Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5fhe; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.9 Å)
- Summary
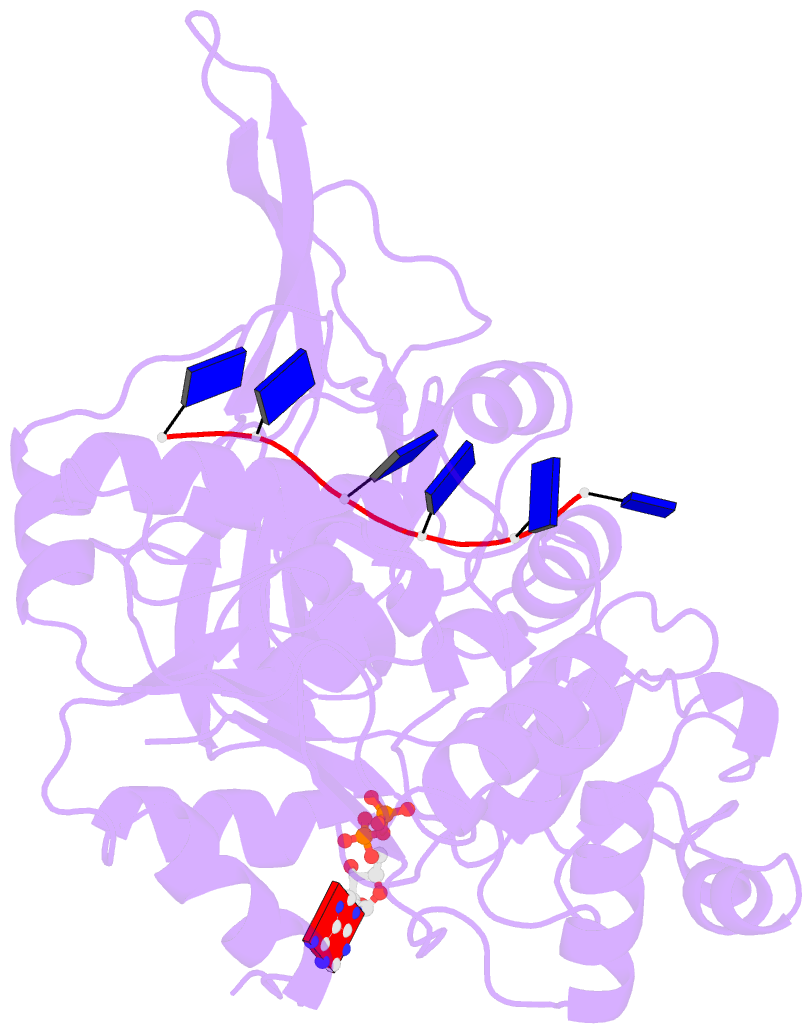
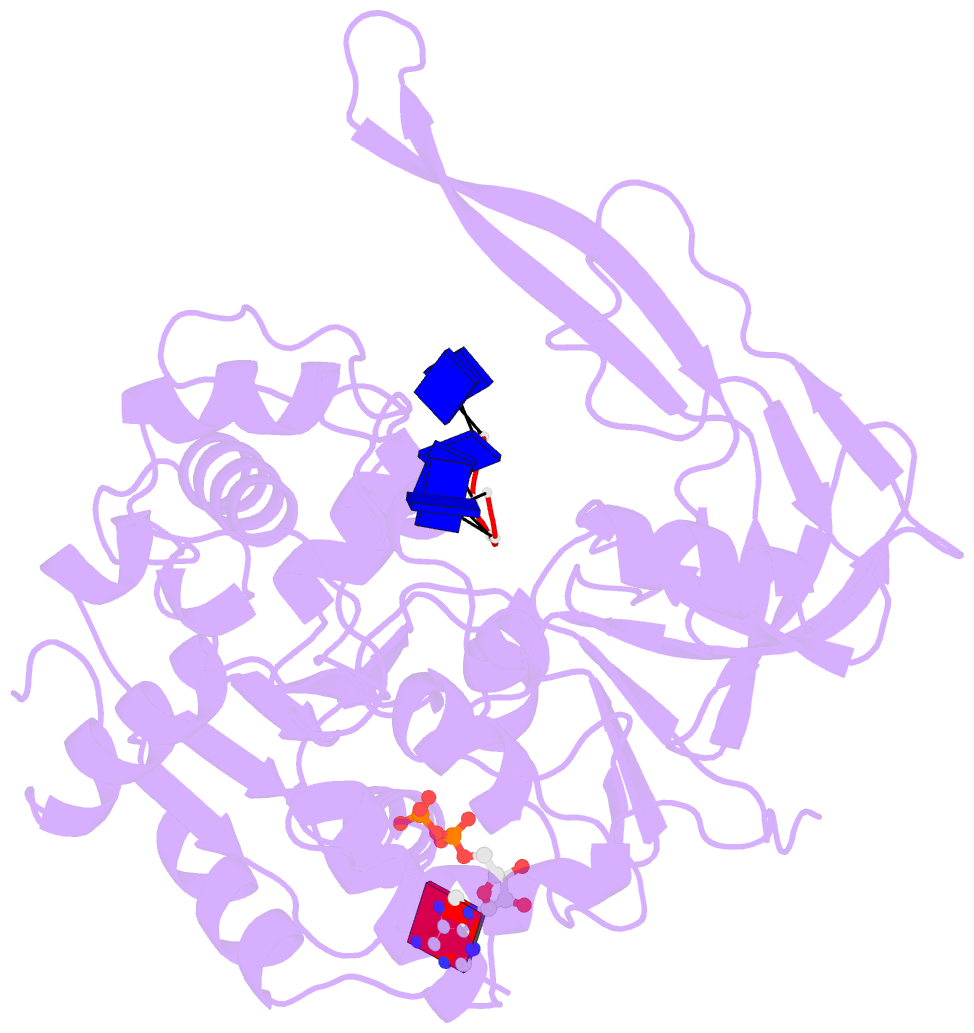
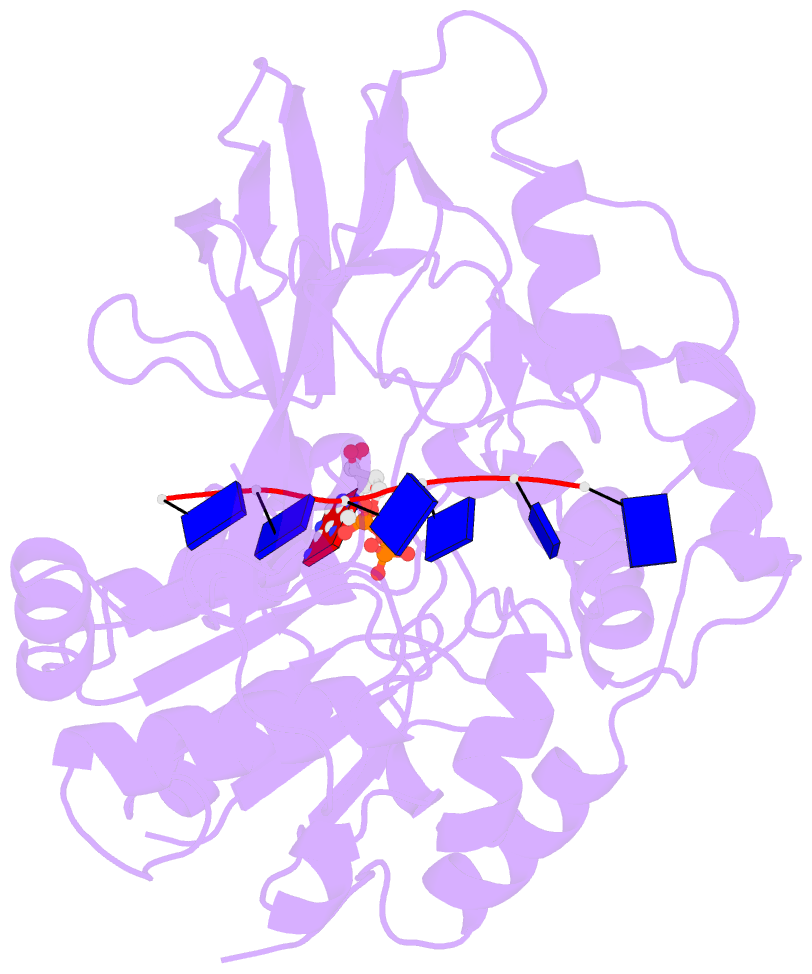
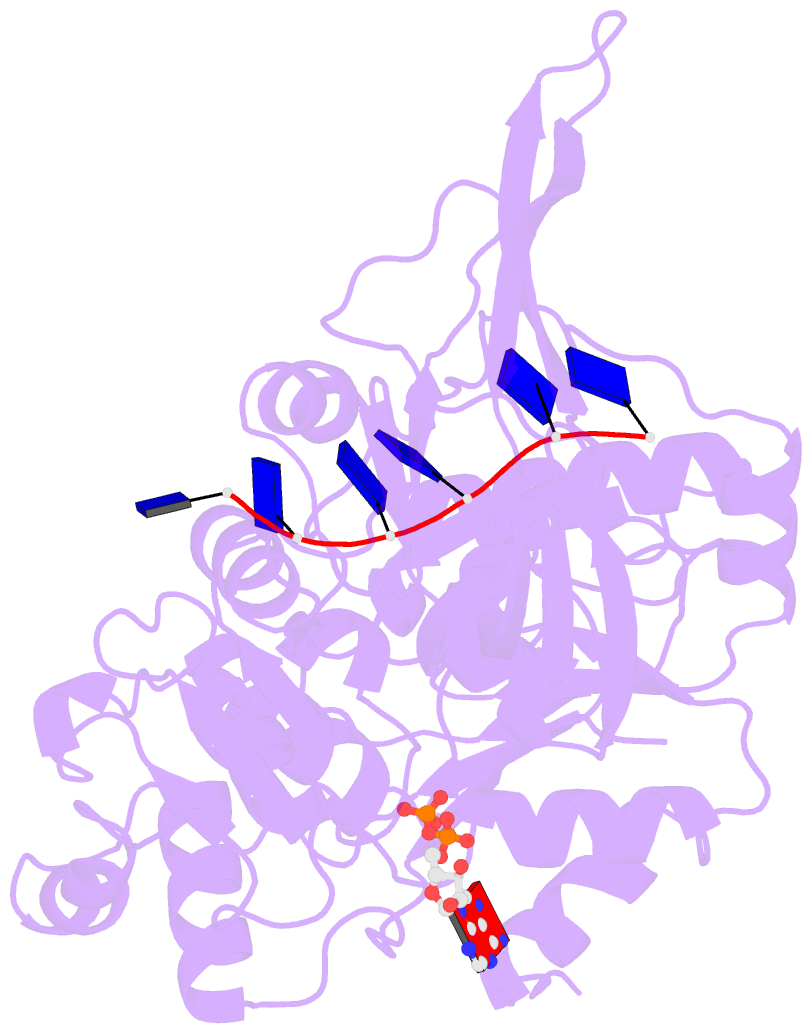
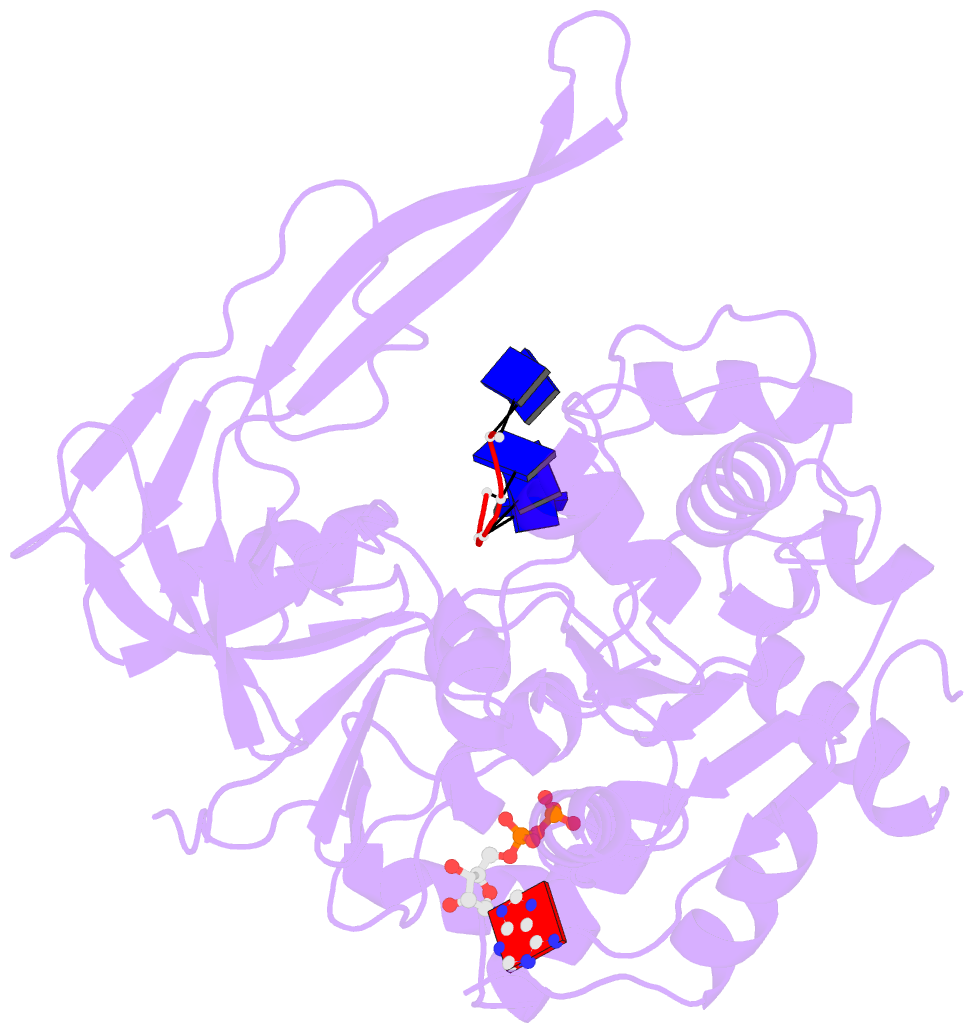
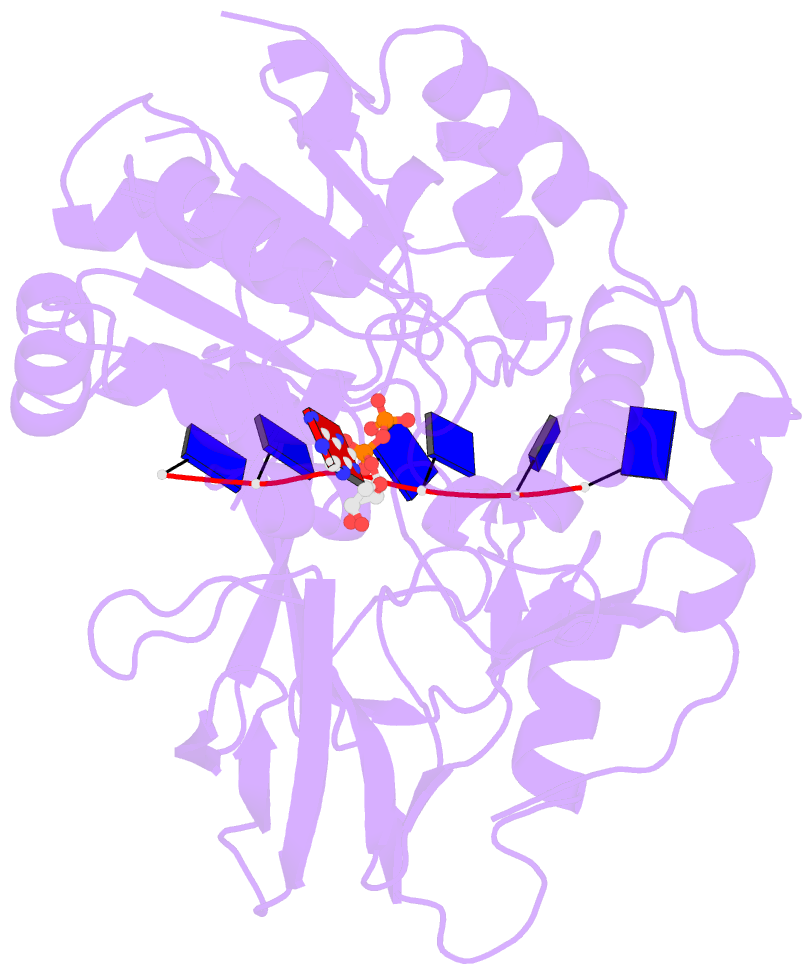
- Crystal structure of bacteroides pif1 bound to ssDNA
- Reference
