Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5gip; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.129 Å)
- Summary
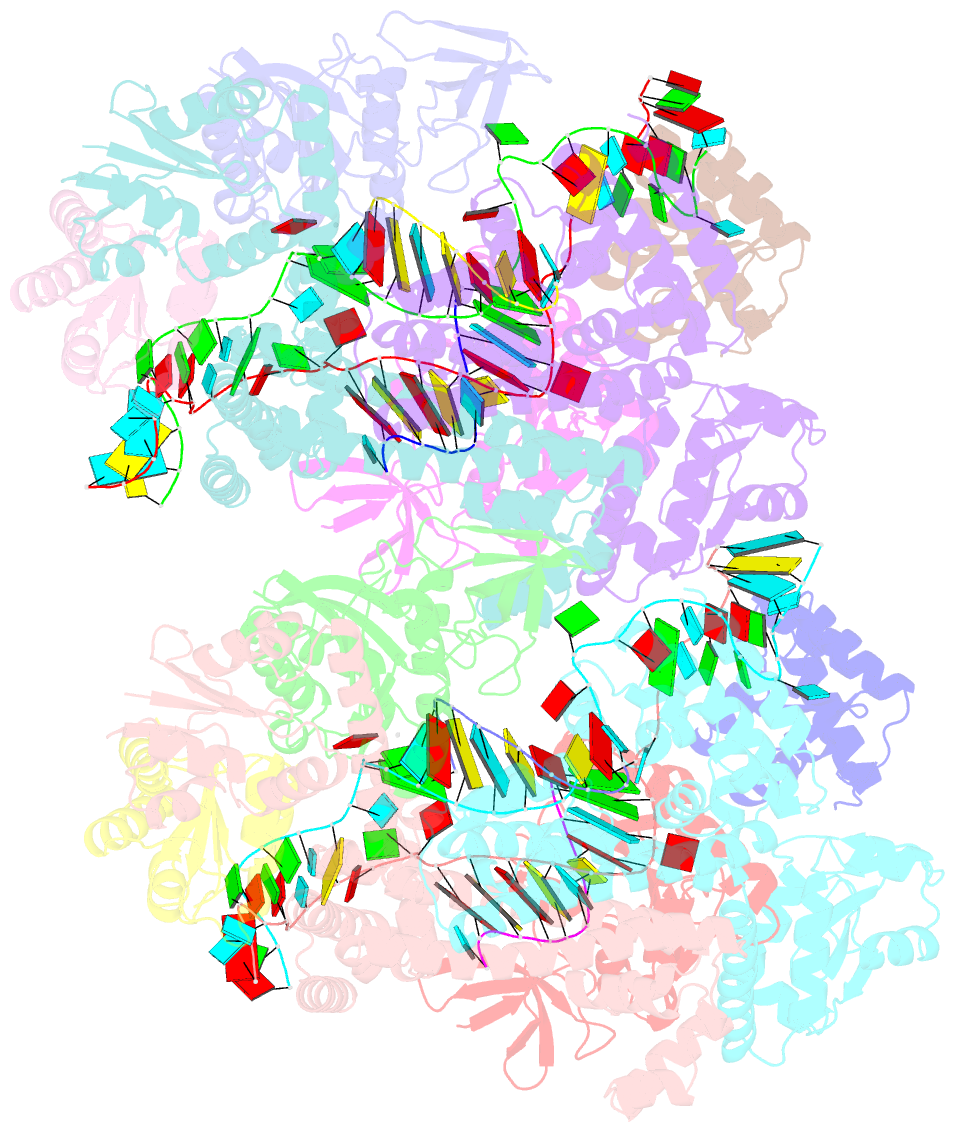
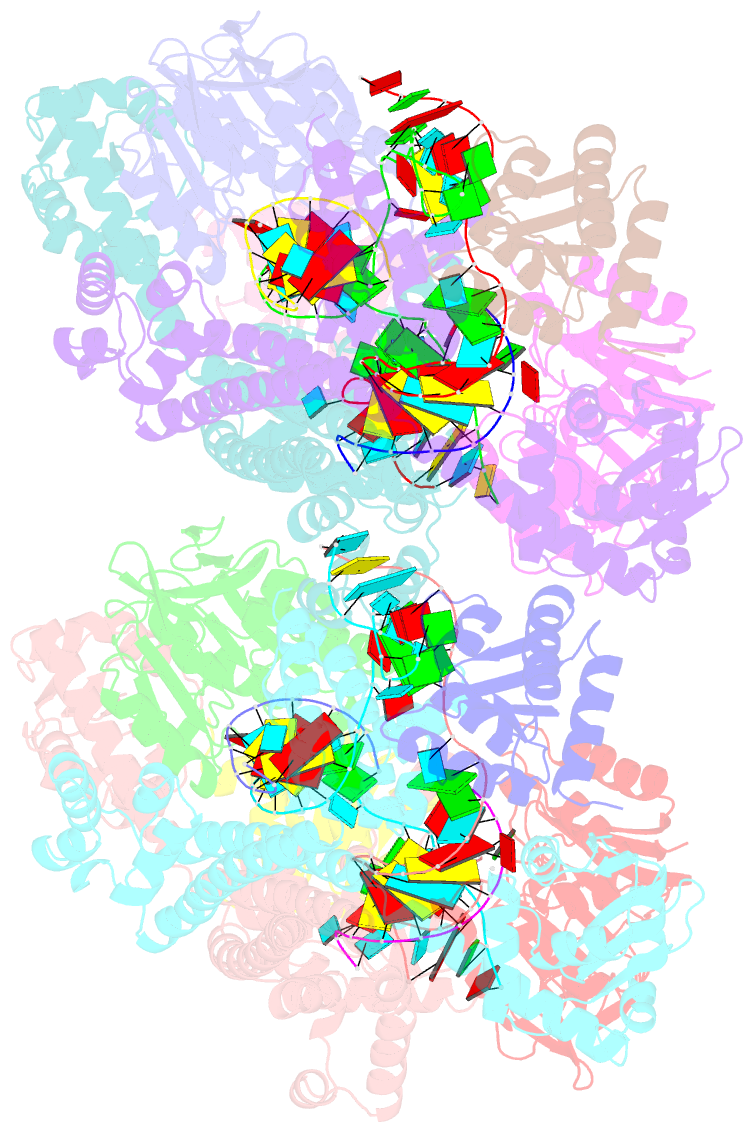
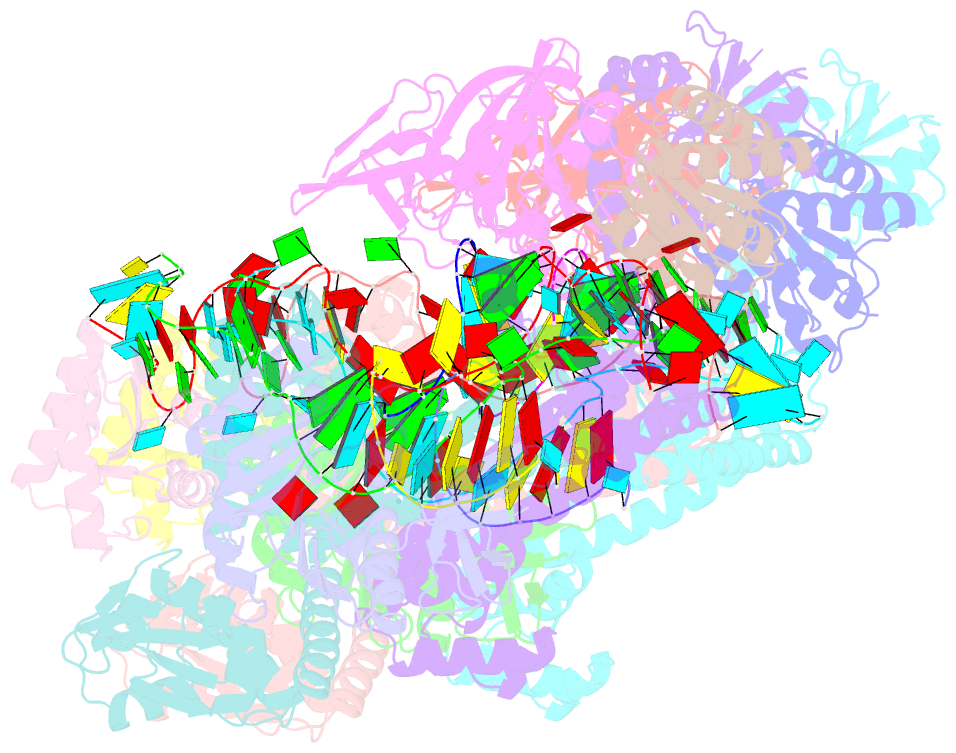
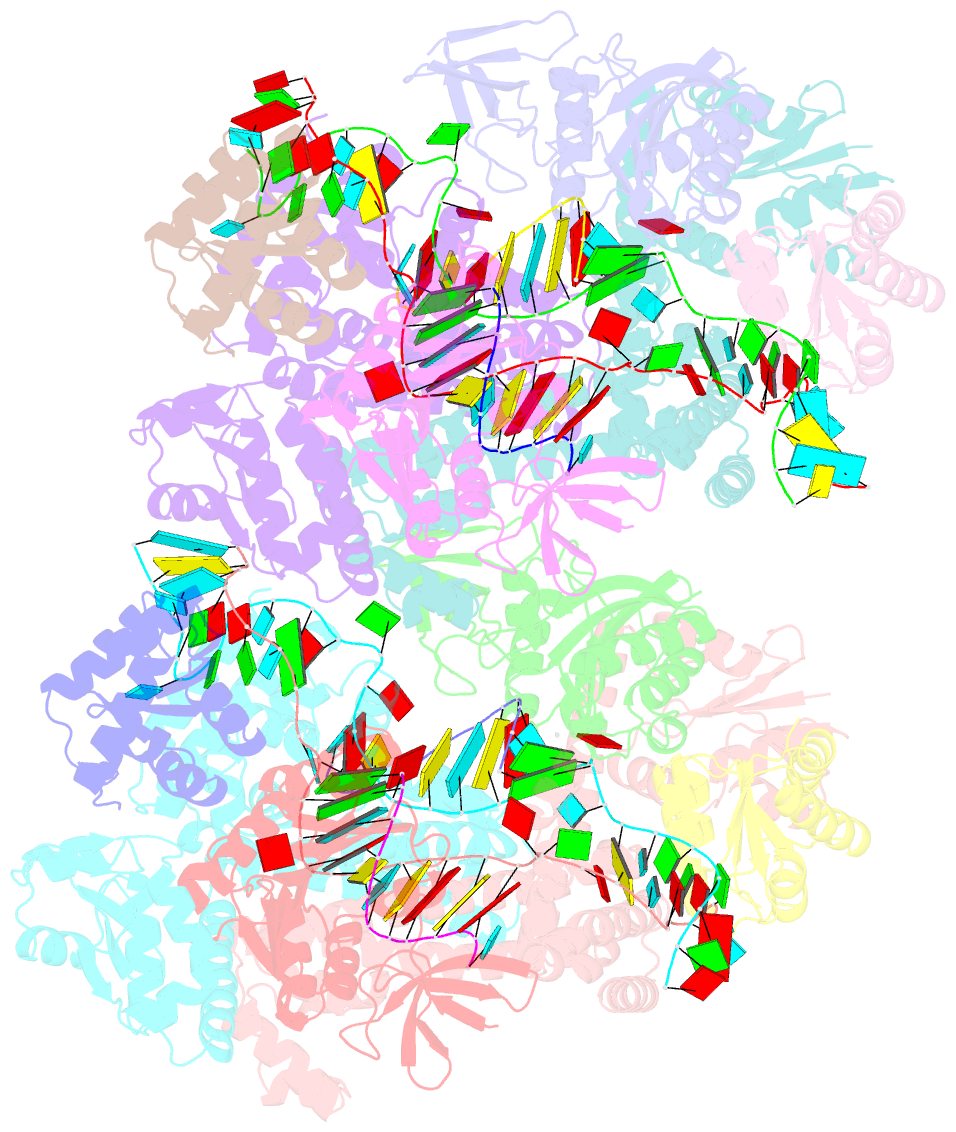
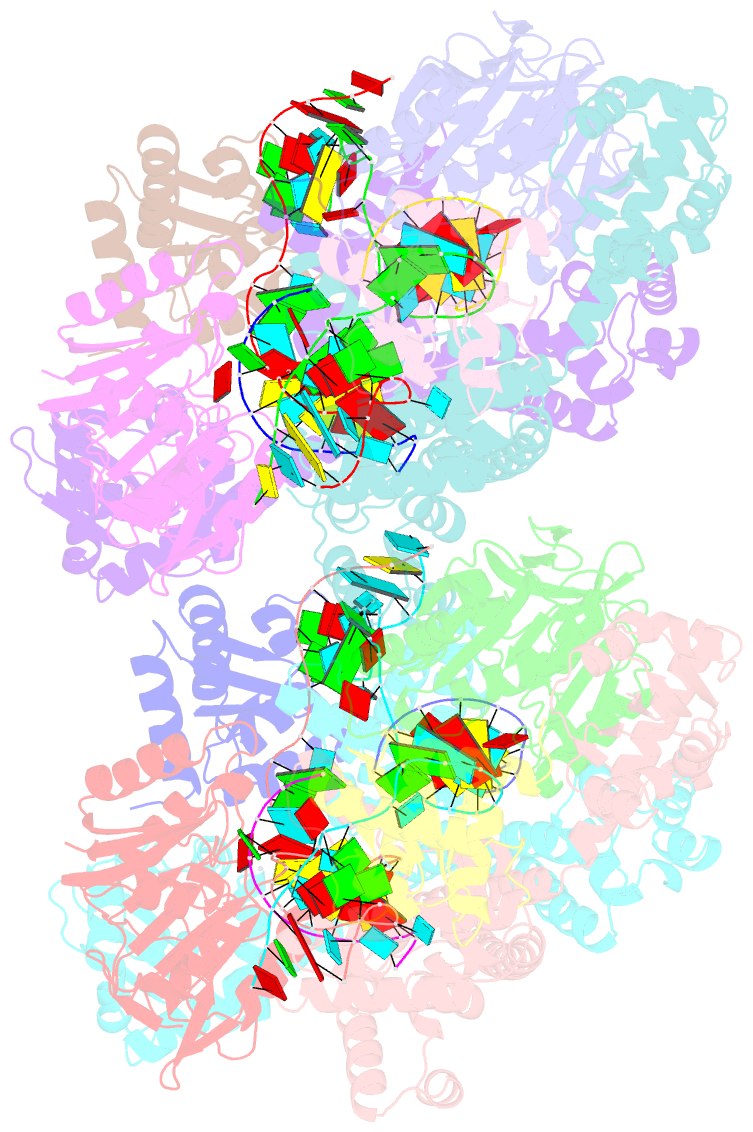
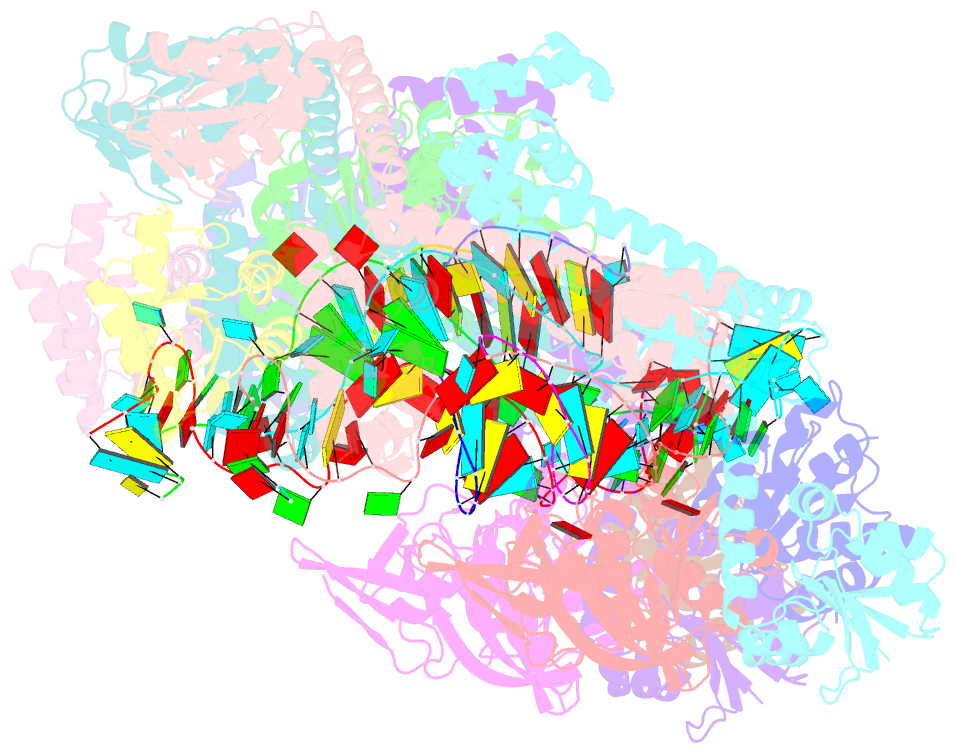
- Crystal structure of box c-d rnp with 13 nt guide regions and 11 nt substrates
- Reference
