Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5box; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
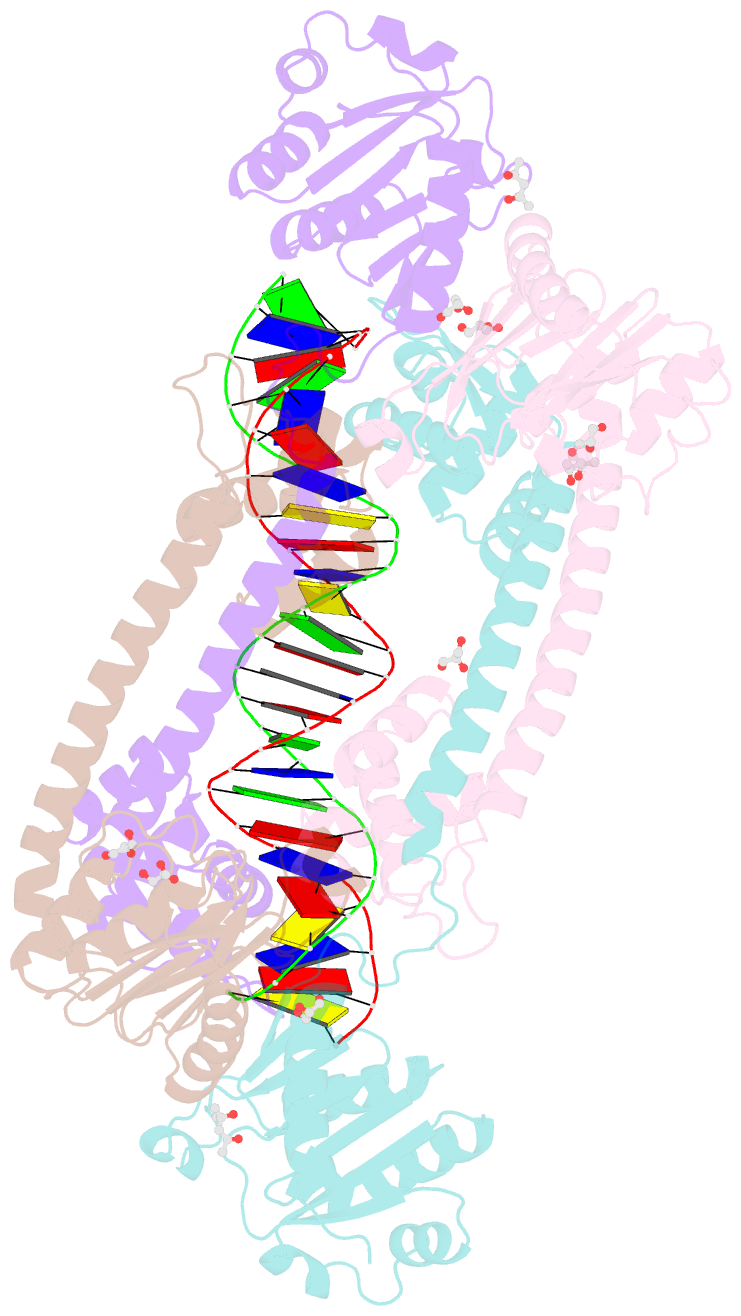
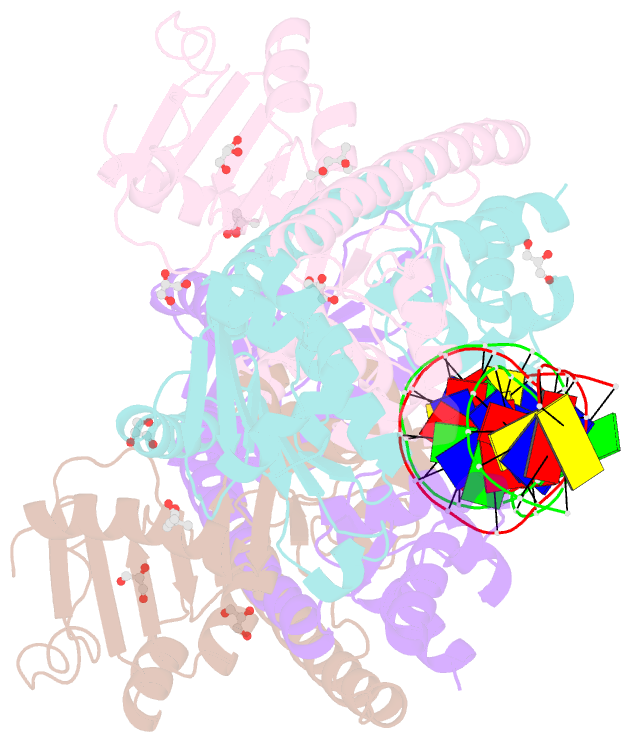
- Structure of trmbl2, an archaeal chromatin protein, shows a novel mode of DNA binding.
