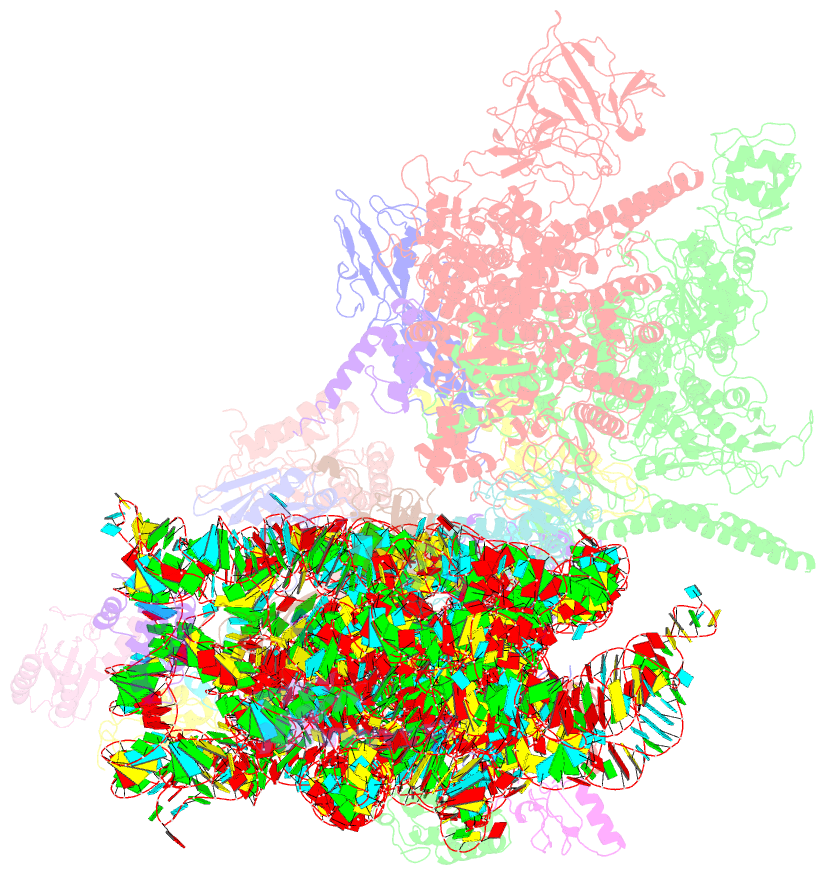
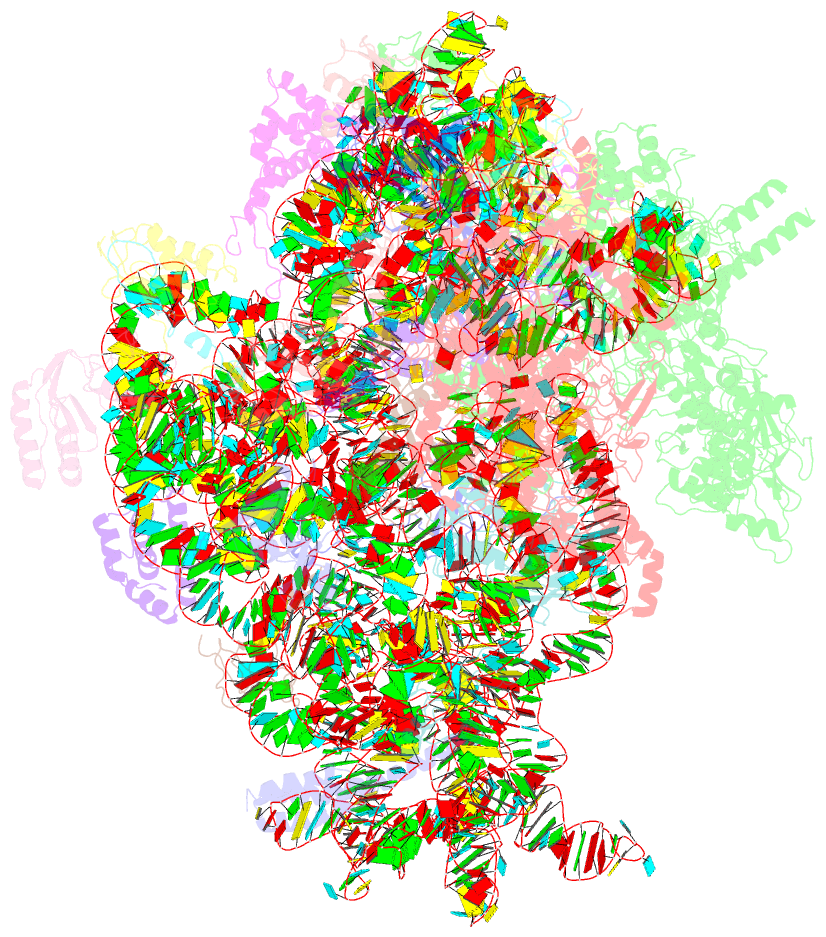
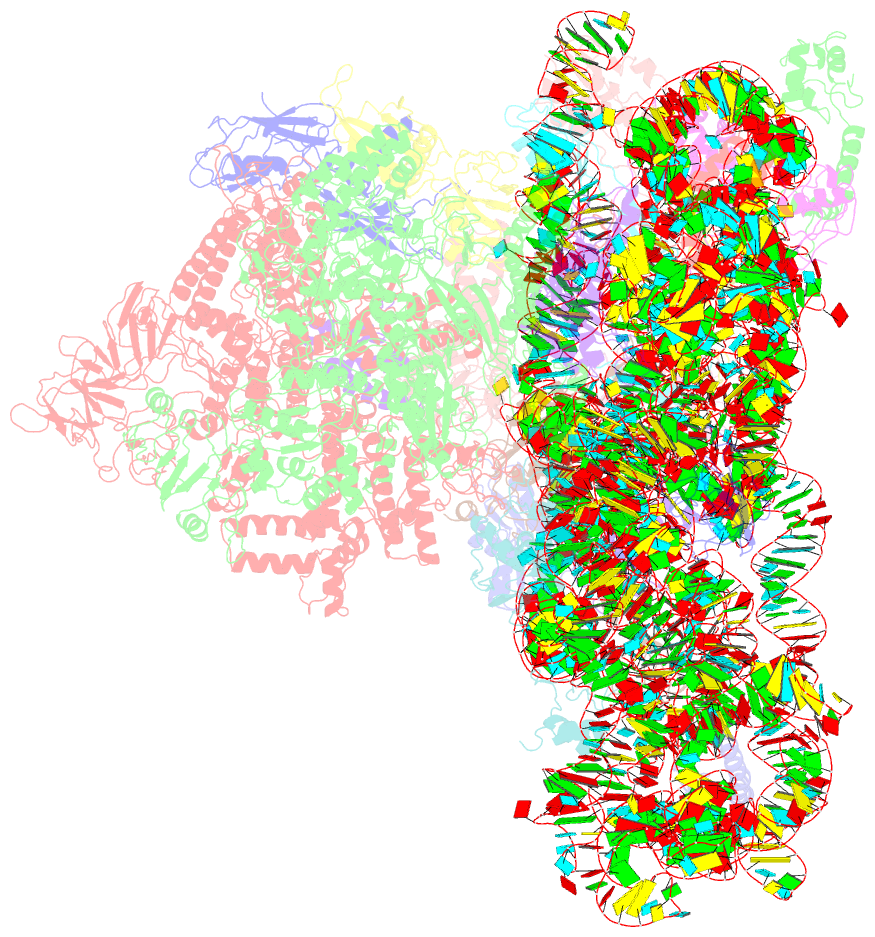
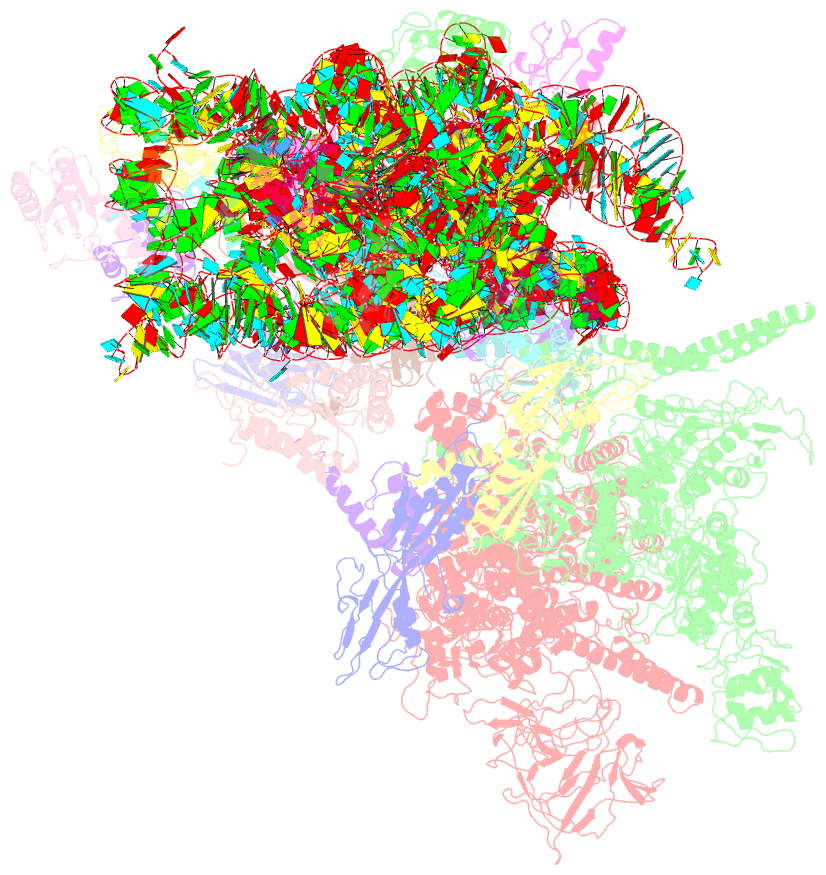
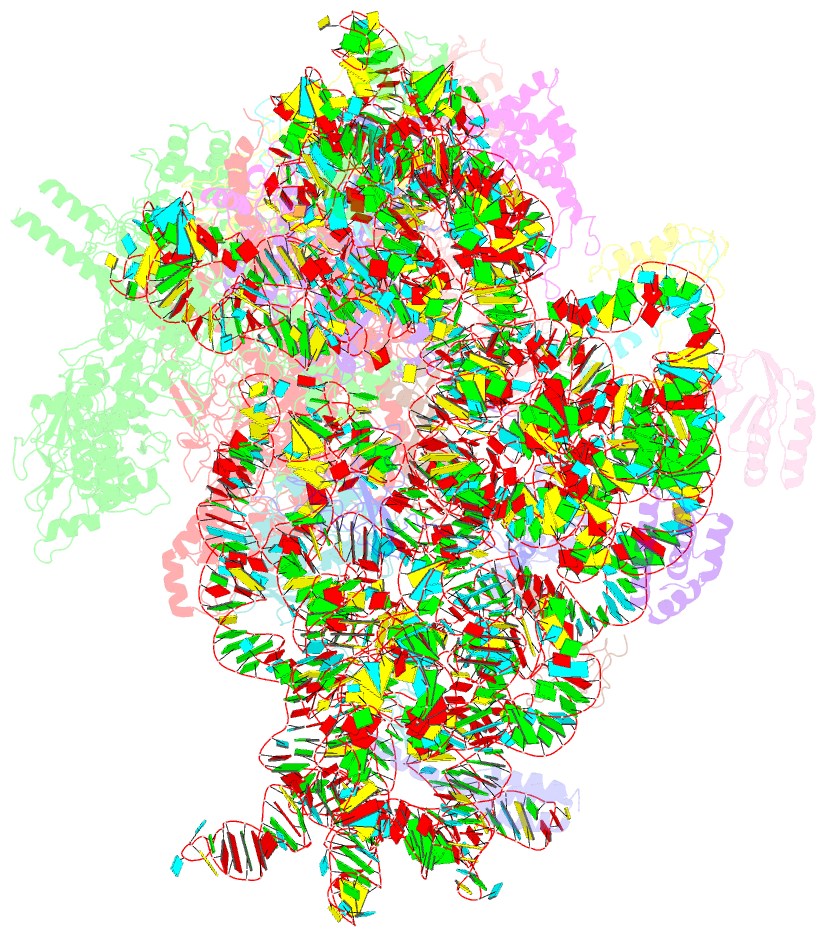
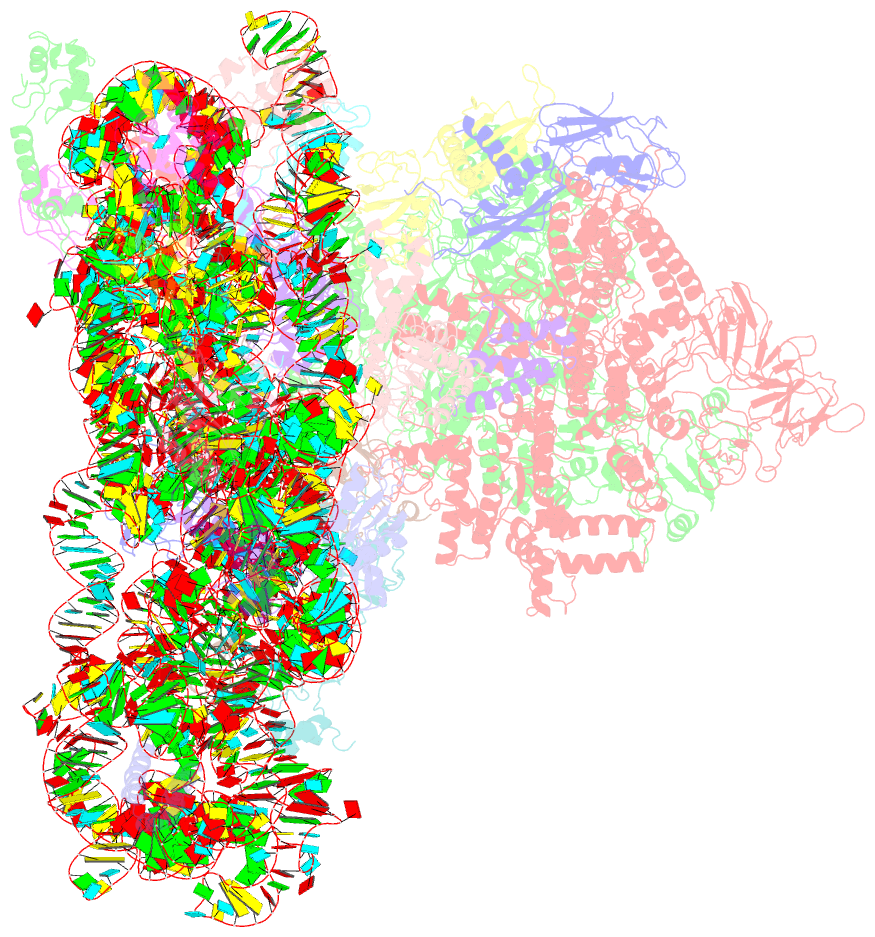
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5my1; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ribosome
- Method
- cryo-EM (7.6 Å)
- Summary
- E. coli expressome
- Reference
- Kohler R, Mooney RA, Mills DJ, Landick R, Cramer P (2017): "Architecture of a transcribing-translating expressome." Science, 356, 194-197. doi: 10.1126/science.aal3059.
- Abstract
- DNA transcription is functionally coupled to messenger RNA (mRNA) translation in bacteria, but how this is achieved remains unclear. Here we show that RNA polymerase (RNAP) and the ribosome of Escherichia coli can form a defined transcribing and translating "expressome" complex. The cryo-electron microscopic structure of the expressome reveals continuous protection of ~30 nucleotides of mRNA extending from the RNAP active center to the ribosome decoding center. The RNAP-ribosome interface includes the RNAP subunit α carboxyl-terminal domain, which is required for RNAP-ribosome interaction in vitro and for pronounced cell growth defects upon translation inhibition in vivo, consistent with its function in transcription-translation coupling. The expressome structure can only form during transcription elongation and explains how translation can prevent transcriptional pausing, backtracking, and termination.