Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5jum; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.6 Å)
- Summary
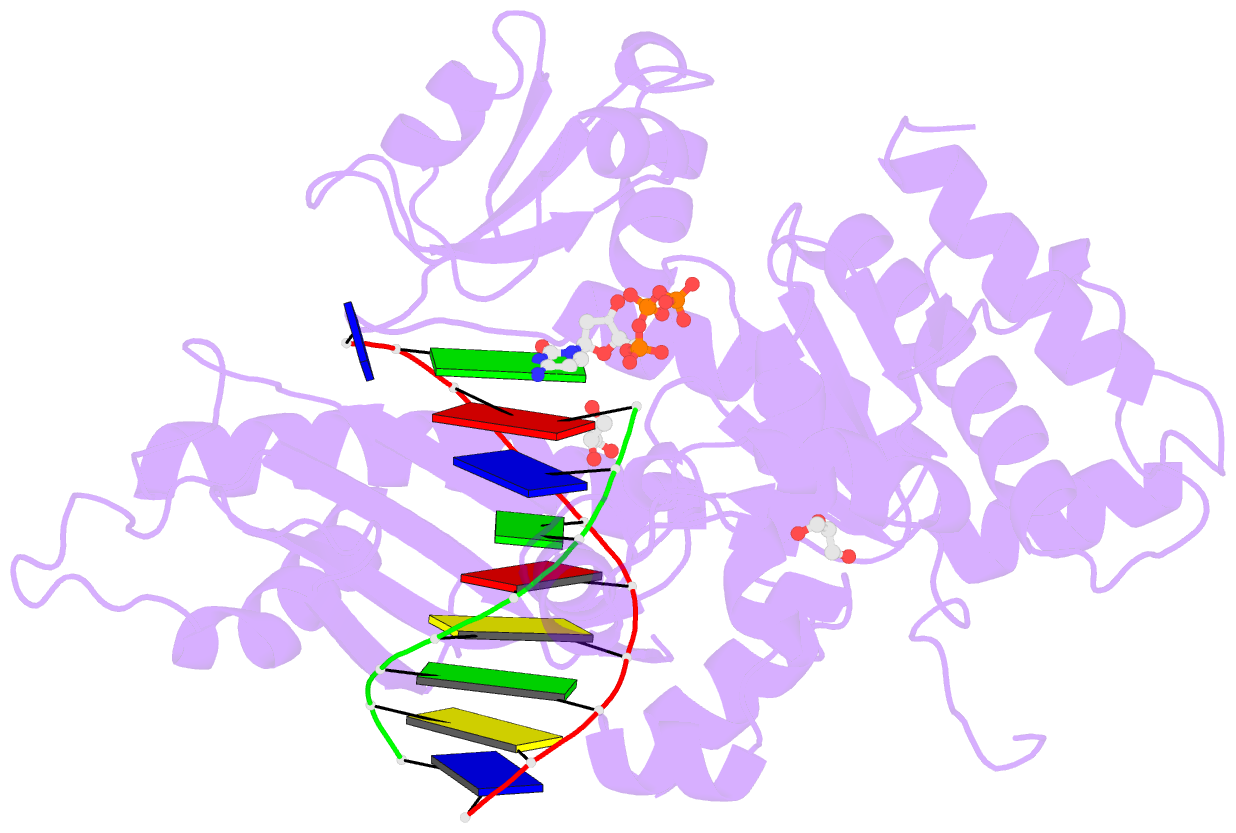
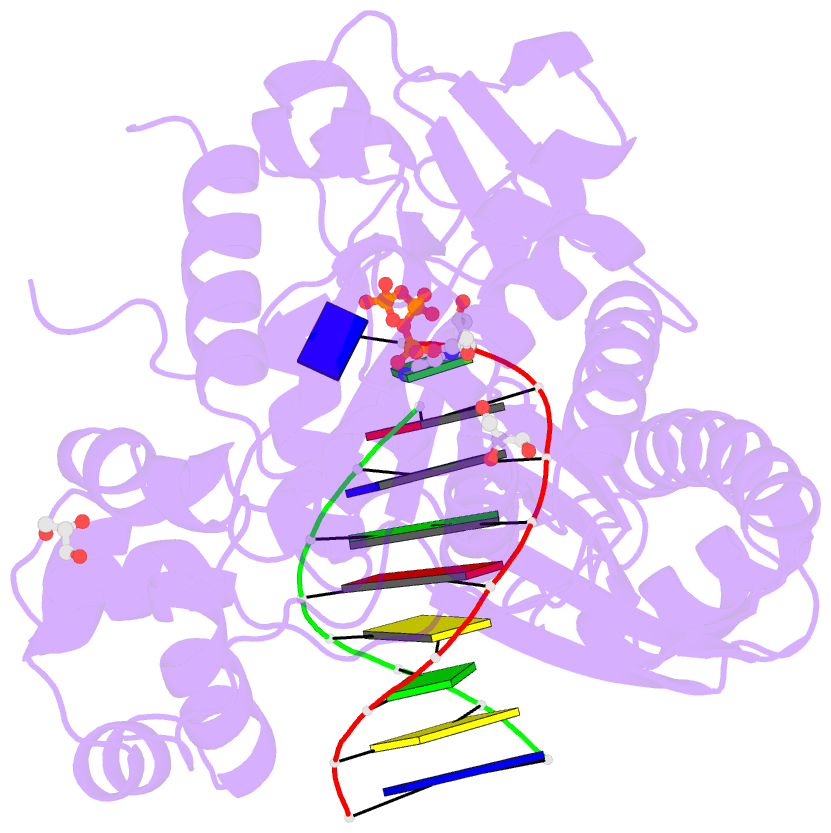
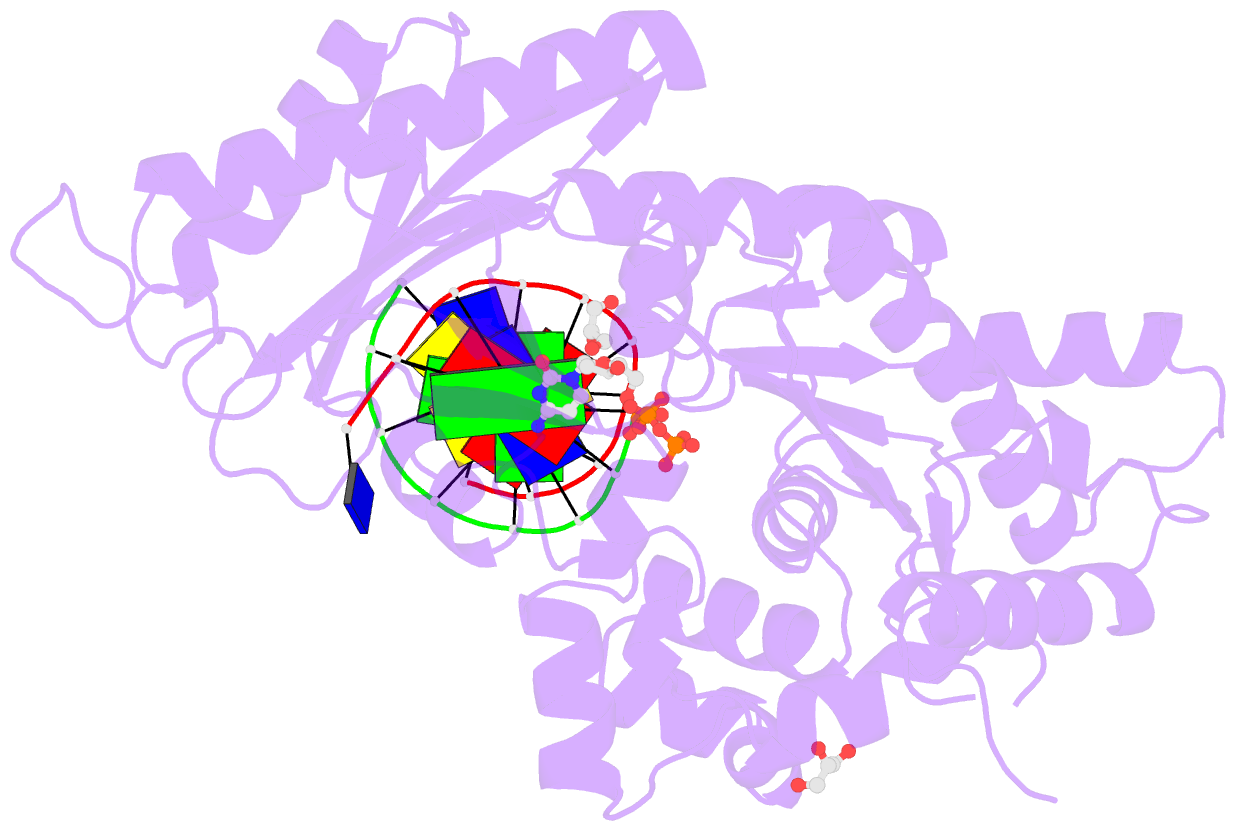
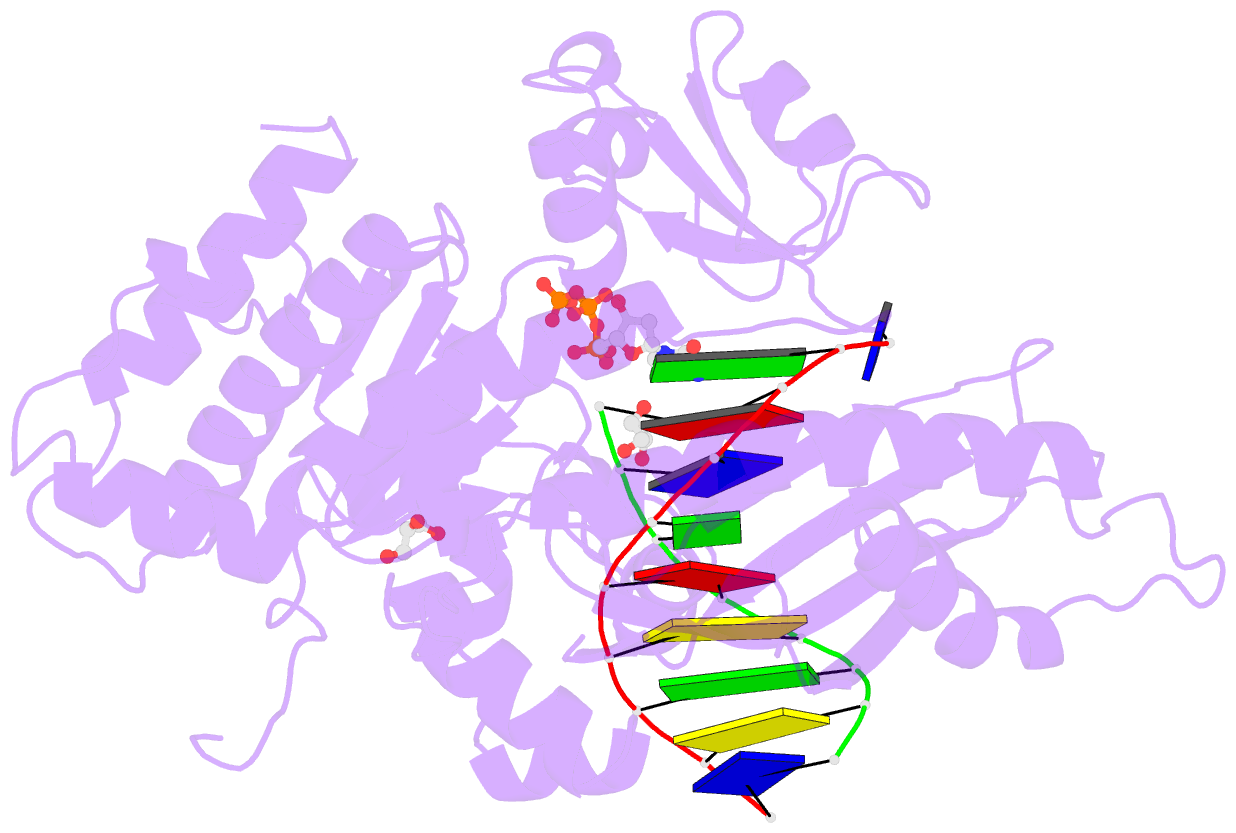
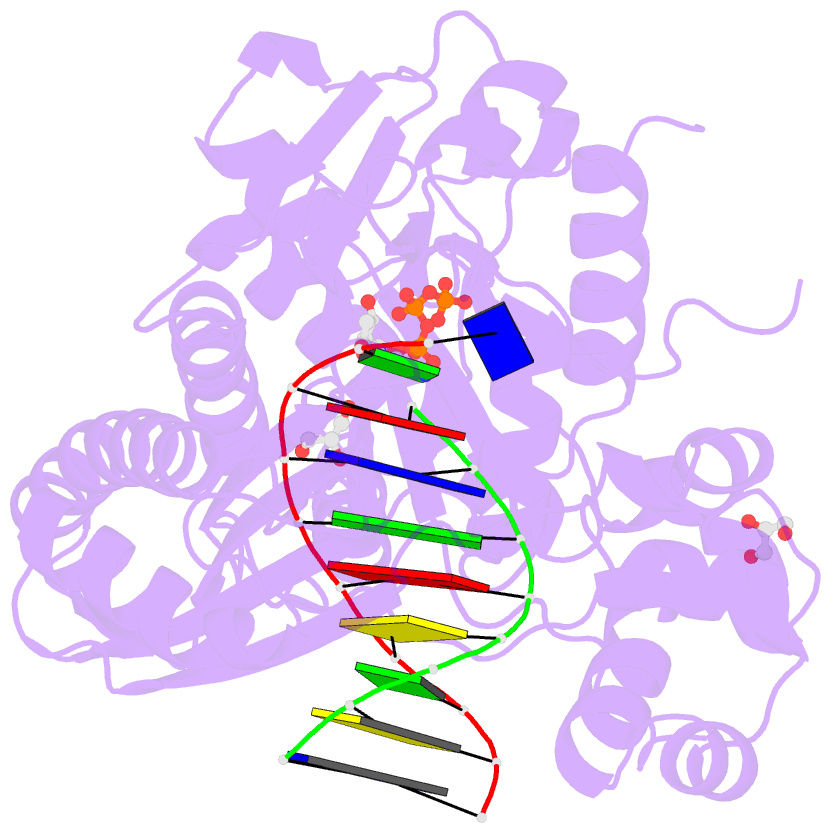
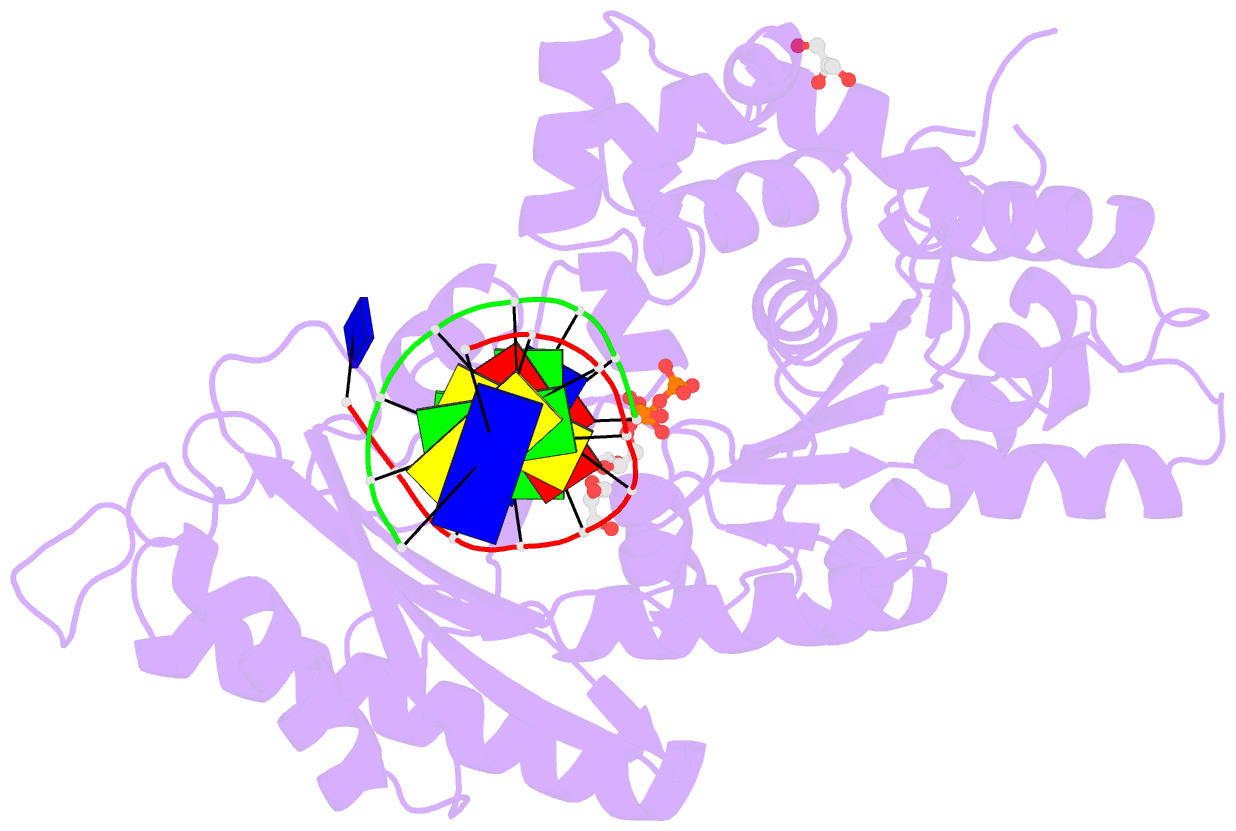
