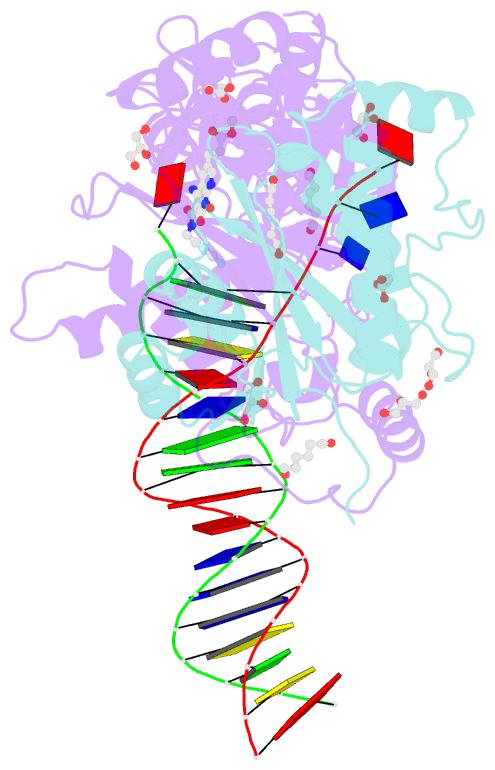
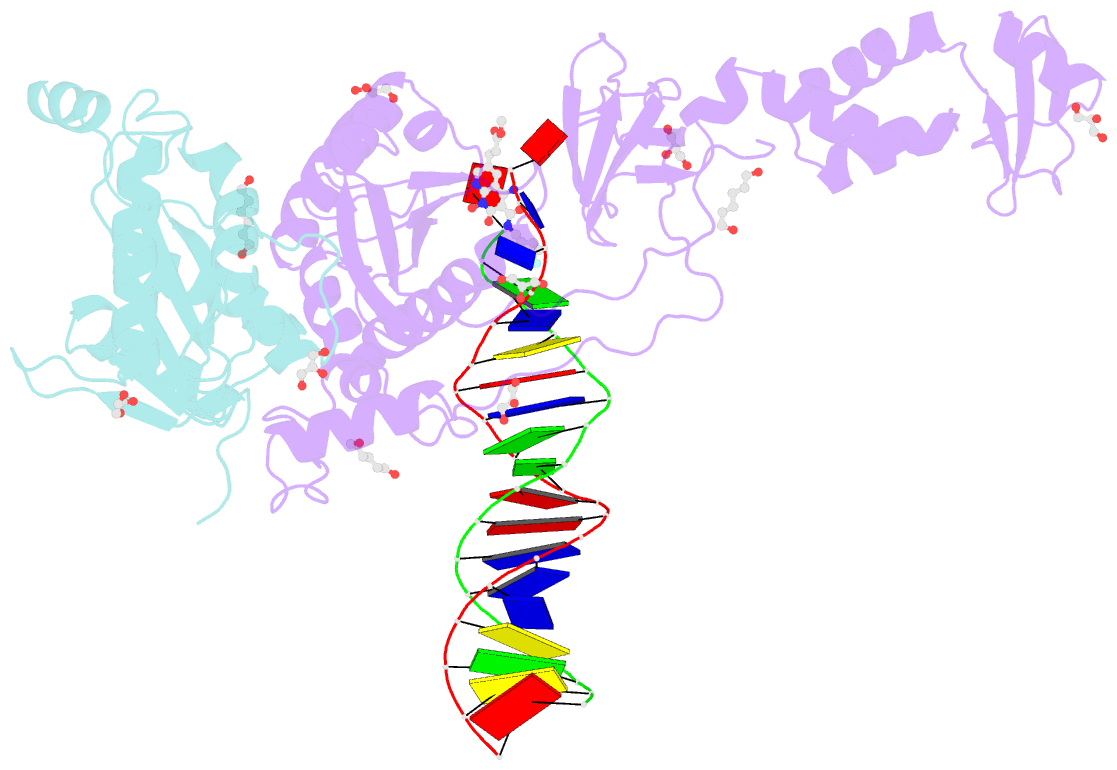
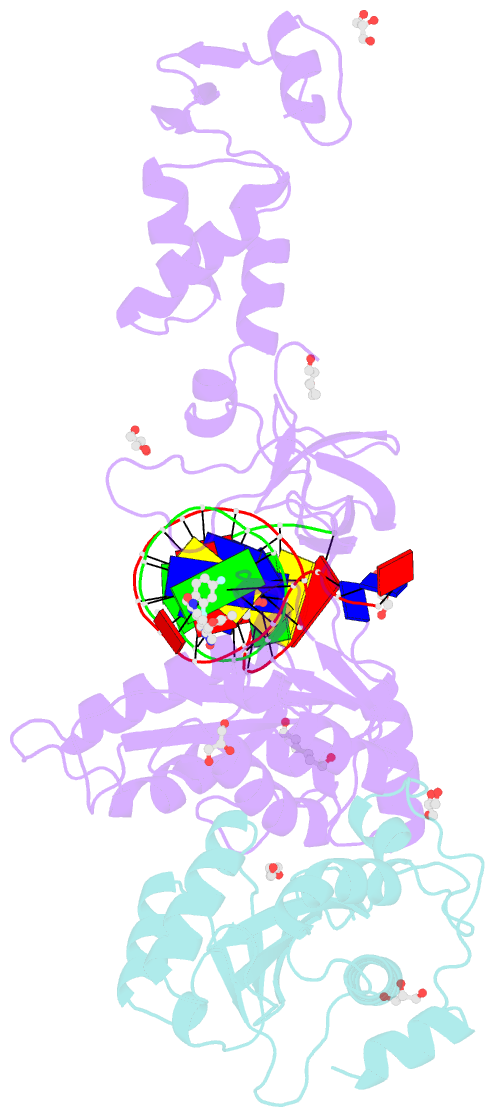
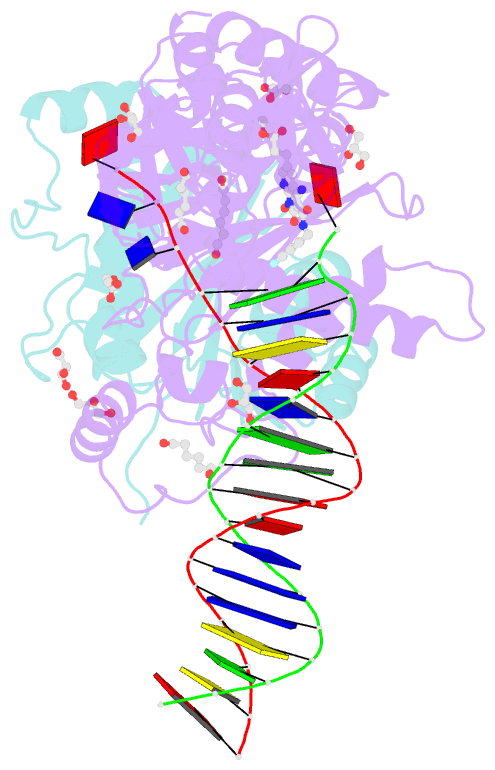
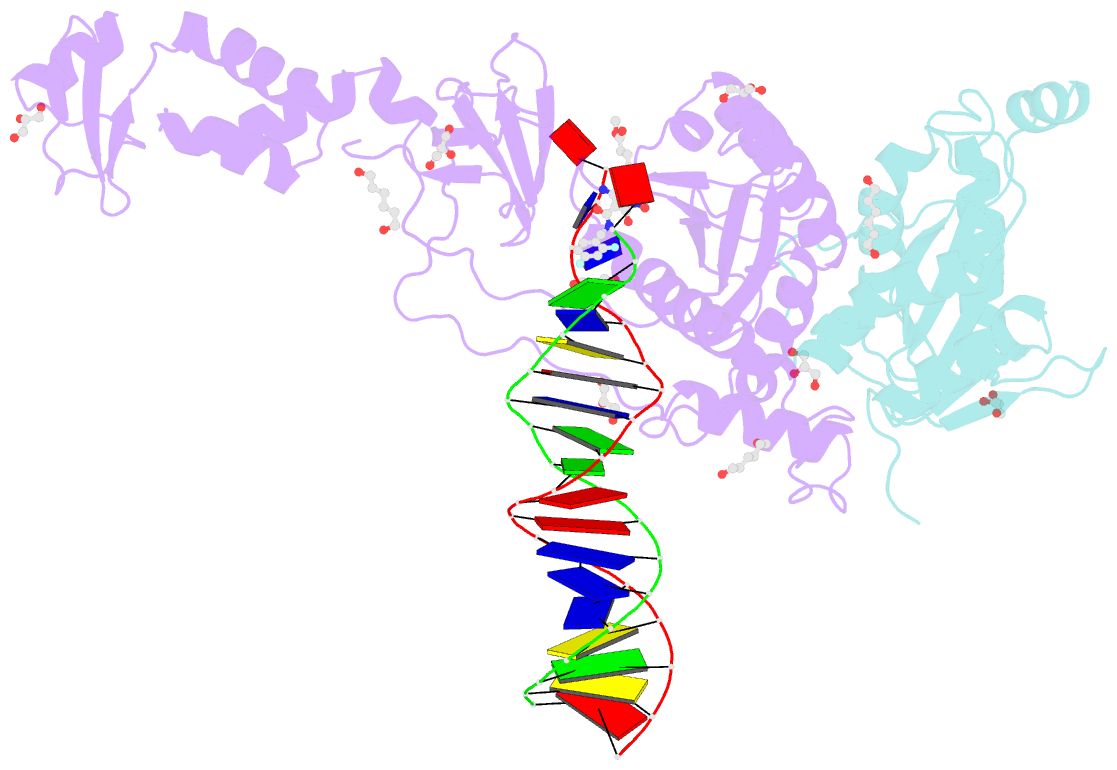
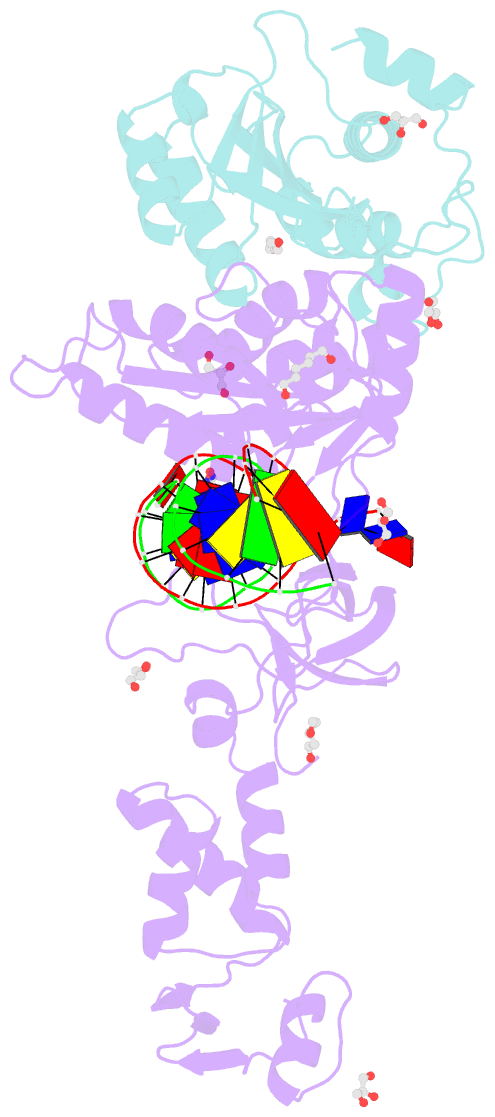
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5mmb; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.77 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of the prototype foamy virus (pfv) intasome in complex with magnesium and the insti xz434 (compound 6p)
- Reference
- Zhao XZ, Smith SJ, Maskell DP, Metifiot M, Pye VE, Fesen K, Marchand C, Pommier Y, Cherepanov P, Hughes SH, Burke TR (2017): "Structure-Guided Optimization of HIV Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors." J. Med. Chem., 60, 7315-7332. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00596.
- Abstract
- Integrase mutations can reduce the effectiveness of the first-generation FDA-approved integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs), raltegravir (RAL) and elvitegravir (EVG). The second-generation agent, dolutegravir (DTG), has enjoyed considerable clinical success; however, resistance-causing mutations that diminish the efficacy of DTG have appeared. Our current findings support and extend the substrate envelope concept that broadly effective INSTIs can be designed by filling the envelope defined by the DNA substrates. Previously, we explored 1-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxamides as an INSTI scaffold, making a limited set of derivatives, and concluded that broadly effective INSTIs can be developed using this scaffold. Herein, we report an extended investigation of 6-substituents as well the first examples of 7-substituted analogues of this scaffold. While 7-substituents are not well-tolerated, we have identified novel substituents at the 6-position that are highly effective, with the best compound (6p) retaining better efficacy against a broad panel of known INSTI resistant mutants than any analogues we have previously described.