- Reference
- Ahmad MU, Waege I, Hausner W, Thomm M, Boos W, Diederichs K, Welte W (2015): "Structural Insights into Nonspecific Binding of DNA by TrmBL2, an Archaeal Chromatin Protein." J.Mol.Biol., 427, 3216-3229. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.08.012.
- Abstract
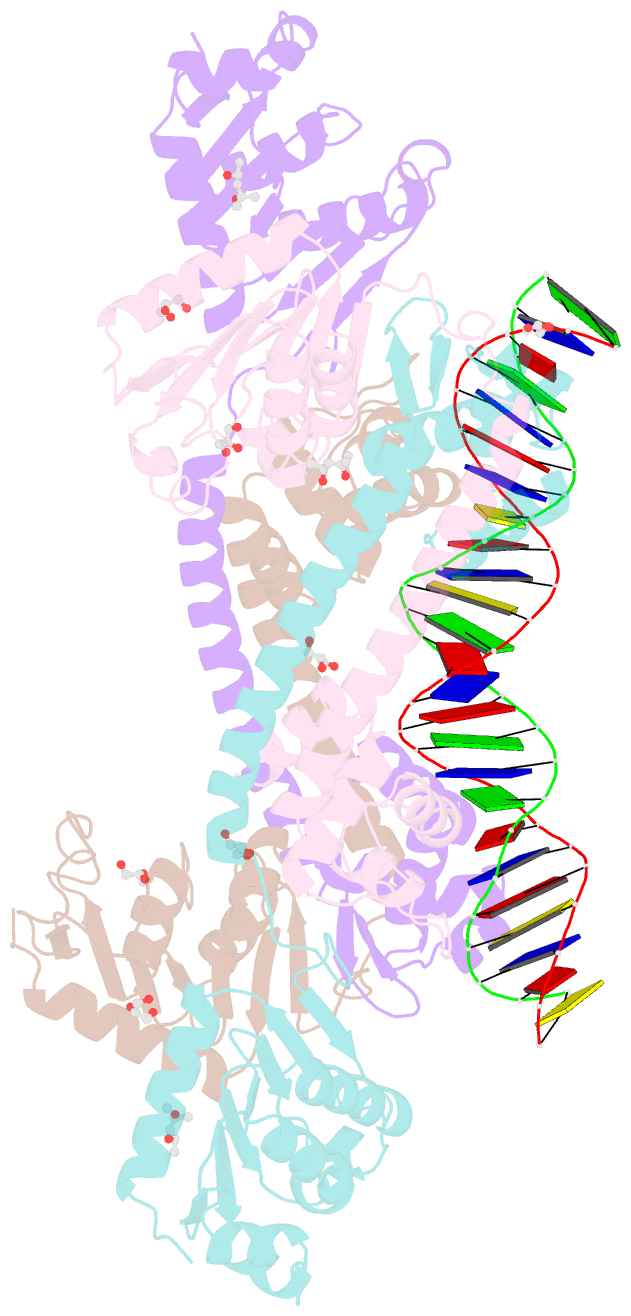
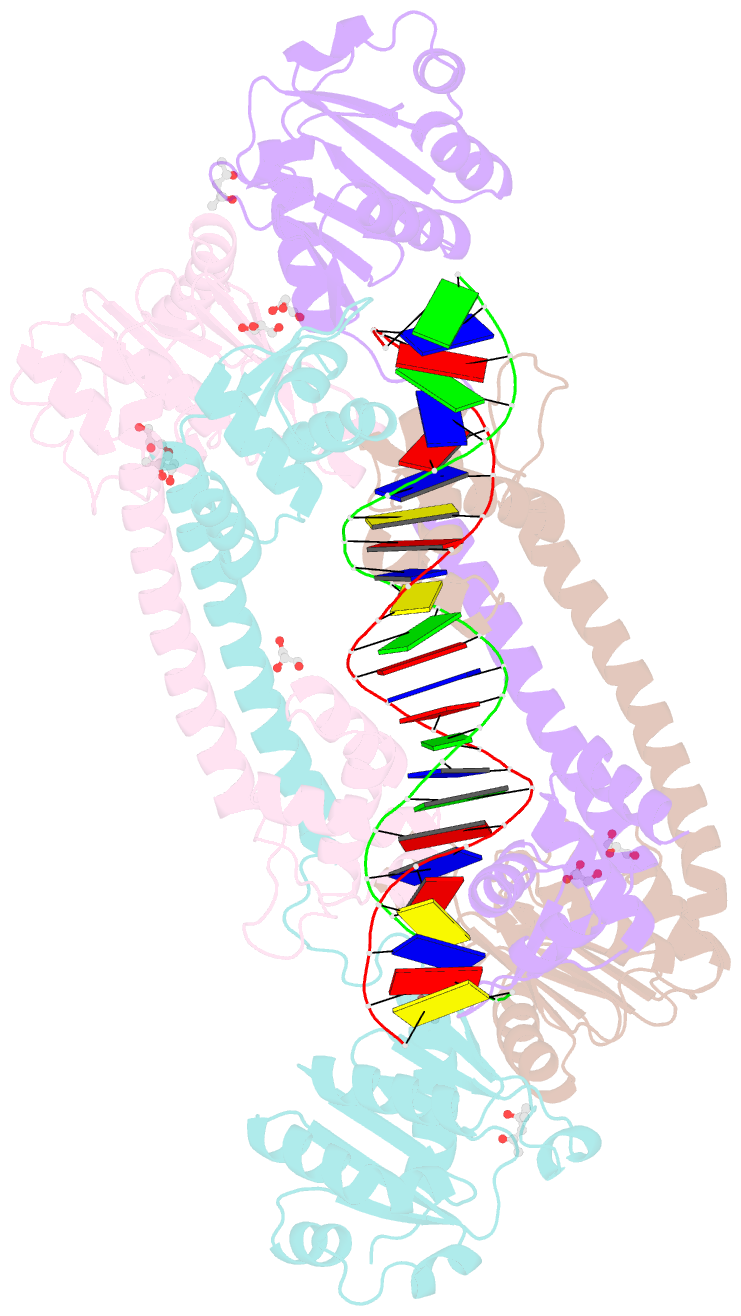
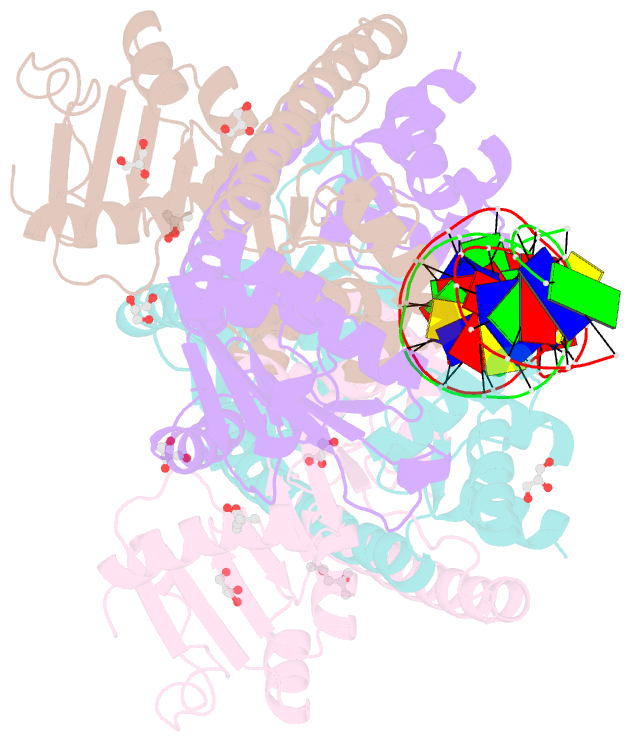
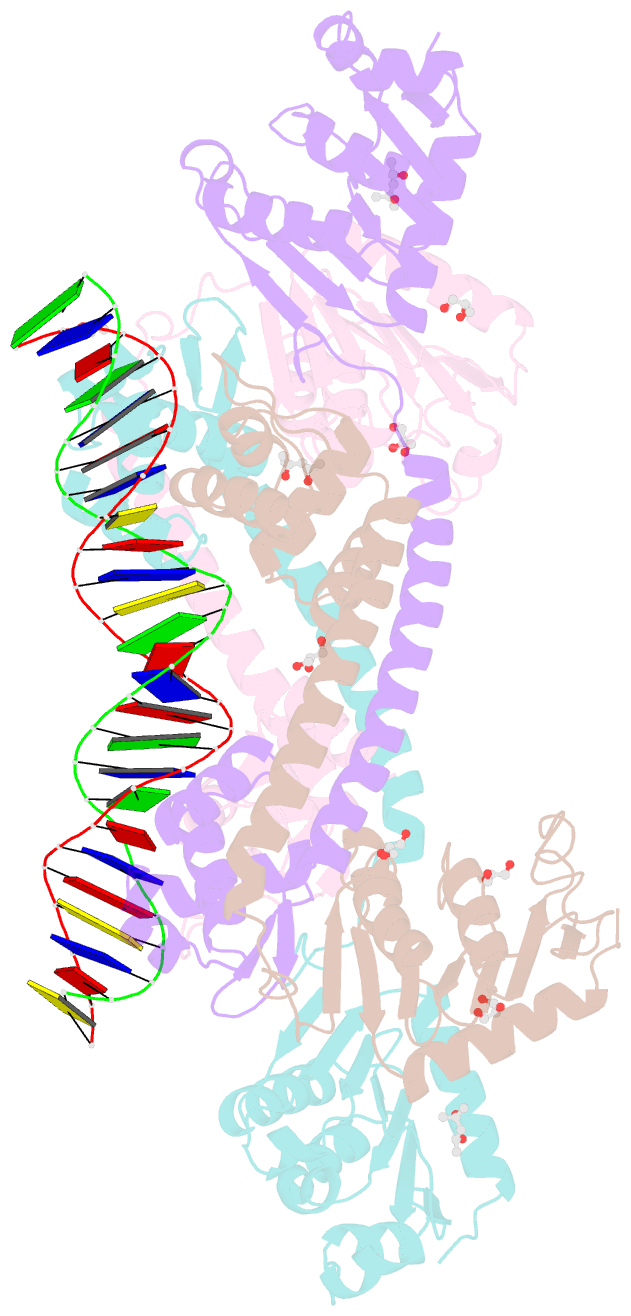
- The crystal structure of TrmBL2 from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus shows an association of two pseudosymmetric dimers. The dimers follow the prototypical design of known bacterial repressors with two helix-turn-helix (HTH) domains binding to successive major grooves of the DNA. However, in TrmBL2, the two dimers are arranged at a mutual displacement of approximately 2bp so that they associate with the DNA along the double-helical axis at an angle of approximately 80°. While the deoxyribose phosphate groups of the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) used for co-crystallization are clearly seen in the electron density map, most of the nucleobases are averaged out. Refinement required to assume a superposition of at least three mutually displaced dsDNAs. The HTH domains interact primarily with the deoxyribose phosphate groups and polar interactions with the nucleobases are almost absent. This hitherto unseen mode of DNA binding by TrmBL2 seems to arise from nonoptimal protein-DNA contacts made by its four HTH domains resulting in a low-affinity, nonspecific binding to DNA.