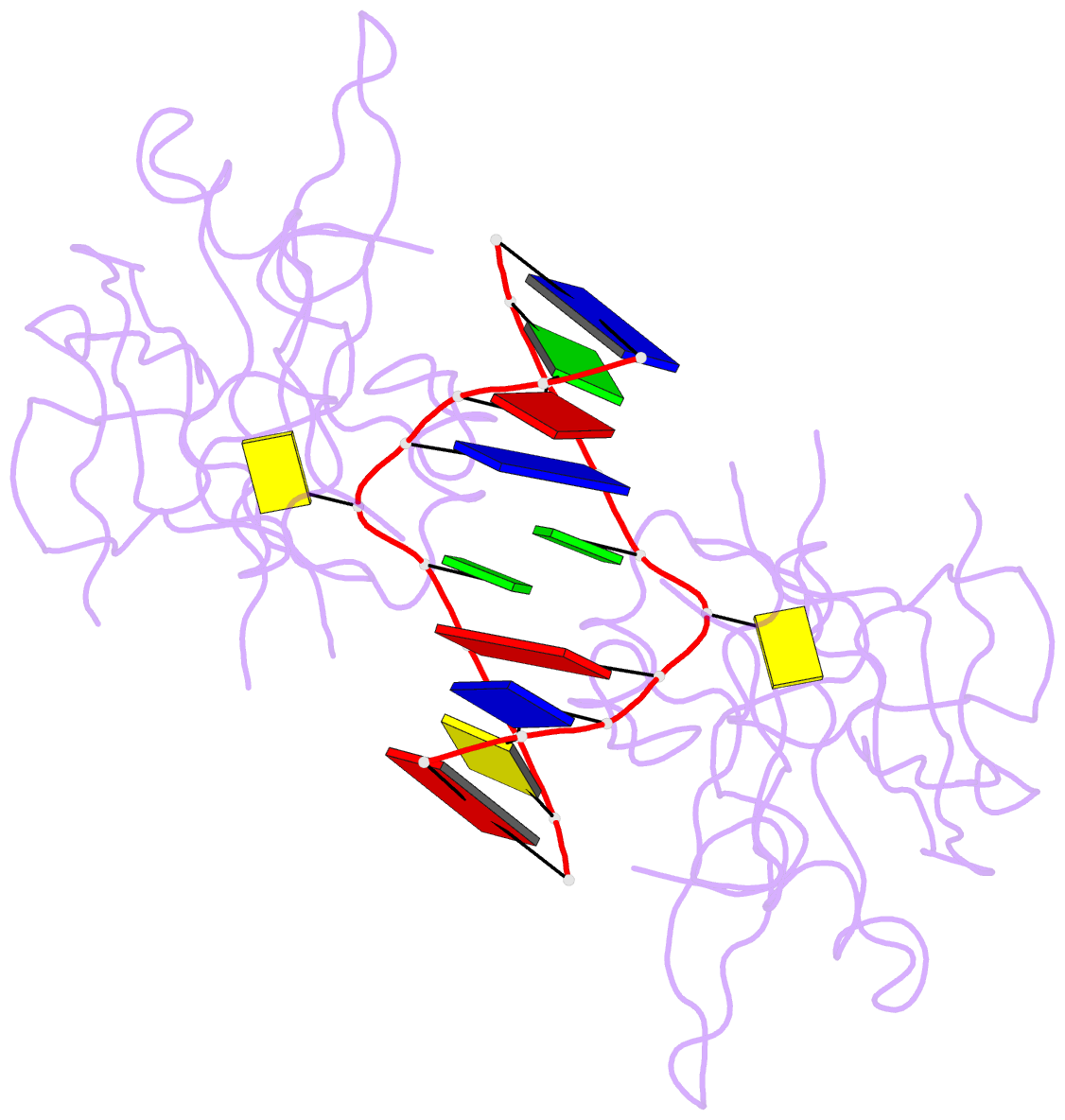
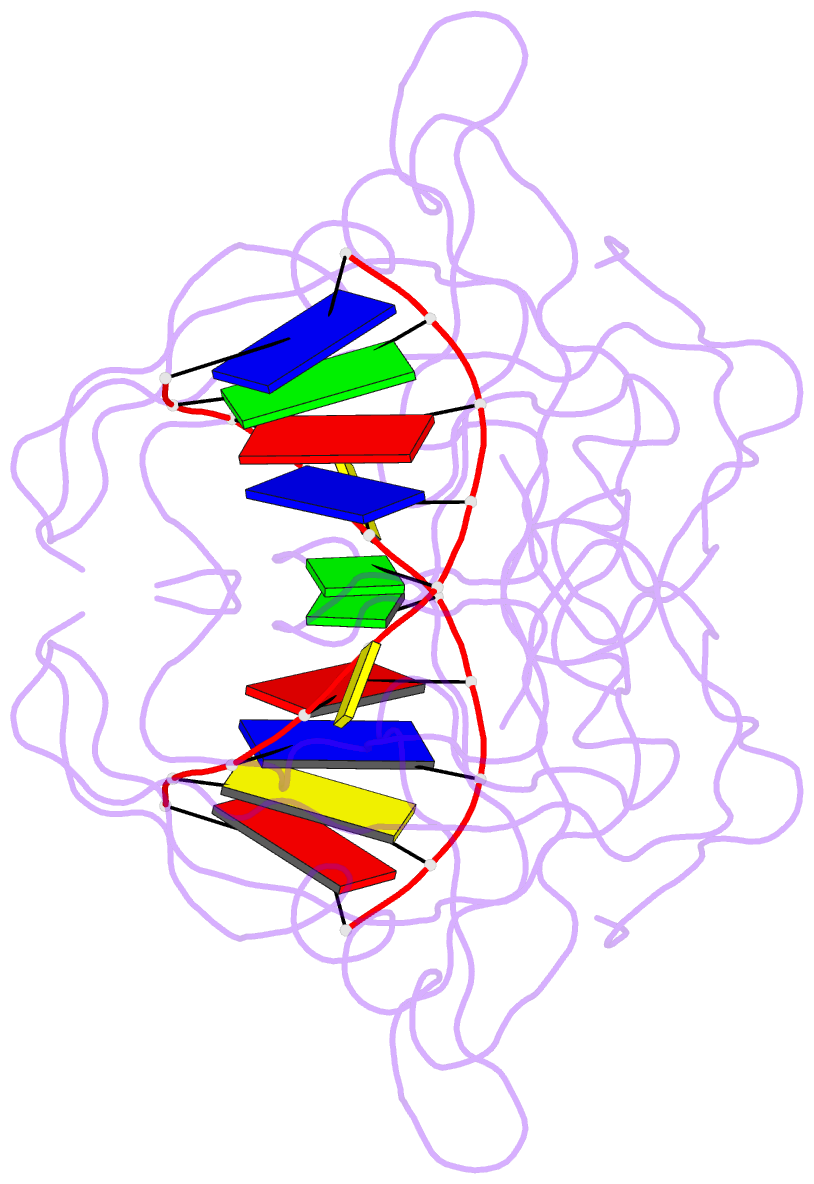
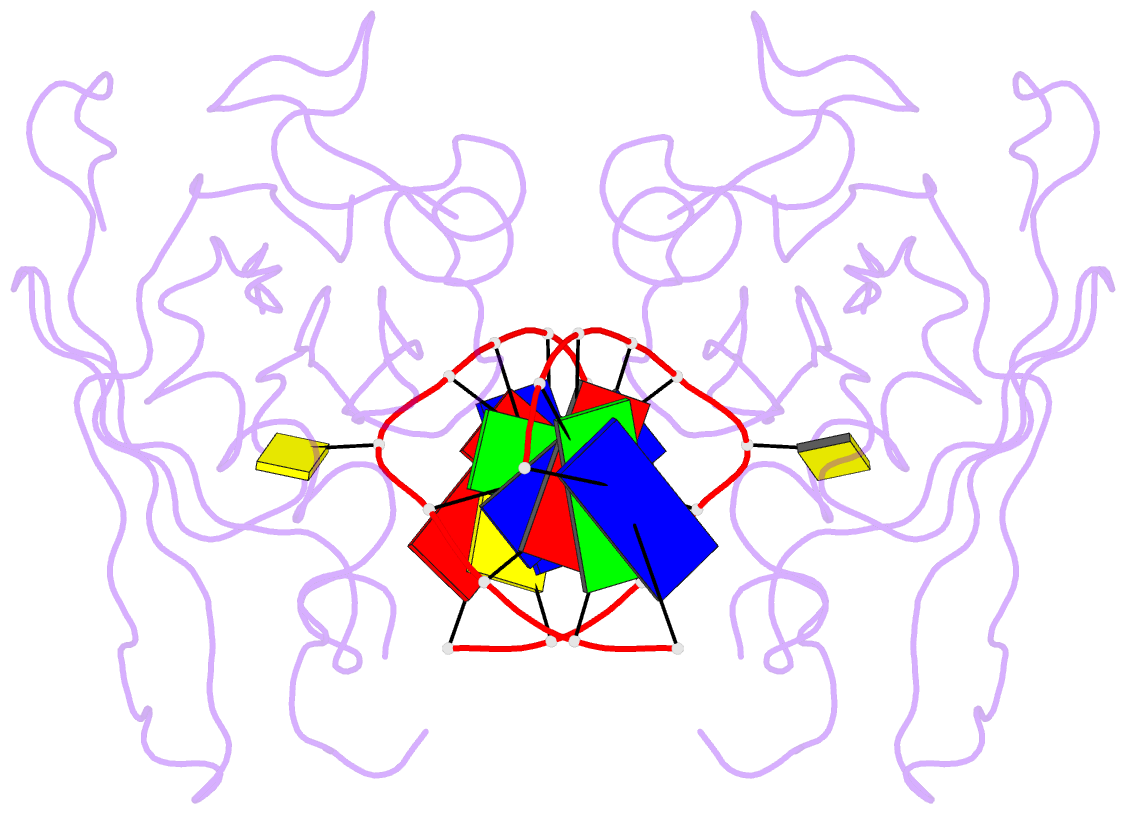
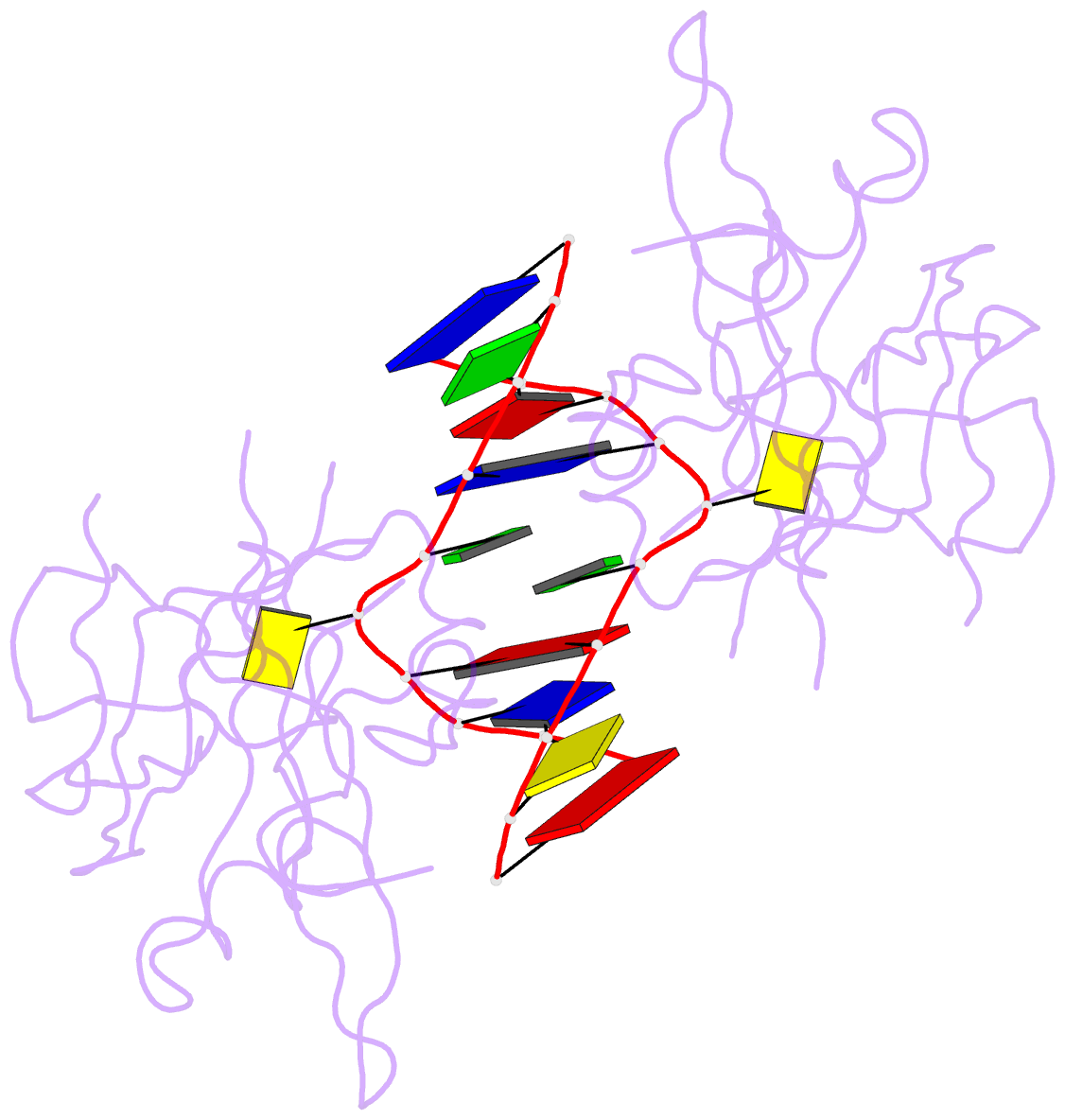
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4ygi; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.6 Å)
- Summary
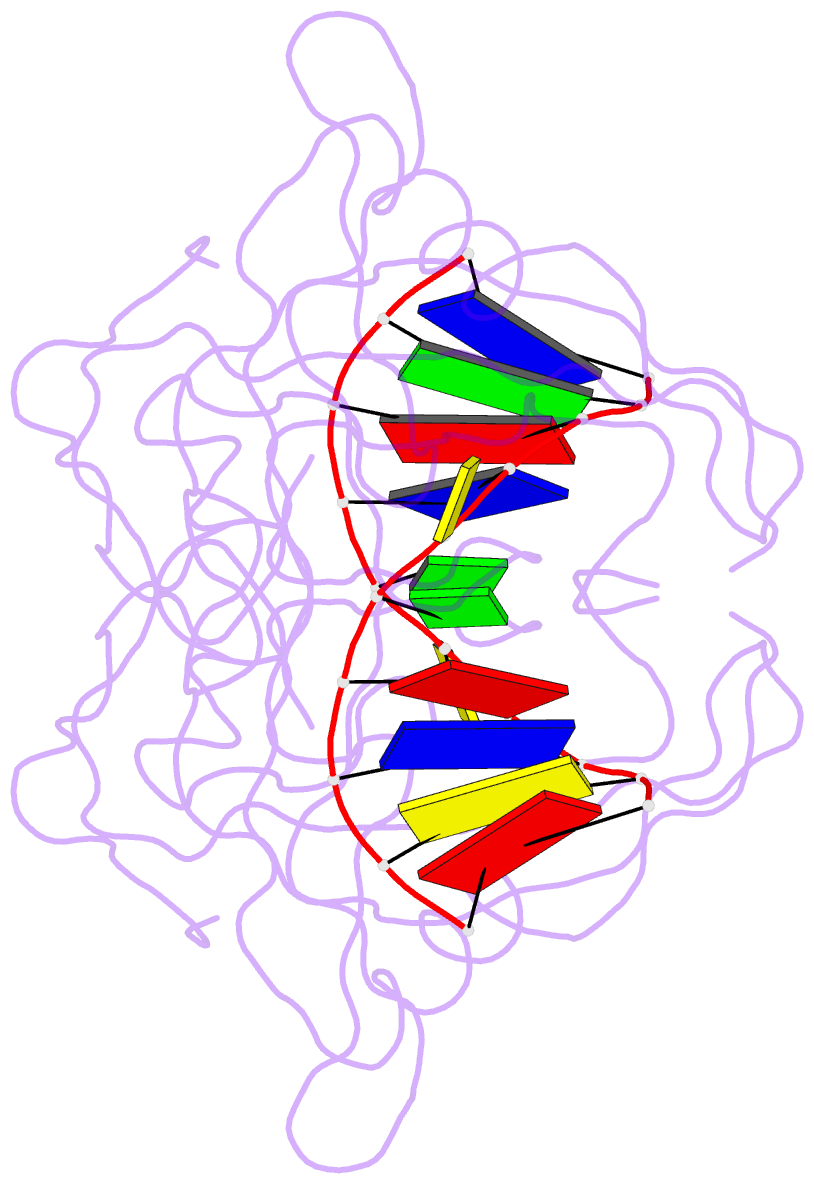
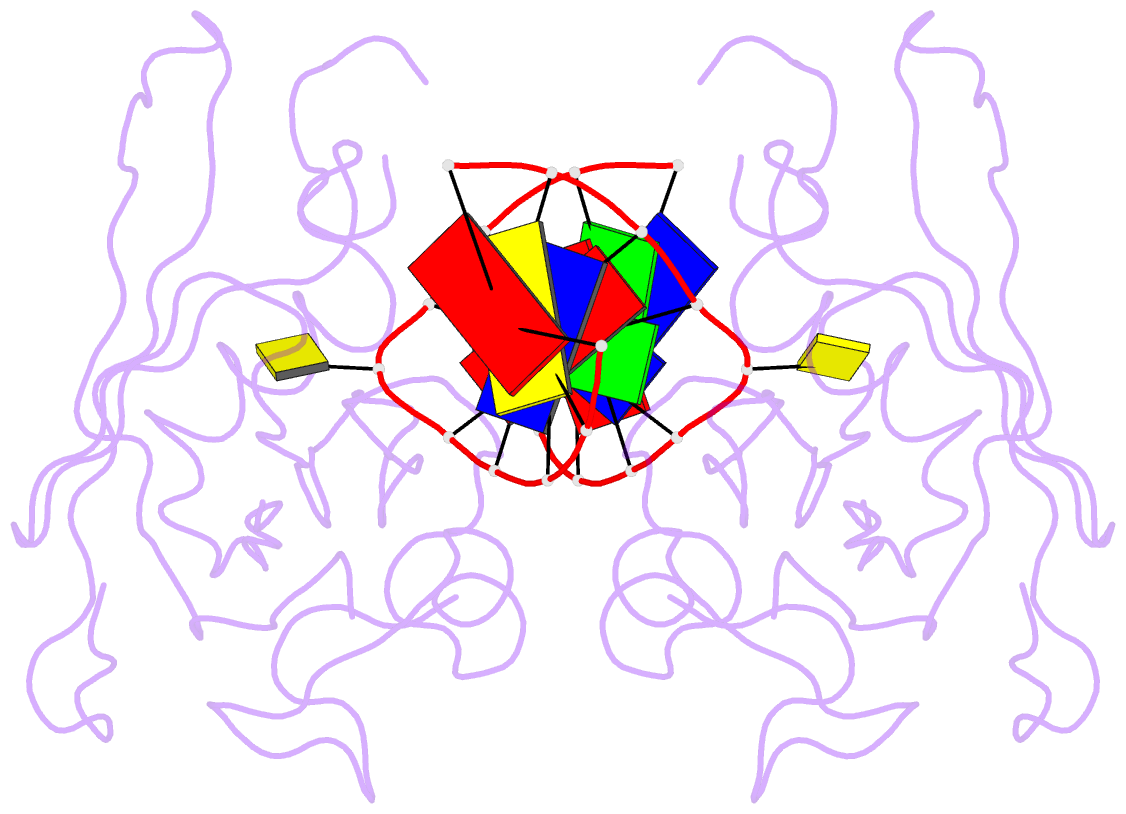
- Crystal structure of suvh5 sra bound to fully hydroxymethylated cg DNA
