Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5hq2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (4.5 Å)
- Summary
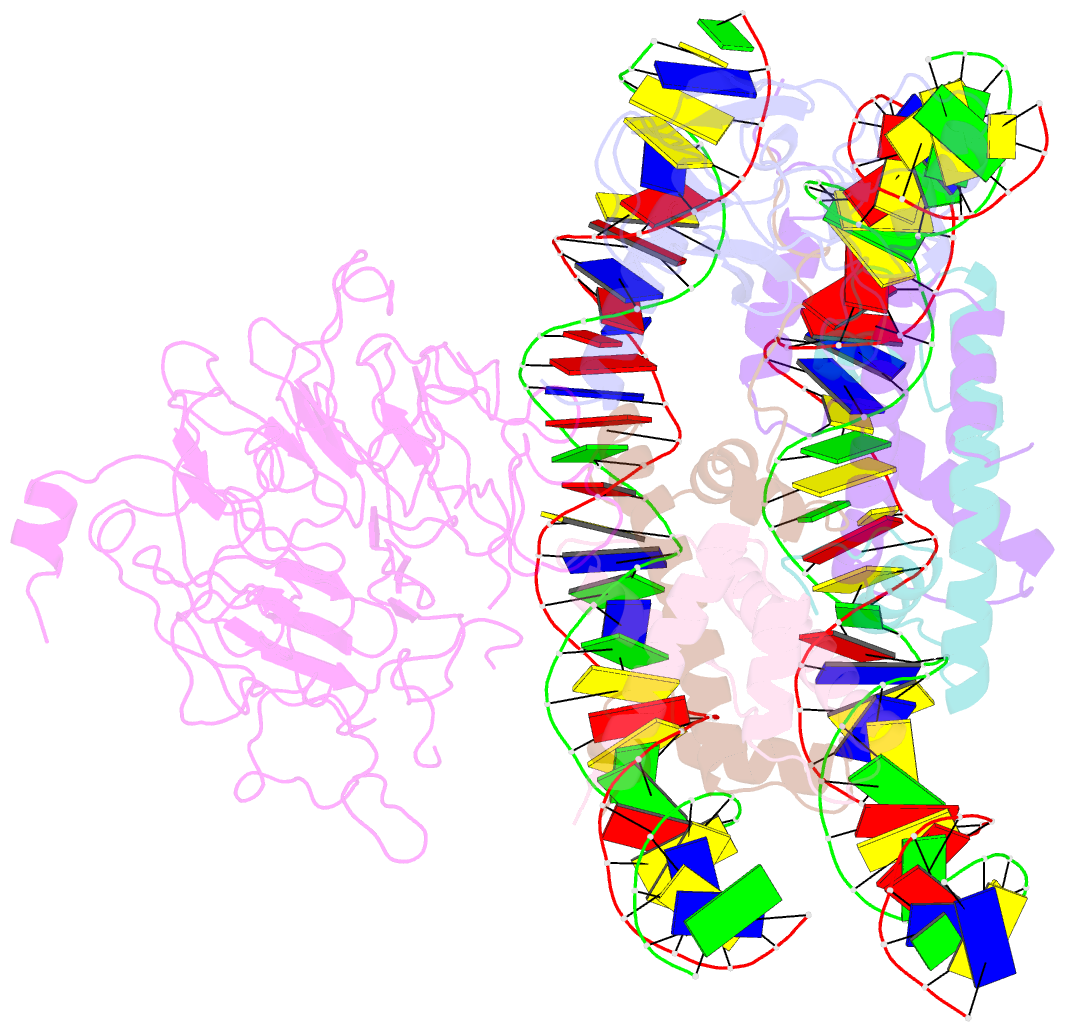
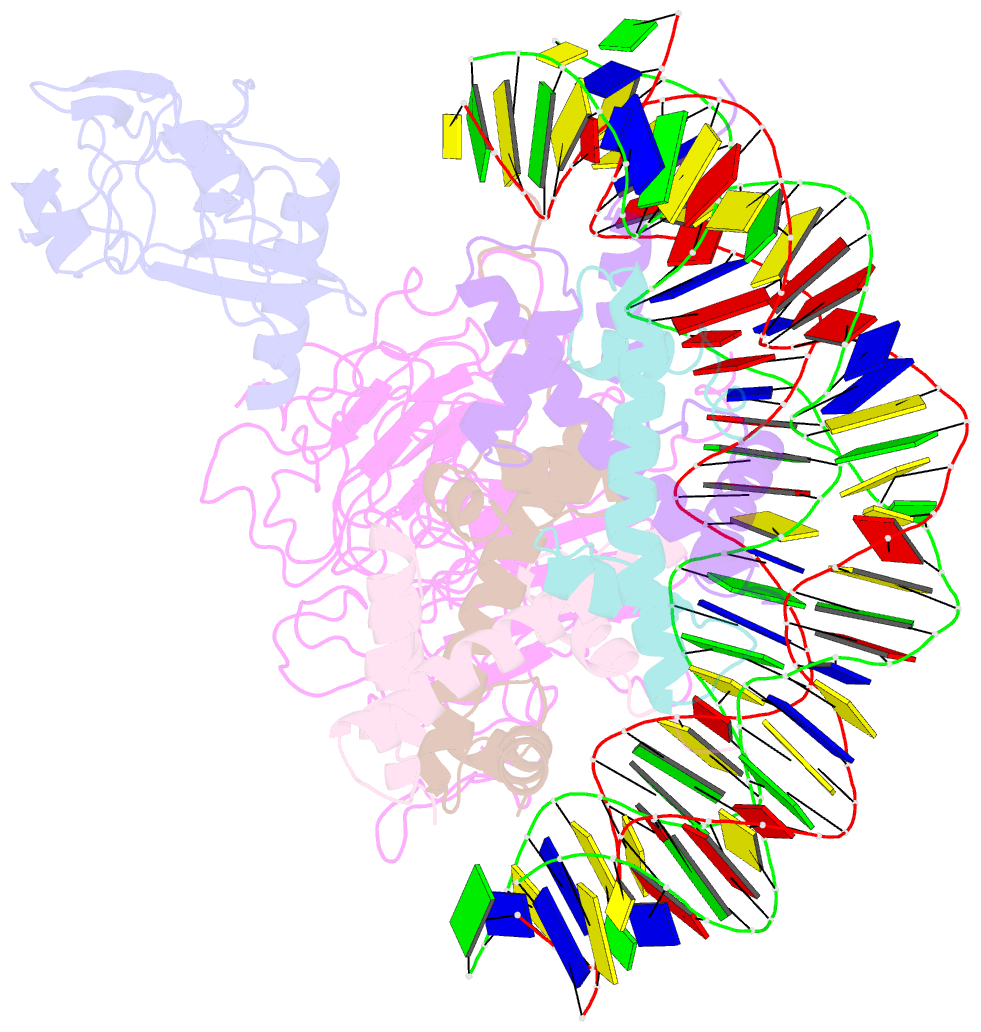
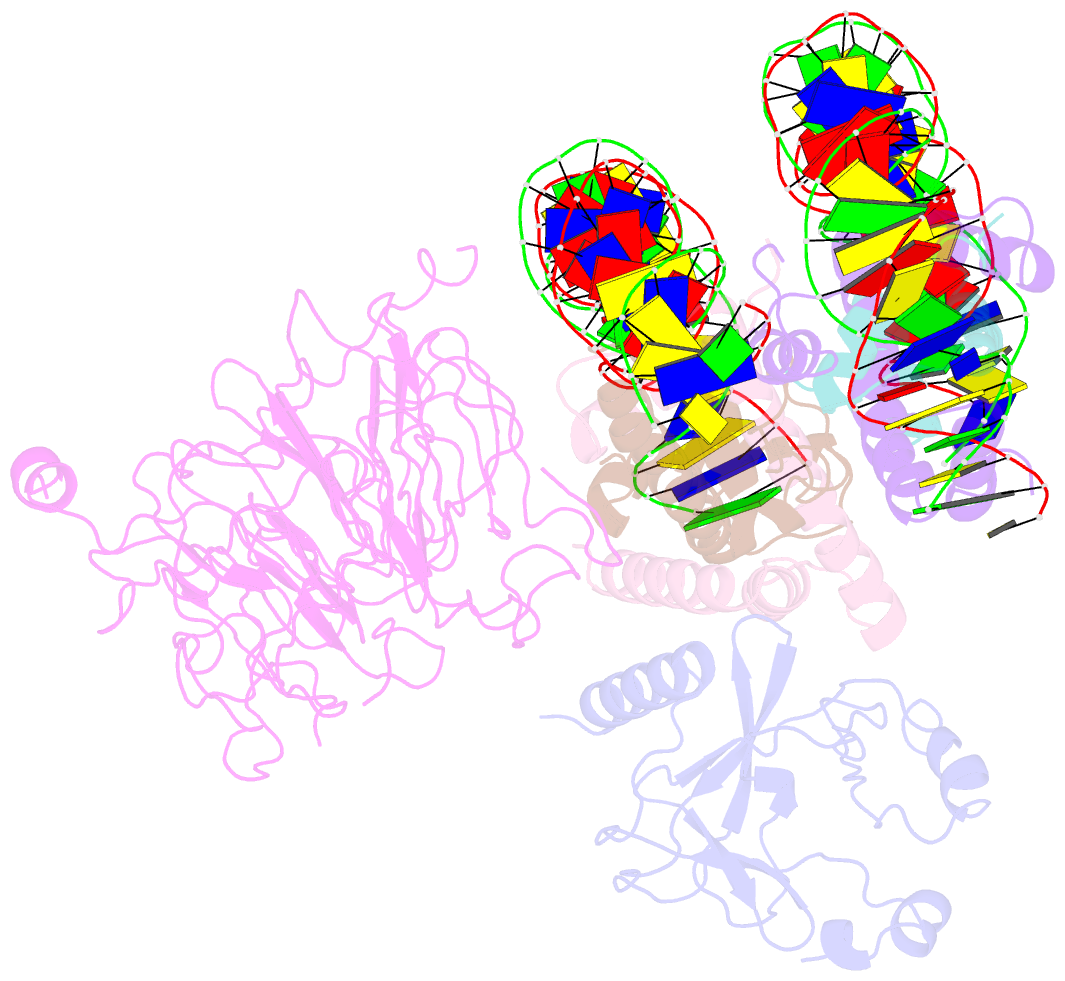
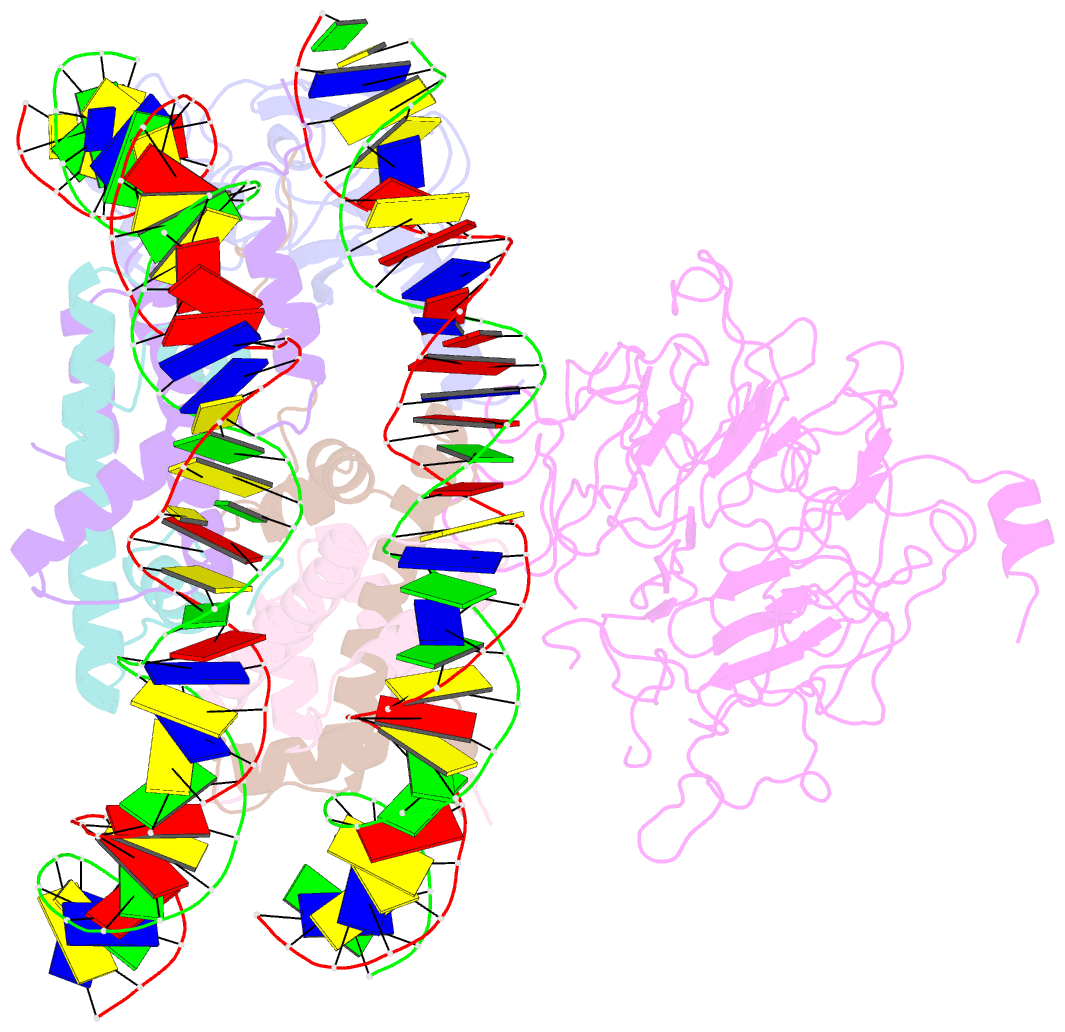
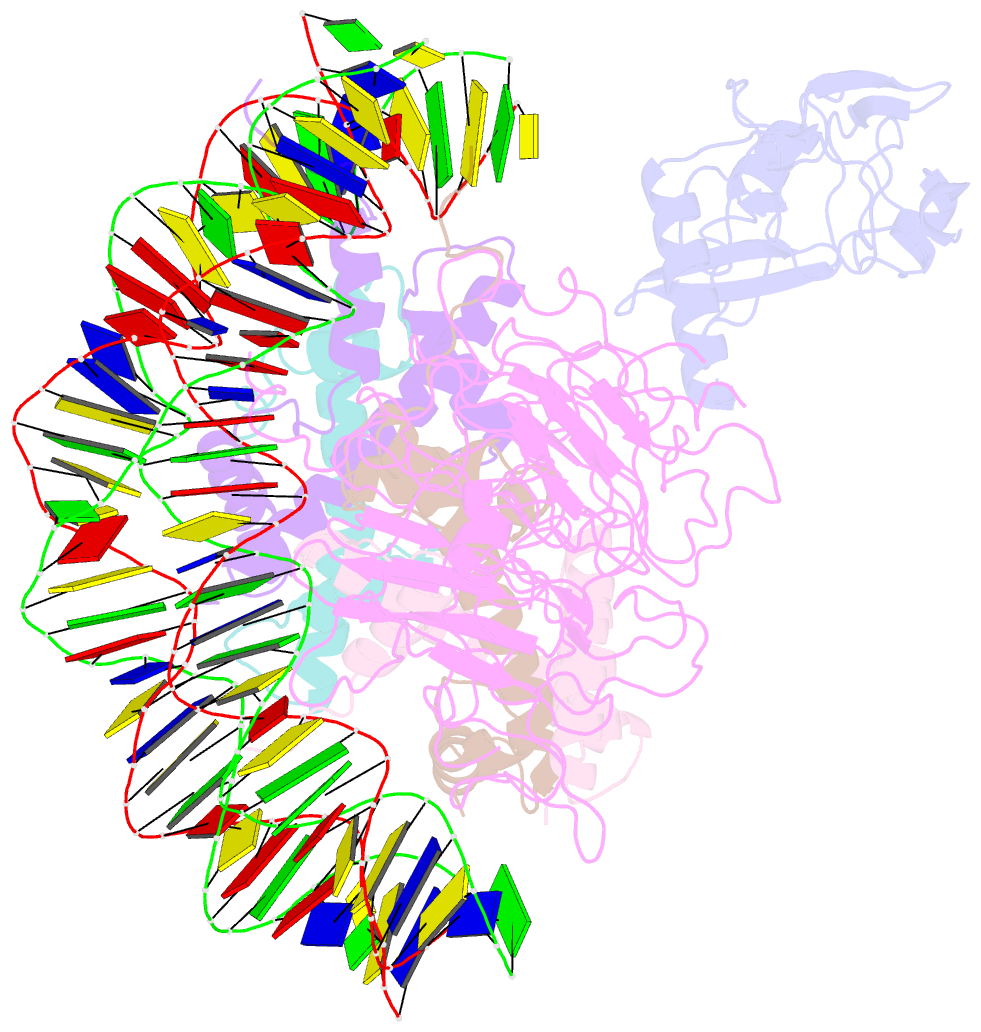
