Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5m1s; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (6.7 Å)
- Summary
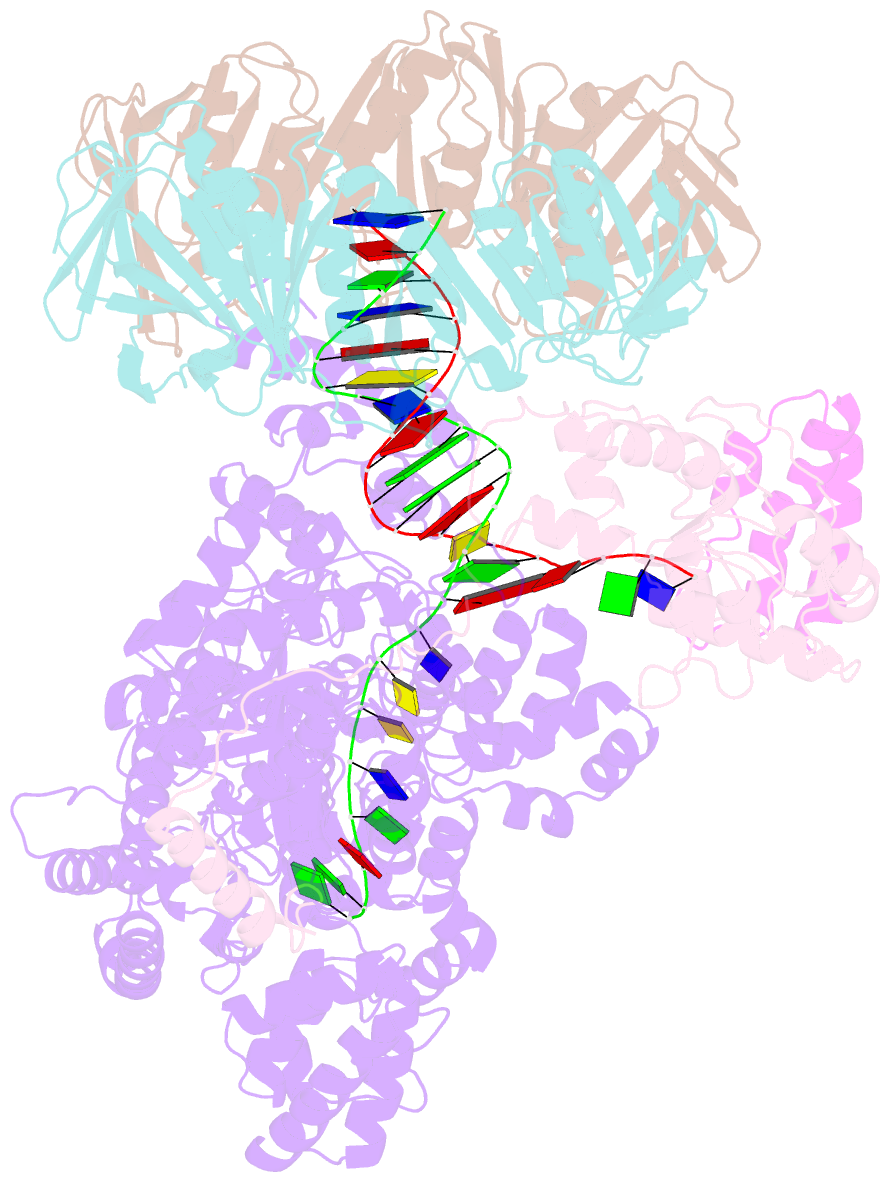
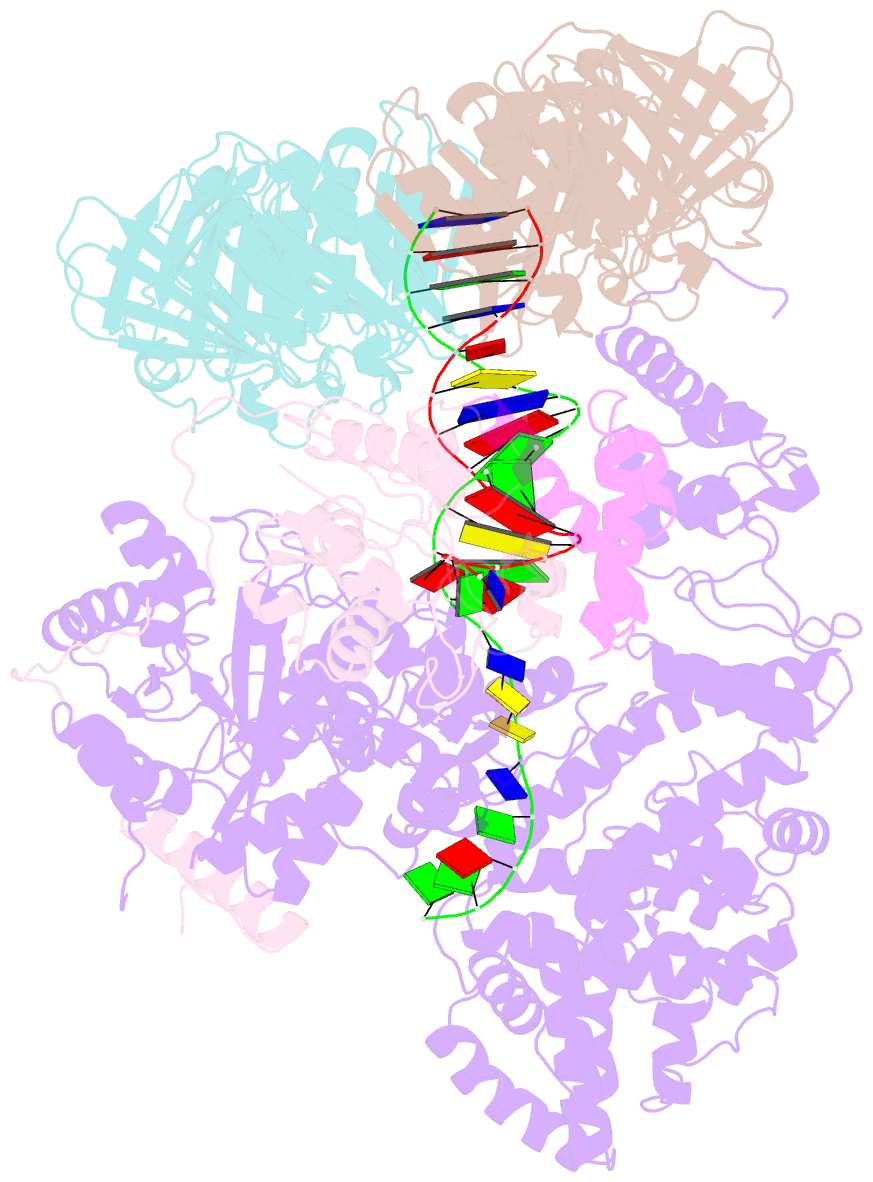
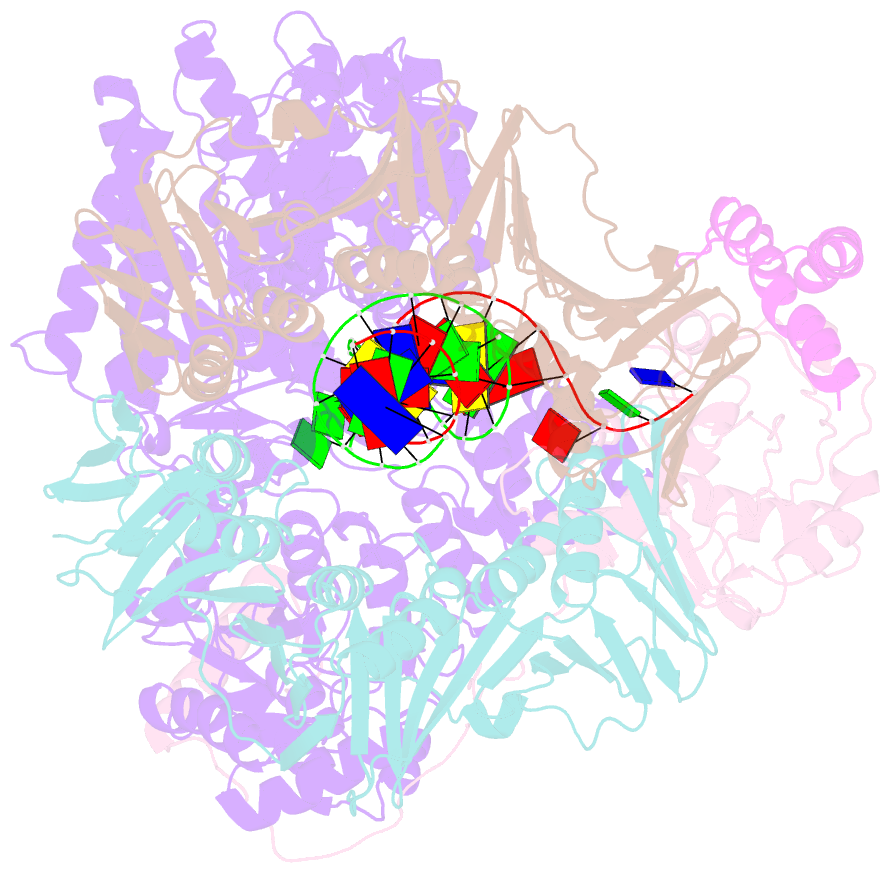
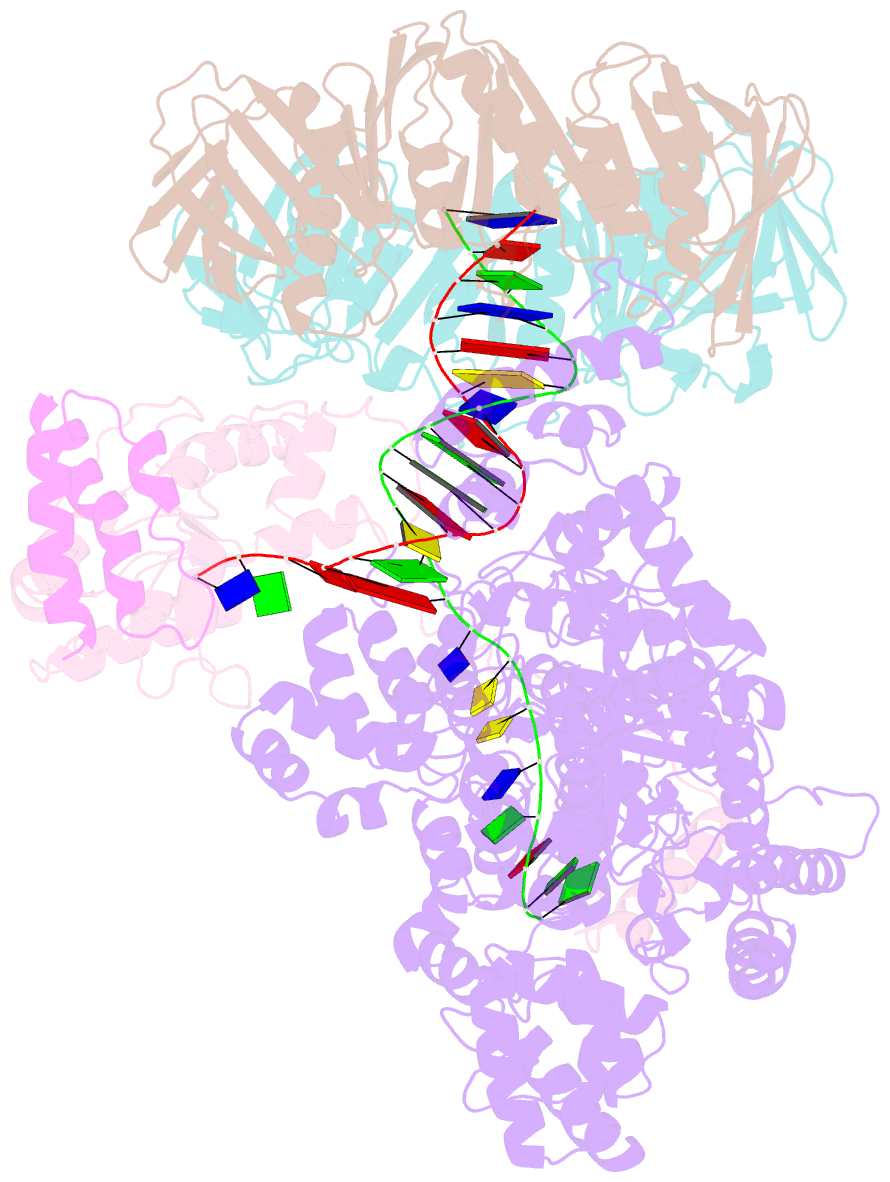
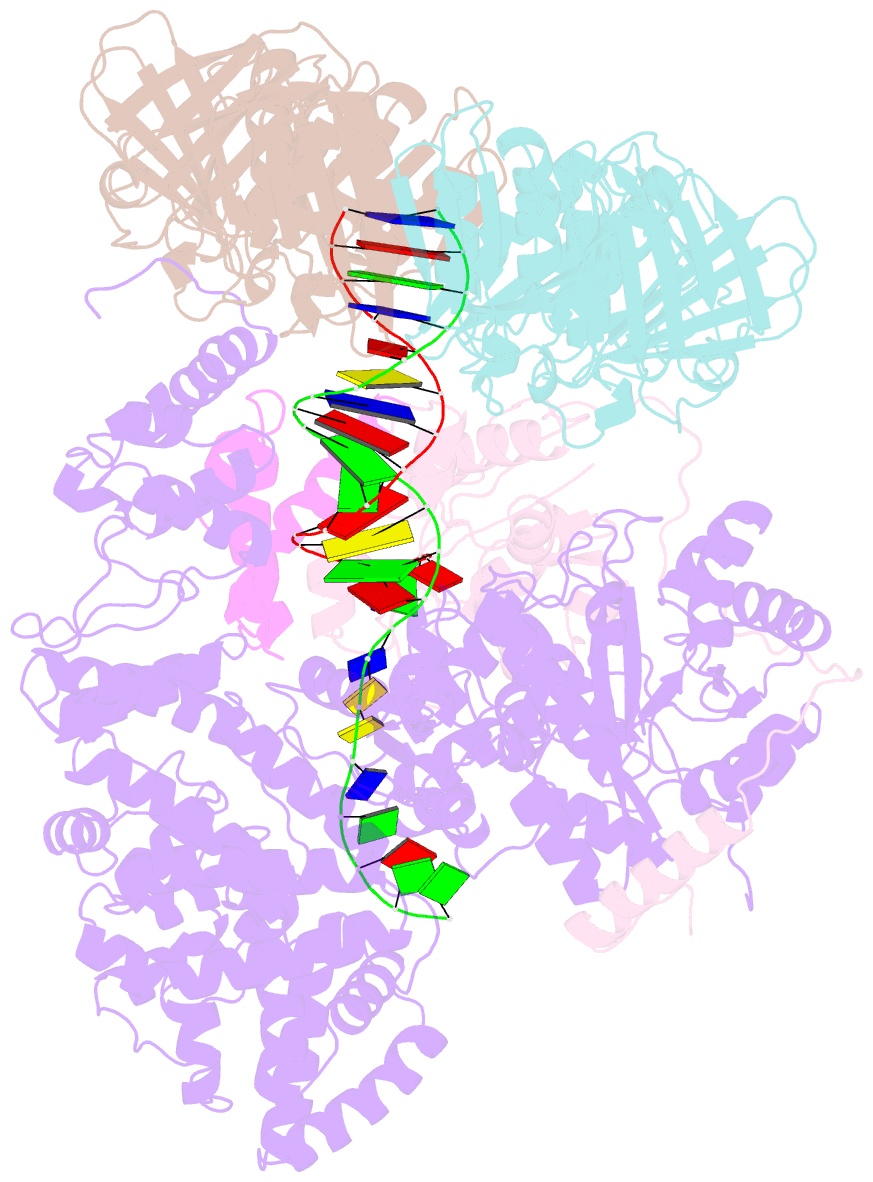