- Zhou X, Ren W, Bharath SR, Tang X, He Y, Chen C, Liu Z, Li D, Song H (2016): "Structural and Functional Insights into the Unwinding Mechanism of Bacteroides sp Pif1." Cell Rep, 14, 2030-2039. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.008.
- Abstract
- Pif1 is a conserved SF1B DNA helicase involved in maintaining genome stability through unwinding double-stranded DNAs (dsDNAs), DNA/RNA hybrids, and G quadruplex (G4) structures. Here, we report the structures of the helicase domain of human Pif1 and Bacteroides sp Pif1 (BaPif1) in complex with ADP-AlF4(-) and two different single-stranded DNAs (ssDNAs). The wedge region equivalent to the β hairpin in other SF1B DNA helicases folds into an extended loop followed by an α helix. The Pif1 signature motif of BaPif1 interacts with the wedge region and a short helix in order to stabilize these ssDNA binding elements, therefore indirectly exerting its functional role. Domain 2B of BaPif1 undergoes a large conformational change upon concomitant binding of ATP and ssDNA, which is critical for Pif1's activities. BaPif1 cocrystallized with a tailed dsDNA and ADP-AlF4(-), resulting in a bound ssDNA bent nearly 90° at the ssDNA/dsDNA junction. The conformational snapshots of BaPif1 provide insights into the mechanism governing the helicase activity of Pif1.