- Yang Z, Lin J, Ye K (2016): "Box C/D guide RNAs recognize a maximum of 10 nt of substrates." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 113, 10878-10883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604872113.
- Abstract
- Box C/D RNAs guide site-specific 2'-O-methylation of RNAs in archaea and eukaryotes. The spacer regions between boxes C to D' and boxes C' to D contain the guide sequence that can form a stretch of base pairs with substrate RNAs. The lengths of spacer regions and guide-substrate duplexes are variable among C/D RNAs. In a previously determined structure of C/D ribonucleoprotein (RNP), a 12-nt-long spacer forms 10 bp with the substrate. How spacers and guide-substrate duplexes of other lengths are accommodated remains unknown. Here we analyze how the lengths of spacers and guide-substrate duplexes affect the modification activity and determine three structures of C/D RNPs assembled with different spacers and substrates. We show that the guide can only form a duplex of a maximum of 10 bp with the substrate during modification. Slightly shorter duplexes are tolerated, but longer duplexes must be unwound to fit into a capped protein channel for modification. Spacers with <12 nucleotides are defective, mainly because they cannot load the substrate in the active conformation. For spacers with>12 nucleotides, the excessive unpaired sequences near the box C/C' side are looped out. Our results provide insight into the substrate recognition mechanism of C/D RNA and refute the RNA-swapped model for dimeric C/D RNP.