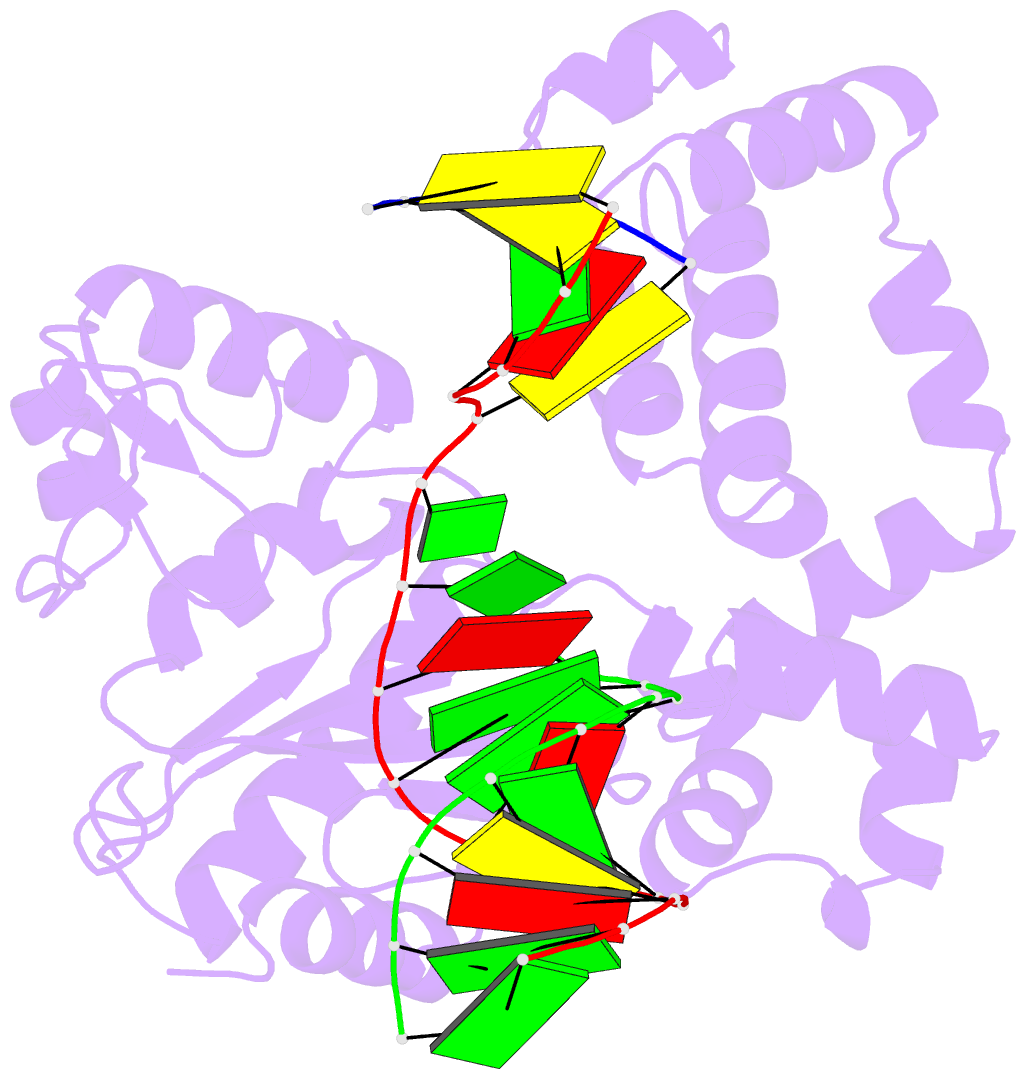
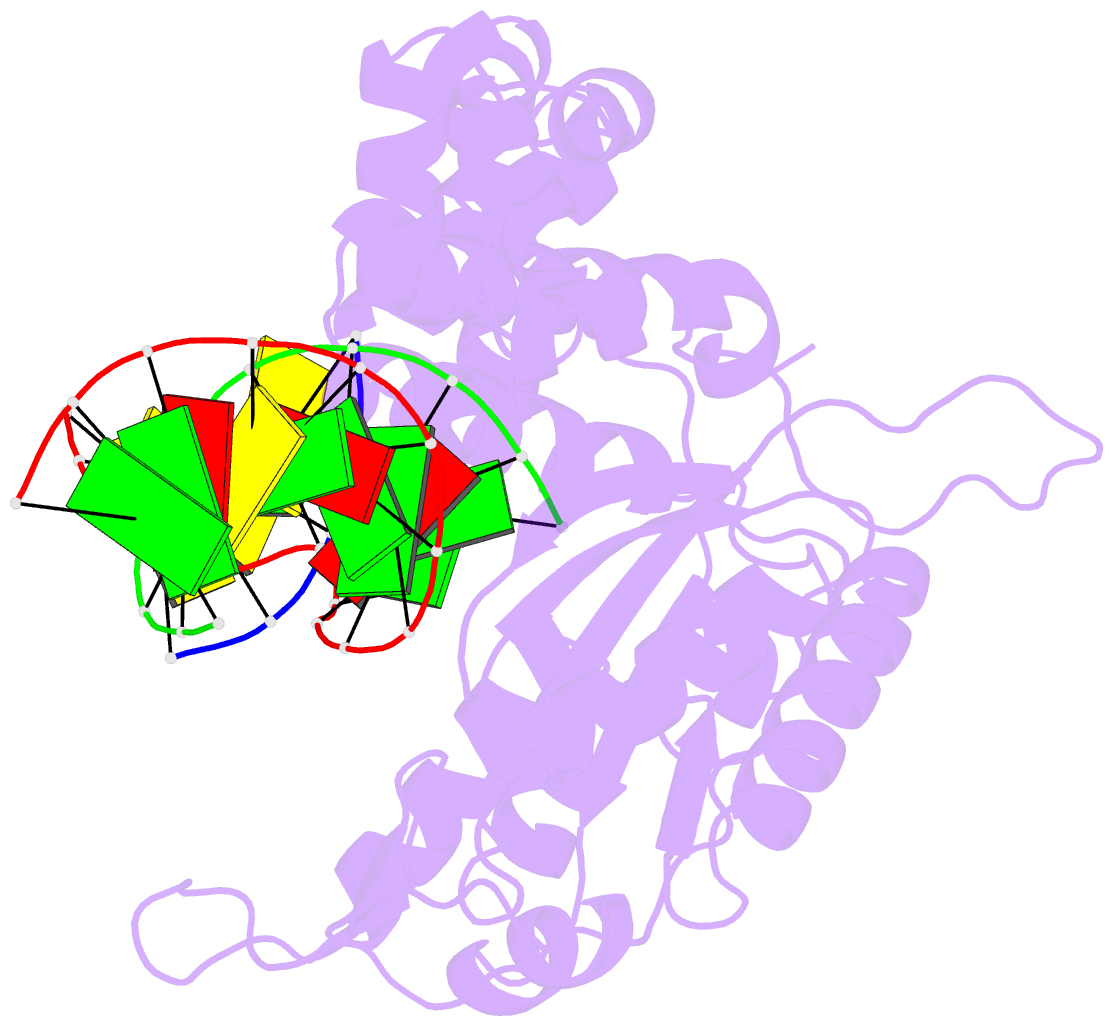
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5hhh; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase, lyase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.363 Å)
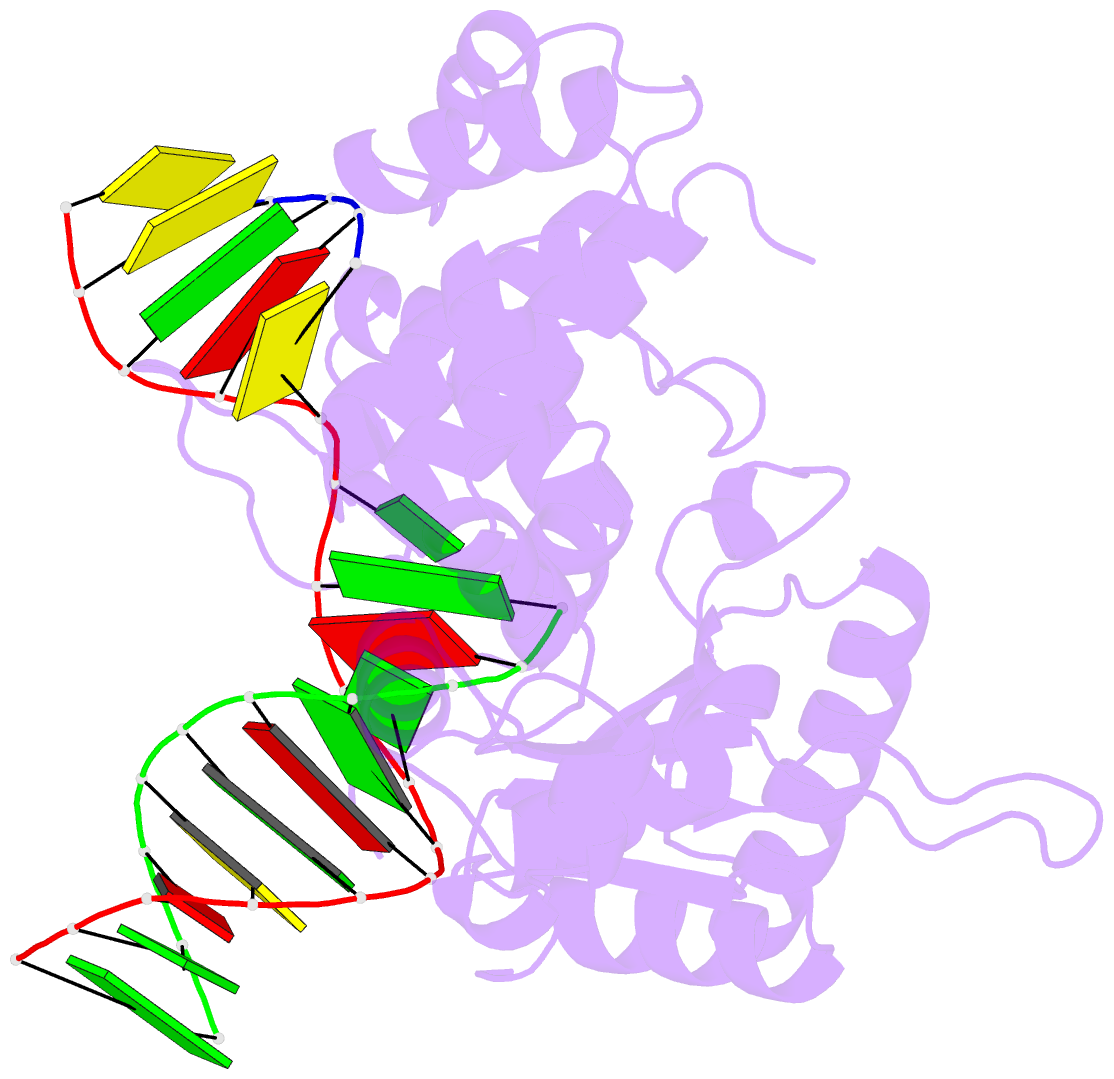
