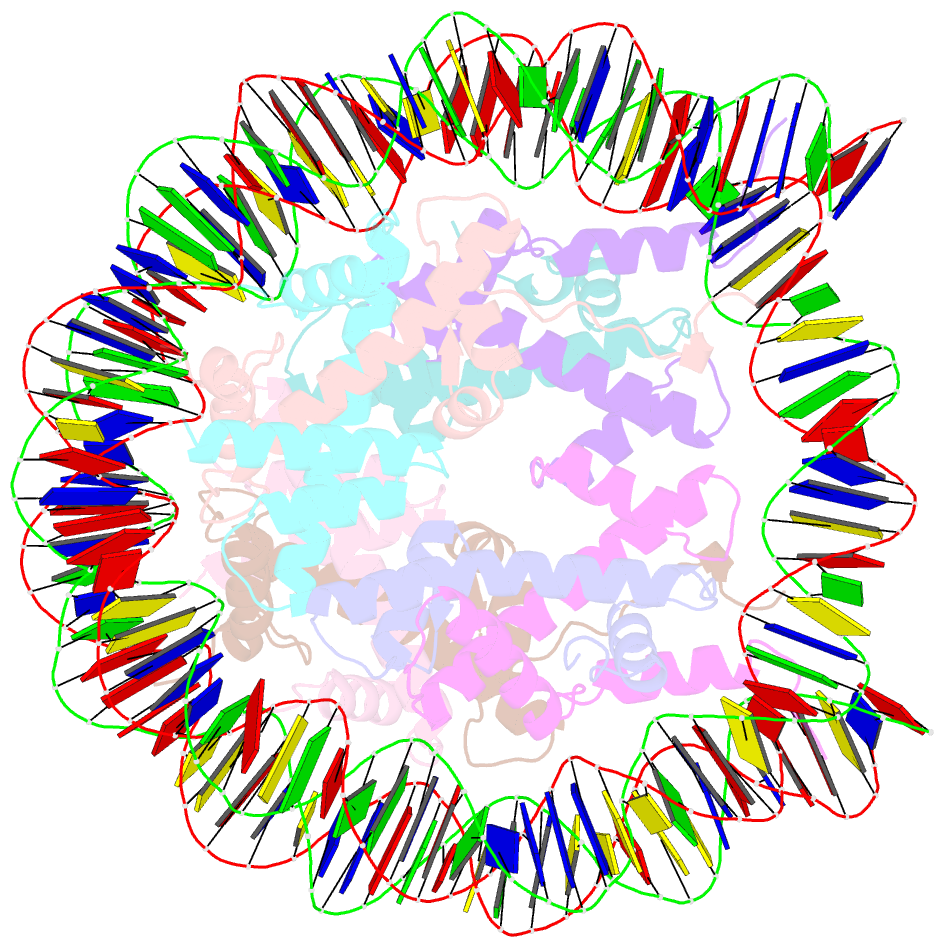
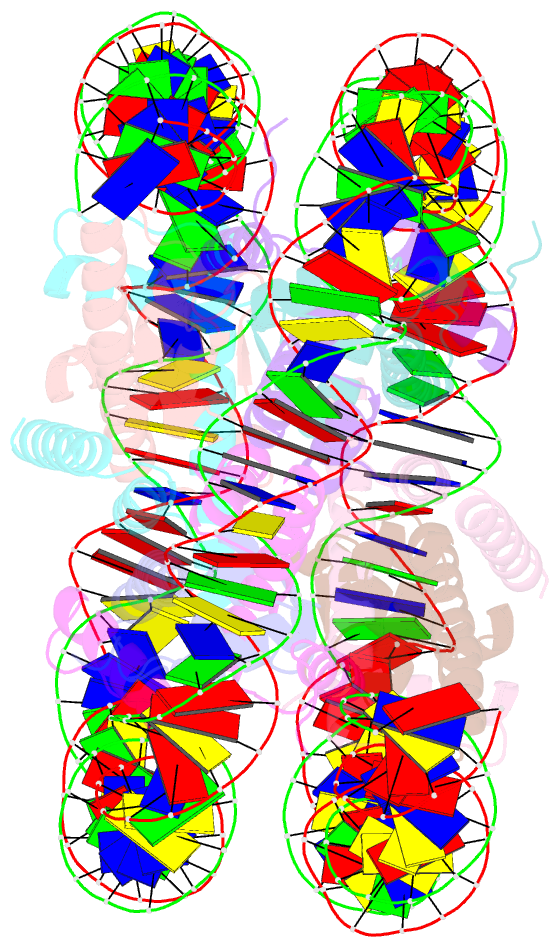
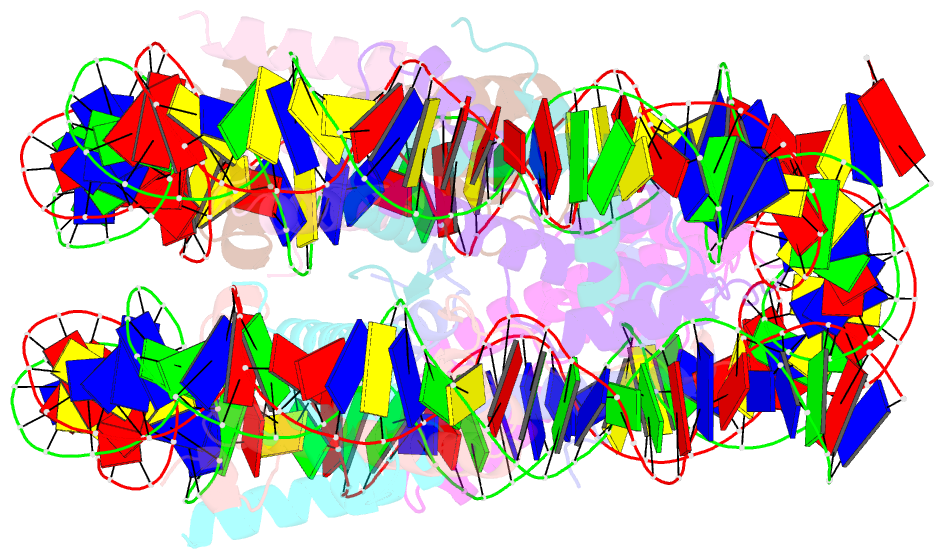
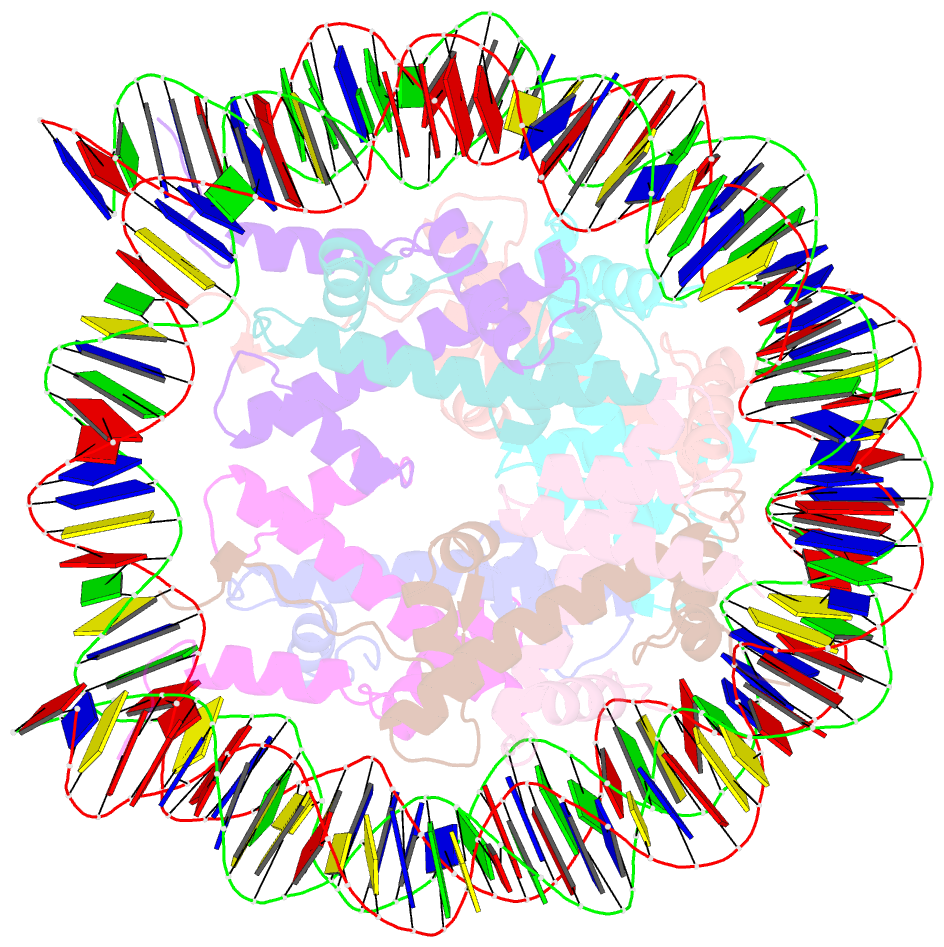
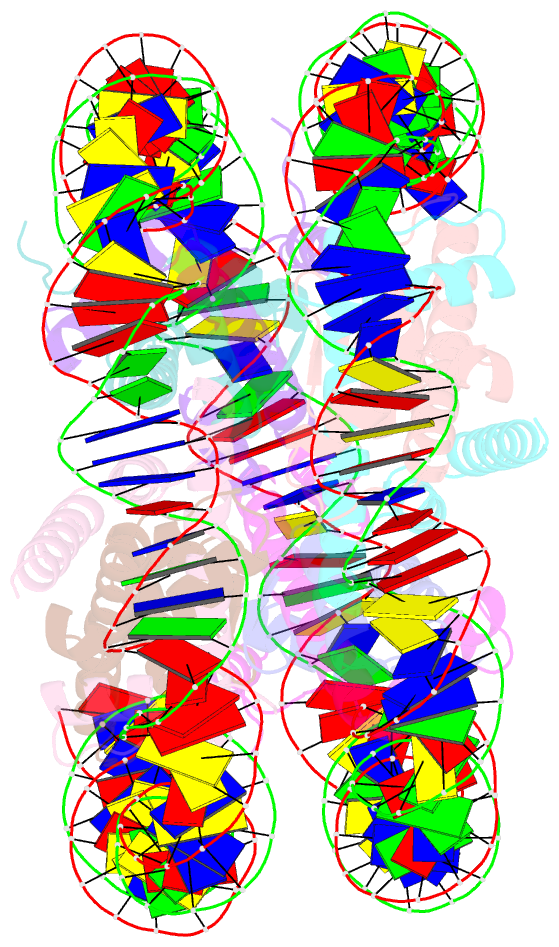
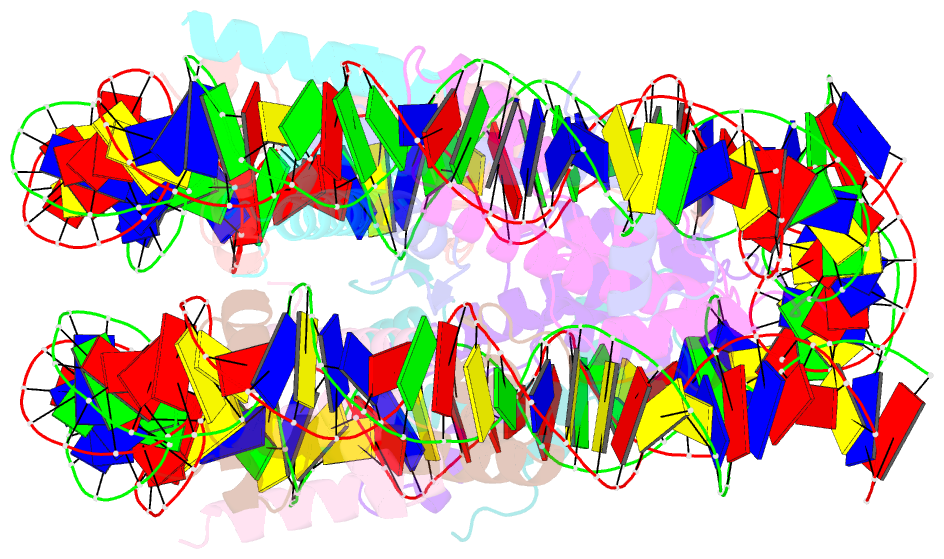
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4z5t; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- structural protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.8 Å)
- Summary
- The nucleosome containing human h3.5
- Reference
- Urahama T, Harada A, Maehara K, Horikoshi N, Sato K, Sato Y, Shiraishi K, Sugino N, Osakabe A, Tachiwana H, Kagawa W, Kimura H, Ohkawa Y, Kurumizaka H (2016): "Histone H3.5 forms an unstable nucleosome and accumulates around transcription start sites in human testis." Epigenetics Chromatin, 9, 2. doi: 10.1186/s13072-016-0051-y.
- Abstract
- Background: Human histone H3.5 is a non-allelic H3 variant evolutionally derived from H3.3. The H3.5 mRNA is highly expressed in human testis. However, the function of H3.5 has remained poorly understood.
Results: We found that the H3.5 nucleosome is less stable than the H3.3 nucleosome. The crystal structure of the H3.5 nucleosome showed that the H3.5-specific Leu103 residue, which corresponds to the H3.3 Phe104 residue, reduces the hydrophobic interaction with histone H4. Mutational analyses revealed that the H3.5-specific Leu103 residue is responsible for the instability of the H3.5 nucleosome, both in vitro and in living cells. The H3.5 protein was present in human seminiferous tubules, but little to none was found in mature sperm. A chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with sequencing analysis revealed that H3.5 accumulated around transcription start sites (TSSs) in testicular cells.
Conclusions: We performed comprehensive studies of H3.5, and found the instability of the H3.5 nucleosome and the accumulation of H3.5 protein around TSSs in human testis. The unstable H3.5 nucleosome may function in the chromatin dynamics around the TSSs, during spermatogenesis.