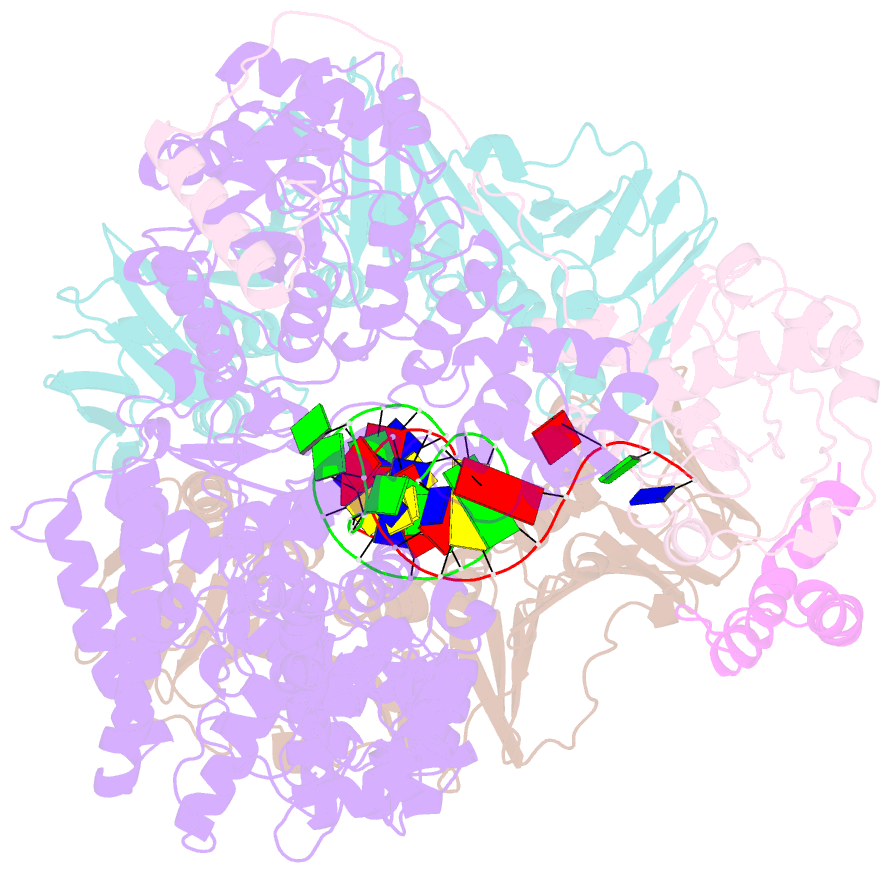
- cryo-EM structure of the e. coli replicative DNA polymerase-clamp-exonuclase-theta complex bound to DNA in the editing mode
- Reference
- Fernandez-Leiro R, Conrad J, Yang JC, Freund SM, Scheres SH, Lamers MH (2017): "Self-correcting mismatches during high-fidelity DNA replication." Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 24, 140-143. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3348.
- Abstract
- Faithful DNA replication is essential to all forms of life and depends on the action of 3'-5' exonucleases that remove misincorporated nucleotides from the newly synthesized strand. However, how the DNA is transferred from the polymerase to the exonuclease active site is not known. Here we present the cryo-EM structure of the editing mode of the catalytic core of the Escherichia coli replisome, revealing a dramatic distortion of the DNA whereby the polymerase thumb domain acts as a wedge that separates the two DNA strands. Importantly, NMR analysis of the DNA substrate shows that the presence of a mismatch increases the fraying of the DNA, thus enabling it to reach the exonuclease active site. Therefore the mismatch corrects itself, whereas the exonuclease subunit plays a passive role. Hence, our work provides unique insights into high-fidelity replication and establishes a new paradigm for the correction of misincorporated nucleotides.