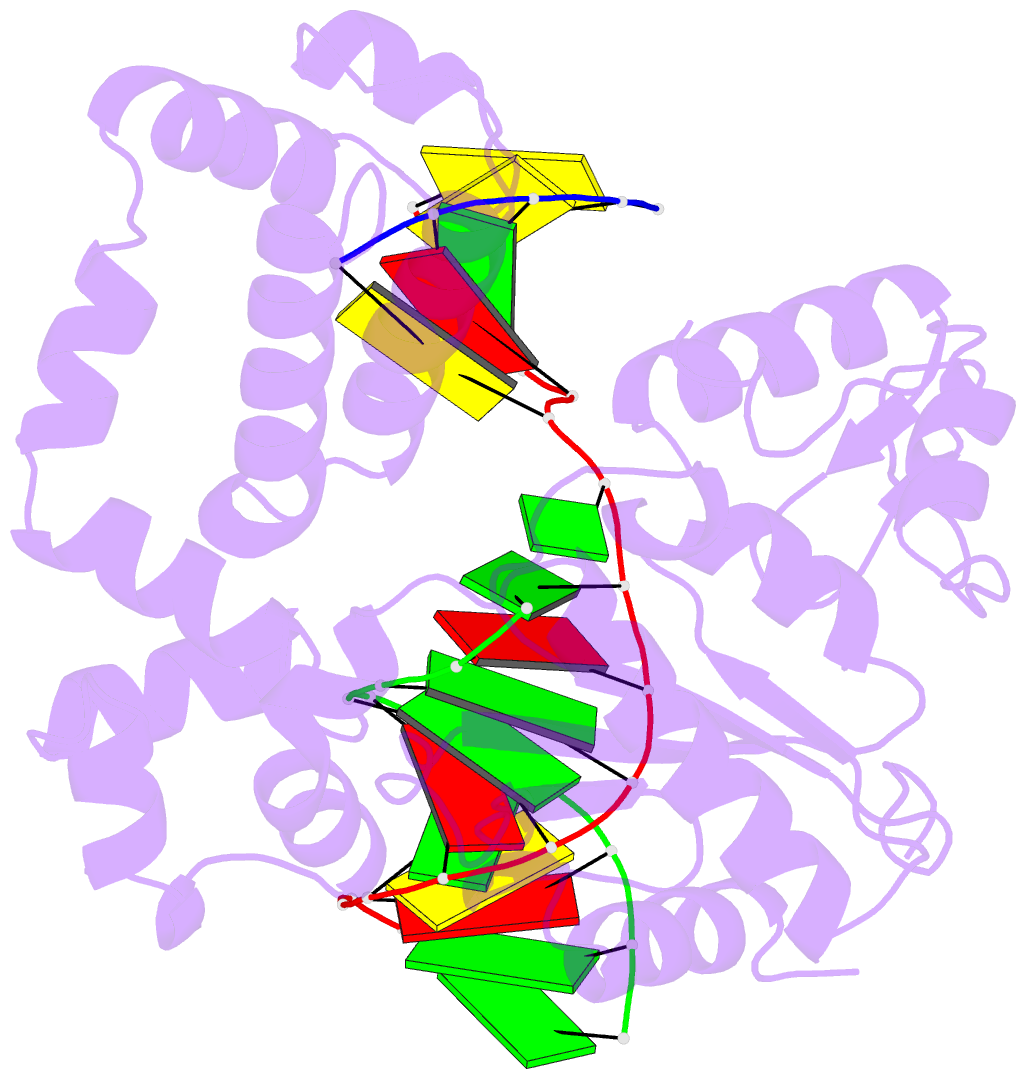
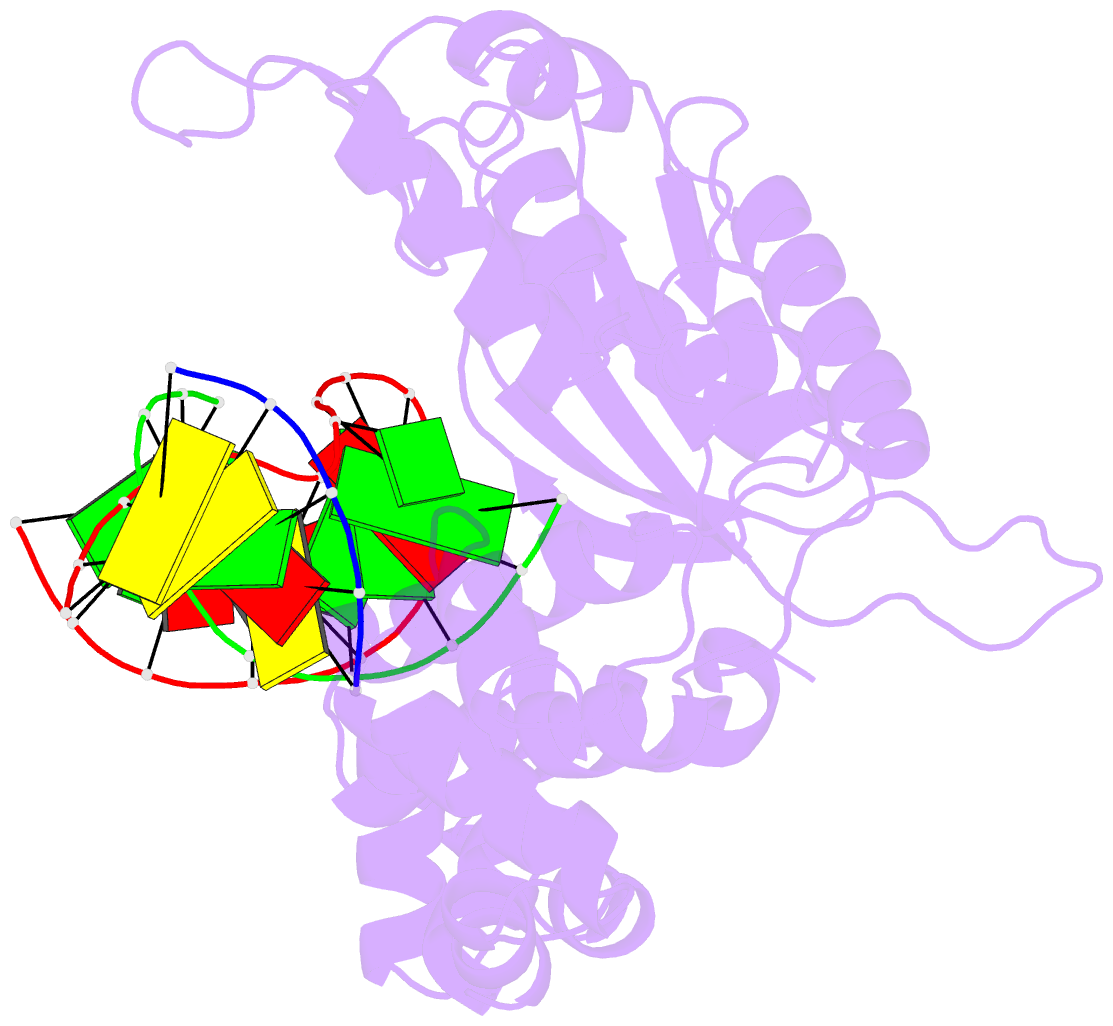
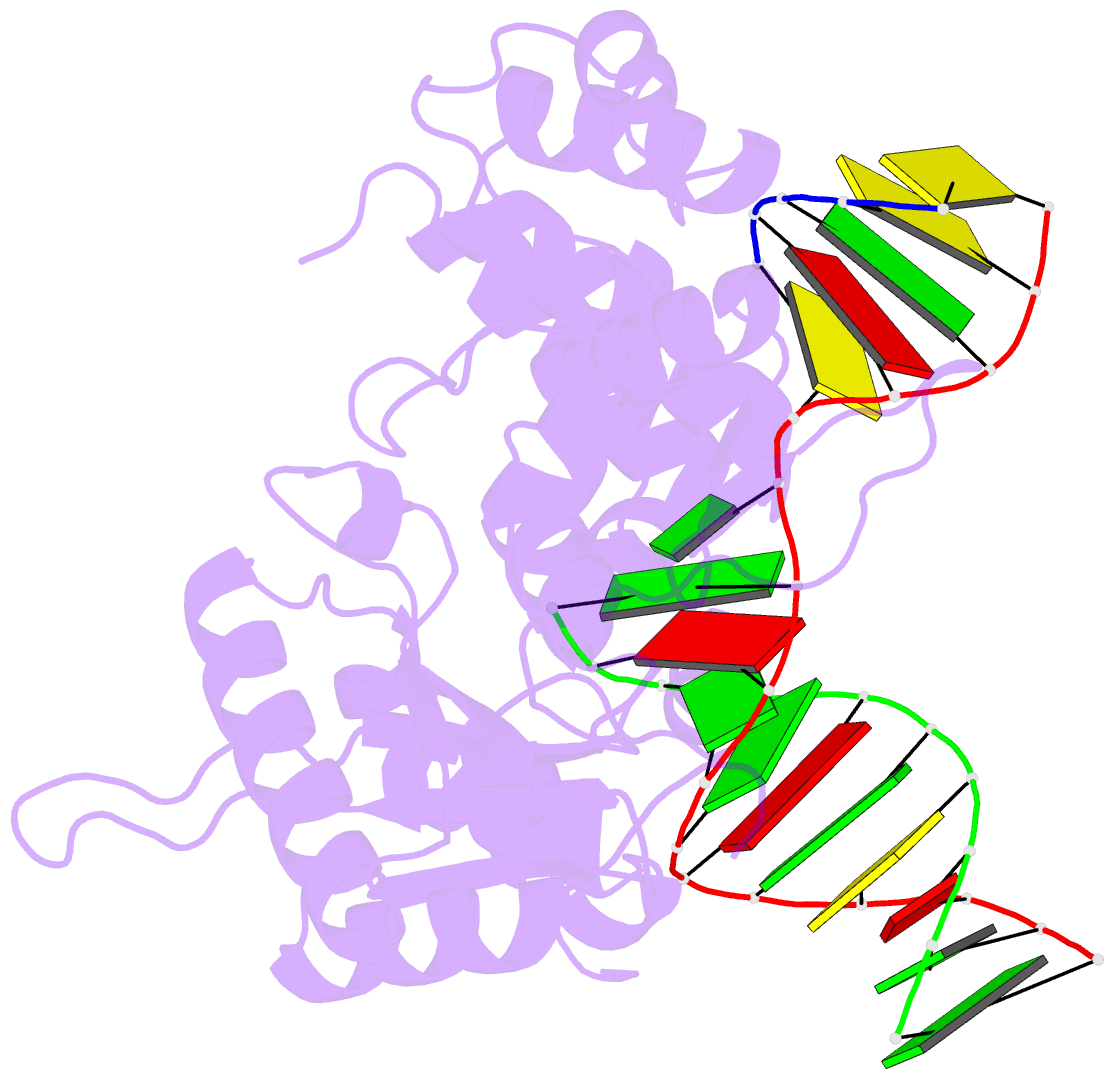
- Summary
- Structure of human DNA polymerase beta host-guest complexed with the control g for n7-cbz-platination
- Reference
- Cheun Y, Koag MC, Naguib YW, Ouzon-Shubeita H, Cui Z, Pakotiprapha D, Lee S (2018): "Synthesis, structure, and biological evaluation of a platinum-carbazole conjugate." Chem Biol Drug Des, 91, 116-125. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13062.
- Abstract
- Cisplatin resistance is caused, in part, by the efficient removal of the helix-distorting cisplatin 1,2-intrastrand cross-links by nucleotide excision repair (NER) machinery. To make a platinum-DNA adduct that causes less helical distortion than the cisplatin 1,2-intrastrand adduct, we designed and synthesized a monofunctional platinum-carbazole conjugate (carbazoplatin). The 2.5 Å crystal structure of carbazoplatin-DNA adduct revealed both the monoplatination of the N7 of a guanine (G) base and the intercalation into two G:C base pairs, while causing a minor distortion of the DNA helix. A 50-mer dsDNA containing a single carbazoplatin lesion was poorly processed by UvrABC endonuclease, the prokaryotic NER machinery that detects helical distortion and performs dual incision around the lesion. Our cell viability assay indicated that the cytotoxic pathways of carbazoplatin might be different from those of cisplatin; carbazoplatin was 5-8 times more cytotoxic than cisplatin against PANC-1 and MDA-MB-231 cancer cell lines.