Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5iff; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.9 Å)
- Summary
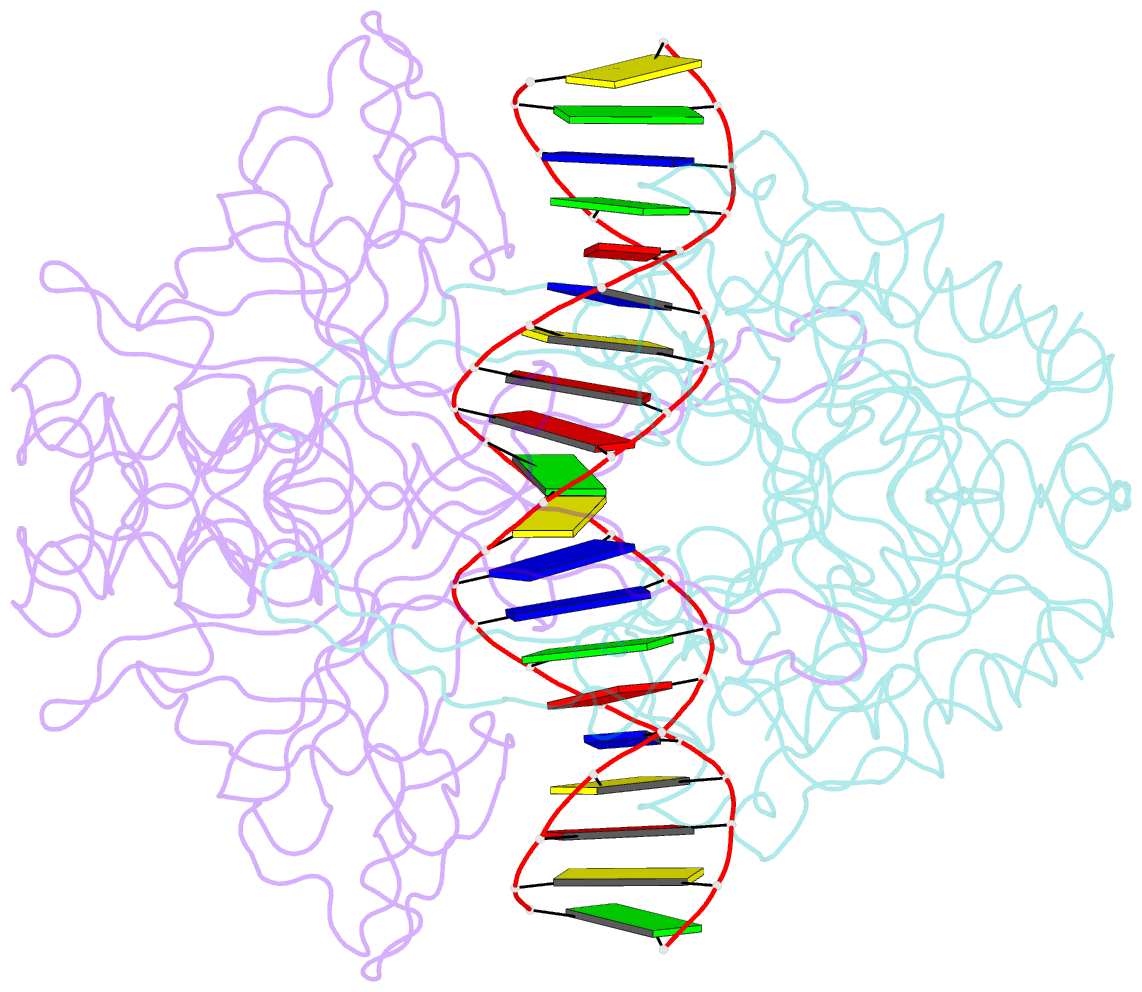
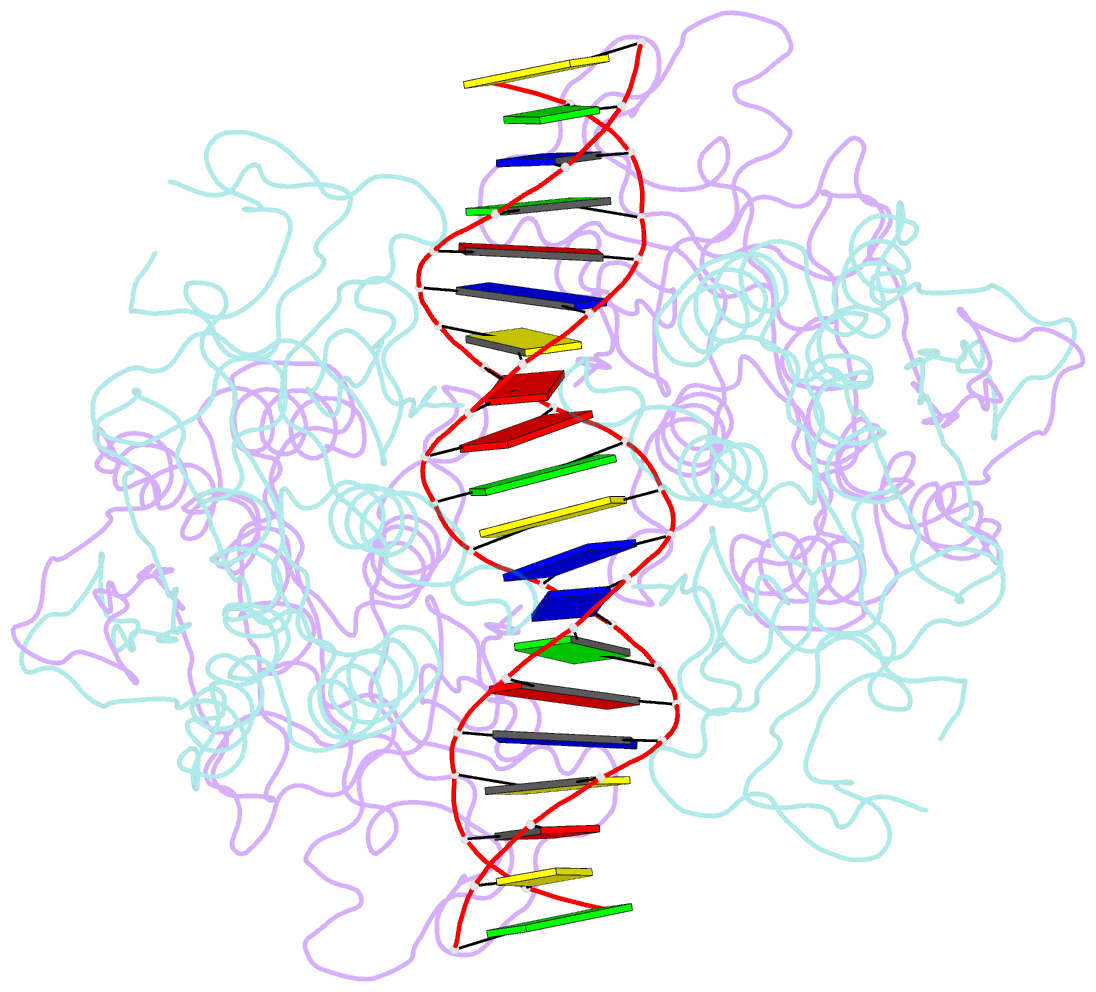
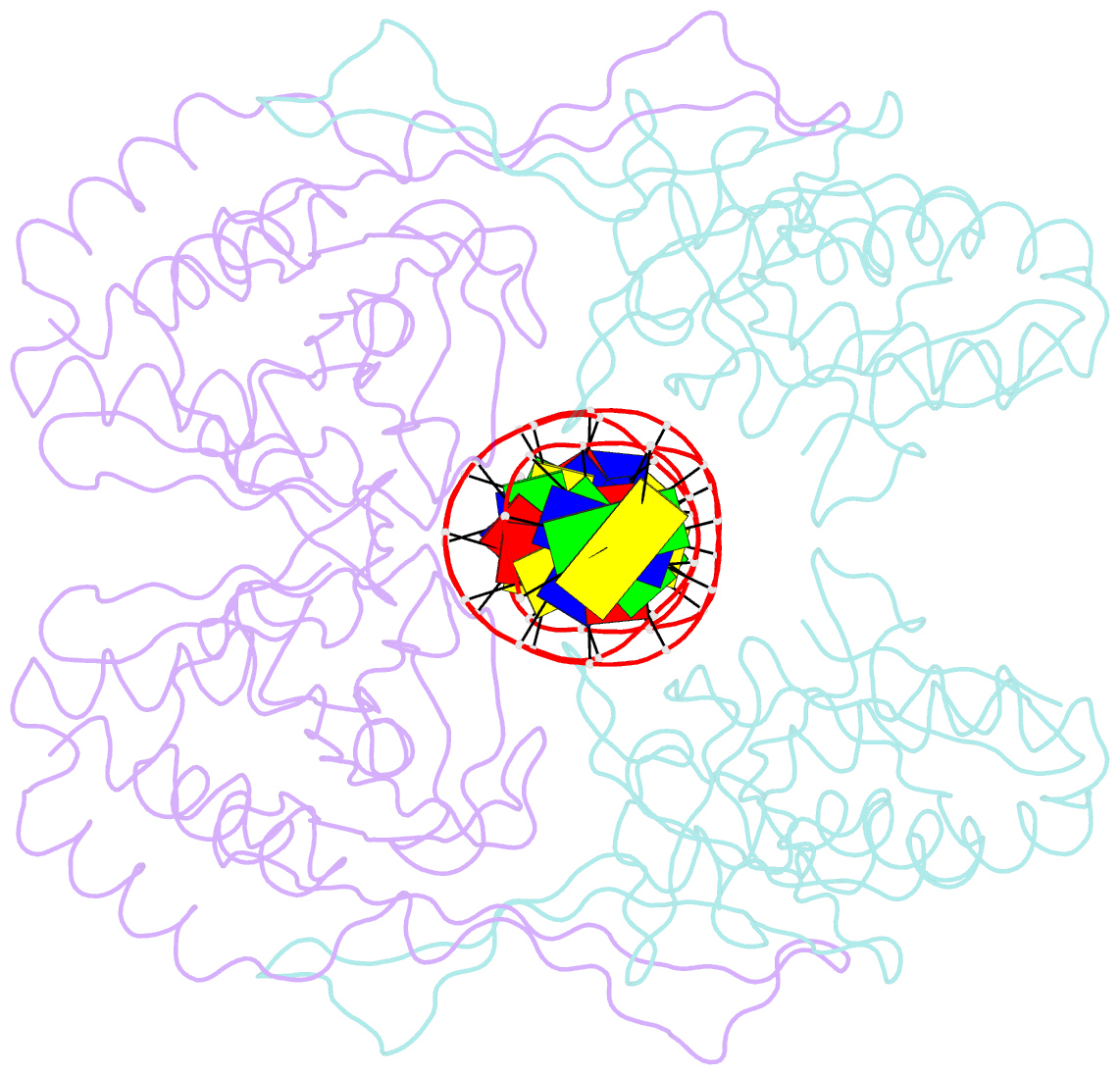
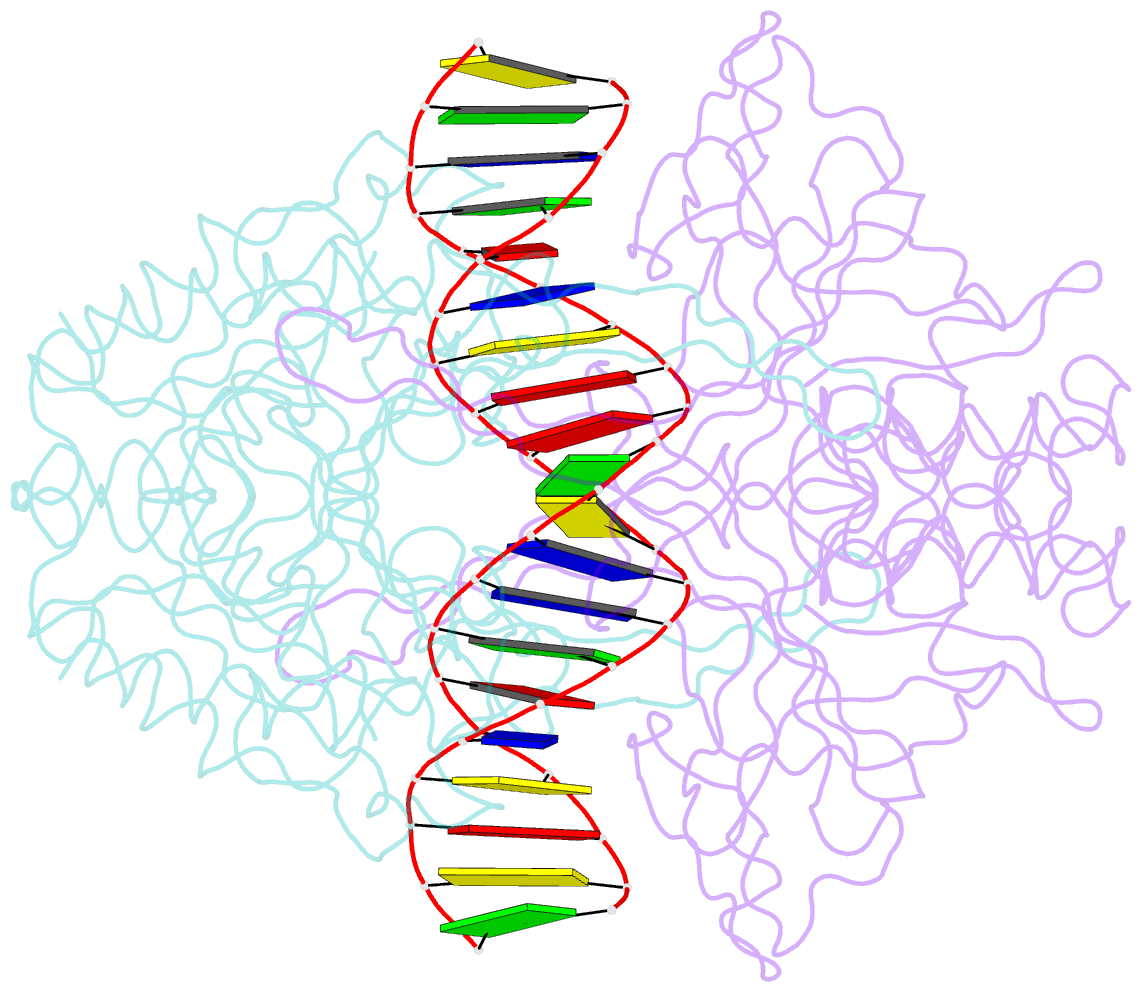
