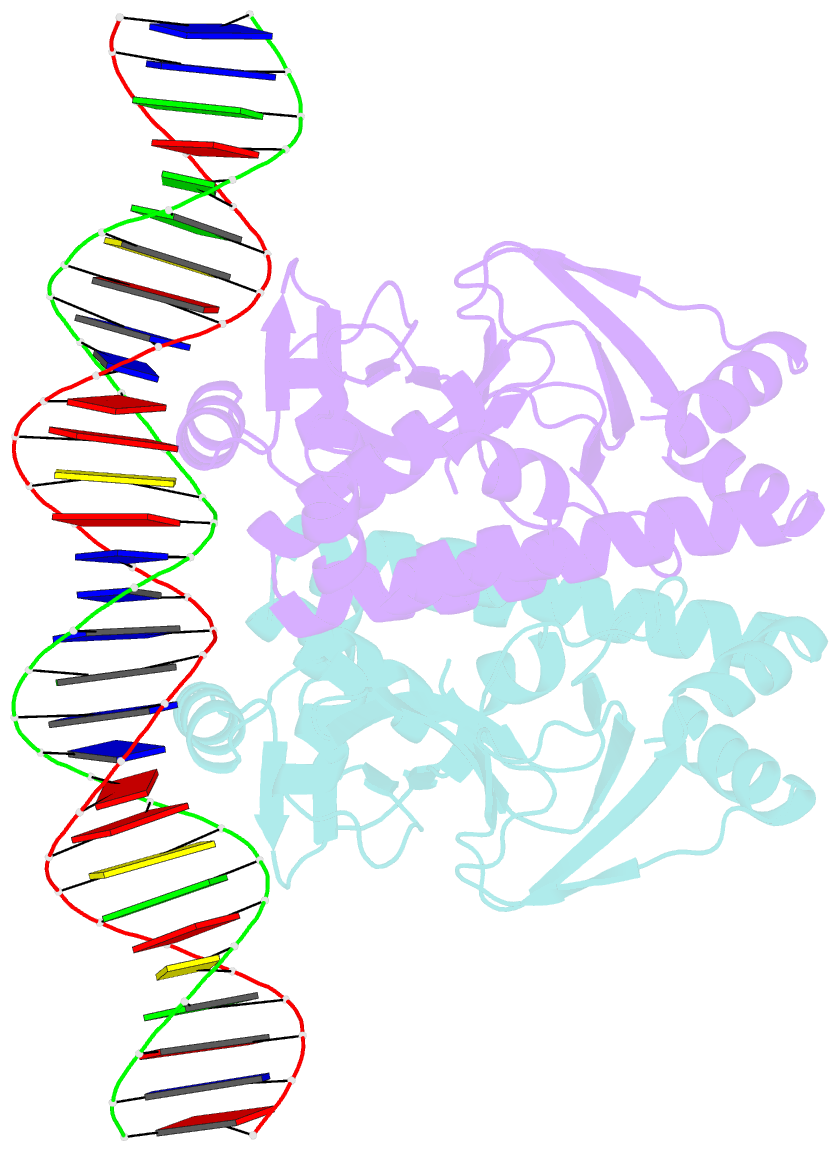
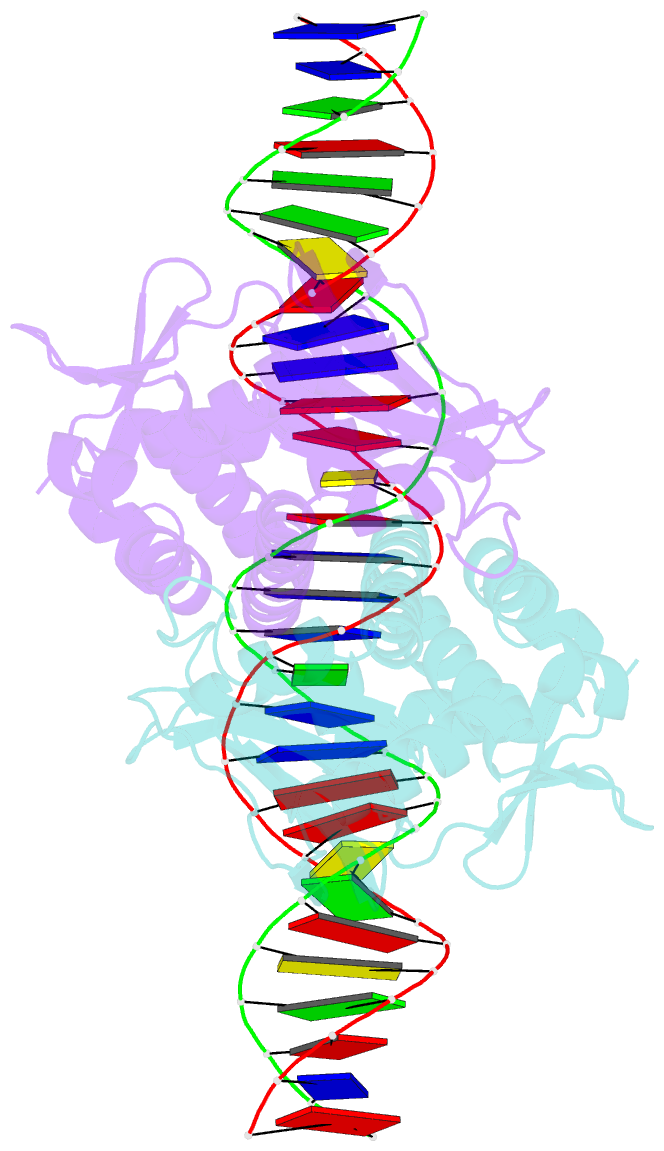
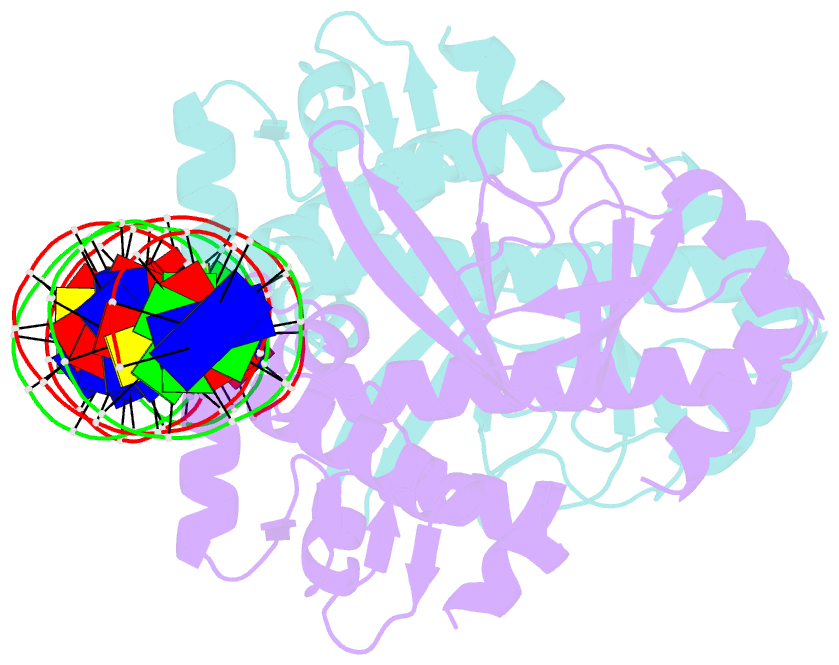
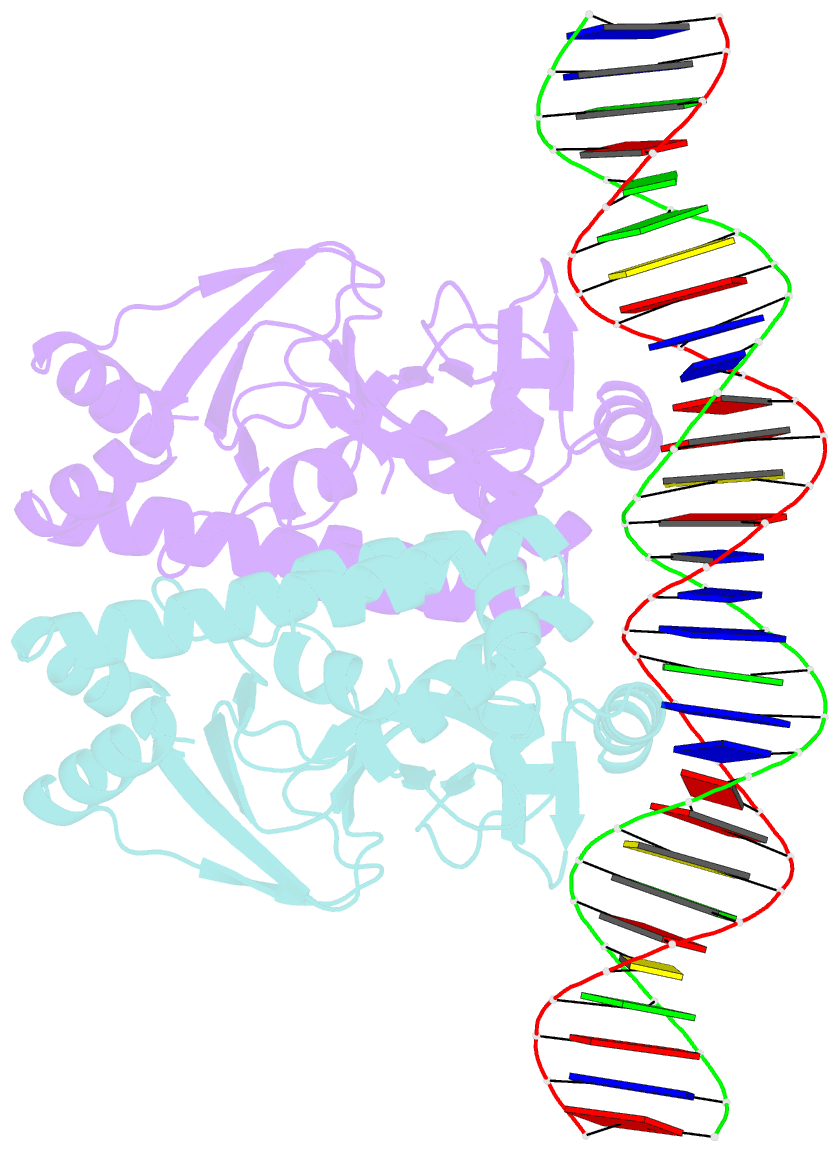
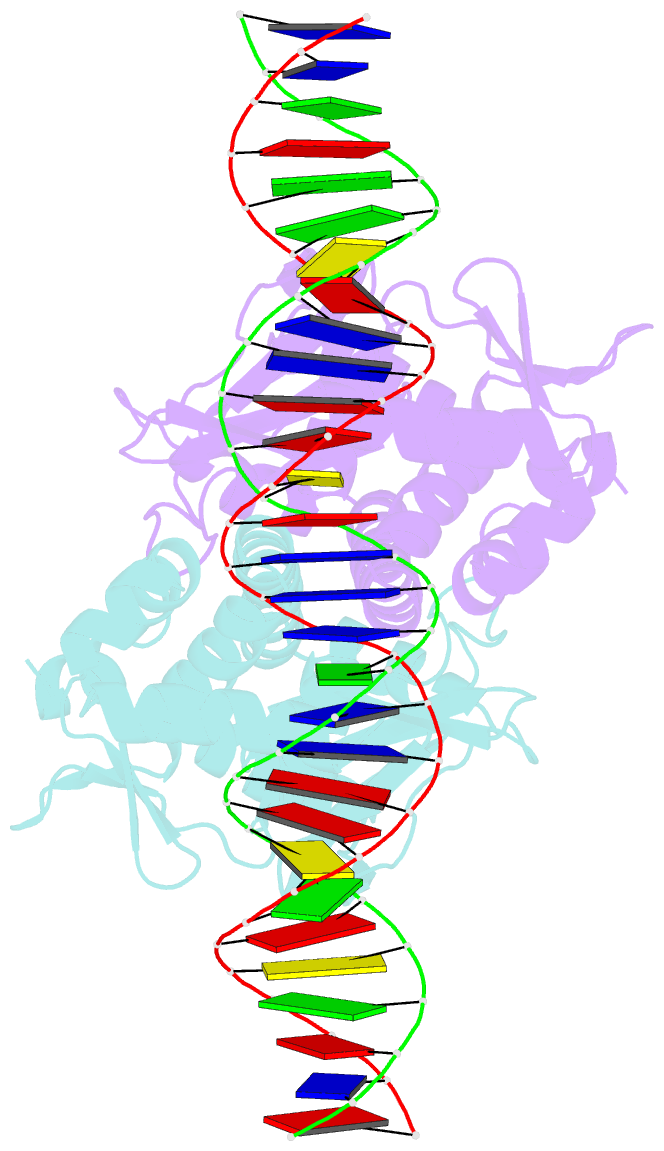
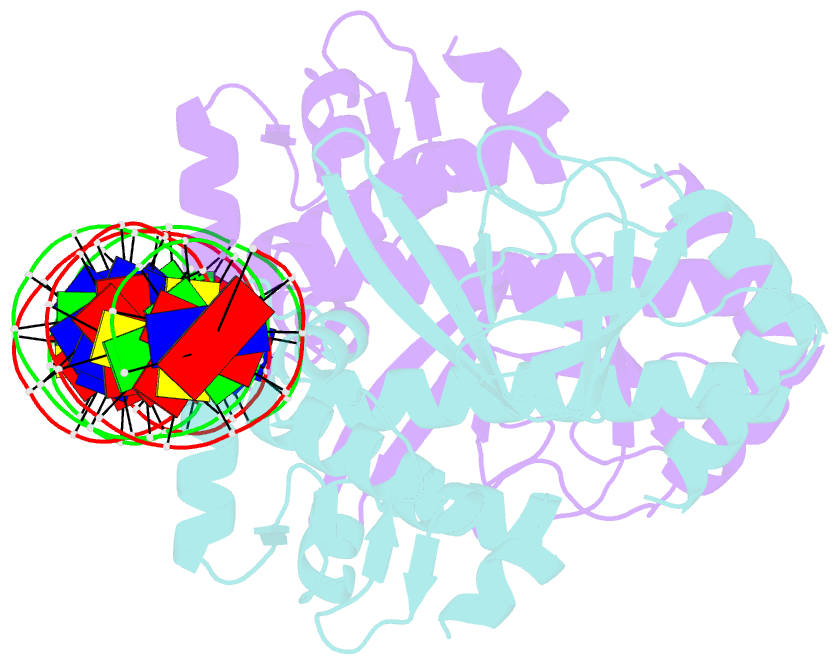
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5lek; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- X-ray (2.8 Å)
- Summary
- The transcriptional regulator prfa-g145s mutant from listeria monocytogenes in complex with a 30-bp operator prfa-box motif
- Reference
- Hall M, Grundstrom C, Begum A, Lindberg MJ, Sauer UH, Almqvist F, Johansson J, Sauer-Eriksson AE (2016): "Structural basis for glutathione-mediated activation of the virulence regulatory protein PrfA in Listeria." Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 113, 14733-14738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1614028114.
- Abstract
- Infection by the human bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes is mainly controlled by the positive regulatory factor A (PrfA), a member of the Crp/Fnr family of transcriptional activators. Published data suggest that PrfA requires the binding of a cofactor for full activity, and it was recently proposed that glutathione (GSH) could fulfill this function. Here we report the crystal structures of PrfA in complex with GSH and in complex with GSH and its cognate DNA, the hly operator PrfA box motif. These structures reveal the structural basis for a GSH-mediated allosteric mode of activation of PrfA in the cytosol of the host cell. The crystal structure of PrfAWT in complex only with DNA confirms that PrfAWT can adopt a DNA binding-compatible structure without binding the GSH activator molecule. By binding to PrfA in the cytosol of the host cell, GSH induces the correct fold of the HTH motifs, thus priming the PrfA protein for DNA interaction.