- Reference
- Rajakumara E, Nakarakanti NK, Nivya MA, Satish M (2016): "Mechanistic insights into the recognition of 5-methylcytosine oxidation derivatives by the SUVH5 SRA domain." Sci Rep, 6, 20161. doi: 10.1038/srep20161.
- Abstract
- 5-Methylcytosine (5 mC) is associated with epigenetic gene silencing in mammals and plants. 5 mC is consecutively oxidized to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5 hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC) by ten-eleven translocation enzymes. We performed binding and structural studies to investigate the molecular basis of the recognition of the 5 mC oxidation derivatives in the context of a CG sequence by the SET- and RING-associated domain (SRA) of the SUVH5 protein (SUVH5 SRA). Using calorimetric measurements, we demonstrate that the SRA domain binds to the hydroxymethylated CG (5hmCG) DNA duplex in a similar manner to methylated CG (5mCG). Interestingly, the SUVH5 SRA domain exhibits weaker affinity towards carboxylated CG (5caCG) and formylated CG (5fCG). We report the 2.6 Å resolution crystal structure of the SUVH5 SRA domain in a complex with fully hydroxymethyl-CG and demonstrate a dual flip-out mechanism, whereby the symmetrical 5hmCs are simultaneously extruded from the partner strands of the DNA duplex and are positioned within the binding pockets of individual SRA domains. The hydroxyl group of 5hmC establishes both intra- and intermolecular interactions in the binding pocket. Collectively, we show that SUVH5 SRA recognizes 5hmC in a similar manner to 5 mC, but exhibits weaker affinity towards 5 hmC oxidation derivatives.