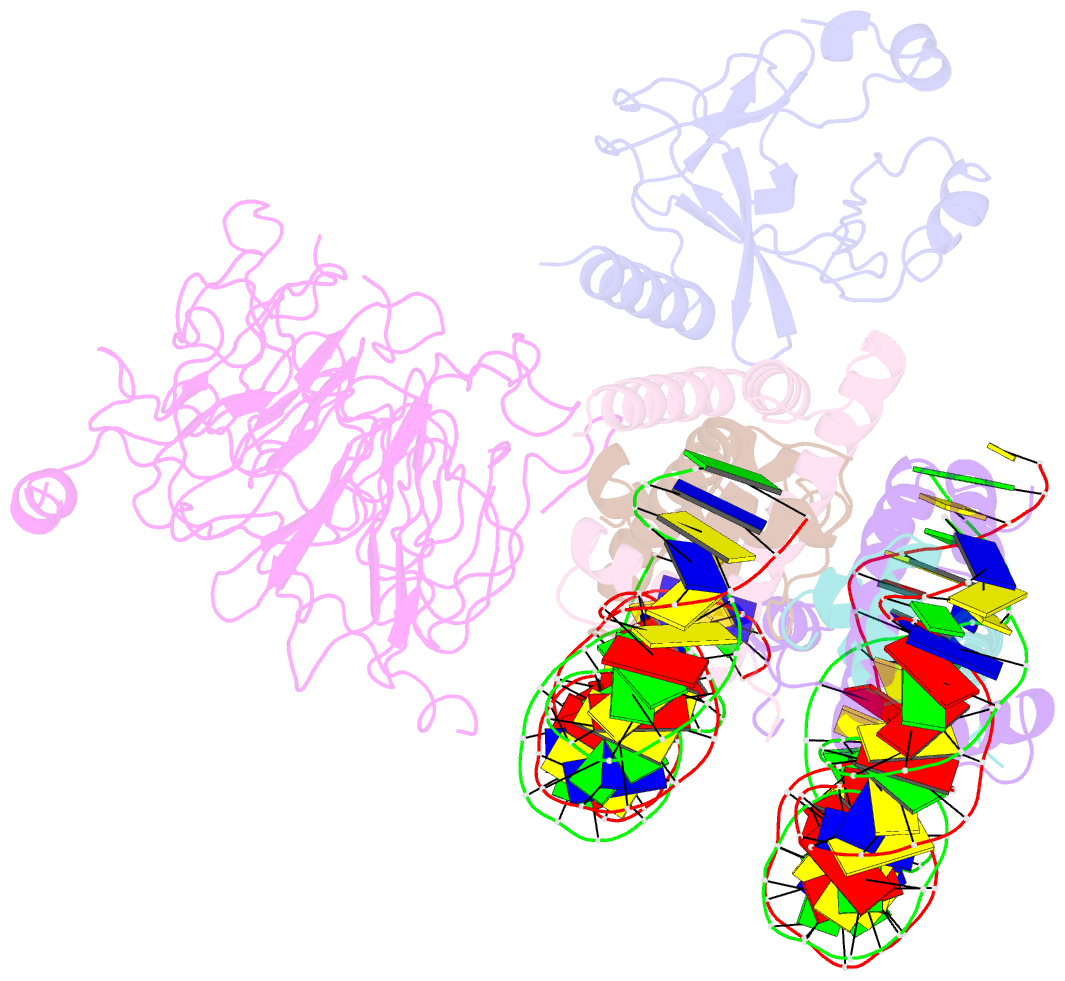
- Structural model of set8 histone h4 lys20 methyltransferase bound to nucleosome core particle
- Reference
- Girish TS, McGinty RK, Tan S (2016): "Multivalent Interactions by the Set8 Histone Methyltransferase With Its Nucleosome Substrate." J.Mol.Biol., 428, 1531-1543. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.02.025.
- Abstract
- Set8 is the only mammalian monomethyltransferase responsible for H4K20me1, a methyl mark critical for genomic integrity of eukaryotic cells. We present here a structural model for how Set8 uses multivalent interactions to bind and methylate the nucleosome based on crystallographic and solution studies of the Set8/nucleosome complex. Our studies indicate that Set8 employs its i-SET and c-SET domains to engage nucleosomal DNA 1 to 1.5 turns from the nucleosomal dyad and in doing so, it positions the SET domain for catalysis with H4 Lys20. Surprisingly, we find that a basic N-terminal extension to the SET domain plays an even more prominent role in nucleosome binding, possibly by making an arginine anchor interaction with the nucleosome H2A/H2B acidic patch. We further show that proliferating cell nuclear antigen and the nucleosome compete for binding to Set8 through this basic extension, suggesting a mechanism for how nucleosome binding protects Set8 from proliferating cell nuclear antigen-dependent degradation during the cell cycle.