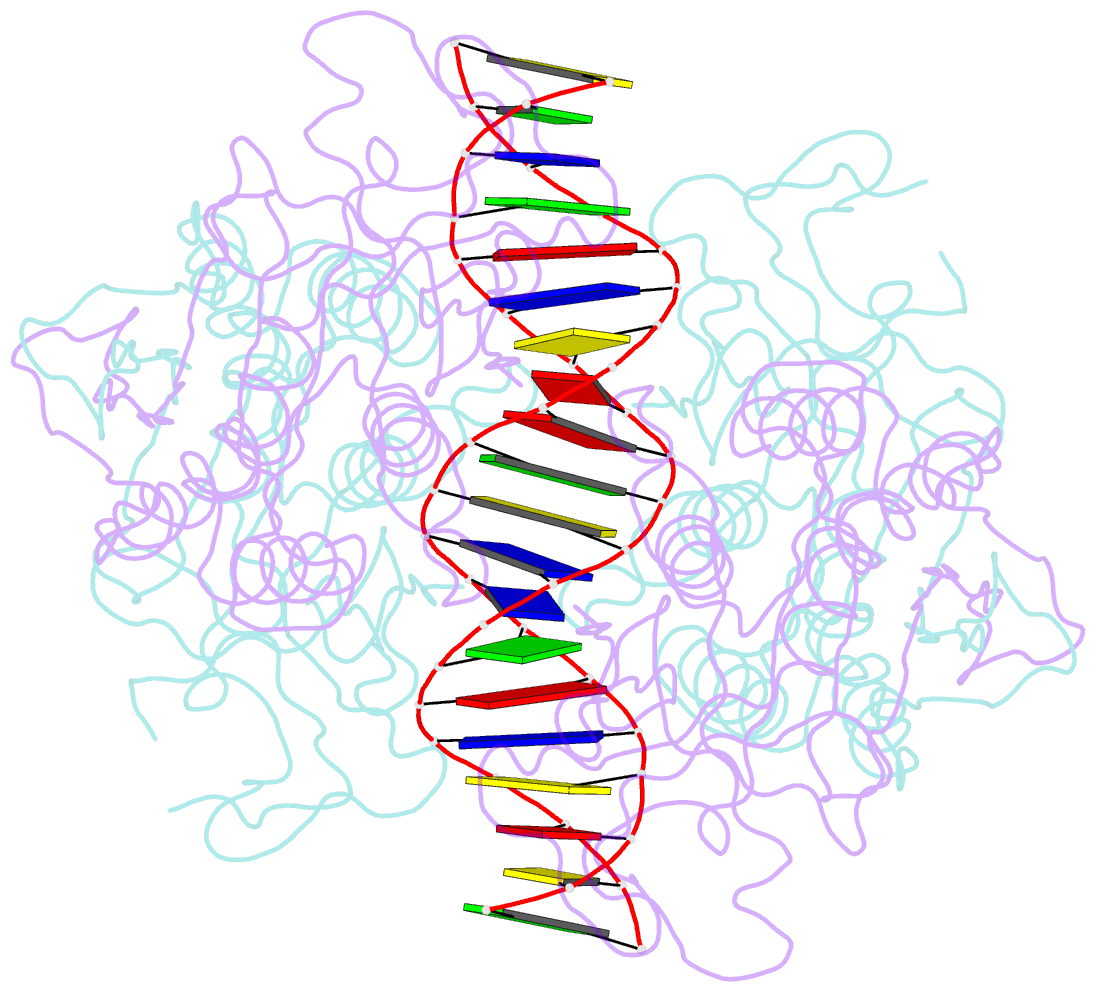
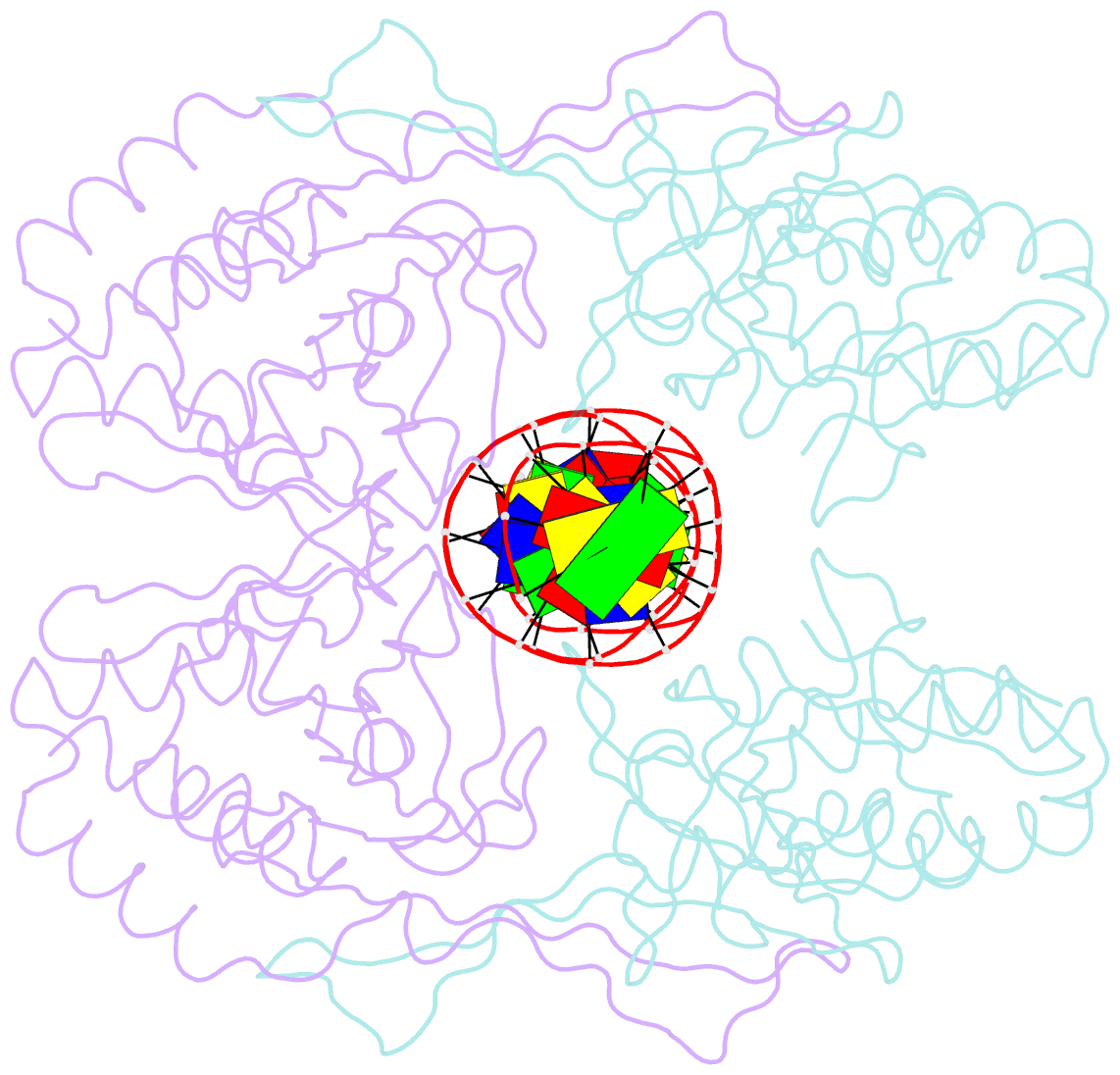
- Crystal structure of r.pabi-nonspecific DNA complex
- Reference
- Wang D, Miyazono KI, Tanokura M (2016): "Tetrameric structure of the restriction DNA glycosylase R.PabI in complex with nonspecific double-stranded DNA." Sci Rep, 6, 35197. doi: 10.1038/srep35197.
- Abstract
- R.PabI is a type II restriction enzyme that recognizes the 5'-GTAC-3' sequence and belongs to the HALFPIPE superfamily. Although most restriction enzymes cleave phosphodiester bonds at specific sites by hydrolysis, R.PabI flips the guanine and adenine bases of the recognition sequence out of the DNA helix and hydrolyzes the N-glycosidic bond of the flipped adenine in a similar manner to DNA glycosylases. In this study, we determined the structure of R.PabI in complex with double-stranded DNA without the R.PabI recognition sequence by X-ray crystallography. The 1.9 Å resolution structure of the complex showed that R.PabI forms a tetrameric structure to sandwich the double-stranded DNA and the tetrameric structure is stabilized by four salt bridges. DNA binding and DNA glycosylase assays of the R.PabI mutants showed that the residues that form the salt bridges (R70 and D71) are essential for R.PabI to find the recognition sequence from the sea of nonspecific sequences. R.PabI is predicted to utilize the tetrameric structure to bind nonspecific double-stranded DNA weakly and slide along it to find the recognition sequence.