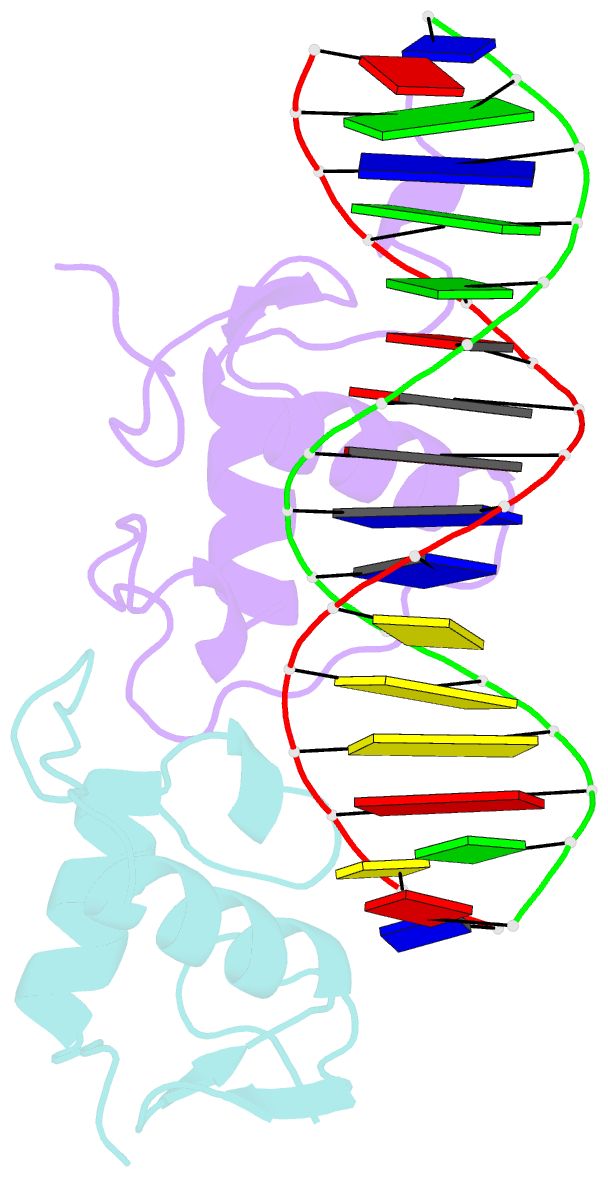
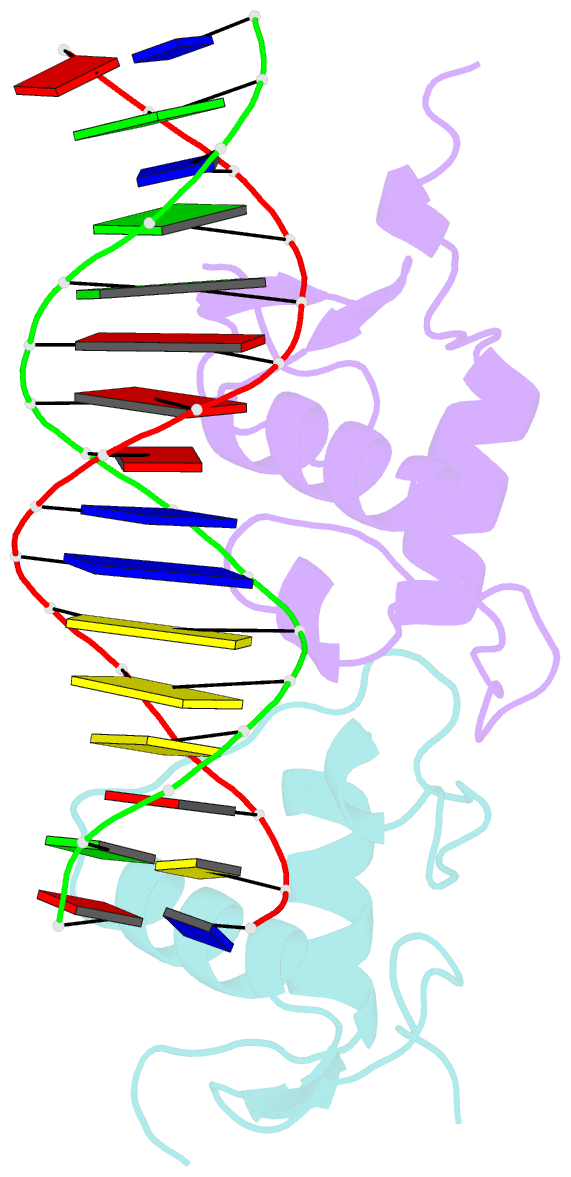
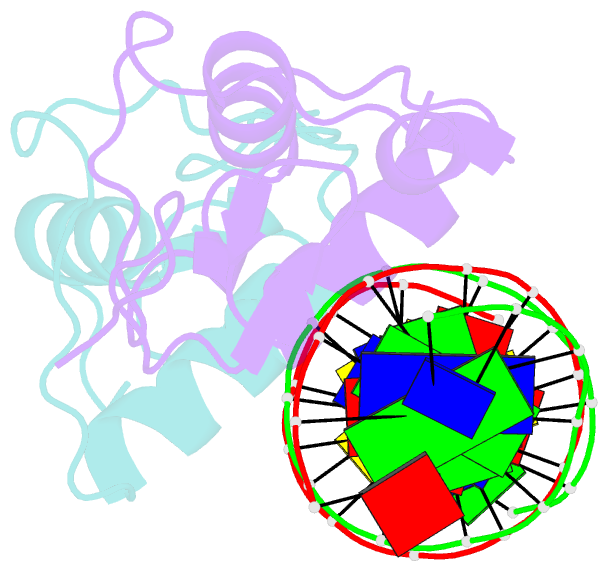
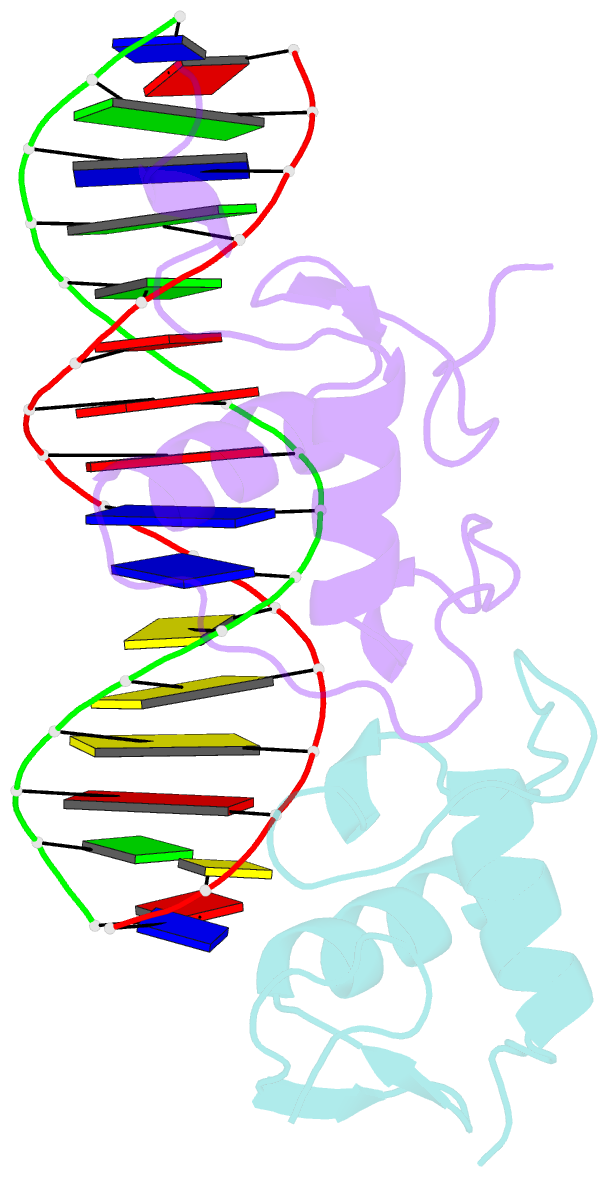
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5e6c; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.2 Å)
- Summary
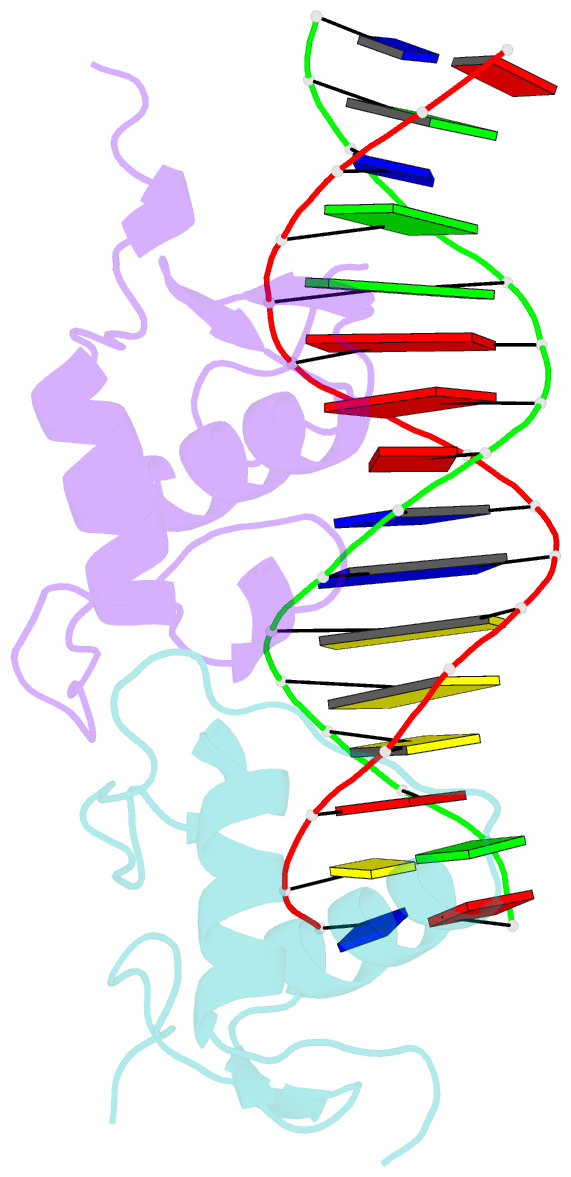
- Glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain - ccl2 nf-kb response element complex
- Reference
- Hudson WH, Vera IMS, Nwachukwu JC, Weikum ER, Herbst AG, Yang Q, Bain DL, Nettles KW, Kojetin DJ, Ortlund EA (2018): "Cryptic glucocorticoid receptor-binding sites pervade genomic NF-kappa B response elements." Nat Commun, 9, 1337. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03780-1.
- Abstract
- Glucocorticoids (GCs) are potent repressors of NF-κB activity, making them a preferred choice for treatment of inflammation-driven conditions. Despite the widespread use of GCs in the clinic, current models are inadequate to explain the role of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) within this critical signaling pathway. GR binding directly to NF-κB itself-tethering in a DNA binding-independent manner-represents the standing model of how GCs inhibit NF-κB-driven transcription. We demonstrate that direct binding of GR to genomic NF-κB response elements (κBREs) mediates GR-driven repression of inflammatory gene expression. We report five crystal structures and solution NMR data of GR DBD-κBRE complexes, which reveal that GR recognizes a cryptic response element between the binding footprints of NF-κB subunits within κBREs. These cryptic sequences exhibit high sequence and functional conservation, suggesting that GR binding to κBREs is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism of controlling the inflammatory response.