals a 13-mer nucleocapsid ring whose diameter, cavity, and pitch/height dimensions agree with EM data from early studies on the Paramyxovirinae subfamily of native RNPs, indicating that it closely represents one-turn in the building block of the RNP helices. The PIV5-N nucleocapsid ring encapsidates a nuclease resistant 78-nt RNA strand in its positively charged groove formed between the N-terminal (NTD) and C-terminal (CTD) domains of its successive N protomers. Six nucleotides precisely are associated with each N protomer, with alternating three-base-in three-base-out conformation. The binding of six nucleotides per protomer is consistent with the "rule of six" that governs the genome packaging of the Paramyxovirinae subfamily of viruses. PIV5-N protomer subdomains are very similar in structure to the previously solved Nipah-N structure, but with a difference in the angle between NTD/CTD at the RNA hinge region. Based on the Nipah-N structure we modeled a PIV5-N open conformation in which the CTD rotates away from the RNA strand into the inner spacious nucleocapsid-ring cavity. This rotation would expose the RNA for the viral polymerase activity without major disruption of the nucleocapsid structure.