- Crystal structure of human DNA polymerase eta inserting dctp opposite n-(2'-deoxyguanosin-8- yl)-3-aminobenzanthrone (c8-dg-aba)
- Reference
- Patra A, Politica DA, Chatterjee A, Tokarsky EJ, Suo Z, Basu AK, Stone MP, Egli M (2016): "Mechanism of Error-Free Bypass of the Environmental Carcinogen N-(2'-Deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-3-aminobenzanthrone Adduct by Human DNA Polymerase eta." Chembiochem, 17, 2033-2037. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201600420.
- Abstract
- The environmental pollutant 3-nitrobenzanthrone produces bulky aminobenzanthrone (ABA) DNA adducts with both guanine and adenine nucleobases. A major product occurs at the C8 position of guanine (C8-dG-ABA). These adducts present a strong block to replicative polymerases but, remarkably, can be bypassed in a largely error-free manner by the human Y-family polymerase η (hPol η). Here, we report the crystal structure of a ternary Pol⋅DNA⋅dCTP complex between a C8-dG-ABA-containing template:primer duplex and hPol η. The complex was captured at the insertion stage and provides crucial insight into the mechanism of error-free bypass of this bulky lesion. Specifically, bypass involves accommodation of the ABA moiety inside a hydrophobic cleft to the side of the enzyme active site and formation of an intra-nucleotide hydrogen bond between the phosphate and ABA amino moiety, allowing the adducted guanine to form a standard Watson-Crick pair with the incoming dCTP.