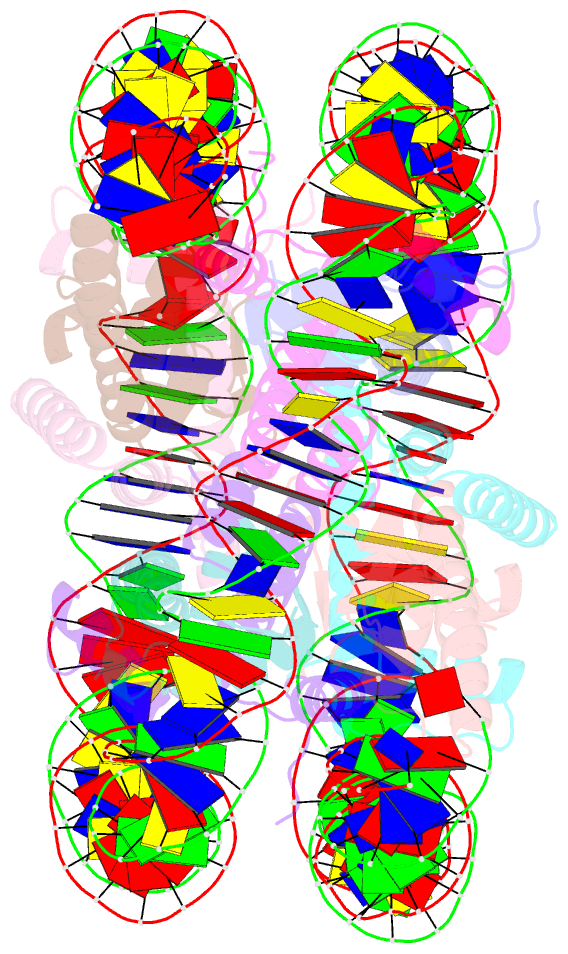
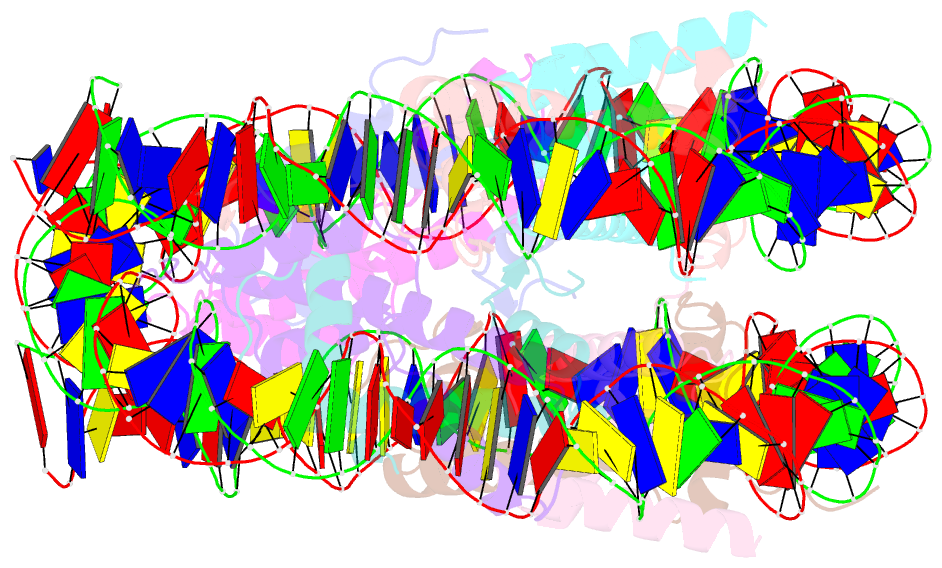
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5b1m; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- structural protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.34 Å)
- Summary
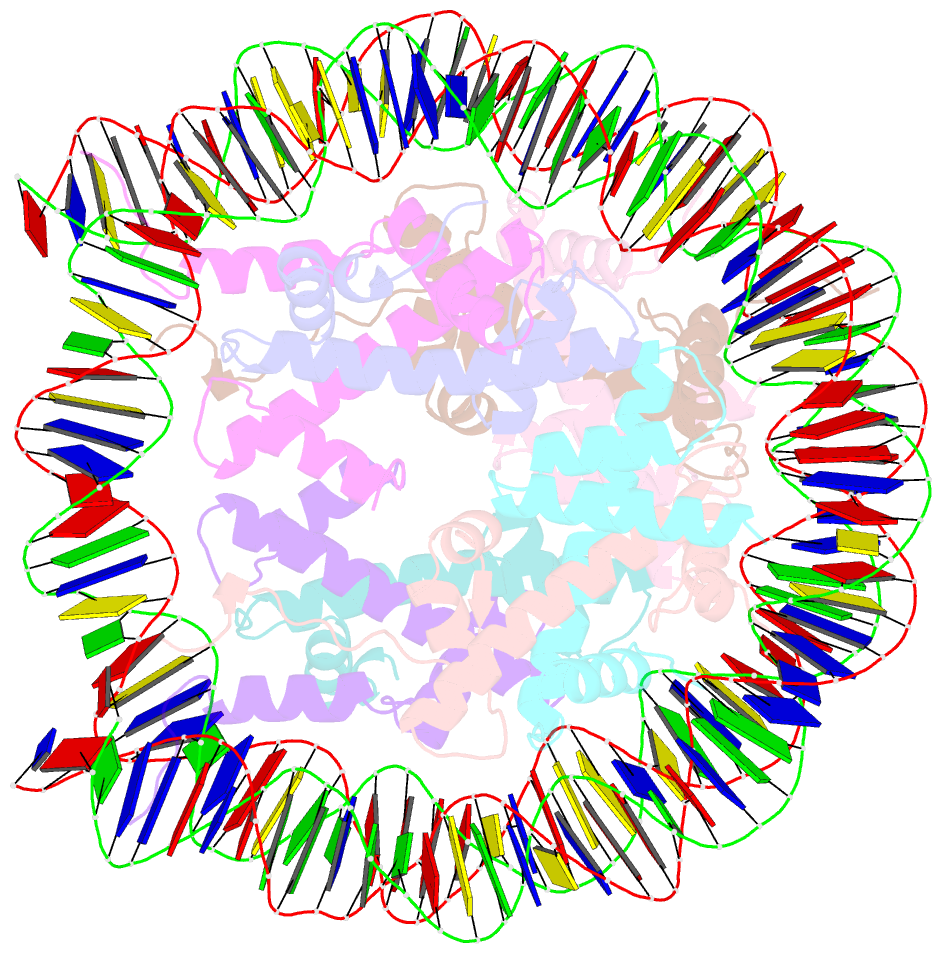
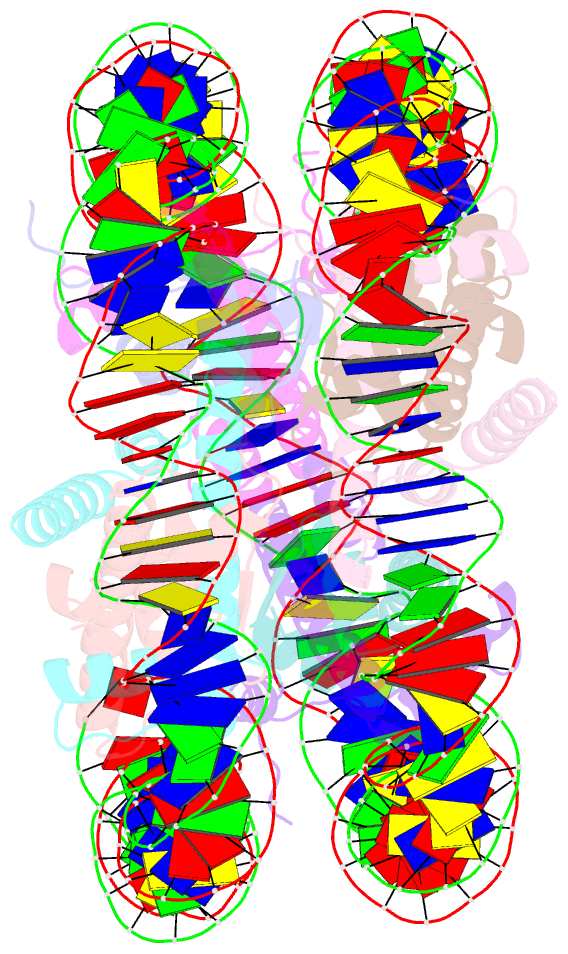
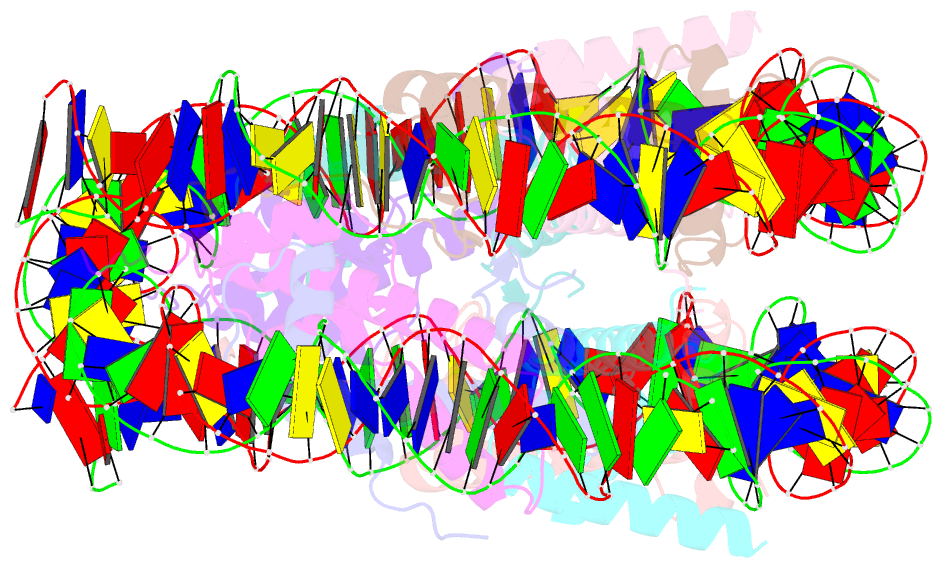
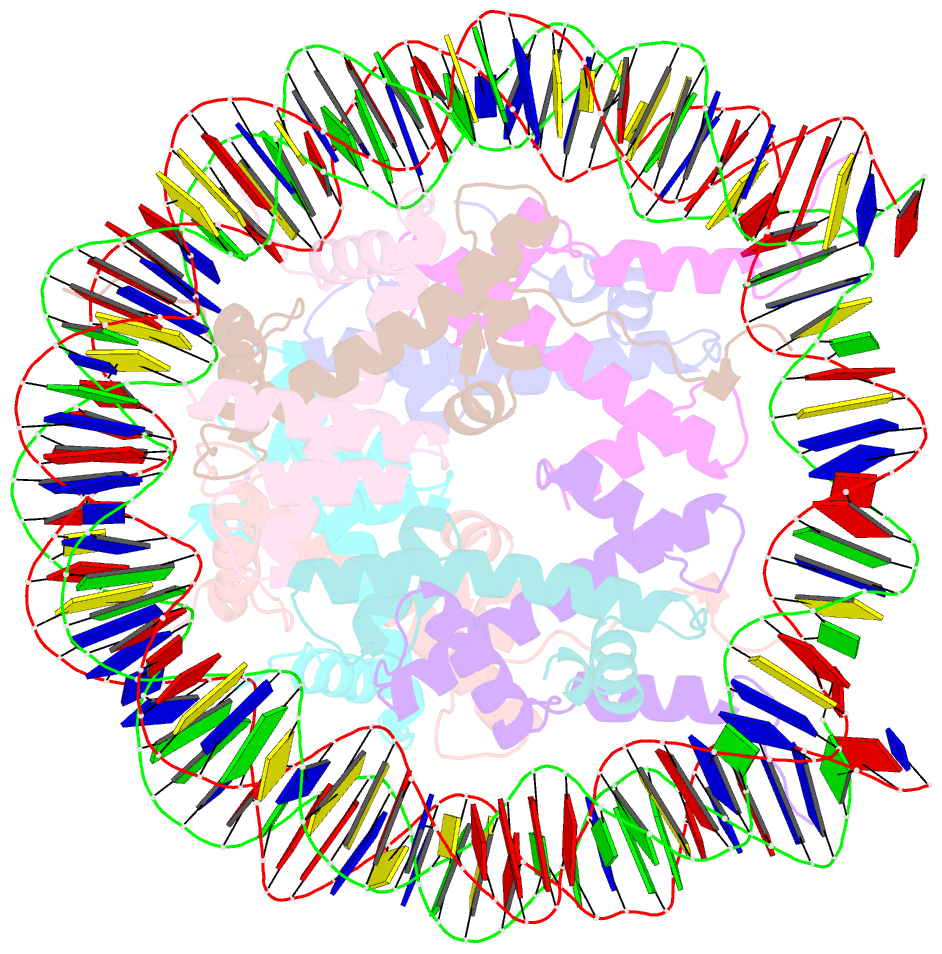
- The mouse nucleosome structure containing h3.1
- Reference
- Ueda J, Harada A, Urahama T, Machida S, Maehara K, Hada M, Makino Y, Nogami J, Horikoshi N, Osakabe A, Taguchi H, Tanaka H, Tachiwana H, Yao T, Yamada M, Iwamoto T, Isotani A, Ikawa M, Tachibana T, Okada Y, Kimura H, Ohkawa Y, Kurumizaka H, Yamagata K (2017): "Testis-Specific Histone Variant H3t Gene Is Essential for Entry into Spermatogenesis." Cell Rep, 18, 593-600. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.065.
- Abstract
- Cellular differentiation is associated with dynamic chromatin remodeling in establishing a cell-type-specific epigenomic landscape. Here, we find that mouse testis-specific and replication-dependent histone H3 variant H3t is essential for very early stages of spermatogenesis. H3t gene deficiency leads to azoospermia because of the loss of haploid germ cells. When differentiating spermatogonia emerge in normal spermatogenesis, H3t appears and replaces the canonical H3 proteins. Structural and biochemical analyses reveal that H3t-containing nucleosomes are more flexible than the canonical nucleosomes. Thus, by incorporating H3t into the genome during spermatogonial differentiation, male germ cells are able to enter meiosis and beyond.