Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5aor; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.08 Å)
- Summary
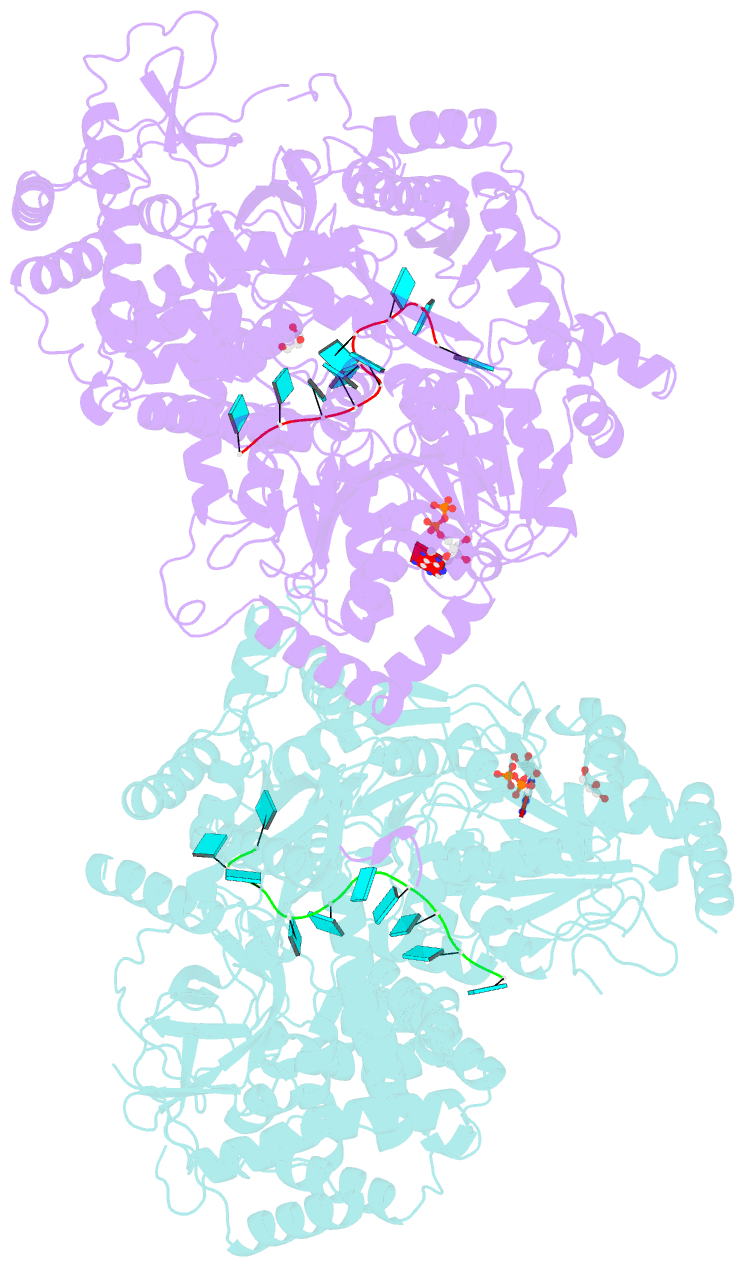
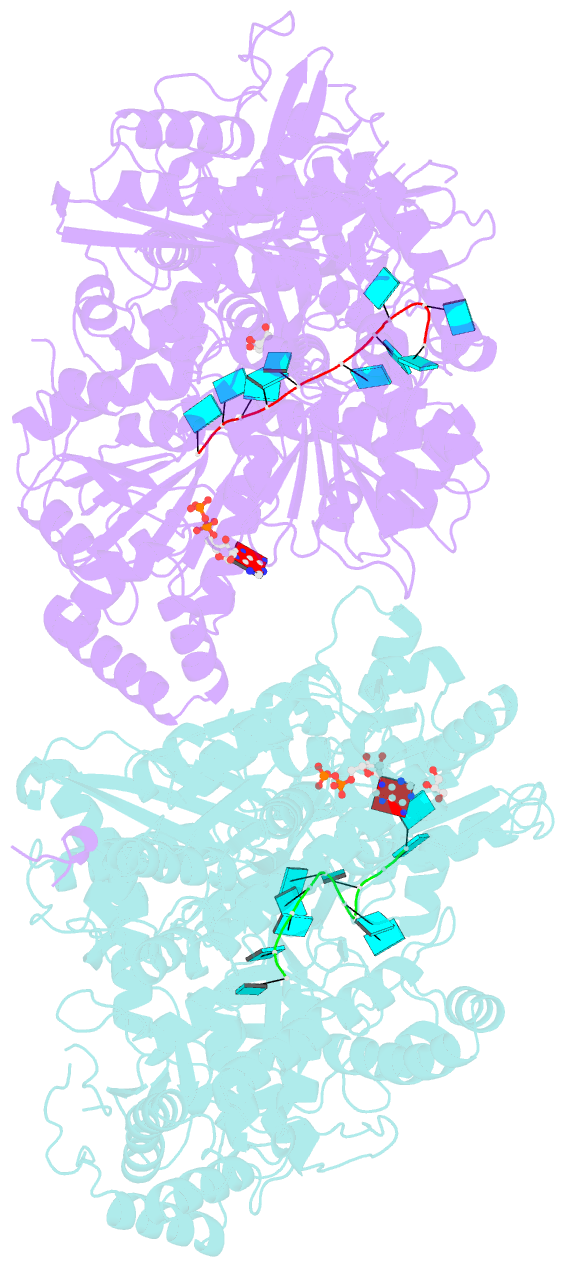
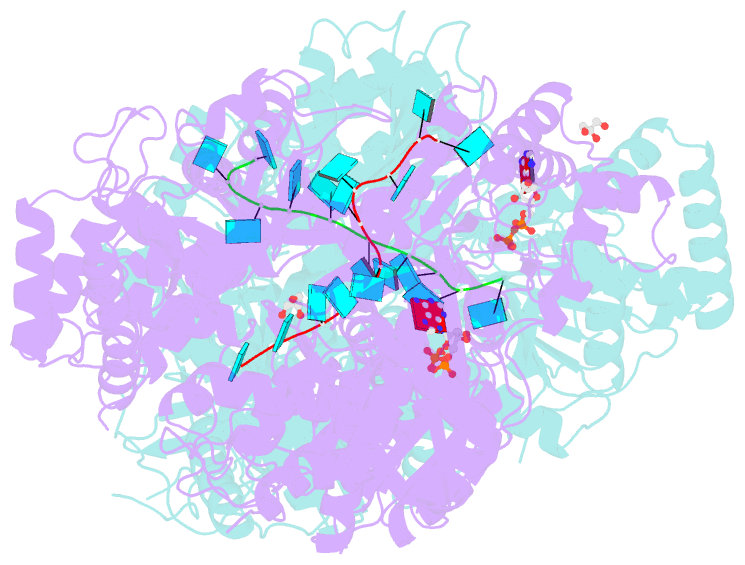
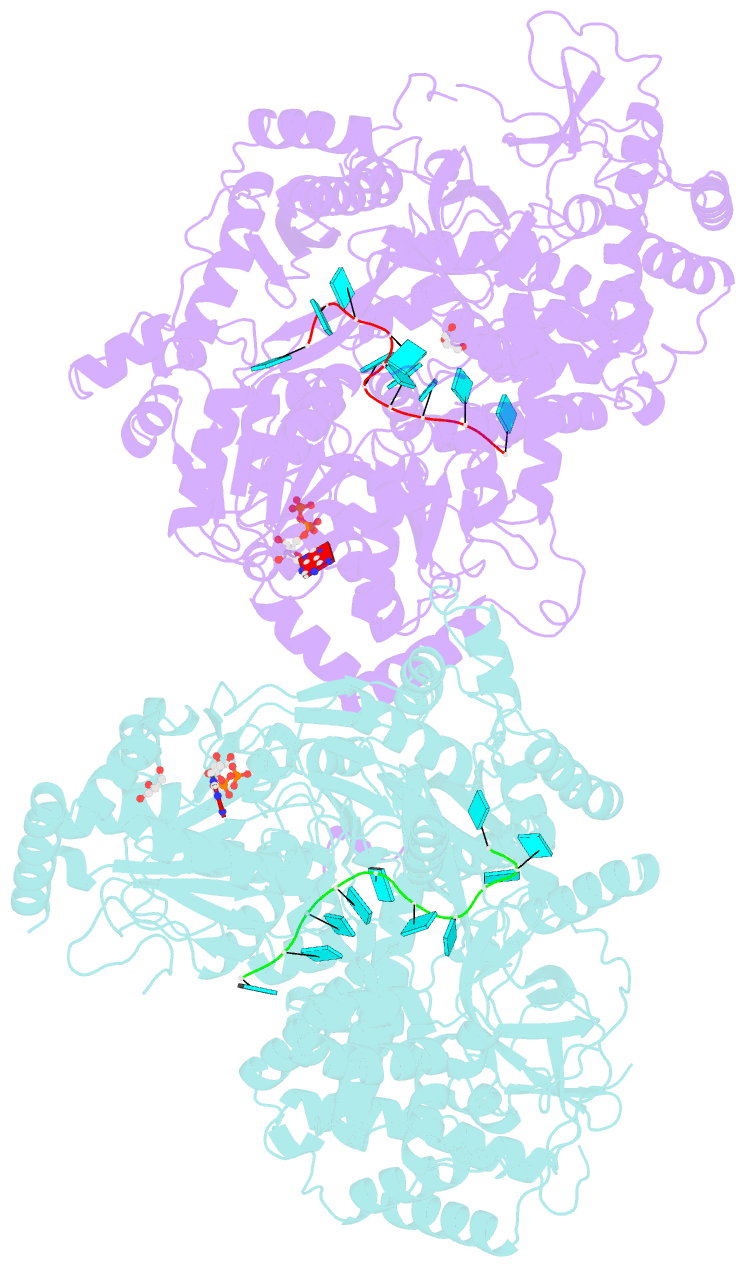
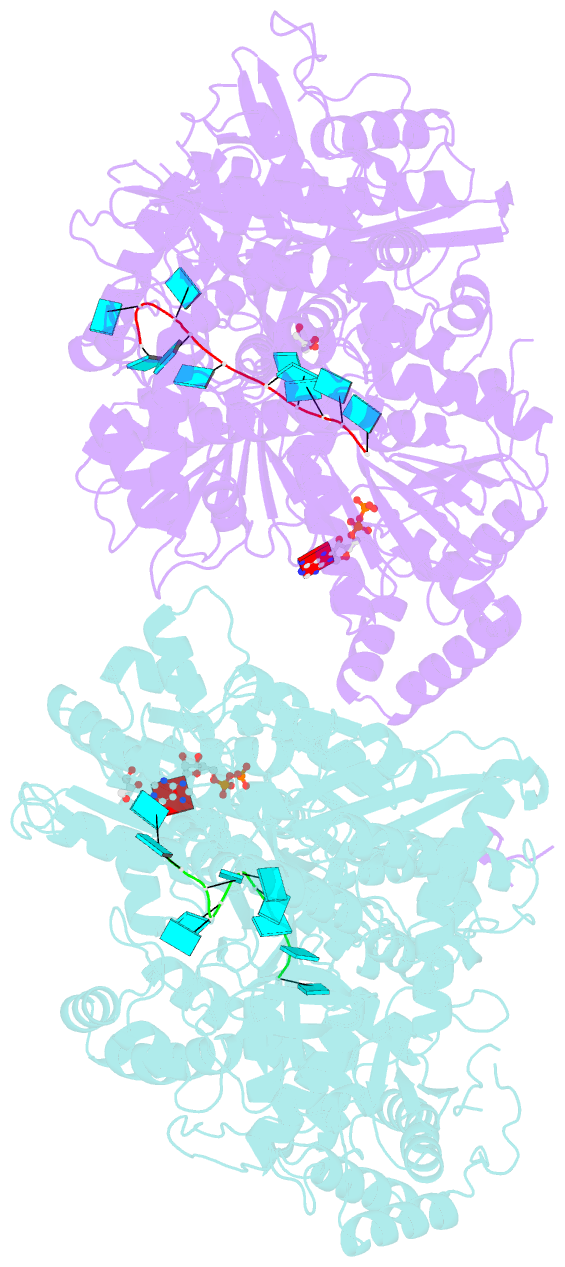
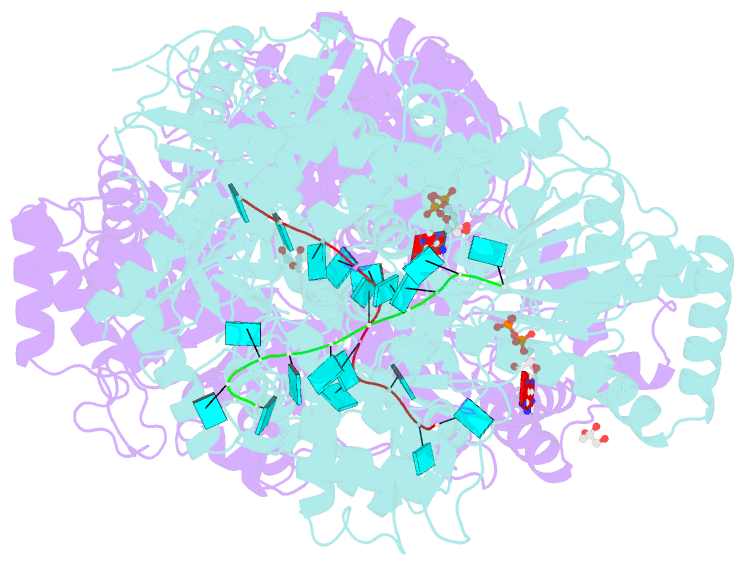
- Structure of mle RNA adp alf4 complex
- Reference
- Prabu JR, Muller M, Thomae AW, Schussler S, Bonneau F, Becker PB, Conti E (2015): "Structure of the RNA Helicase Mle Reveals the Molecular Mechanisms for Uridine Specificity and RNA-ATP Coupling." Mol.Cell, 60, 487. doi: 10.1016/J.MOLCEL.2015.10.011.
- Abstract
- The MLE helicase remodels the roX lncRNAs, enabling the lncRNA-mediated assembly of the Drosophila dosage compensation complex. We identified a stable MLE core comprising the DExH helicase module and two auxiliary domains: a dsRBD and an OB-like fold. MLEcore is an unusual DExH helicase that can unwind blunt-ended RNA duplexes and has specificity for uridine nucleotides. We determined the 2.1 Å resolution structure of MLEcore bound to a U10 RNA and ADP-AlF4. The OB-like and dsRBD folds bind the DExH module and contribute to form the entrance of the helicase channel. Four uridine nucleotides engage in base-specific interactions, rationalizing the conservation of uridine-rich sequences in critical roX substrates. roX2 binding is orchestrated by MLE's auxiliary domains, which is prerequisite for MLE localization to the male X chromosome. The structure visualizes a transition-state mimic of the reaction and suggests how eukaryotic DEAH/RHA helicases couple ATP hydrolysis to RNA translocation.